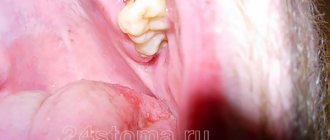
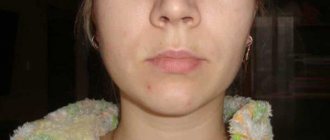
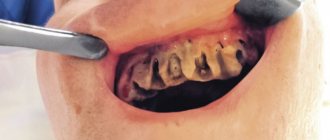
A purulent formation on the gum is popularly called gumboil. Very often it is not taken seriously, but it is not just a small swelling that will go away on its own. Flux is an ontogenic periostitis, a complex infectious disease that affects the periosteum and jaw bone. Periostitis occurs quite often, but without adequate treatment it is fraught with serious complications, including blood poisoning.
It is almost impossible to cure gumboil without the help of a dentist. The treatment program includes therapeutic, physiotherapeutic, and surgical methods.
Have you noticed purulent formations on your gums and swelling of your cheeks? Do you have acute pain in your tooth or gum? Come for a consultation with a dentist at our clinic. Timely treatment of flux allows you to get rid of the problem within about 7 days.
Why does flux form?
Dental diseases are always the precursor to gumboil. Most often lead to suppuration:
- Untreated caries. If caries is not treated, the inflammatory process begins to spread to other tissues. Pulpitis and periodontitis gradually develop.
- Mechanical injury. Injury can lead to more than just crown destruction. Very often, an inflammatory process develops in injured tooth or gum tissues. Without treatment, purulent processes develop and gumboil forms.
- Periodontitis. In more than half of the cases, gumboil develops precisely against the background of periodontitis, as its complication. This is due to the fact that purulent processes from periodontal pockets can spread to the neck of the tooth.
- Poorly sealed canals. Before filling, the canals must be completely cleaned and the filling material must completely fill the cavity. If at least one of the conditions is violated, the infection from the canal spreads to other tissues.
Hematoma
Description
If there is a swollen lump on the gum filled with blood, most likely it is a hematoma. This tumor occurs as a result of an incorrectly removed tooth or injury. Such a lump on the gum above the tooth, as a rule, does not hurt.
Treatment
Dissolves on its own. But if the lump hurts, consult your dentist for advice. The doctor will prescribe painkillers.
When do you need dental help?
Flux has pronounced symptoms. The main one is the appearance of an abscess on the gum next to the diseased tooth. The abscess develops gradually. At first, the gums swell a little and a small red or whitish bump is noticeable on it. After some time, a noticeable fistulous tract forms on the lump, from which pus flows. The development of periostitis is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Swelling and swelling of the gums, lips, cheeks. Sometimes they can be so large that facial features are distorted.
- Severe cutting pain in the tooth area. Innervates the temporal region, orbits.
- The diseased tooth begins to become very loose, even if there was no mobility before or it was insignificant.
Since flux is caused by infection, it is characterized by symptoms that appear during any infectious process. The patient feels unwell, his temperature rises, his head hurts, and weakness appears. Lymph nodes on the head and neck become enlarged.
Any of these symptoms is a reason to consult a doctor. The more advanced the case, the higher the risk of complications. This disease is often accompanied by other pathological processes. For example, a cyst may form in tissues affected by infection.
Why gums may turn blue
Experts identify a large number of factors that can affect the condition of the gums.
Reasons for discoloration of gums in a child:
- Eruption of baby or molar teeth. Due to strong mechanical pressure on the soft tissue vessels, a blue hematoma appears.
- Bruise or cut. Due to mechanical trauma to the gums, a blood clot accumulates at the site of the bruise, causing the gums to turn blue.
In an adult, soft tissues may change color for the following reasons:
- Improper functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- Kidney diseases;
- Problems with the thyroid gland;
- Inflammatory diseases of teeth and gums: gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, herpetic and candidal stomatitis, which are accompanied by increased accumulation of bacterial plaque on the enamel.
- Carious formations localized in the cervical area of the tooth.
- Errors in orthopedic treatment. An incorrectly made crown or denture reduces blood flow along the gingival margin, which causes the periodontium to turn blue. In this case, the color change occurs due to a violation of the blood supply to the soft tissues.
- Surgical interventions. After tooth extraction, the soft tissue in the area of the formed hole may turn blue.
- Burns (regular thermal or chemical burns). A chemical burn can occur due to contact with the mucous membrane of an aggressive substance that is used in the treatment of root canals.
Flux treatment methods
Treatment should be started as early as possible. If an abscess on the gum opens spontaneously, there is a risk of infection entering the bloodstream. With such an infection, blood poisoning develops, and such a complication can lead to serious consequences, including the death of the patient.
