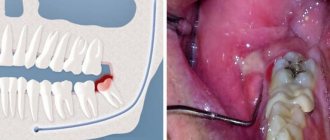
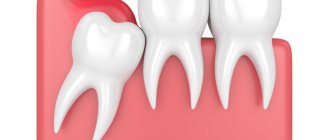
The inflammatory process of the periodontal soft tissues that occurs during complicated or improper teething is called pericoronitis. Inflammation during teething can occur in both adults and children, regardless of the location of the problem tooth, but most often pericoronitis of the wisdom tooth develops (it is also often called the “eight” or third molar).
Causes of inflammation and swollen gums during teething
The main prerequisites for the development of pericoronitis are:
- Mechanical injuries to the gingival tissue over the tooth germs due to hard foods, too hard toothbrushes, as well as due to other damaging factors.
- Long-term or difficult teething.
- Favorable conditions in the mouth for the accumulation of bacterial plaque and food particles under the gingival margin (insufficient hygiene, peculiarities of microflora in the oral cavity).
Swollen gums during teething are easily susceptible to traumatic influences, which leads to the development of inflammation. In this case, teething itself can be difficult for the following objective reasons:
- Dense bone tissue in the “eight” zone; bone compaction is most often formed because there are no milk teeth in this zone.
- There is not enough space for the “eight” in the dentition.
- Thickening of the gums and periosteum in the posterior part of the jaw is usually explained by the characteristics of embryogenesis.
Even one of these factors can cause the disease.
Why do gums become inflamed in children?
The cause of inflammation in a child’s mouth is improper hygiene. If you brush your teeth haphazardly, over time, bacterial plaque begins to accumulate on the enamel and in the gum area.
Pathogenic bacteria (Porphyromonas gingivalis) produce toxins and provoke an inflammatory process.
Factors contributing to gum inflammation in children:
- a sharp decrease in immunity, for example, during a cold;
- injury to the oral mucosa from hard or hot food;
- infection due to poor personal hygiene (children constantly put toys or dirty fingers in their mouths);
- malocclusion, crowding of the front teeth (while the gum tissues experience increased mechanical stress);
- vitamin deficiency (lack of vitamins C, E and B);
- hormonal imbalances (usually observed in adolescents).
In addition, childhood gingivitis can be a consequence of chronic illnesses, for example, diabetes, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or cardiovascular system.
Features and risk factors
During difficult and prolonged eruption, the tooth germ practically does not change its position, and a significant part of its chewing surface is covered with a flap of gingival or mucoperiosteal tissue, the so-called “hood”. The flap covering the tooth germ forms a kind of pocket in which food debris and bacterial plaque accumulate. A moist nutrient medium creates optimal conditions for the intensive reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, which, in turn, actively secrete waste products that are toxic to our body. This provokes the development of an infectious-inflammatory process in the tissues surrounding the problematic tooth germ.
Most often, inflammation of the gums occurs when a wisdom tooth erupts in the lower jaw, which is due to the anatomical structure of the jaw and the lack of space for third molars. In modern people, the jaw arch is approximately 1-1.2 cm smaller than in our distant ancestors, but the size of the teeth has remained the same. This is why the “eights” are cut much later, when the body as a whole and the dental system in particular have already formed - and because of this, it is difficult for the new tooth to find the “right” place on the dental arch.
Since wisdom tooth pericoronitis is the most common type of disease, people over the age of 18 are primarily at risk (usually “eights” are cut at the age of 20-25, but for some this process can take up to 30 years) . As for pericoronitis in children, it usually occurs against the background of insufficient oral hygiene in a child or with infectious diseases of the oral cavity (caries, gingivitis, stomatitis), which complicate teething in children and require treatment. Accumulations of plaque and hard dental deposits significantly increase the risk of developing the disease, so timely and regular removal of tartar can serve as a good preventative method.
Reasons for the development of gingivitis in children
The abundance of causes of the disease can be divided into two large groups.
Common reasons include:
- colds, especially if they occur frequently;
- sore throat and chronic sinusitis;
- hormonal disorders;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
Among the local reasons it is worth highlighting:
- poor-quality fillings, which, when destroyed, injure soft tissues;
- caries (infection from the cavity quickly enters the gums);
- crowded teeth;
- violations during the installation of braces;
- Tight lips that interfere with quality teeth cleaning.
Separately, it is worth noting the most important reason, since all of the above are only a catalyst for the development of the disease. So, the main reason why gingivitis begins to develop is poor oral hygiene, which can manifest itself both in improper brushing of teeth and in incorrectly selected toothpaste and brush.
Symptoms of the disease
Gingivitis has quite a few characteristic signs by which one can guess the onset of the disease:
- bleeding gums;
- pain during cleaning;
- swelling of the gums;
- severe redness of the gums in the case of an acute phase of inflammation;
- when the disease becomes chronic, the gums may acquire a bluish tint.
Often with the naked eye you can notice a large amount of accumulated plaque and tartar, and there may also be many teeth affected by caries.
