If the dental crown breaks almost at the very root, there is a risk of it becoming overgrown with gum tissue. A tooth can break for various reasons - mechanical damage, trauma, for example, a strong blow, carious process, etc. Small fragments gradually come out on their own, but the root remains inside the gum. Gum tissue grows, gradually covering the rest of the tooth.
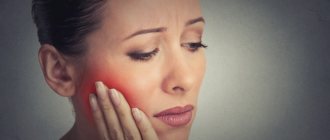
An overgrown root may not bother the patient for a long time. As the pathological process develops, painful sensations appear, the gums become inflamed and swollen. Patients often complain of pain when chewing.
An overgrown root must be removed, as overgrowth is quite dangerous and can cause serious problems:
- Dental disorder.
- Damage to adjacent teeth.
- Inflammation of the gums.
If a crown breaks off, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. The specialist will assess the complexity of the problem and select a treatment program.
If the tooth is overgrown and the pathological process has spread to the surrounding tissues, the patient will face a rather complicated operation with a long recovery period. The wound may take a long time to heal. A timely visit to the clinic will help avoid this.
Hyperplasia as the main cause of pathology development
Why does this phenomenon occur when gums grow on a tooth? Most often this is due to the proliferation and enlargement of its cells. Scientifically, this process is called hypertrophy or hyperplasia (i.e. proliferation and increase in volume of tissue). The problem in most cases occurs against the background of an inflammatory process occurring in the oral cavity or metabolic disorders and hormonal imbalances in the body.
On a note! Hyperplasia or hypertrophy is a pathology in which soft tissue cells begin to grow uncontrollably, and the gums themselves can become inflamed and increase in size, they can begin to “crawl” onto the crown, partially or even completely (in the most advanced situations) block it.
Prerequisites for the development of hyperplasia
Various reasons can serve as prerequisites for accelerated and enhanced cell division:
- excessive accumulation of hard tartar and bacterial plaque above and below the gums,
- malocclusion: in such a situation, some teeth and, accordingly, the soft tissues and mucous membrane that surrounds them are subject to increased stress and pressure, they are constantly injured. The nutrition and blood circulation of tissues is disrupted, as a result of which their cells can begin to grow rapidly,
- endocrine diseases,
- genetic predisposition and heredity,
- long-term use of steroid hormonal drugs, antidepressants, anticonvulsants,
- hormonal imbalance during pregnancy, after childbirth, during menopause in women, changes in hormonal status in adolescents during puberty1,
- acute vitamin deficiency: hyperplasia often occurs due to a lack of vitamin C,
- traumatic damage to the mucous membrane due to incorrectly installed fillings, artificial crowns or braces,
- teething,
- leukemia
Causes
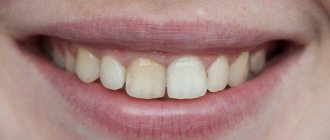
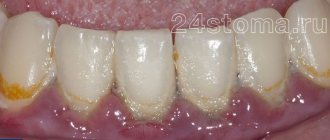
Exposed necks indicate periodontal damage. Most often the problem occurs for the following reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. When exposed to this factor, a person can very diligently monitor the health of his smile, but will still periodically encounter unpleasant dental symptoms.
- Mechanical and thermal damage. The habit of gnawing on foreign objects, eating too hot food, using a hard brush are all provocateurs that contribute to irritation.
- Poor oral hygiene. If the patient neglects basic hygiene rules, a lot of plaque is deposited on the crowns. Pathogenic microorganisms spread in it. The gums become irritated, turn red, and bleed. Gradually they begin to move away from the teeth. It is important to use a brush and paste twice a day, and undergo professional hygiene at the dentist’s office annually.
- Poorly performed prosthetics or mistakes made during filling. It is necessary that the dentures fit as tightly as possible to the bases and do not fall under pressure, otherwise the gums will be constantly injured and inflamed.
- Curvature of the bite, problems with teething “eights”, uneven edges of the crowns. All this causes the gums to move away from the tooth.
