01 June 2020
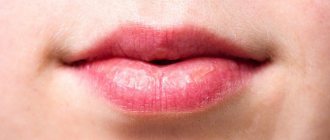
Cheilitis is an inflammatory process that affects the border, mucous membrane and skin of the lips. The disease has a long-term recurrent nature.
Cheilitis is an inflammatory process that affects the border, mucous membrane and skin of the lips. The disease has a long-term recurrent nature. In young people, the course is more favorable and self-healing is possible. In old age there is a risk of leukoplakia and malignancy.
Causes of cheilitis
The inflammatory process can begin for multiple reasons. One of the most common of them is mechanical injuries: for example, accidental biting can cause inflammation.
The development of the disease can also be provoked by:
- unfavorable environment (people who spend a lot of time outdoors and are exposed to wind, frost and other weather conditions are more likely to suffer from cheilitis);
- aggressive action of cosmetics or an allergic reaction to some of their components;
- lack of vitamin B2, which is responsible for the division and growth of epithelial cells;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, lack of immunity.
What triggers the development of the disease
There is practically no protective layer on human lips, so they are highly susceptible to external factors. For this reason, people are often concerned about the drying out of the mucous membrane, which leads to the appearance of microcracks and further infection.
The most common causes of the problem are the following:
- changes in air temperature, sun, wind - these natural factors dry out the skin and it cracks,
The sun, wind, sudden changes in temperature can affect the condition of the lip mucosa - the use of low-quality lipstick or hygiene balms - the lanolin they contain can clog the pores with a secretion that does not allow the skin to breathe,
- dermatoses, allergic reactions - dangerous chemical compounds in contact with the surface of the epithelium cause rashes, cracks or wounds,
- the predominance in the diet of spicy, sour, salty or hot foods that irritate the epithelium and mucous membranes,
- congenital, acquired diseases of the thyroid gland, immunodeficiency states - these pathologies negatively affect the skin,
- skin tuberculosis, venereal infectious diseases, lichen,
- diseases of the central nervous system - because of them, patients may feel itching,
- chemotherapy,
- vitamin deficiency - a lack of nutrients in the body negatively affects the functioning of all its systems,
- mechanical damage.
If a child breathes through his mouth during sleep, his lips may become dry.
Sometimes pathology occurs in a child if he breathes through his mouth during sleep. However, if an adult has a chronic runny nose, he will also breathe through his mouth. With such a violation of the physiological state, the sensitive skin and oral mucosa dries out, then unpleasant defects appear.
Types of the disease, their symptoms
There are a large number of types of disease, each of which has its own symptoms. Cheilitis happens:
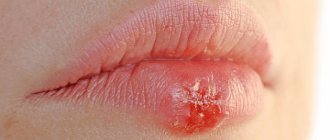
- catarrhal, resulting from injury. Its characteristic symptoms are redness, peeling, swelling and soreness of the lips.
- eczematous, developing due to the occurrence of eczematous processes. The reason is an allergy to a certain type of food, cosmetics (lipstick, cream).
- glandular, associated with an abnormality of the salivary glands. It happens that cheilitis on the lips accompanies periodontal disease, lupus, etc. The lower lip often suffers and begins to peel.
- meteorological. It is caused, as the name suggests, by weather conditions (high air humidity, strong wind, decreased or increased temperature, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, etc.).
- exfoliative, characterized by a chronic course. It is divided into two forms - dry (the blood supply to the lips is disrupted and, as a result, dry scales are formed, which can be easily removed, but after a few days they appear again) and exudative (the border swells and becomes inflamed, crusts appear).
- angular, called jam. Due to streptococci, inflammation begins in the corners of the lips. Vitamin deficiency and frequent licking of lips can also provoke it.
- atopic, accompanying atopic dermatitis. The red border of the lips flakes and itches, the lips crack.
- hypovitaminosis, which occurs due to a lack of B vitamins. Dryness and a pronounced burning sensation affect not only the lip area, but also the entire mucous membrane of the mouth, including the tongue. In this case, the mucous membrane turns red, and vertical cracks form in the area of the red border.
Regardless of the type of cheilitis, common symptoms will be:
- peeling of the lips, observed both only near the border and over the entire surface;
- swelling and swelling, burning and itching in the lips, the appearance of cracks and crusts on them.
