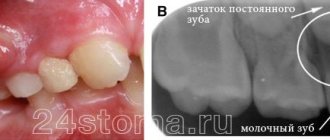
If you notice an abscess or lump on your child’s gum, this is a reason to go to the doctor. Such formations in most cases indicate inflammatory processes inside the dental canals. The same applies to gumboil on a child’s gums - this is inflammation that has involved soft tissue, and has not broken into a fistula (bump), as in the first case.
Both flux and the appearance of a fistula require contacting a specialist. Let's talk about each of the options - what they look like, what the reasons are for their appearance, and what concerned parents should do about them.
What is a fistula
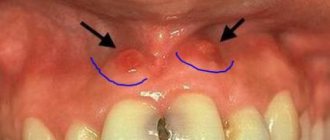
A fistula (gingival fistula) is a small seal on the gum. It is characterized by the presence of an open canal, as well as the constant discharge of pus. In many cases, the presence of such a fistula can be recognized visually when a tubercle appears on the child’s gum, the diameter of which usually does not exceed 2 cm. It has a reddish tint, gradually becomes inflamed, and a small funnel appears. As inflammation progresses, more signs of a problem appear.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that a child has such a pathology as early as possible. If this problem is not detected, the fistula can cause serious complications that will have a significant negative impact on the child’s health.
This phenomenon is especially dangerous for the reason that it often occurs in children when they do not yet know how to speak and cannot complain to their parents or describe the essence of the problem.
Next, we will talk about why a child has fistulas on the gums, what to do to prevent them and properly treat them.
Important:
You must understand that if your child has a lump on the gum or a fistula with purulent discharge, it is useless to self-medicate. No amount of rinsing, application, herbs or even the strongest antibiotics will cope with the source of inflammation at the apex of the root. At best, you will only contribute to the transition of acute inflammation to chronic. Those. if the lump bursts or the fistula closes, all this only indicates a temporary subsidence of the process, which will proceed more imperceptibly, still negatively affecting the germ of the permanent tooth and the entire body as a whole.
Such chronic foci of purulent inflammation are especially dangerous if the child already has concomitant diseases (heart, respiratory organs, joints, etc.). But if there are no such diseases, then the presence of a chronic purulent focus of inflammation increases the risk of many somatic diseases, including lymphadenitis, sore throat, constant exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis and colds.
How to prevent ulcers on the gums - only proper oral hygiene of the child, as well as proper nutrition, can help with this, which will reduce the activity of the carious process in the oral cavity. Read about the age at which you should brush your teeth and how to do it correctly in our article at the link above. The use of additional methods of protection against caries, which include:
- remineralizing therapy,
- fluoridation of teeth,
- sealing dental fissures.
Causes of gum fistula in a child
In most cases, the occurrence of a fistula is provoked due to the fact that pathogenic microflora is created in the child’s oral cavity. The active development of pathogenic microorganisms leads to the fact that suppuration begins to gradually accumulate in the gingival tissues.
Dentists especially emphasize that fistula should not be perceived as an independent disease. Often this is just a symptom showing that there are serious problems with the child’s health, and an inflammatory process is developing in the body. And where there is inflammation, there are sources.
There are several reasons that can contribute to suppuration:
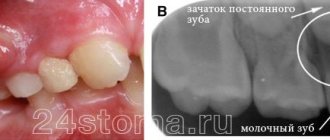
- Periodontitis. It often causes problems in young children when parents do not pay attention to caries of baby teeth. Often it is due to severe tooth decay that the inflammatory process begins. If baby teeth have already been replaced by molars, the source of inflammation will be located right next to the root. In this place suppuration begins to form. It gradually breaks through, and a fistula canal is formed with all the attendant dangers.
- Cyst. Often a fistula occurs at the site of a dental cyst. This is the name for a formation on a child’s gum, inside of which fluid begins to accumulate. Then everything happens according to the same mechanism as in the case of periodontitis. Once there is too much liquid, it begins to break out.
- Osteomyelitis. Another common source of inflammation. It concentrates in the gum area. If you do not start treatment on time, you may experience bone tissue decomposition. A focus of infection is created, the inflammatory process is constantly progressing. The appearance of a fistula is inevitable, because at some point there is too much pus and the tissues cannot hold it.
- Gum injury. The reasons may be different - too hard a toothbrush, improper oral hygiene, scratches, gum punctures when eating food. Such a small wound becomes a source of infection in the body.