- Unbalanced diet. If a person eats only soft foods and sweets, he does not actively chew food. As a result, blood circulation in the oral tissues slows down, less saliva is released, and periodontal deposits are actively formed. These are the prerequisites for a recession.
- A large amount of tartar. Despite the fact that dentists recommend removing stones annually or even more often, many patients do this very rarely. You shouldn't wait until a serious problem arises. It is easier and cheaper to prevent it than to treat it later.
- Hormonal imbalance. Most often, this reason concerns women, for example, during pregnancy, menopause, and breastfeeding. With hormonal fluctuations, the mucous membranes become especially vulnerable. Even minor mechanical impacts cause recession.
Don't forget about the negative effects of tobacco smoke. According to statistics, smokers are much more likely to suffer from gum disease and exposed necks. They accumulate plaque faster. Therefore, if you want to have a healthy smile and visit the dentist less often, stop smoking.
Main diseases characterized by tissue hyperplasia
Fibrous or hypertrophic gingivitis
Between the teeth there are gingival papillae, which during the development of fibrous gingivitis begin to gradually increase in size, they become denser and grow. In this case, the mucous membrane remains painless for a long time, and there is no bleeding.
Read more about all types and symptoms of gingivitis in a separate article on the website.
The disease develops against the background of poor oral hygiene and the accumulation of a large amount of plaque; it can appear due to poor-quality prosthetics and constant trauma to the mucous membrane. People who have hormonal imbalances or gastrointestinal diseases also encounter fibrous gingivitis. The disease often occurs in both adults and children.
Important! A growth over a tooth is not always associated with hyperplasia; it can be nothing more than a gumboil, abscess, fistula or cyst, indicating advanced dental diseases. Most often, such manifestations are very painful, they are white in color, because... pus accumulates in them.
Fibromatosis
This is a hereditary disease and therefore often manifests itself in childhood. It is characterized by the growth of individual areas of the gums and proceeds very slowly. The color of the affected tissues is usually no different from healthy ones; they are painless.
The disease occurs mainly in the frontal area of the smile, and soft tissues can grow so much that they cover the crowns by more than 2/3. If fibromatosis is not treated, it is fraught with destruction of interdental septa, osteoporosis, and a severe violation of the aesthetics of the smile.
Fibropapilloma
If the gums have grown onto the crown, then a disease such as fibropapilloma may be to blame. This is a benign tumor. The tumor is hard to the touch, but painless. Its appearance in childhood is more dangerous, because can lead to disruption of the formation, growth and eruption of permanent elements.
Epulis
Epulis, like fibropapilloma, is a benign formation. It has a mushroom shape, because the tumor grows on a stalk. Appears as a result of chronic irritation and tissue injury. The most common location is the area of the incisors or canines. If the tumor is not removed, it can lead to pathological mobility and tooth loss.
Why does the problem appear in children and when should you see a doctor?
The situation when gums grow on a child’s tooth most often occurs during the period of teething, as well as the change from a primary bite to a permanent one. During eruption, the mucous membrane swells and increases slightly in size, because it is irritated, blood circulation increases in it, but in this case we are not talking about hyperplasia. However, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the child’s oral cavity over time.
You should consult a doctor in the following situations:
- if 2-3 months after the crown “hatched”, it did not come out completely, and most of it remains under the gum or soft tissue hangs over it, partially covering it,
- the baby tooth did not fall out during the change of bite, but gums are growing on it: perhaps a permanent element is “hiding” under the formed tubercle, which did not have enough space, and it began to make its way in a different direction or into the second row,
- the growth is filled with white contents, and the child has a bad smell from the mouth: perhaps we are talking about the presence of advanced dental diseases, which are complicated by a fistula, abscess or cyst.
Prevention
Preventive measures are carried out in healthy people, as well as in patients after treatment. In order to reduce the likelihood of primary periodontitis or its relapse, it is necessary to follow some rules:
- Brush your teeth daily and thoroughly with a suitable toothbrush and toothpaste.
- Use additional products (dental floss, balms, etc.).