Treatment of various types of cheilitis
The course is developed taking into account the type of diagnosed disease and the general condition of the body.
- For exfoliative cheilitis, additional consultations with a neurologist and neuropsychiatrist are recommended. The patient is prescribed a course of sedatives. Effective methods of local treatment include laser therapy, ultrasound or radiation therapy, and the use of moisturizing cosmetic creams and ointments. According to indications, hormonal medications and vitamin complexes are prescribed.
- Glandular cheilitis is removed with anti-inflammatory ointments. Local treatment consists of cauterization or desquamation of enlarged salivary glands, and during the rehabilitation period, the use of drugs to eliminate dryness or excess moisture of the mucous membrane.
- When treating atopic cheilitis, the goal is to eliminate any irritating factors. The local course is based on the use of anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic drugs in the form of external ointments. Patients are also recommended to have a hypoallergenic diet that excludes the consumption of fish, citrus fruits, spicy foods and alcohol.
- For meteorological cheilitis, treatment tactics include taking vitamin preparations, using local healing agents and ointments with a high UV filter.
Timely initiation of treatment and the patient completing its full course guarantees relief from the unpleasant symptoms of cheilitis with a long-term effect.
Cheilitis in children
Depending on the age of the child, he may experience a certain type of cheilitis.
Newborns suffer from a catarrhal disease caused by the prolonged presence of a pacifier or bottle in the mouth. Plus, saliva accumulates on the nipples of the lips, irritating sensitive baby skin.
If the disease is ignored, hoping that it will go away on its own, cheilitis will develop into an exfoliative form, accompanied by the formation of scales, which the child will not be able to remove himself (parents are highly discouraged from interfering in this process, since attempts to tear off the crusts can cause cracks, which will only aggravate the situation ).
Constant sucking of the mother's breast is an equally common cause of the development of the disease: during feeding, cracks form on the nipples, into which bacteria penetrate, which causes cheilitis.
Symptoms of angular cheilitis
Typical symptoms of angular cheilitis depend on the type of pathogen, as well as the age of the patient:
- Streptococcal infection.
It is more often recorded in children and is characterized by the formation of blisters in the corners of the mouth, which gradually burst with the formation of painful erosions. Gradually, the ulcers become covered with a crust, but when the mouth is opened, they burst, which causes pain. With streptococcal seizures, there is pain with any movement of the lips.
- Yeast or fungal.
With this form of inflammation, a crust does not form. The erosion itself is covered with a whitish coating, which is easily removed. However, it may not be noticeable when closing the mouth. Often this pathology is combined with fungal stomatitis.
Types of disease
Cheilitis is a fairly large group of diseases that vary in their clinical manifestations and origin. For example, with absolutely similar symptoms, sometimes different reasons for the development of the problem are identified. In this regard, treatment methods also differ - medications of various effects are prescribed for oral administration, ointments, creams or physiotherapy.
Important! Cheilitis can be an independent type of disease or accompanying with more serious pathologies. Treatment cannot be delayed, because due to frequent damage to the epithelium, the risk of developing malignant tumors increases.
This disease must be correctly classified in order to determine how and with what to treat it. Accordingly, you should not engage in self-diagnosis; it is better to go to a doctor to clarify the cause. All types of cheilitis encountered in practice can be divided into two large categories: independent and symptomatic. The former arise as a reaction of the body to certain phenomena, the latter – as a symptom of the underlying disease. Cheilitis is also divided according to the nature of its manifestations and the nature of its origin. Next, we will consider these classifications in more detail.
Drugs for drug treatment
You can get rid of itching and other uncomfortable symptoms with the help of drug therapy. In such situations, the following drugs are usually prescribed:
- antifungal agents (or antibacterial) taking into account the type of pathogen,
- antihistamines (to get rid of allergic manifestations),
- psychotropic and sedative against cheilitis of a neurological nature,
- vitamin complexes, immunoboosting agents,
- glucocorticosteroids for severe inflammatory processes,
- antiseptics and softening gels or ointments for treating wounds.
Do not start taking medications without first consulting a specialist. All funds are selected on a strictly individual basis.
