Why does pathological formation occur?
The main reason for the development of the pathological process is injury to the soft tissue of the gums. The disease also often develops against the background of:
- Caries.
- Inflammation of the gum pocket.
- Violation of the rules of oral hygiene.
- Infectious diseases: tonsillitis, furunculosis, etc.
Pathology is characterized by gradual development:
- The initial stage is characterized by the appearance of mild pain when touching the gums.
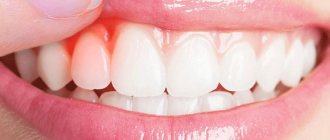
- In the second stage, swelling and redness of the gums develop, and the pain becomes intense.
- If left untreated, pus appears in the gum pocket, body temperature rises, and swelling spreads to the cheek.
- Next, an extensive inflammatory process develops, characterized by the appearance of acute throbbing pain and an increase in the area of edema. The patient's general condition deteriorates significantly.
What is tooth flux
Tooth gumboil is usually an exacerbation of diseases such as periodontitis or periodontitis. An acute inflammatory process begins in the area of the tooth root, when the nerve has already died and an infection develops in the root canal.
Periostitis is a common disease among children and adults. The inflammatory process manifests itself as follows: a cavity filled with pus appears on the mucous membrane of the jaw - a purulent bubble. As a rule, flux is accompanied by severe swelling of the cheek, pain and increased body temperature.
In the absence of professional dental care, the inflammatory process will develop further. Tooth flux can cause serious complications: phlegmon and sepsis. The patient will need a lot of time to recover.
Types of disease
Flux is classified according to its development into the following types:
- Odontogenic. Pathology occurs against the background of advanced diseases of teeth and gums,
- Hematogenous. The disease develops when infection penetrates through the circulatory system.
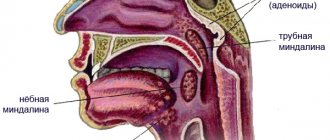
- Lymphogenic. The cause of the disease is pathogenic microorganisms in the lymphatic system.
- Traumatic. Flux occurs at the site of injury to the periosteum, often after unsuccessful dental procedures during dental treatment.
According to the degree of spread, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- An ordinary flux that does not affect the periosteum.
- Fibrous flux, characterized by the onset of inflammation in the tissues of the periosteum.
- Orthodogenic flux, which develops as a complication - osteomyelitis, which requires tooth extraction.
- Albuminous flux, characterized by a chronic course, subfertile temperature and the occurrence of suppuration.
How does flux appear?
Flux occurs during an inflammatory process in the connective tissues that are located around the tooth. In this case, inflammation with pus appears, the tissues swell, and the area of the diseased tooth hurts. Most often, flux appears due to the penetration of infection from a diseased tooth into the pulp area. The disease is dangerous due to the fact that when the pulp is damaged, its tissue begins to die, and for this reason the patient no longer feels severe pain and decides that there is no need to see a doctor for now. At the same time, the absence of pain does not mean that recovery has occurred, and untimely treatment leads to serious complications. And it often happens that the patient is so afraid of the dentist that he decides to endure even severe pain until the last.
Diagnostic methods and treatment methods
An accurate diagnosis is a guarantee of successful treatment. To do this, the doctor conducts the necessary examination. It includes a diagnostic examination and fluoroscopy. To assess the degree of the inflammatory process, laboratory blood tests are performed.
There are two methods of flux treatment used in dentistry:
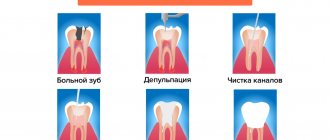
- Making an incision on the gum to open the purulent sac. After removing the pus, drainage is installed, which prevents premature healing.
- Cleaning an abscess through a root canal. This procedure is carried out when the cause of the flux is caries or the infection has penetrated through an existing crack in the tooth.
Special rinses are effective in treating flux. Solutions have regenerating and anti-inflammatory properties, therefore they can speed up healing. The simplest composition that can be used for rinsing with flux is a soda solution. If you carry out the procedure every couple of hours, you can quickly reduce pain and inflammation. To prepare the composition, dissolve a couple of teaspoons of soda in a glass of warm water. This amount of solution is enough for a day.
You can reduce swelling with a weak solution of manganese. This composition has strong disinfectant properties, which makes it possible to fight pathogenic microorganisms. For a similar effect, you can use the antiseptic agents Chlorhexedine or Miramistin. These drugs need to be used to irrigate the oral cavity.
An effective medicinal preparation for rinsing is Rotokan. It has a natural composition and contains extracts of chamomile, yarrow and calendula. For the solution, one spoon of the product is dissolved in a glass of warm water. Rinsing is carried out 4-5 times a day.
How do doctors treat flux?