- Periodically have your mouth professionally cleaned at your dental clinic.
- Visit the dentist at least twice a year.
- Treat caries and other dental diseases in a timely manner.
- Try not to injure your gums.
- If gums become inflamed, painful or bleeding, consult a doctor immediately.
- Include vitamins and minerals in your diet.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits.
These simple recommendations will help maintain the oral cavity in proper condition and prevent the development of many dental diseases, including periodontitis.
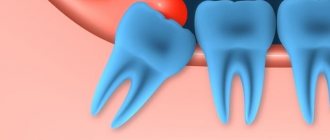
Gum growth on wisdom teeth
There are situations when gums have grown on a wisdom tooth. And this is not related to the phenomenon of hyperplasia. If the third molar has only recently begun to erupt outward, one of its cutting edges has already appeared, and suddenly you feel pain, bad breath appears, and upon examination, inflammation, swelling of the soft tissues and their overhang over the tooth are discovered, then you probably have pericoronitis began.
Pericoronitis is an inflammation of the gingival hood over the third molar. The disease develops due to the fact that small pieces of food begin to get into the gap between the gum and the “eight” that has not fully penetrated, which rot because they are difficult to remove.
For more information about what pericoronitis is and how it is treated, read the feature article on the website.
Surgery to close gum recession
The gum itself, as you understand, will not rise, it will not “bounce into place”, it needs to be put back in its original place, and this is called closing the gum recession.
But I repeat once again: there are also indications and contraindications for the operation, in accordance with certain classes of gum recession according to Miller.
If this is a class one recession, then one forecast. If this is class II gum recession, the prognosis is different. There are many contributing factors to both successful gum recession and failure. That is, at the very beginning of the treatment path, the doctor must determine all the factors for successful closure of gum recession.
If a broken tooth is healed
Situations where a tooth broken at the very root is overgrown with gums are not uncommon. It can break due to injury or collapse due to advanced dental disease. After this, many people are in no hurry to remove the root, and in some cases it gradually grows over from above (this process can last several years), and then does not bother or hurt for a long time. However, sooner or later, unpleasant sensations still appear: it becomes painful to chew, overgrown tissues swell and are constantly injured.
“My gums have grown on my back tooth, which broke off three years ago. I completely forgot about him, because... It didn’t give me any trouble, only sometimes after cleaning it would scavenge, but I didn’t attach any importance to it. All this was revealed during an examination at the dentist, when I went there with a completely different problem. In principle, the doctor decided everything quickly: he opened this growth and removed the root, then put stitches, but then it healed for a very long time and painfully. It was also very disappointing to hear that if I had contacted him immediately after the tooth was chipped, it could have been restored, but I immediately decided for myself that it was lost. That’s it!”
Varvara, review from 32top.ru
Remember that if a tooth is broken, then either its timely removal or restoration and prosthetics is necessary, because a serious inflammatory process can begin under the overgrown tissues or at the root, which can spread to the jaw, cheek, can develop deep into the body, lead to periostitis and osteomyelitis.
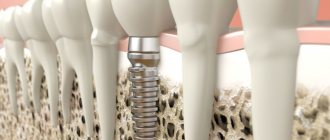
How is an overgrown tooth removed?
Root extraction is a fairly common dental operation. It is performed under local anesthesia and, as a rule, does not cause complications. An overgrown root cannot be removed using traditional methods, since it is completely covered with gum tissue and there is no access to it. Treatment is carried out in several stages:
- Examination by a dentist, x-ray examination. X-ray allows the doctor to see the size, position, and depth of the root. The dentist assesses the risk of damage to adjacent teeth during surgery.
- The operation is performed under anesthesia. First, the doctor makes an incision in the gum, providing himself with access to the root. After this, the root is removed and sutures are applied.
- During the rehabilitation period, the doctor selects anti-inflammatory drugs and agents that accelerate wound healing.
The process of removing an overgrown root is individual in each case. The complexity of the operation is influenced by many factors:
- Tooth location. Removal of roots on the upper and lower jaws has its own characteristics and is carried out using various dental instruments.