Determining the causes of inflammation and suppuration becomes the main task of the dentist. It is important to understand what exactly caused the fistula. Our dentists use advanced diagnostic methods to identify the source of the problem as quickly as possible and eliminate it using one of the available methods.
Reasons for appearance
In medicine, a hole in the gum is called a fistula. A fistula appears as a consequence of the activity of harmful microorganisms that are located in the area of the alveolar process. As a rule, the causative agents of pathology are coccus bacteria.
That is, the main reason for the formation of a fistula is a large amount of pathogenic microflora in the mouth. Lack of hygiene, the accumulation of soft plaque and the formation of tartar provoke the appearance of a fistula in the gums. Over time, tartar grows and begins to put pressure on the gums. In addition, soft dental deposits spoil the aesthetics of a smile; pigment spots may appear on the enamel.
Another reason for the appearance of a fistula near a tooth may be infectious inflammation. Diseases such as tonsillitis, ARVI, and whooping cough reduce immunity, creating all the conditions for the proliferation of bacteria.
Features of fistula of a milk tooth
Many parents wonder whether there is a risk of developing a fistula when the child’s baby teeth have not yet been replaced by molars. There is a common myth that in this case there will be no chance of suppuration.
But in practice, even with baby teeth, a fistula can develop. Its main source is caries. If you do not deal with timely treatment, caries can greatly destroy the tooth, a dangerous infection will be introduced into the gums, and the gradual development of suppuration will be stimulated.
The more damaged the tooth, the higher the risk. Therefore, our dentists recommend paying close attention to preventive examinations of baby teeth in children. It is necessary to visit the dentist's office regularly to prevent an increase in the risk of the disease.
The main symptoms of gum fistula in children
It is very important to understand that a child is at risk of developing a fistula at a very early stage. But often parents in precisely this situation cannot find any signs of a problem. Inflammation can indeed form without serious external manifestations.
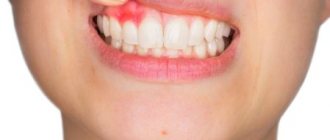
But as the disease progresses, the symptoms become more and more severe. First of all, a small swelling appears at the site of inflammation. Over time, it begins to become more and more pronounced, turns red, and the tissues can warm up from the inside.
Symptoms change with development. Among the important indications:
- It's a dull pain. Usually it turns out to be quite strong, the child begins to complain and be capricious. It may pass for a while and this will lull your vigilance. But there is a serious risk that the sensations will soon return and be even more noticeable.
- Swelling on the gum. It may look like a small abscess, similar to those that sometimes appear on human skin.
- Cone development. Usually it is quite large in size and has a whitish tint. In the inflamed area, the pain intensifies and other unpleasant sensations appear.
- Tooth mobility. It becomes more noticeable as the disease spreads. The tooth becomes very loose, and in the later stages it can even come out of the gums.
- Discharge from the inflamed area. When you press on the gum, it begins to ooze pus and blood.
Also, in the later stages of inflammation, a strong bad breath appears, and other unpleasant symptoms may develop.
It is often possible to find a fistula even on your own during an external examination. Moreover, without a properly selected treatment program, inflammation can spread deeper into the tissue and gradually worsen.
Diagnostic methods
Typically, parents or a dentist detect fistulas at a very early stage. They are localized on the outer or inner side of the gums and reveal themselves by noticeable swelling and the appearance of a whitish lump.
It is very important not to self-treat when a problem is discovered. If your baby has baby teeth, improper treatment can pose a risk to the formation of the dentition. When the teeth are molars, there will also be a lot of problems, and there is a risk of needing extraction.
At the dentist's appointment, the doctor will carefully examine the child and take an x-ray. The location of the inflammation, its nature, and estimated depth are taken into account. Already at the first visit, the doctor begins to develop treatment methods to try to solve the problem without surgical intervention.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a fistula at the beginning of the disease do not manifest themselves in any way. Then, depending on the degree of development of the disease, characteristic signs appear:
- At an early stage, pain develops in the area of the tooth, which intensifies when touching the formation on the gum or when eating food.
- At a later stage - redness of the gums, swelling of the mucous membrane, discharge of purulent contents from the fistula opening, causing loose teeth and the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity.
- In a complicated course against a background of weakened immunity, osteomyelitis may develop in infants. With the progressive form of the fistula, hyperthermia, enlarged lymph nodes, and facial asymmetry due to swelling of the upper lip and neck are noted.