As we wrote above, rinsing is an auxiliary technique. They must be combined with therapeutic applications and physiotherapy. Of the latter, the following are effective:
- UHF;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy.
The purulent acute form of the disease always requires surgical manipulation. The doctor opens the subperiosteal or submucosal abscess and installs a drainage tube into the gum. All procedures are performed under local anesthesia, so the patient does not feel pain.
Afterwards, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and rinses, and is told what precautions must be taken to avoid complications of periostitis. As a rule, recovery occurs within one week. If the crown and roots are severely damaged or inflammation is advanced, tooth extraction may be required.
Recommendations after opening the flux
When the first symptoms of flux development appear, you should not self-medicate. It is a mistake to believe that swelling and pain can be relieved with warm compresses, lotions based on herbal infusions or other folk remedies. Independent experiments aimed at combating flux can lead to complications.
It is important to remember that you should not take painkillers less than 3 hours before visiting the dentist. Otherwise, there will be problems with making a diagnosis. After the tooth flux has been exposed, you should not take aspirin, as it increases the risk of bleeding. If after 12 hours the condition has not improved, you should consult a doctor immediately.
How does soda work for flux?
Baking soda or sodium bicarbonate has an antiseptic effect. The beneficial properties of weak alkali make it possible to effectively use the substance when you need to soothe itching, normalize the acidity of the stomach, relieve the burning sensation of heartburn, and disinfect skin lesions.
Sodium bicarbonate is commonly used to whiten teeth and eliminate bad breath. At home, a solution of soda can relieve the inflammatory process and reduce gumboil, but to reliably eliminate the causes and prevent consequences, go to the dentist as soon as possible.
Prevention
Understanding what gumboil is, you need to monitor the condition of your teeth and gums. Prevention consists of following hygienic rules for caring for the oral cavity. It is important to buy a quality toothbrush and good toothpaste to minimize the risks of developing caries. You need to brush your teeth twice a day: morning and evening.
After eating, it is necessary to remove food debris from the interdental spaces and use a mouth rinse to treat the oral cavity. To do this, you can buy the product at the pharmacy or prepare it based on propolis tincture, sea or table salt.
It is important to visit the dentist twice a year for preventive examinations. All diseases at the initial stage are successfully treated. Tartar should be removed regularly. It is in these deposits that pathogenic bacteria multiply, which, if the soft gum tissue is accidentally injured, can cause the development of gumboil.
To strengthen your gums, you must include fresh fruits and vegetables in your daily diet: apples, carrots, etc. They clean plaque on tooth enamel, which reduces the likelihood of tartar formation.
Causes
Suppuration in the tooth area can occur in the following cases:
Delaying a visit to the dentist to treat caries is the first cause of gumboil. From the carious cavity, pathogenic bacteria (most often staphylococci) enter the pulp, where the inflammatory process begins to develop. The patient learns about this by acute or aching pain. If in this case the dentist’s help is ignored, the inflammation spreads to the periodontal tissue, where pus begins to accumulate. Pulpitis, periodontitis, alveolitis, suppuration of jaw cysts can also cause pain. Hence the conclusion that you need to regularly visit the dentist to have your teeth examined and carry out professional oral hygiene.
Poor preparation for prosthetics, incompletely filled root canals, complications after tooth extraction are the second cause of gumboil. Not all doctors are highly qualified, so treatment must be carried out in a clinic with a good reputation.
Injuries to teeth and jaws. Microbes that enter the wound “trigger” the inflammatory process.
Sometimes the infection enters the periosteum through the lymph flow or through the bloodstream. This is usually observed in acute and chronic ENT diseases, as well as after influenza and ARVI. Often the cause of flux is hypothermia of the body.
Compresses and lotions with soda
In addition to rinsing with baking soda, you can prepare a product for compresses and lotions, which are no less effective.
To prepare, you need to take a small piece of gauze or napkin and fold it several times. Then you should wet the resulting gauze cloth with water and put 5 grams of a substance on it, namely, baking soda. This lotion should be applied to the inflamed area and kept for at least three to four hours.
It is recommended to carry out such manipulations 2-3 times a day to achieve the best effect. You cannot make gauze compresses with soda if the abscess has opened, because this can cause infection.
Flux diagnostics
The diagnosis of “periostitis” can only be made by a specialist. In order to identify the disease at an early stage, you will need to visit the dentist's office. Therefore, if such primary signs as hyperemia, accumulation of infiltrate, etc. are detected, we recommend immediately consulting a doctor for diagnosis. If an odontogenic type of periostitis develops in the mouth, then there is almost always a decayed tooth in the oral cavity, which is the cause of the pathogenic process.
Diagnosis is made using fluoroscopy. If the disease is in an acute stage, then it will not be possible to determine changes in the shape of the jaw using this research method, but it can be used to identify granulating periodontitis, which is a catalyst for the development of the inflammatory process.