There is hardly a person who has not suffered from tonsillitis at least once in his life. The causative agents of tonsillitis are staphylococci, streptococci and pneumococci. There are acute tonsillitis and chronic tonsillitis.
Acute tonsillitis (or tonsillitis) is an infectious disease that affects the palatine tonsils, as well as the lingual, laryngeal and nasopharyngeal tonsils.
In acute tonsillitis, the throat hurts, it is difficult to swallow, the body temperature rises, general weakness, chills, aching joints, and headache appear. With proper treatment and compliance with the instructions of the otorhinolaryngologist, the disease is cured in 5-7 days.
1
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis in MedicCity
2 Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis in MedicCity
3 Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis in MedicCity
Chronic tonsillitis is a common infectious disease in which the focal infection is in the palatine tonsils. The formation of a chronic inflammatory focus in the tonsils occurs due to prolonged exposure of microbes to the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils.
Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by periodic exacerbations - sore throats, but a non-angina form of the disease also occurs.
What is chronic tonsillitis
The human oropharynx has special structures called tonsils; they protect the body from pathogenic microorganisms. In childhood, these structures are subject to enormous stress, because every day the child comes into contact with new microbes that are not yet familiar to him.
When bacteria “settle” on the surface of the tonsils on the back wall of the pharynx, and the immune system cannot cope with them, inflammation develops - tonsillitis. If this inflammation persists for a long time, acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) turns into a chronic inflammatory process.
Tonsils in chronic tonsillitis do not perform their functions, but on the contrary, they become a source of infection. This leads to infectious and autoimmune complications.
Treatment of sore throat
Parents need to understand that seeing a doctor is an integral part of successful therapy. Self-medication can cause irreparable harm to children's health.
General recommendations
Sore throat is a highly contagious disease that requires temporary isolation from the sick child.
Young children are especially susceptible to infection. Transmission of infection through close contact is possible from the first day of illness. Acute tonsillitis is almost always accompanied by high fever; parents need to ensure that the child remains in bed. To speed up the removal of infection from the body and prevent dehydration, the baby must be given large amounts of clean water, compotes, fruit drinks and other liquids.
In addition, parents should know the recommendations for baby nutrition: if you have a sore throat, you should exclude hot, rough, spicy, fried and highly salty foods (to prevent pharyngeal irritation). The children's diet should contain boiled, baked or steamed dishes, pureed non-acidic fruits and vegetables, and low-fat broths.
Elimination of the pathogen
The treatment tactics for the inflammation itself depend on the type of infection that caused damage to the tonsils.
So, with a bacterial form of sore throat, the child is prescribed antibiotics (selected taking into account the sensitivity of a particular pathogen). For viral tonsillitis, the doctor selects antiviral drugs, for fungal tonsillitis - antifungal agents. Often, antibacterial and antiviral agents negatively affect the functioning of the baby’s gastrointestinal tract. To prevent diarrhea, bloating and other unpleasant symptoms, your doctor may prescribe a course of prebiotics and probiotics.
Relieving symptoms of sore throat
In addition to eliminating the causative agent of the disease, it is necessary to direct efforts to relieve the unpleasant symptoms of the disease and improve the overall well-being of the baby.
If the body temperature is high, the child is given antipyretics. At the pharmacy you can buy products that reduce body temperature in various forms of use. For infants, it is recommended to give preference to rectal suppositories; at older ages, oral medications are usually prescribed. Topical sprays, syrups, or lozenges may be used to relieve inflammation and sore throat. Such drugs act directly on the microorganisms that cause the disease.
Often a sore throat is accompanied by severe swelling of the tissues of the pharynx, which causes breathing problems in the baby. In such cases, the doctor may prescribe antihistamines. The remedies not only help to cope with swelling in the throat, but also enhance the effectiveness of antipyretic and painkillers.
The choice of agents and their dosage is determined taking into account the age characteristics of the patient and the severity of the manifestations of the disease.