- The degree of damage to the root and nearby tissues, the presence of fragments. Sometimes, for a successful and as painless removal for the patient as possible, the root is destroyed by a drill into several parts. Separation is required in cases where the tooth has several strong, deep roots. As a rule, after destruction, individual parts are easily removed using ordinary tools.
- The presence of pathology in the surrounding bone tissue, inflammation of the gums.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
If there is no inflammation, the gum is carefully separated from the alveolus and the tooth is removed using suitable dental forceps. The inflammatory process “melts” the surrounding tissue, so for successful removal it is enough to provide access to the root by making an incision in the gum. Application of forceps does not require labor, and there is no need to additionally separate the gingival tissue from the alveoli. In difficult cases, elevators are used.
How long does the gum “grow” and the stages of development of hyperplasia
Pathology can develop slowly if it is caused by fibromatosis, epulis or fibropapilloma. And it can develop more rapidly if it occurs against the background of gingivitis.
As for the stages of development of hyperplasia, doctors identify the following:
- first stage: the gingival papillae thicken and thicken, while there are no other alarming signs,
- second stage: soft tissues grow and can cover up to half of the crown. Due to the volume, tissues are easily injured during oral hygiene and when chewing food, they can begin to bleed,
- third stage: the most rare stage. The tissues grow so much that they can even cover the cutting area of the crown. Granulations appear on the affected areas.
If you break off a tooth, gum growth may take several years.
Gum recession - symptoms and treatment
Since recession gradually progresses and can turn into a serious complication, it is necessary to undergo timely therapy in the early stages of the disease. This guarantees the effectiveness of complete cure of recession and getting rid of cosmetic defects.
The main treatment for gum recession [6] involves surgery. Thanks to the operation, the gingival contour is restored and the tooth root is closed. However, treating recession with surgery is not suitable in all cases. For example:
- surgical treatment of class I and class II recessions allows for maximum coverage of the tooth root surface;
- in the surgical treatment of class III recession, full success is observed only in some cases;
- For class IV pathology, surgical operations are not performed.
Who is indicated for the removal of dental recessions?
Carrying out such a procedure is necessary if:
- the client is not satisfied with this defect for aesthetic reasons;
- tooth enamel is highly sensitive;
- orthopedic therapy is planned;
- progression of the disease is observed.[7]
Methods of surgical treatment
Surgical treatment involves obtaining excellent results and guaranteed elimination of all symptoms of the disease. In this case, surgical intervention can be carried out using one of the following methods.[8]
Lateral flap technique . To perform the manipulation, a fragment on a stem is used, which is taken from areas adjacent to the operation site. Such plastic surgery is allowed if there is a sufficient amount of soft tissue.
At the initial stage of therapy, the doctor eliminates inflammation and eliminates deposits on the teeth. After this, a flap for transplantation occurs (as a rule, it is formed from gum tissue or hard palate). The final stage involves suturing the fabric. The use of local anesthesia is mandatory.
The relevance of this technique remains in both localized and generalized forms of the disease. Its advantage is considered to be effective restoration, since the materials are 100% identical. The only drawback of the manipulation is the feeling of slight discomfort for some time at the site of donor tissue collection. There are also cases when the flap does not take root in the transplanted area.
Resorbable membranes. This procedure belongs to the classic methods of treating gum recession and can effectively eliminate it. The manipulation is carried out in two stages:
- they begin with the installation of a membrane that has high rigidity, which avoids repeated intervention;
- after some time, the membranes are removed.
It should be noted that such operations are characterized by poor results: damaged tissues may not recover completely. Therefore, progressive doctors try not to use this technique.
Therapy with regeneration potentials of biological elements. The basis for these components are certain components that contribute to the rapid formation of renewed healthy gums. For this purpose, protein enzymes and the substance amelogenin are used. They form high-quality enamel and help restore the structure of tooth roots, and the enamel matrix allows the formation of a hard layer on damaged gum tissue.