- There is difficulty breathing due to inflammatory manifestations and an increase in the amount of pus, leading to blockage of the nasal passage.
- Swelling of the eyelids and corners of the eyes is possible.
- Symptoms of a fistula , the predecessor of which was the chronic form of single-genus sinusitis. They are different and depend on the age of the child. Infants and young children experience redness of the upper jaw and signs identical to those of osteomyelitis. In adolescents, inflammation spreads to many facial sinuses.
The symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- Heat.
- Migraine.
- Respiratory dysfunction.
- Swelling of facial muscle tissue.
- Acute pain in the trigeminal nerve area.
- Painful palpation of the fang pit and gums.
- The skin and mucous membrane of the nostrils and upper lip have changes in color.
Attention! If you notice one or another symptom in a child that is characteristic of a fistula on the gum, you should contact a dental clinic and receive qualified medical care.
The main risks of gum fistula and the risk of complications
Without proper timely treatment, fistulas often cause complications. They can affect not only the oral cavity, but also the internal organs of the baby.
There are several common risks:
- Severe intoxication of the body. Occurs because pus is constantly secreted from the wound. The pathogenic microflora that develops poses a great danger.
- Tooth loss. Sometimes it is necessary to remove only the one whose root has been affected. But cases with gradual spread of inflammation are also common, when several teeth need to be removed.
- Damage to the periosteum. It has far-reaching consequences associated with inflammation of tissues and bones, and the need for surgical intervention.
- Sinusitis. The infection quickly spreads to the human maxillary sinuses and begins to rapidly progress, covering ever larger areas.
Other dangerous potential complications include the need for perforation of the cheek, flux, removal of tonsils, and gastrointestinal disorders.
As with any other type of inflammation, the hours begin to count. Therefore, if a problem occurs, you need to seek dental help as quickly as possible.
Additional recommendations
During the treatment period, it is very important to follow not only the doctor’s recommendations, but also measures aimed at increasing the effectiveness of therapy. You should exclude hot and salty foods, sweets, solid foods and carbonated drinks from your diet, which can cause irritation to the affected area of the gums. The diet should be nutritious, but gentle, and it is better to give preference to products with a soft, delicate consistency, and after eating it is necessary to rinse the mouth.
You will have to give up carbonated drinks
After treatment of the fistula, rehabilitation measures are necessary aimed at preventing the recurrence of the formation: laser therapy, ultrasound or rinsing the mouth with regenerating solutions.
- Fistula on the gum - how to recognize and treat at home
Main treatment methods
The answer to the question of how to treat a fistula on the gum in a child is given by the dentist after a careful examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis. It is important that the doctor considers the process comprehensively, using not only medication, but also therapeutic methods. Sometimes proper local surgical intervention is also necessary. Let's talk about each of the listed measures in more detail.
First aid methods
When parents and a child visit the dentist, they need to answer questions about how long ago the first symptoms appeared and whether the child has other concomitant diseases. At the first stage, the symptoms of the disease are relieved, and then a deeper plan is drawn up to eliminate the root cause of poor health.
There are several basic first aid methods:
- Relieving pain syndrome. If the baby has a high fever and all signs of inflammation, you can give him antihistamines - Nurofen, Cifecon, paracetamol.
- Reducing swelling. It is best to use safe gels, such as Kalgel.
- Removal of pathogenic bacteria. Most often, this reduces inflammation. It is recommended to rinse or carefully treat the affected area with Miramistin or Chlorhexidine.
First aid helps to slow down the spread of the inflammatory process and reduce it. But you should take medications only with a clear understanding that the baby is not intolerant to them. It is best to consult a doctor.
Subsequent drug treatment will be based on taking properly selected antimicrobial drugs, antiseptics, anti-inflammatory and antihistamines.
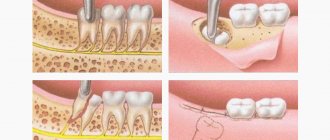
Surgical intervention
Surgery is usually the last option to correct the situation. Doctors resort to it when other means are completely ineffective.
The main reason for prescribing such treatment is the widespread spread of soft tissue inflammation. The area becomes more and more extensive, and pus is actively flowing from the fistula.
In this case, the doctor removes the fistula and scrapes out the affected tissue. Today, laser processing is used for this purpose, which automatically seals small vessels. The likelihood of infection is minimal and the procedure itself is much faster and painless than using traditional surgical instruments.