Rinse
Rinsing with antiseptic and anesthetic solutions helps relieve inflammation and eliminate pain. However, this method of treatment is suitable only for those children who know how to gargle without the help of adults without swallowing the solution. For young children, it is recommended to replace rinsing with mouth irrigation. This treatment method allows you to moisturize the oral cavity, wash away purulent and mucous formations from the surface of the tonsils along with pathogenic microorganisms.
Physiotherapy
In addition to medicinal methods of treating sore throat in children, physiotherapeutic methods have proven themselves to be effective:
- inhalation;
- UHF;
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- phototherapy.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is accompanied by local symptoms directly in the throat, and general symptoms from other organs and systems.
Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by repeated recurrence of tonsillitis.
Main symptoms:
- pain and discomfort in the throat, it hurts the child to swallow solid food;
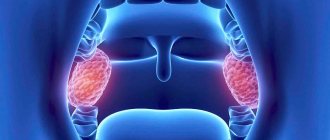
- enlargement and tenderness of the cervical lymph nodes;
- increase in body temperature to 37-38 degrees;
- bad breath;
- signs of intoxication - fever, headache, weakness;
- abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting;
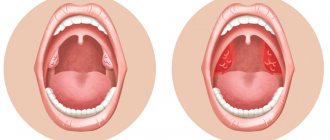
- upon examination, redness of the pharynx, tonsils are visible, possibly with a white coating (normally, the tonsils do not protrude from the palatine arches, they are not visible).
The infectious process is not limited to the throat; symptoms of tonsillitis are followed by a runny nose, hoarseness, and cough. Possible development of conjunctivitis, otitis, meningitis.
Symptoms of a sore throat
In children, the symptoms of sore throat are much more pronounced than in adults. The baby becomes restless, cries, and refuses to eat. Often the disease becomes chronic and subsequently recurs. General signs of sore throat in a child:
- increase in body temperature above 39.0C
- intense sore throat;
- pain when swallowing;
- general weakness;
- poor appetite;
- moodiness and tearfulness (in young children).
If left untreated, symptoms of cardiovascular disease may occur: tachycardia, hypotension, chest pain.
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the form of acute tonsillitis. In medicine, it is customary to distinguish catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, fungal, herpetic and ulcerative-necrotic tonsillitis.
Manifestations of catarrhal tonsillitis
The mildest and most common form of the disease is catarrhal. Catarrhal tonsillitis is characterized by superficial damage to the tonsils: their swelling and redness. This form rarely exists as an independent disease, being one of the manifestations of other pathologies of the upper respiratory tract. General symptoms are not very acute - there is an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels (37.1-38C), sore throat and moderate pain in the throat, painful swallowing.
Manifestations of follicular tonsillitis
Follicular (purulent) tonsillitis manifests itself with high body temperature (over 38C), severe sore throat, inability to swallow normally, and increased salivation. Small whitish or yellowish pustules, 1-2 mm in diameter, form on the tonsils. There is an increase in lymph nodes in the neck and back of the head; when palpating the lymph nodes, the child feels pain.
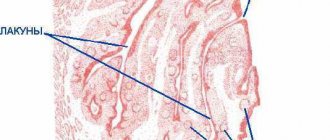
Manifestations of lacunar tonsillitis
The symptoms of lacunar tonsillitis are similar to those of the follicular form. However, in this case the clinical picture is more pronounced. Purulent discharge does not occur on the follicles of the palatine tonsils, but on their ducts (lacunae).
Manifestations of fungal sore throat
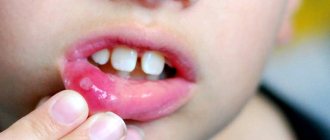
With the fungal form of the disease, the child experiences enlargement and slight redness of the tonsils and low-grade body temperature. The main symptom that distinguishes this form is the presence of a bright white cheesy coating on the tonsils, which can be easily removed from the palatal tissues.
Manifestations of herpetic sore throat
The main difference between the herpetic form of the disease is the formation of rashes in the form of many small blisters on the tonsils. Inside each bubble is a colorless liquid. In some cases, small ulcers occur with herpetic sore throat.