Non-surgical treatment
A conservative method is to treat gum recession with collagen . It is recommended mainly at the initial stage of development of the disease, when slight exposure of tooth roots occurs. With the help of collagen, an excellent effect is achieved, especially if gum recession occurs due to inflammatory manifestations. When this component is introduced into the gum tissue, an aesthetic improvement of the damaged area occurs. In addition, the exposed area of the tooth is covered, which avoids undesirable effects on the general condition.[1][8]
Choosing a treatment method
Analyzing the reviews of patients and dentists about the listed therapeutic methods for treating gum recession, you can see how diverse they are.
The thing is that for some patients conservative treatment methods are perfect. However, others note that surgical intervention turned out to be effective. This means that only an experienced specialist can choose the appropriate treatment after examination and a thorough examination.
Signs and symptoms of hyperplasia
Those who have this problem rarely experience pain right away. But almost all patients notice a visual violation of the aesthetics of a smile, because the gums become voluminous and loose, which, as a rule, is the reason for visiting a doctor.
Discomfort and pain appear after the tissues have grown significantly, and they involuntarily have to be constantly injured during hygiene procedures and eating food. Another sign is the appearance of bad breath, which does not go away after careful hygiene or quickly returns again.
Preventive measures
To prevent gums from moving away from the tooth, you need to follow simple recommendations:
- brush your teeth twice a day;
- use a properly selected brush and paste;
- visit the dentist in a timely manner;
- prevent tartar from forming;
- no smoking;
- eat more solid foods;
- Healthy food.
At the first sign of a recession, you should see a doctor. Then the disease can be stopped very quickly.
Consequences and complications if the pathology is not treated
Many patients see overgrown gums as only one problem – a significant disruption to the aesthetics of their smile. However, this is not so: if the pathology is not eliminated and it is allowed to progress further, then this is fraught with serious complications for the health of the oral cavity and the body as a whole.
If left untreated, the patient may develop degenerative diseases of periodontal tissues, leading to the destruction of the interdental septa and supporting ligaments that hold the teeth in the sockets. You may lose your teeth much earlier than you would like.
Hypertrophied tissues are subject to constant trauma, which is why any benign formation can sooner or later become malignant. Another common complication is osteoporosis.
For children, the lack of treatment is fraught with disruption of the formation, as well as the timing of the loss of milk and the eruption of permanent elements.
If a single growth appears on the gum, this may not always indicate hyperplasia or hypertrophy. Some people mistake the growth for a fistula, cyst, or abscess. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner for these pathologies, the purulent contents from these neoplasms can spread throughout the body, causing damage to the cardiovascular and circulatory systems, gastrointestinal diseases, sepsis and even a brain abscess.
About orthodontic treatment to stop gum recession
These can be orthodontic structures: braces, or aligners, or something else - this is what the orthodontist will choose, it is he who determines which technique for correcting the bite in a given case of recession will be best applicable for each specific patient. There are no universal treatments. The only question that is subject to discussion is how long orthodontic treatment will take in one way or another.
As a result of treatment, the orthodontist must place the teeth in a physiological occlusion so that the tooth/teeth do not bear such a load that they experience excessive chewing stress at the time of contacting the doctor.
And then, when the tooth is placed in the functionally correct position, the following happens to the gum. Gum recession stops. And again, if it stops at such a level that closing the recession is possible, then the gums subsequently rise and the recessions close.
And after some intervention, perhaps the gums will return in full.
Cases where orthodontic treatment eliminates recession
We cannot always close all gum recessions with the help of orthodontics. We remove the cause of the recession, that is:
- malocclusion,
- we correct occlusal contacts that lead to this recession,
- eliminating improper stress on teeth,
- We eliminate the lack of load in the case of an extracted tooth and the overload, in turn, of neighboring teeth.
And after the doctor has normalized the patient’s bite and normalized the correct closure of his teeth, we refer him to a periodontist who will perform gum plastic surgery.
In any case, the pathological process of gum loss stops after our treatment; it no longer progresses. And we always wait after removing braces (or other orthopedic structures) from 3 to 6 months
for the gums to recover and calm down. And after this, if necessary, plastic surgery of the frenulum, plastic surgery of the vestibule of the oral cavity is performed - all this is done only after orthodontic treatment.