Next, depending on the situation, the question of the need to remove the tooth is considered. Often it can be preserved and done with simple filling of the canals. A more detailed answer to the question about treatment methods can only be given after a careful examination of the patient.
First aid
It is impossible to cure a fistula on your own, since it appears due to an inflammatory process in the gum tissue. The only thing parents can do in this situation is to eliminate discomfort and make the baby feel better. If a child has a fever, you need to give him an antipyretic drug in accordance with his age, possibly in combination with an antihistamine that will relieve swelling of the gums. To relieve pain and discomfort, it is recommended to lubricate the gums with Metrogyl Denta gel or products used for teething (Kalgel, Cholisal, Dentinox, etc.). To disinfect the oral cavity, it is necessary to treat the affected area with an antiseptic solution or rinse your mouth with it.
- Fistula on the gum: treatment at home
"Metrogil Denta"
Table. Antiseptics for mouth rinsing in children.
| Name | Release form and method of application | special instructions |
| "Chlorhexidine" | It comes in the form of a ready-to-use solution that you need to rinse your mouth with several times a day. Has no age restrictions | It has a bitter taste; with prolonged use, it can stain the surface of teeth; it is ineffective against some types of microbes. |
| "Miramistin" | Available in the form of a spray, which is sprayed onto the affected area 3-4 times a day. | Not recommended for use in children under 3 years of age due to risk of ingestion. The drug should not be used for more than 10 days in a row, as it can cause oral dysbiosis |
| "Stomatofit" | Concentrated solution of medicinal herbs for mouth rinsing. Before use, the drug must be diluted with water in the proportion of 10 ml to half a glass of water. | The product contains alcohol, so it can only be used from the age of twelve. Sometimes causes allergic reactions |
| "Tantum Verde" | Antiseptic and anti-inflammatory spray for treating the oral cavity. Spray on affected areas 2 times a day | Contraindicated for use in children under 12 years of age |
| "Betadine" | Solution for disinfecting the oral cavity and treating mucous membranes. Before use, you need to dilute it with water (the concentration depends on the age of the child), then rinse your mouth with it or lubricate the affected gum. | The main component of the drug is iodine, which, even when applied topically, can be absorbed into the blood. For this reason, the drug should be used with caution in children with thyroid dysfunction. |
To rinse your mouth with a fistula, you can use a solution of soda and salt (a teaspoon per glass of water) or drop a few drops of iodine into a glass of water. In addition, decoctions of medicinal herbs - chamomile, oak bark, calendula, St. John's wort, strawberry leaves - help eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Calendula decoction
Treatment of the oral cavity in children under two years of age should be carried out very carefully, as there is a high risk of ingesting antiseptics and the occurrence of adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract.
What should parents not do in cases where a child is diagnosed with a fistula? First of all, you should not apply a heating pad to the affected area - thermal procedures cause active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. It is forbidden to treat your gums or rinse your mouth with concentrated products such as hydrogen peroxide - they can cause a burn to the gum mucosa. Finally, it is strictly forbidden to open fistulas on your own or try to squeeze pus out of them, as this will lead to the spread of the infectious process.
Treatment of gum fistula with antibiotics
How to treat a fistula at home
We emphasize that home treatment is only one of the auxiliary methods prescribed by a doctor.
At home, you will need to treat the oral cavity using special decoctions with a pronounced calming and antiseptic effect. You can use decoctions of calendula and chamomile, solutions of salt and soda.
Also allowed are lotions made from aloe and Kalanchoe, and the application of special ointments prepared at home. They are made using crushed chamomile herbs mixed with sea buckthorn oil.
This home treatment can significantly speed up the recovery period and reduce your child’s discomfort.
Prevention methods
Fistula can appear in any child, so it is very important to correctly approach the methods of its prevention. Among them are:
- Strict adherence to oral hygiene practices.
- Moderate consumption of sweets, avoidance of candies and anything that can hurt your gums.
- Regularly inspect your gums for damage.
- Treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases.
- Periodic examinations at the dentist.
The sooner the problem is identified, the easier it will be to get rid of it and the less harm it will cause to the baby’s body.
Complications
If the pathology is not eliminated in a timely manner, complications may develop. Among them:
- tonsillitis;
- flux;
- destruction of healthy gum tissue;
- inflammatory processes in the stomach and intestines (purulent contents enter the digestive tract with saliva);
- improper eruption of permanent teeth;
- tooth loss.