Flux treatment is always complex. The treatment program depends on the degree of tooth decay and the spread of infection.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Types of gingivitis
Gingivitis differs in the nature of its course:
- Acute gingivitis is a disease whose symptoms appear suddenly and progress quite quickly.
- Chronic gingivitis is a sluggish process, the symptoms of which increase gradually.
- Aggravated gingivitis (recurrent stage of a chronic process) is an increase in the symptoms of a chronic disease.
- Gingivitis in remission is the moment of complete relief of all symptoms.
The form is:
- catarrhal gingivitis, which is manifested by swelling and redness;
- ulcerative (ulcerative-necrotic) gingivitis, with necrotic (dead) areas of the gums;
- hypertrophic gingivitis, in which there is a significant increase in the volume of gum tissue and its bleeding;
- atrophic gingivitis, on the contrary, is characterized by a decrease in the volume of gingival tissue;
- desquamative (geographic) gingivitis, which is manifested by intense redness and abundant desquamation of the epithelium of the mucous membrane.
According to its distribution in the oral cavity, gingivitis can also be local (affects some areas of the teeth) and generalized (the process affects the gums of the entire jaw or both jaws). And according to severity - mild, moderate and severe gingivitis.
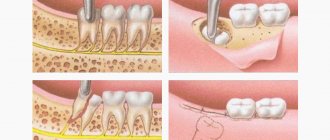
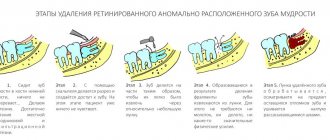
Opening an abscess on the gum
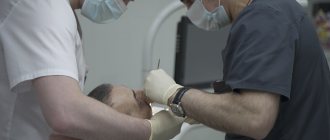
The abscess is always opened. This reduces the risk of spontaneous opening, which can cause complications. The flux is opened under local anesthesia. If the patient has panic or other indications, the doctor may choose a different method of anesthesia.
A small incision is made on the anesthetized gum in the area of the gumboil, no more than 2 cm in length. After the dissection, the doctor completely cleans and sterilizes the purulent cavity and treats it with antiseptics. A crust should not be allowed to form in the area of the incision, as it will interfere with the outflow of ichor and purulent contents. To do this, a drainage is inserted into the incision. After the cavity is cleared of pus, you can begin general treatment, the purpose of which is to eliminate the causes that caused periostitis.
Epulis
Treatment
The lump on the root of the tooth is attached to a stalk and is either red or gum-colored. It affects the lower jaw and occurs as a result of malocclusion, permanent mechanical damage, and poor quality dentures. Often observed in women with hormonal imbalance.
Treatment
It is removed by one of three methods: scalpel, diathermocoagulation or cryodestruction. The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia.
General treatment
Methods depend on the reasons that caused the flux. The only exception is periostitis, which develops against the background of periodontitis. In this case, immediately after opening the abscess, the doctor begins periodontal treatment. No medical manipulations with the tooth are required. In other cases of dental disease you need to treat:
- Pulpitis. First, the dentist drills out carious cavities and performs pulp removal. After this, endodontic canal treatment is performed.
- Periodontitis. Treatment depends on whether depulpation and canal filling have been previously performed. If periodontitis has developed for the first time, the doctor will remove the pulp, clean and fill the canals. If filling of the canals has already been performed previously, they need to be unfilled and treated again. Since it is very important that the pus comes out of the flux completely, when treating complicated pulpitis and periodontitis, a temporary filling is not placed.
- Tooth after restoration. At the first stage, the doctor is faced with the task of completely removing inflammation. After this, the damaged tissue of the root apex is removed. If the condition of the root allows, the tooth is restored again using a core tab or pin and an artificial crown. When the damage is very severe, it is more advisable to remove the tooth.
Symptoms of hematomas in the oral cavity
The most noticeable sign is the spread of vesicles with bloody contents throughout the mucosa. Often there are no other symptoms of pathology. Sometimes patients complain of itching and tingling in the area of damaged tissue. Doctors say that this is a reaction to additional chemical and mechanical irritation of the inflamed mucous membrane under the influence of saliva, contact with teeth, etc. When hematomas form on the oral mucosa during tooth eruption, there are sensations of bursting and pressure from within the gum tissue. If inflammation has become a complication of a burn, pain is a logical consequence of mechanical irritation of the mucous membrane.
Signs of the appearance of blood balls on the cheeks in the mouth, requiring immediate examination and diagnosis, are included in a separate group. Among them:
- relatively frequent appearance of a large number of points of inflammation;
- the duration of wound healing, despite the measures taken to treat them;
- hematomas that are too large, interfering with eating and full communication;
- formation of bloody balls on the lips.