Methods for diagnosing the problem
Many people facing the above problems do not know which doctor can help them. Therefore, experts remind that treatment for cheilitis should only be prescribed by a dentist, who, if necessary, can refer the patient to the office of an endocrinologist, dermatologist, immunologist, therapist or allergist. Doctors carry out the following manipulations: carry out a visual inspection of the affected areas, analyze the patient’s complaints and the totality of manifestations, study the results of blood tests (biochemical, general). In some cases, the affected tissues are subjected to histological examination.
Only a specialist can diagnose the problem and prescribe treatment
Possible complications of the disease
Many people perceive the disease as a cold, and then do not pay due attention to symptomatic treatment. No one thinks about how to cure it, and in the meantime, without timely treatment, the problem develops into severe stages. The most dangerous complications are:
- development of malignant processes,
- the appearance of superinfections - the attachment of other strains of viruses to the affected cells.
Complicated forms of pathology can make it difficult to eat and even worsen the general condition of the body (provoke dizziness and weakness). Speech defects also occur, because crusts impede lip mobility. And pronounced aesthetic defects on the face often become the cause of psychological problems.
Traditional medicine
To speed up the healing process, therapy with well-proven folk remedies is allowed. So, at home, anti-inflammatory, wound-healing decoctions and infusions are often used:
- aloe juice - peeled lower leaves of the plant are crushed, and the liquid from them is mixed with boiled vegetable oil in a ratio of 1:3. The resulting thick mixture is used to treat the affected areas at least 3-4 times a day,
Aloe juice is good for treatment - boiled sage or calendula - 2-3 tbsp. l. dry plants, pour 500 ml of water and boil for about 10 minutes. The mixture is filtered and applied to the affected areas every 30 minutes,
- oak bark - 40 g of crushed bark is poured into 200 ml of chilled water and kept for 30 minutes over low heat. The lips are lubricated every few hours with cooled and strained liquid.
“I once had meteorological cheilitis. I got rid of it very easily and quickly by regularly lubricating my lips with regular vegetable oil. It moisturizes the skin well and relieves the feeling of tightness.”
Yana S., 34 years old, Volgograd
The use of any traditional medicine recipes must be agreed upon with the attending physician. Otherwise, self-treatment can only aggravate the situation and lead to undesirable consequences.
Prevention of the disease
The following preventive measures will help to avoid the problem and prevent its progression:
- frequent, regular moisturizing of lips with hypoallergenic products containing natural ingredients,
- correct diet - excluding unhealthy foods from the menu, switching to a dairy-vegetable diet,
- avoiding contact with allergens,
- oral hygiene and timely visits to the dentist,
- taking multivitamins,
- regular exercises to strengthen the muscles of the cheeks and lips,
- giving up addictions (drinking alcohol and tobacco products).
Hypoallergenic hygiene products are perfect for prevention.
The main condition for a speedy recovery is a timely visit to doctors and implementation of therapy under their supervision. There is no need to take risks and self-medicate or use some folk method without additional medications, since the problem can become dangerous and the recovery process will drag on for a long period.
General treatment recommendations
After determining the exact form of the disease, the doctor must assess its severity and how to cure it. If the problem is not severe and protracted, then it is effective to apply local correction of the endocrine glands using physiotherapy. The following activities are most often prescribed:
- laser therapy,
- ultrasound therapy,
- UV radiation,
- electrophoresis,
- blood transfusion.
In some cases, laser therapy is prescribed.
It is worth noting that in difficult cases, more radical treatment options are prescribed - electrocoagulation, laser ablation, surgical enucleation.
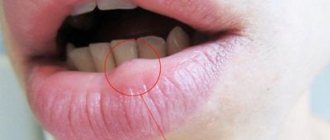
Main signs of cheilitis
All manifestations of the inflammatory process have varying degrees of severity, but the following symptoms are mainly noted:
- dry skin around the mouth,
- cracking, appearance of small wounds,
- bleeding at the site of damage to the integrity of the epithelium,
- redness and swelling of the red border,
- loss of elasticity of the epithelium, appearance of a keratinized layer,
- pain in the area of inflammation,
- the occurrence of painful sensations caused by mechanical irritation of erosive areas during chewing food,
- change in color of the affected areas of the mucous membrane.
Cracks and wounds indicate a problem.
If even one of the symptoms described above appears, it would be a good idea to see a doctor. The sooner a pathological condition can be recognized, the faster it can be eliminated.