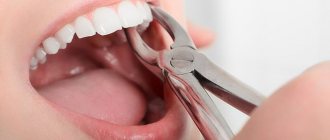
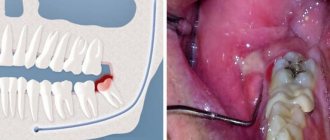
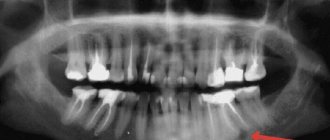
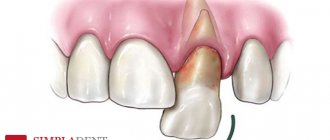
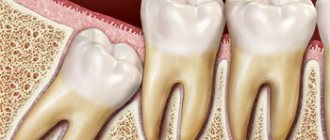
Wisdom teeth (third molars, “eights”) are rightfully considered the most problematic teeth. For a rare lucky person, their eruption proceeds safely. After all, even if the number eight has enough space in the dentition - which is rather an exception in modern realities - while passing through the gums, this large multi-tubercular tooth causes a lot of suffering to its owner. That is why in America, for example, wisdom teeth are removed prophylactically, before eruption - even during their formation.
What problems can arise from wisdom teeth?
Reasons for the formation of pus in the gums
There are several reasons for the formation of pus:
- The inflammatory process causes a disease such as periodontal disease (gingivitis).
- Periodontal disease.
- Mechanical damage to the gums.
- Chemical or thermal burn.
- Unprofessional removal of tartar, which affected the gums.
- Extensive caries causes pulpitis.
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards when performing dental procedures.
- Unsanitary oral cavity.
- Types 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Summing up the causes of purulent inflammation of the gums, we can highlight the main factor that causes this disease – the vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms.
Tooth abscess - symptoms and treatment
A tooth abscess does not go away without treatment. If you open it yourself, the pain may decrease significantly, but this does not eliminate the need for dental treatment. If the abscess is not drained, the infection can spread to the jaw tissue and other areas of the head and neck, which can lead to various complications.
Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis
When the veins are located close to the source of infection, a serious complication such as thrombophlebitis develops - inflammation of the vein with subsequent formation of a blood clot. First, the inflammatory process affects the walls of blood vessels (phlebitis), then spreads to the tissue surrounding the vein (periphlebitis) and finally covers the entire wall of the vein. Due to damage to the vessel, blood flow becomes slower, the composition of the blood changes, and clotting increases. All this contributes to the formation of a blood clot. In some cases, blood clots form in the venous sinuses of the brain.
Mediastinitis
Mediastinitis is an inflammation of the mediastinum (a complex of organs located in the chest cavity between the left and right mediastinal pleura, the posterior surface of the sternum and the thoracic spine and rib necks). Can be fatal.
The infection can penetrate into the mediastinum by contact, through the blood or lymph flow. The purulent exudate is so active that it can melt the intermuscular septa and walls of large arteries. In this regard, the infectious process spreads quickly and creates the risk of severe bleeding.
The source of the spread of infection leading to mediastinitis is usually inflammation in the area of the apex of the tooth root (sometimes in combination with infection of the tonsils or damage to the oral mucosa).
Acute or chronic sepsis
Sepsis is the most severe complication of a tooth abscess, which occurs when the immune system fails. The body cannot resist the infection, and it spreads throughout the body. Depending on the speed of onset of symptoms, sepsis can be fulminant (1-2 days), acute (5-7 days), subacute (1-2 weeks) and chronic. First of all, the functioning of the lungs is disrupted, and then other organs: liver, kidneys, etc. Subsequently, septic shock develops: blood circulation in the organ tissues slows down, and failure of several organ systems develops - multiple organ failure syndrome. When this syndrome occurs, most patients die within 2-3 days [8].
Meningeal diseases
Meningeal complications of a tooth abscess (meningitis, brain abscess, etc.) are not so common, but their mortality rate is quite high: it reaches 40-90%. Most often, these diseases arise due to the spread of infection from primary foci, the temporal region, pterygopalatine or infratemporal fossa.
Signs of pus and purulent inflammation
- severe pain in the area of the wisdom tooth; when you press on the gum, pus is released;
- redness of the gums and swelling;
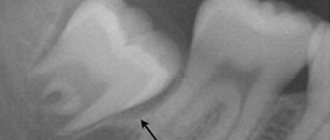
- a large carious cavity is filled with softened soft tissue;
- colored plaque on the tooth and tartar;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- change in facial contour. It becomes asymmetrical.
What to do if the gums above the wisdom tooth are inflamed?
- Clean thoroughly, even if it bleeds and hurts. After all, as you already know, the cause of inflammation is that plaque and food debris around the “eight” were regularly not cleaned. The plaque microbes did their job - pericoronitis occurred. To more successfully clean plaque around a wisdom tooth, it is better to purchase a brush with elongated front bristles.
Brush with extended front bristles
- Make salt baths (dissolve 1 teaspoon of salt in 1 glass of water at room temperature - never hot!). It is recommended to put the saline solution in your mouth and hold it on the side of the inflamed tooth for several minutes. Such baths are carried out every hour; it is optimal to alternate them with rinsing with chlorhexidine.
- If the swelling does not decrease within a day or two, it is better to consult a dental surgeon. Perhaps an incision (pericoronarotomy) and the prescription of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are needed. If you have a fever and it hurts to swallow, you can’t hesitate, you need to urgently go to a dental surgeon!