Each of these signs can be a symptom of serious disorders in the body. Therefore, the optimal solution would be to refuse self-medication and schedule a consultation with a qualified dentist.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are used as additional ones. They allow you to quickly cope with the infection and stop the inflammatory process. The following methods can achieve good results:
- Fluctuarization. The inflamed tissues are exposed to low voltage current.
- Electrophoresis with lidase. Electrical current is applied to the tissue, allowing the drug to be effectively distributed.
- Ultrahigh frequency therapy. The method is based on the influence of an electromagnetic field.
- Ultrasound therapy. The effect of ultrasound on infected tissues accelerates their regeneration.
- Laser therapy. Damaged tooth tissue is treated with a laser beam.
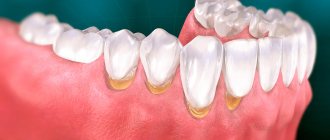
Periodontitis
Description
A hard lump on the gum, an abscess formed at the base of the tooth root. In the absence of therapy, it transforms into a benign tumor.
Treatment
If such compaction of the gums under the tooth appears, contact your dentist. The teeth are unfilled and root canals are cleaned. After removing the exudate, oral baths with medicinal herbs or soda solution are prescribed. Treatment for periodontitis may require multiple visits to the doctor.
Rinse
They are used as an additional treatment in order to completely remove pus and ichor from an opened abscess and prevent the infection from spreading to healthy areas. Soda-salt baths and rinsing with antiseptic solutions help make treatment more effective and speed up gum healing. When rinsing, you must adhere to the following rules:
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
Expert advice
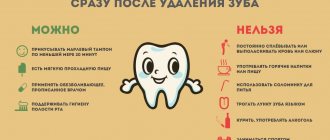
To avoid complications after tooth extraction, you must follow your dentist's recommendations.
- For the first week after surgery, do not eat solid foods or drink drinks through a straw.
- Do not take a hot bath or visit the bathhouse or sauna until the wound has completely healed.
- Use a toothbrush with soft bristles to avoid damaging your oral tissues.
- If pain or other unpleasant symptoms occur, contact your doctor.
How to remove and alleviate the general condition
By following simple recommendations, you can get rid of the complications that have arisen or at least minimize their severity:
- After the operation is completed, ice is applied to the site where the implant is installed for 15 minutes . At home, the patient must perform this procedure at least five times a day.
- The dentist applies dental paste to the wound to promote speedy healing and reduce discomfort.
- The patient should try to be in an upright position more often . At night, sleep on a high pillow to improve blood flow from the wound.
- Treat teeth located next to the implant with 3% hydrogen peroxide.
- Rinsing the mouth with an antiseptic solution after eating disinfects and promotes healing of damaged mucous membranes.
- Avoid spicy, hard, or too hot foods.
- To relieve pain, you must take anti-inflammatory and painkillers prescribed by your doctor.
- Use heparin-based ointments to speed up the resorption of the hematoma.
- To brush your teeth, use a new, soft brush with natural bristles.
- Quit smoking for at least 2-3 weeks.
How to avoid negative consequences
- The choice of clinic and specialist should be conscious. To do this, you need to get acquainted with the opinions of other patients about the work of doctors, study certificates for equipment and other materials that will be used during implantation.
- At the preparation stage, you should not refuse additional examinations to identify all problematic issues that may become contraindications to the procedure.
- It is necessary to provide accurate information about your state of health, medication use, existing diseases (without hiding their exacerbation).
- Complete restoration of the dentition in just 4 days!
more detailsRoott Pterygoid Implants Sinus lift is no longer needed!
more details
Once and for life! Express implantation in 4 days with a permanent ReSmile prosthesis
more details
All-on-4, All-on-6, ReSmile, Zygomatic implantation We use all modern methods of dentition restoration
more details
How to prevent the problem
High-quality care and systematic teeth cleaning are two basic rules, the observance of which will, to a certain extent, protect oneself from inflammatory and carious processes. In addition, do not forget that every time after eating you need to thoroughly rinse your mouth and use dental floss. It is also important to choose the right toothpaste and brush, especially if you have sensitive gums. And of course, don’t forget to visit the dentist regularly.
If a bluish spot appears on your gum, do not put off your visit to the dentist. The longer you ignore the problem, the higher the likelihood of developing truly serious complications.
- Balakhnichev, D.N. The influence of fixed orthopedic structures on the periodontium of abutment teeth, 2011.
Cyst
Description
A hard, bone-like compaction of gums under a tooth, up to 1 cm in diameter. Occurs in people with weakened immunity, genetic predisposition, as well as due to acute infectious diseases, mechanical damage to the soft tissue of the oral cavity.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out in the same way as for fibroma - by excision. After surgery, mouth rinses and baths are necessary, as well as repeated visits to the doctor to monitor recovery.