In addition, gingivitis can be caused by diseases that have nothing to do with the oral cavity:
- heart and vascular diseases;
- disorders affecting the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory diseases.
The above factors reduce immunity, as a result of which the gums lose their ability to resist toxins formed in plaque.
What is the best way to treat?
As was said a little above, gingivitis occurs due to accumulated soft plaque, so the first thing you need to do is get rid of it. Plaque can be removed using ultrasound - this is a simple and absolutely painless procedure. Using a special attachment, the dentist touches dental plaque, which is destroyed by ultrasound. By the way, ultrasound allows you to get rid of not only soft plaque, but also hardened formations on the teeth.
It is necessary to understand that plaque can be effectively removed, especially if inflammation has begun, only with ultrasound: rinsing with various means, using special toothpastes and gels with the addition of antibiotics can temporarily remove the symptoms of gingivitis, but these methods are not able to eliminate its cause. As soon as you stop using these medications, bleeding will return and the disease will continue to progress. Therapy aimed at reducing the inflammatory process is justified only after the deposits have been removed.
Anti-inflammatory therapy is usually prescribed as follows:
- Rinse with Chlorhexidine solution. The maximum duration of use of the drug is 10 days. Rinsing should be done twice a day for at least 30-40 seconds per procedure. The solution, which has a bitter taste, which not all children will like, has no contraindications based on the child’s age.
- Rinse with Miramistin (prescribed after the child reaches the age of 3 years). You need to rinse three times a day. The drug is inferior in its effectiveness to Chlorhexidine and is significantly higher in price.
- Rinse with infusions of chamomile or sage (it is not recommended to use oak bark).
In addition to rinses, many doctors prescribe ointments and gels. It is believed that the gel is more effective than ointment because, due to its consistency, it has the ability to remain on the gums for a long time, which promotes better absorption. In addition, the medicinal substances contained in the product penetrate much better into the tissues from the gel than from the ointment.
The most effective and proven gels on the positive side are the following:
- Cholisal is a drug that simultaneously has two effects: analgesic and anti-inflammatory. It is used for gingivitis and the beginning of teething (the drug is rubbed directly into the place where the tooth is emerging). There are no age restrictions. The gel can be used for a maximum of one and a half weeks, twice a day. After applying the product, it is recommended to eat within two, or preferably three, hours.
- Metrogil Denta. Used after 6 years. Apply directly with your finger or a cotton swab to the gums near all teeth; there is no need to rinse off the gel.
Many parents often decide to treat their child on their own, not wanting to see a dentist. But you need to understand that the use of anti-inflammatory drugs will have no effect if you do not get rid of the deposits, so you will still have to set aside time to visit the dentist. If you ignore the advice, then:
- symptoms of bleeding will disappear, but will reappear after completion of the course of therapy;
- gingivitis can become chronic, causing periodontitis.
In addition to anti-inflammatory therapy, oral cavity sanitation and silvering are carried out - a method that does not require drilling, but has a lot of disadvantages.
How to avoid the occurrence of gingivitis?
The following remedies will help prevent gum bleeding:
- High-quality oral hygiene. Parents should instill in their children oral care skills from an early age. Not all adults know that hygiene measures must begin before the first tooth begins to erupt.
- Using the right paste. If the child does not have gingivitis, then you can use any paste designed for children. If your child does not brush their teeth well enough, you can purchase a paste with amino fluoride.
- Stick to your diet - avoid snacking, limit the consumption of fast carbohydrates (carbonated drinks, sweets). Of course, you don’t need to completely deprive your child of sweets, but you can give them only immediately after the main meal, after which you should brush your teeth.
Pericoronitis, symptoms and types
With pericoronitis, the symptoms largely depend on the form of the disease - acute or chronic. Acute pericoronitis is characterized by:
- Aching intense pain in the area of the cutting tooth, the pain intensifies under the influence of food and mechanical irritants (hygienic procedures, chewing, touching, etc.).
- Difficulty chewing food, complicated swallowing. A few days after the onset of inflammation, it becomes difficult to open the mouth and severe pain appears.
- Swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes, sometimes the lymph nodes become painful when touched.
- Externally noticeable swelling of the cheeks a few days after the onset of the inflammatory process.
- General deterioration in health - weakness, lethargy, prolonged low-grade fever (increased temperature to 37-37.5 degrees).
- Bad breath, which is caused by the decomposition of food particles and the active activity of microorganisms in the “hood” space.
Acute pericoronitis can occur in a serous (catarrhal) or purulent form: in the first case, the signs of inflammation are more pronounced, the pain is more intense, and there is no purulent discharge. In the second case, purulent exudate flows freely from the inflammatory focus, due to which tissue tension is somewhat reduced and the symptoms are less pronounced. A person may feel like their condition is gradually improving, when in fact the infection is simply spreading to other tissues in the mouth.
If treatment for acute pericoronaritis was not carried out or was carried out at home, the disease gradually becomes chronic: the severity of symptoms decreases, while exacerbations of pain and discharge of pus into the oral cavity are periodically observed. In this case, there is a high risk of developing severe complications.