Manifestations of ulcerative necrotic tonsillitis
This form of acute tonsillitis is one of the most severe. In a child, areas of necrotic (dead) tissue appear on the palatine tonsils. After the dead tissue is separated, deep ulcers form on the tonsils.
Causes of chronic tonsillitis
Tonsillitis
- infection. Among the pathogens that can cause tonsillitis are:
- bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci, diphtheria bacillus, etc.);
- ARVI (influenza viruses, parainfluenza, adenoviruses);
- herpes viruses (cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus);
- measles virus;
- yeast fungi (candida).
Provoking factors include hypothermia, consumption of cold foods, contact with sick people, stress, and poor nutrition. Candidal tonsillitis may indicate immunodeficiency.
Complications due to improper self-medication and lack of treatment for tonsillitis
There are a simple form of tonsillitis - accompanied only by local symptoms, and a toxic-allergic (complicated) - manifestations of intoxication and dysfunction of all organs and systems come to the fore.
Toxic-allergic manifestations are characteristic of chronic tonsillitis of streptococcal origin. With this form, antibodies to streptococci are formed in the blood, which are also capable of attacking the body’s own tissues. The most vulnerable to such autoimmune aggression are the kidneys, heart and joints. Therefore, chronic tonsillitis leads to the following complications:
- glomerulonephritis and subsequently renal failure;
- endocarditis, myocarditis, pericarditis;
- rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus.
Therefore, any tonsillitis should be examined and adequately treated. It is necessary to monitor the child’s condition for 3-4 weeks after recovery. If alarming symptoms appear in the heart (chest pain, rapid heartbeat, high temperature), joints (pain with movement, stiffness), kidneys (swelling, lower back pain), seek medical help.
Recommendations for the prevention of tonsillitis
To prevent the development of chronic tonsillitis, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- avoid hypothermia of the child;
- protect him from communicating with sick people;
- monitor the child’s nutritional status;
- promptly show the child to a pediatrician or pediatric ENT doctor when the first symptoms of a sore throat appear;
- Visit the dentist with him in a timely manner to remove carious teeth, which are a source of bacterial growth in the mouth.
Prevention of sore throat
In order to reduce the likelihood of tonsillitis (acute tonsillitis) to a minimum, parents need to take a competent approach to strengthening the child’s immune system. To do this, the following preventive measures should be observed:
- Lead an active lifestyle - take frequent walks in the fresh air, involve your child in sports activities (running, swimming, football, cycling, etc.).
- Provide the child with a balanced diet - introduce a large amount of fresh vegetables and fruits, herbs, low-fat protein foods into the children's diet, and also limit the consumption of fatty, fried foods, fast food, and fast carbohydrates.
- Monitor the child’s personal hygiene, develop in young children the habit of brushing their teeth and washing their face daily (dental caries can cause infection in the tonsils).
- Ensure comfortable conditions in the children's room - maintain optimal humidity and air temperature (no more than 23C at a humidity of 50-60%), carry out daily wet cleaning and ventilation of the rooms.
- If any symptoms of diseases of the ENT organs occur, bring your child for medical examinations in a timely manner, trust only qualified specialists!
We employ experienced doctors of various specialties who will establish an objective diagnosis and select the correct treatment so that the baby can return to his normal lifestyle as soon as possible!
Diagnosis and treatment of tonsillitis
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis is made based on symptoms and examination data. To assess the general condition of the child, additional examination methods may be prescribed:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- chest x-ray;
- electrocardiography.
With chronic tonsillitis, a child may show signs of damage to other organs. Therefore, if necessary, a pediatric otolaryngologist can refer him for examination to specialized specialists (nephrologist, cardiologist, ophthalmologist, etc.).
Chronic tonsillitis involves drug treatment: gargling, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapy.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, the child is indicated for a tonsillectomy (surgical removal of the tonsils).