Why is plastic surgery done AFTER, and not BEFORE, bite correction?
Because a scar is formed inside the operated tissue, which in the future can interfere with the movement of teeth when correcting the bite.
Methods of treating pathology in dentistry
The most common method of removing overgrown tissue is surgical excision using a scalpel or laser. Scientifically, this surgical operation is called gingivectomy. The procedure is performed under anesthesia.
About the indications, types and complications after gingivectomy - in the feature article on the website.
If there are few damaged tissues, then doctors may suggest their removal using cryodestruction, when under the influence of low temperatures they die off on their own over time.
If tissue proliferation is accompanied by an inflammatory process, then electrophoresis and darsonvalization may additionally be prescribed.
In addition to excision of excess tissue, treatment should be carried out aimed at eliminating the cause that provoked the development of the pathology. If the cause is a malocclusion, then the patient needs to see an orthodontist, who will prescribe devices to correct the position of the dentition. If there is a fragment of a tooth inside the overgrown gum, then it is necessary to remove it or use prosthetics, if the situation allows. In case of internal diseases of the body, the patient will be referred to specialized specialists - endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, etc.
Dentists are required to sanitize the oral cavity and remove hard and soft bacterial plaque.
Where does the treatment of dental recession begin?
Treatment of recession must begin, first of all, by eliminating the cause - what caused it, what caused the gum recession.
After this, depending on the Miller class, surgical treatment is performed - closing the exposed area. Since gum recession occurs in conditions of a broken bite, it is logical to begin treatment in order to stop the process of recession itself. And here we should note the professionalism of our orthodontists.
We, at the German Implantology Center, effectively follow the approach: first we correct the bite and stop the recession, and only then we treat the recession itself and restore the gum level. To immediately restore gums without eliminating the cause is a symptomatic treatment, extremely ineffective and, in fact, useless.
Our clinics value the time of our patients and offer only proven treatment methods that meet the principles of reliability and effectiveness in the long term.
Recovery period after surgery
If the gum has grown on the tooth, then now you know what to do - you need to contact a dentist who will prescribe adequate treatment.
Since treatment for hyperplasia involves surgical manipulation, there will be a recovery period after it, taking from 5-7 to 10-14 days. At this time, you need to follow all the doctor’s recommendations: take prescribed anti-inflammatory and wound-healing agents, rinse with antiseptics, and use painkillers as pain occurs.
During the rehabilitation period, it is important to exclude “irritating foods” from the diet: spicy and salty, cold and hot, solid foods. And, on the contrary, you need to diversify your diet with foods rich in vitamins C, E, B, A, calcium and phosphorus.
To care for the oral cavity, you need to use a brush with soft bristles and a non-abrasive toothpaste; you should avoid using an irrigator for a few days.
Surgical techniques
In advanced situations, plaque removal alone is not enough. Then there may be a need for open or closed curettage. It is indicated if the gums are very severely detached from the dental neck and the bone structure is changed.
The dentist-surgeon treats the lesion with an antiseptic, makes a small incision and removes purulent deposits and affected tissue . Then the gum is sutured. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia. This means that the patient is conscious and can communicate with the doctor, but does not feel pain.
For a speedy recovery after curettage, antibiotics and mouth rinsing with an anti-inflammatory solution are prescribed. If the pain after surgery is very severe, the patient can use painkillers.
Is it possible to get rid of the problem on my own?
Some people use decoctions of medicinal herbs and plants (chamomile, oak bark, sage and others), as well as solutions to relieve gum inflammation (such as Chlorophyllipt or Stomatophyte) to get rid of the problem. However, you need to understand that hyperplasia cannot be cured by rinsing. This measure will not reduce the volume of overgrown tissue, but will help relieve signs of the inflammatory process and alleviate the condition during teething, and is also well suited as a concomitant therapy after surgical excision of excess gum tissue, which is carried out in a dental office.