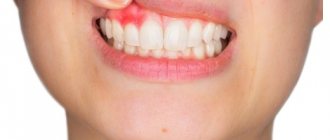
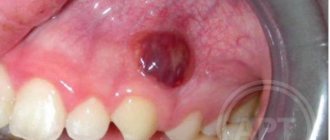
A common reason for visiting a dentist is a lump on a child’s gum. Upon examination, the doctor discovers a round formation of varying degrees of density, painless or with a mild pain symptom.
In most cases, in the area where the pathological element occurs there is a dilapidated or filled tooth. But sometimes the tooth turns out to be intact (undamaged), and the surrounding gum has a normal color. The reasons for the appearance of a lump can be varied. To determine them, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible.
Reasons for the formation of an abscess
Young children do not properly care for their oral cavity. Poor brushing of teeth promotes the accumulation and proliferation of bacteria. Penetrating into the tissue, they provoke the development of inflammatory processes, including a purulent lump.
Other factors also influence the formation of an abscess:
- New teeth.
In some babies, the eruption of baby teeth is preceded by the appearance of small tumors filled with white fluid. If such a lump on the child’s gum does not hurt, then there is no reason to urgently consult a doctor.
- Gum injury.
Damage occurs due to the active lifestyle of babies, solid foods or accidental biting. The injured area becomes red and inflamed. Usually everything goes away on its own, but sometimes, when an infection occurs, ulcers and lumps appear.
- Oral diseases:
- caries;
- pulpitis;
- periostitis;
- cyst;
- fistula;
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis.
Inflammatory processes on the gums are often accompanied by abscesses. Purulent complications can be avoided by promptly consulting a doctor.
Why does a lump appear on a child’s gum?
The formation of a growth on a child’s gum can be caused by:
- advanced stage of caries;
- inflammation of gum tissue;
- mechanical trauma to the jaw;
- teething.
The most common reason for the formation of a “pimple” on a child’s gum is carious infection. In the absence of professional treatment, there is a risk of suppuration near the apex of the root. The pus requires release and begins to collect under the mucous membrane near the diseased tooth. This forms a cyst (flux), which looks like a white dot on a child’s gum.
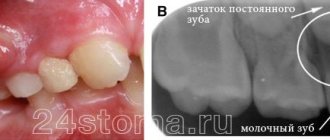
Infants and children of the second year of life may also develop “cysts,” but white bumps on the gums of a child of this age are associated with teething. They occur infrequently, but can greatly bother the baby until the teeth come out completely.
Symptoms of an abscess
The initial stage of the formation of a white bump on the gum may be asymptomatic. The abscess gradually increases, leading to the following symptoms:
- formation of a painful protrusion;
- smell from the mouth;
- bleeding from gums;
- pain when eating.
If you do not help the child at this stage, further development of inflammation will lead to intoxication. The baby's temperature will rise and signs of weakness and malaise will appear.
What is a fistula
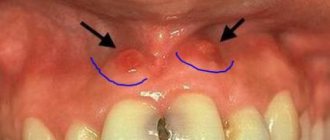
A fistula (gingival fistula) is a small seal on the gum. It is characterized by the presence of an open canal, as well as the constant discharge of pus. In many cases, the presence of such a fistula can be recognized visually when a tubercle appears on the child’s gum, the diameter of which usually does not exceed 2 cm. It has a reddish tint, gradually becomes inflamed, and a small funnel appears. As inflammation progresses, more signs of a problem appear.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that a child has such a pathology as early as possible. If this problem is not detected, the fistula can cause serious complications that will have a significant negative impact on the child’s health.
This phenomenon is especially dangerous for the reason that it often occurs in children when they do not yet know how to speak and cannot complain to their parents or describe the essence of the problem.
Next, we will talk about why a child has fistulas on the gums, what to do to prevent them and properly treat them.
Treatment of inflammation
Removal of a lump with pus on a child’s gum should be started immediately. Only a dentist can help the baby.
IMPORTANT! Self-medication, as well as piercing and squeezing are strictly prohibited! Such an intervention will lead to serious complications.
When an abscess forms over a baby's baby tooth, the doctor most often removes it. Such measures are necessary to exclude the possibility of destruction of the rudiments of the root. If a child has a lump on his gum next to a permanent tooth, treatment begins with a thorough examination. Sometimes the dentist will send you for an x-ray to assess the extent of the damage. Removal of a permanent tooth is carried out in extreme cases.
Treatment of lumps on the gums of a child
If a cyst or ulcer appears on your baby’s gum, you should immediately consult a doctor. Treatment tactics are selected based on the cause of the pathology:
- Flux. When there is purulent inflammation of a baby tooth, it is important to prevent infection of the permanent one. Therefore, the temporary tooth is mainly removed. If flux appears on a permanent tooth, the doctor looks at the degree of its destruction. Sometimes the tooth can be saved.
- Teething. In this situation, if a child's gums become white, intervention is usually not required. But parents still need to show their baby to the dentist to make sure there are no oral diseases.
- Injury. If, after a fall or injury from a hard object, a hematoma or a white spot appears on the child’s gum, monitor his well-being. If your baby complains of pain and the affected area is very swollen, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Having discovered a suspicious “pimple” on the gum, parents should not:
- try to open it;
- give the child any medications without a doctor’s prescription;
- stop daily hygiene procedures;
- rinse the child’s mouth with hot herbal decoctions;
- apply hot compresses to the gums.