Chronic tonsillitis is a focal infection that must be removed from the body as quickly as possible to preserve the child’s health.
Frequent sore throat in a child: causes, how to treat?
Causes of the disease
The most common type of this pathology in childhood is bacterial tonsillitis. It is usually caused by group A beta hemolytic streptococcus or staphylococcus. In second place are viral sore throats. The cause of their occurrence is such types of viruses as Coxsackie enterovirus, adenoviruses, and herpetic viruses. In third place are fungal diseases. They are caused by fungi of the Candida family. Provoking factors in the development of the disease in a child are a decrease in general or local immunity.
Symptoms of the disease
Bacterial sore throats most often occur with severe intoxication. In a general blood test, in this form of the disease, significant leukocytosis, increased ESR and a high content of neutrophils are observed.
Viral sore throats, or herpangina, are very common in children, especially in the summer. Clinically they manifest themselves as follows:
- very severe intoxication;
- chills, fever;
- sore throat.
Small, red rashes on the tonsils, soft and hard palate are also characteristic. They may burst and disappear spontaneously within 3-5 days.
As for fungal tonsillitis, the clinical picture is often moderate. High fever is rare, and a characteristic cheesy coating is present on the tonsils.
What are the possible complications?
Untimely or unqualified treatment of the disease can lead to a number of complicated consequences. Among which the most common are:
- otitis media;
- phlegmon of the neck;
- sinusitis;
- acute lymphadenitis.
If we talk about dangerous complications, the early ones include: infectious-toxic shock, sepsis, meningitis, pharyngeal abscess. They occur in the first days of the disease. And in the later period, lymphatic fever may develop, which we have heard a lot about as rheumatism, sinusitis, nephritis. These are pathologies of vital organs - heart, kidneys. Unfortunately, they can lead to disability of the child and serious complications to the baby’s health.
Therefore, experienced pediatricians at children's medical centers are always very afraid of the development of complications of streptococcal sore throat, and in this situation it is imperative to prescribe antibiotics.
Marshall syndrome in children
Imagine the condition of parents whose child suffers from a sore throat every month. We are talking about Marshall syndrome, which many treated like a regular sore throat. And the baby received a monthly dose of antibiotics. In fact, antiviral and antibacterial drugs are absolutely ineffective for this pathology. The only effective method of treating the disease in this case is the use of glucocorticosteroid drugs such as Prednisolone or Dexamethasone. But this does not guarantee that in a month the child will not again develop symptoms of Marshall syndrome. The radical treatment method in this case is removal of the tonsils.
When is it necessary to remove tonsils?
Experts recommend removing tonsils in children if:
- your child suffers from sore throats more than four times a year;
- conservative therapy does not help;
- disorders of the heart, kidneys, and joints are noted;
- the child has a violation of nasal breathing, a deformation of the facial part of the skull is formed, and the habitus is disrupted;
- frequent otitis occurs;
- the disease is complicated by an abscess.
But before deciding on surgical removal of the tonsils, a mandatory consultation with an ENT doctor is necessary. If complications develop, consultations with a nephrologist and cardiologist will also be required.
Correct diagnosis
The necessary competent examination by the attending physician begins with a general blood and urine test. It is also necessary to take a swab from the throat for a nutrient medium. This study is carried out over several days. At home, you can use a special product called “streptatest”. It is sold in pharmacies, the instructions are very detailed and clearly describe how to use it. The result will be ready within 5 minutes. If it comes back positive, it means you need to use an antibiotic right away.
The next test to determine the presence of viruses is a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test. Currently, this method is considered highly accurate, and in our Healer clinics you can come and carry out all the necessary tests in one place. At a high professional level, our experienced laboratory doctors will qualitatively examine your child and give you absolutely correct, reliable results that will help cure your baby.
I wish your children and you good health. To prevent the pathologies that I described above, I recommend hardening your children. This procedure allows you to boost the body’s immune system, which in turn prevents the development of various chronic lesions, as well as the occurrence of sore throat in a child.