Complications of the disease
In the case when treatment of the gums during complicated tooth eruption was not carried out, serious complications of the inflammatory process develop:
- Periostitis, or flux, is inflammation of the periosteum.
- Osteomyelitis - in this disease, inflammation affects both the bone tissue itself and the bone marrow, gradually leading to bone resorption. This can cause abnormal jaw fractures.
- An abscess when the infection spreads to nearby tissues. Purulent inflammation leads to the melting of muscles and fatty tissues with the formation of a large accumulation of pus.
- Cellulitis is the next stage of a purulent process after an abscess, which does not have clear boundaries. Such purulent inflammation is a serious threat to the patient and is treated in a maxillofacial hospital.
These complications are usually difficult to treat, require a serious systemic approach and can lead to irreversible consequences. Therefore, if a person suspects he has pericoronitis, treatment should begin without delay in order to prevent the condition from worsening. You need to be especially careful if gum inflammation occurs during teething in children, since the children's immune system is still immature, the body's resistance to infections is lower and the process quickly becomes more severe.
Treatment of inflammation
Removal of a lump with pus on a child’s gum should be started immediately. Only a dentist can help the baby.
IMPORTANT! Self-medication, as well as piercing and squeezing are strictly prohibited! Such an intervention will lead to serious complications.
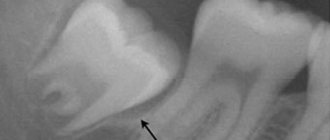
When an abscess forms over a baby's baby tooth, the doctor most often removes it. Such measures are necessary to exclude the possibility of destruction of the rudiments of the root. If a child has a lump on his gum next to a permanent tooth, treatment begins with a thorough examination. Sometimes the dentist will send you for an x-ray to assess the extent of the damage. Removal of a permanent tooth is carried out in extreme cases.
Pericoronitis, treatment in children and adults
It should be noted right away that for pericoronitis, treatment at home can only reduce the symptoms of inflammation, but not solve the problem. Therefore, all home methods (rinsing with antiseptics, applying anti-inflammatory ointments, etc.) can only be used as a way to relieve inflammation during the eruption of wisdom teeth and reduce pain - this is a temporary measure before visiting the dentist.
In a dental clinic, in case of complicated teething, treatment will depend on whether the problem tooth should be preserved or whether it should be removed. If preserved, the doctor performs surgical excision of the “hood” under local anesthesia. This eliminates conditions for the accumulation of food and the growth of bacteria, and also facilitates teething. After excision of the “hood,” the patient is prescribed antiseptic therapy (rinses, baths) and, if necessary, antibiotic therapy.
In cases where tooth extraction is indicated due to their incorrect position on the jaw, lack of antagonists, or insufficient space for full eruption, the doctor immediately removes the problematic tooth and prescribes antiseptic therapy to the patient.
In some cases, at the initial stages of the inflammatory process, conservative therapy can be preliminarily applied - local treatment with antiseptic rinses and the introduction of an iodoform tampon into the “hood”. However, local therapy does not always give a positive result; moreover, it is appropriate only at the initial stage of the disease; in other cases, surgical intervention will be required.
When it comes to teething in children, treatment is always aimed at preserving the teeth (except for those cases when dystopia is clearly expressed and the doctor sees that preserving is useless).
Diagnostic features
History of the disease Pericoronitis sometimes looks like a completely different disease of the oral cavity - for example, its symptoms can be confused with periodontitis (inflammation of the peri-apical tissues of the oral cavity) or pulpitis (inflammation of the dental pulp). The pain in these diseases is very similar, and periodontitis is often accompanied by hyperemia and swelling of the gums. One disease can be distinguished from another by the following signs: with pulpitis there is no pain when opening the mouth and no noticeable swelling of the gums, and periodontitis develops only at the tops of the roots of fully erupted teeth. You also need to pay attention to the presence of a characteristic “hood” - a photo will help you assess how it looks with pericoronaritis.
Prevention
In some cases, especially when it comes to inflammation of the gums during teething in children, preventive measures will help prevent the disease: careful regular oral hygiene, timely removal of tartar and soft deposits, visits to the dentist for diagnostic examinations at least once every six months.
If pericoronitis is caused by the anatomical features of the structure of the dental system and the lack of space for the lower “eights” on the dental arch, preventive measures will only smooth out the course of the inflammatory process (due to timely cleaning of the oral cavity from bacterial plaque and food particles that create favorable conditions for inflammation) and identify the problem in time (subject to regular dental examinations).
Why is gingivitis dangerous in children?
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that occurs as a result of the adverse effects of local and general factors. In children, it occurs quite often: between the ages of two and four years, its prevalence is 2%, and by the age of thirteen, gingival inflammation occurs to one degree or another in 80% of children. Often the disease does not progress beyond gingivitis, since it can be easily cured, avoiding more serious problems. However, if the process is started, the inflammation from the gums will spread to other periodontal tissues (the child will develop periodontitis) and will become a chronic condition, the symptoms of which will need to be relieved with each relapse.