To register at the Doka-Dent clinic, fill out an application on the website and wait for the administrator to call, or call the branch you are interested in in Moscow.
The main symptoms of gum fistula in children
It is very important to understand that a child is at risk of developing a fistula at a very early stage. But often parents in precisely this situation cannot find any signs of a problem. Inflammation can indeed form without serious external manifestations.
But as the disease progresses, the symptoms become more and more severe. First of all, a small swelling appears at the site of inflammation. Over time, it begins to become more and more pronounced, turns red, and the tissues can warm up from the inside.
Symptoms change with development. Among the important indications:
- It's a dull pain. Usually it turns out to be quite strong, the child begins to complain and be capricious. It may pass for a while and this will lull your vigilance. But there is a serious risk that the sensations will soon return and be even more noticeable.
- Swelling on the gum. It may look like a small abscess, similar to those that sometimes appear on human skin.
- Cone development. Usually it is quite large in size and has a whitish tint. In the inflamed area, the pain intensifies and other unpleasant sensations appear.
- Tooth mobility. It becomes more noticeable as the disease spreads. The tooth becomes very loose, and in the later stages it can even come out of the gums.
- Discharge from the inflamed area. When you press on the gum, it begins to ooze pus and blood.
Also, in the later stages of inflammation, a strong bad breath appears, and other unpleasant symptoms may develop.
It is often possible to find a fistula even on your own during an external examination. Moreover, without a properly selected treatment program, inflammation can spread deeper into the tissue and gradually worsen.
The main risks of gum fistula and the risk of complications
Without proper timely treatment, fistulas often cause complications. They can affect not only the oral cavity, but also the internal organs of the baby.
There are several common risks:
- Severe intoxication of the body. Occurs because pus is constantly secreted from the wound. The pathogenic microflora that develops poses a great danger.
- Tooth loss. Sometimes it is necessary to remove only the one whose root has been affected. But cases with gradual spread of inflammation are also common, when several teeth need to be removed.
- Damage to the periosteum. It has far-reaching consequences associated with inflammation of tissues and bones, and the need for surgical intervention.
- Sinusitis. The infection quickly spreads to the human maxillary sinuses and begins to rapidly progress, covering ever larger areas.
Other dangerous potential complications include the need for perforation of the cheek, flux, removal of tonsils, and gastrointestinal disorders.
As with any other type of inflammation, the hours begin to count. Therefore, if a problem occurs, you need to seek dental help as quickly as possible.
How to treat a fistula at home
We emphasize that home treatment is only one of the auxiliary methods prescribed by a doctor.
At home, you will need to treat the oral cavity using special decoctions with a pronounced calming and antiseptic effect. You can use decoctions of calendula and chamomile, solutions of salt and soda.
Also allowed are lotions made from aloe and Kalanchoe, and the application of special ointments prepared at home. They are made using crushed chamomile herbs mixed with sea buckthorn oil.
This home treatment can significantly speed up the recovery period and reduce your child’s discomfort.
Features of fistula of a milk tooth
Many parents wonder whether there is a risk of developing a fistula when the child’s baby teeth have not yet been replaced by molars. There is a common myth that in this case there will be no chance of suppuration.
But in practice, even with baby teeth, a fistula can develop. Its main source is caries. If you do not deal with timely treatment, caries can greatly destroy the tooth, a dangerous infection will be introduced into the gums, and the gradual development of suppuration will be stimulated.
The more damaged the tooth, the higher the risk. Therefore, our dentists recommend paying close attention to preventive examinations of baby teeth in children. It is necessary to visit the dentist's office regularly to prevent an increase in the risk of the disease.
Causes of gum fistula in a child
In most cases, the occurrence of a fistula is provoked due to the fact that pathogenic microflora is created in the child’s oral cavity. The active development of pathogenic microorganisms leads to the fact that suppuration begins to gradually accumulate in the gingival tissues.
Dentists especially emphasize that fistula should not be perceived as an independent disease. Often this is just a symptom showing that there are serious problems with the child’s health, and an inflammatory process is developing in the body. And where there is inflammation, there are sources.
There are several reasons that can contribute to suppuration:
- Periodontitis. It often causes problems in young children when parents do not pay attention to caries of baby teeth. Often it is due to severe tooth decay that the inflammatory process begins. If baby teeth have already been replaced by molars, the source of inflammation will be located right next to the root. In this place suppuration begins to form. It gradually breaks through, and a fistula canal is formed with all the attendant dangers.
- Cyst. Often a fistula occurs at the site of a dental cyst. This is the name for a formation on a child’s gum, inside of which fluid begins to accumulate. Then everything happens according to the same mechanism as in the case of periodontitis. Once there is too much liquid, it begins to break out.
- Osteomyelitis. Another common source of inflammation. It concentrates in the gum area. If you do not start treatment on time, you may experience bone tissue decomposition. A focus of infection is created, the inflammatory process is constantly progressing. The appearance of a fistula is inevitable, because at some point there is too much pus and the tissues cannot hold it.
- Gum injury. The reasons may be different - too hard a toothbrush, improper oral hygiene, scratches, gum punctures when eating food. Such a small wound becomes a source of infection in the body.
Determining the causes of inflammation and suppuration becomes the main task of the dentist. It is important to understand what exactly caused the fistula. Our dentists use advanced diagnostic methods to identify the source of the problem as quickly as possible and eliminate it using one of the available methods.