- If inflammation of the gums around the wisdom tooth occurs regularly and you have repeatedly visited the dentist for an incision in the gum area above the wisdom tooth, this is an indication for removing the “eight”. Surgeons recommend removing the tooth as planned, not during an exacerbation or during an active inflammatory process. Such removal will be easier for you, painless and the body will need much less time to recover.
After reading the article, did you remember your torment with the eruption of wisdom teeth? We invite you to a consultation with a dental surgeon at the KANO clinic network. Our specialists will prescribe the necessary diagnostic X-ray and tell you what to do with the problem “eight”.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed after a visual examination of the oral cavity and determination of the source of pus. Treatment of purulent inflammation can be:
- In a therapeutic way with the help of medicinal drugs.
- Physiotherapeutic.
- Surgery.
If purulent discharge does not stop after a course of therapeutic treatment, the doctor will prescribe surgery. Before the operation, plaque and tartar are cleaned and the mouth is disinfected.
An injection with a local anesthetic is injected into the gum and the gum is cut. The gum mucosa is cleaned of pus. If the fistula through which pus flowed is large, then a drainage is inserted. In the postoperative period, the patient is prescribed therapeutic treatment, which includes taking antibiotics and rinsing the mouth with a 0.05% chlorhexide solution, and is prescribed a complex of vitamins and minerals.
Every day, until complete healing, the patient must come to the dentist, where he is given an antibacterial application on the gum of the wisdom tooth. The patient must strictly follow all the dentist’s recommendations for oral care and consume only liquid foods.
Causes of dental inflammation
Bacterial damage to dental tissues can occur due to poor oral hygiene and insufficient patient attention to dental health issues. Among the common reasons:
- gum pathologies (periodontitis, periodontal disease, gingivitis);
- spread of caries;
- dental cysts, granulomas;
- cracks, chips on the tooth surface;
- oral injuries (for example, while eating);
- untimely change of toothbrush;
- poor quality teeth cleaning;
- weakening of the immune system.
However, the source of infection can be located in other parts of the body, and bacteria are carried into the gums by the bloodstream. Therefore, close attention should be paid to the treatment of any infectious diseases (especially ENT diseases) and increasing immunity.
Features of professional help
After determining the cause of inflammation, a specific method of intervention is prescribed.
- Taking medications . Antibiotics are indicated for low-grade fever, enlarged lymph nodes, and spread of inflammation to adjacent tissues.
- Operation . It is carried out in case of pericoronaritis, incorrect positioning of the tooth, acute purulent pathologies.
- Dissection of the damaged gum . If the hood above the figure eight is inflamed, it is cut. It is carried out during prolonged tooth eruption.
- Novocaine blockade . Reduced symptoms of radiating pain.
- Physiotherapeutic techniques (laser exposure). Improvement of condition. Often prescribed in combination with other methods.
How to help yourself at home
- Painkillers . Analgin, Nimesil, Ketoral will relieve pain for a couple of hours.
- Using gels and ointments to relieve inflammation. Children's gel Kalgel, Kamistad, Cholisal will provide the desired effect.
- Decoctions of medicinal herbs . Traditional ingredients - chamomile, sage, St. John's wort. Prepare the decoction for baths (pour into mouth, do not rinse).
- Antiseptics . An aqueous solution of Chlorhexidine, Furacillin or Miramistin is used for rinsing.
To relieve inflammation, you can prepare an antiseptic solution. Mix 1 tsp. soda and salt in a glass of water, mix, pour in 2-3 drops of iodine. Rinse your mouth with liquid 2-3 times a day.
It is forbidden to apply compresses to the inflamed gums or rinse with warm or hot water. Heating the affected area leads to dangerous complications.
Who treats an abscess
Only a dentist can cure a tooth abscess. If you suspect an abscess, you should contact your general practitioner. He will conduct an examination and, if necessary, schedule a consultation with a dental surgeon.
Preventing a tooth abscess is easier than curing it. To do this, it is necessary to carefully observe oral hygiene, promptly eliminate inflammatory processes in the body, and visit the dentist twice a year. A balanced diet and vitamin-mineral complex products will help compensate for the lack of vitamins and minerals necessary for dental health.
Inflammation of the gum hood: types and form of the disease
According to the nature of the pathological process, chronic and acute pericoronitis are distinguished. Characteristic signs of chronic :
- Pain syndrome.
- Impaired chewing function.
- Formation of purulent formation.
- Periodic exacerbations.
- Mobility of dental elements.
The gum hood may become swollen due to inflammation of the soft tissues. Acute pericoronitis is expressed as follows:
- Pronounced pain syndrome.
- Presence of swelling and redness.
- Bad breath.
- Throbbing pain.
- Deterioration in general health.
Acute pericoronitis has the following types:
Catarrhal. The initial stage, when inflammation forms around the erupting element of the dentition. Swelling and pain when biting or chewing food may be observed.
Ulcerative. Characterized by the formation of lesions with a white coating. The clinical picture is expressed in bleeding, enlargement of regional lymph nodes. The patient may have pain in the hood above the tooth.
Purulent. Purulent contents are formed. Accompanied by severe pain, especially when swallowing and chewing food. In addition to the fact that the gum hood hurts, there may be a putrid odor from the mouth and a rise in temperature.
Posteriormolar. Inflammation near the wisdom tooth near the periosteum of the alveolar process of the jaw. The patient experiences pain when opening the mouth and chewing food. Treatment may require excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth, followed by cleaning the cavity and treating it with a special compound.
In all these cases, immediate contact with a specialist is required. Self-treatment leads only to temporary elimination of the symptoms of inflammation and increases the risk of complications.