General overview of the procedure
Gum coagulation in dentistry is a process during which diseased tissue is treated, cauterized, and also excised under ultra-high temperature. The procedure can be performed using different heating sources: heated instruments, electrocoagulators. Also, such an operation is often performed using a laser - it has the most gentle effect.
The description of the procedure sounds a little scary, but in fact this technique is completely safe for the patient’s health, as well as his psychological state. Do you agree that the absence of a scalpel (in the classical sense) and the need to carry out extensive intervention immediately puts you in a positive mood? In addition, the procedure is performed under local anesthesia, which means you will not feel any pain and will not have to be afraid of extremely high temperatures.
On a note! Thanks to the influence of special devices during cutting off damaged areas, the specialist performs the procedure with maximum accuracy and comfort for the patient. The soft tissues on which the intervention is performed are immediately cauterized using an instrument, so they do not bleed and remain sterile (they are disinfected), and also heal quickly during the rehabilitation period, which avoids complications and significantly reduces treatment time.
What is “hot” filling?
The correct name is the method of vertical condensation of hot gutta-percha. Long, difficult, not clear. Let's figure it out now!
Yes! “Hot” filling is only possible for root canals! There are no “hot” fillings (well, except maybe metal ones - although very few clinics work with them these days).
So, when filling the measles canal, the dentist’s main task is to fill the canal as tightly as possible with filling material. Not even the smallest gap should be allowed between the filling material and the wall of the root canal. If such a gap (empty space) is left, an infection will certainly begin to develop in it, which will ultimately lead to complications and the need to re-treat the tooth. Or even removal.
Today there are four main methods of filling root canals:
- one paste method;
- single pin method;
- method of lateral condensation of cold gutta-percha;
- method of vertical condensation of hot gutta-percha.
The first two methods, despite their fairly frequent use, cause quite a lot of complications, because cannot provide maximum obturation (filling) of the root canal with filling material. And if you really have to choose, then you have to choose between the methods of lateral (cold) or vertical (hot) condensation.
Read more about filling root canals
What is the difference between “cold” and “hot” filling?
With “cold” lateral condensation, the doctor inserts several gutta-percha pins of different diameters into the lumen of the root canal until the canal lumen is filled as densely as possible. Additional sealing is achieved through the preliminary (before the pins) introduction of a special paste into the canal - a sealer.
A gutta-percha pin is a thin column of a special plastic material (somewhat similar to rubber), which is inserted into the lumen of the root canal to seal it. Gutta-percha points come in different diameters. They should not be confused with titanium or fiberglass posts that are used as a basis for attaching a filling.
So, with “cold” filling, the lumen of the root canal is filled with several gutta-percha pins of different diameters until the entire canal is filled.
During “hot” filling, one thermoplastic pin, preheated in a special oven, is inserted into the lumen of the root canal. The diameter of the “hot” pin is selected so that it fills the entire lumen of the root canal. And, of course, the pins for cold and hot filling are different from each other and are not interchangeable!
Why is the gum most often cauterized?
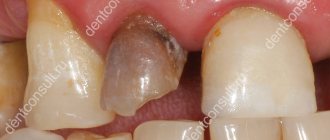
Most often, patients are recommended to apply electric shock to the affected areas due to hyperplasia or overgrowth of soft gum tissue, also called papillae. They fill the interdental spaces and are very sensitive to any impact. Their excessive enlargement and inflammation are caused by household injuries (occurring when using floss to remove plaque, toothpicks, brushes with hard bristles, or eating hard foods), dental diseases, poor oral hygiene, malocclusions, or hormonal disorders.
In the absence of proper treatment, the area of the interdental papillae increases, the soft tissues begin to become inflamed and bleed, causing pain and discomfort. In addition, the formation of such growths can cause problems with the correct pronunciation of sounds, impaired blood circulation in the gums, lack of adequate nutrition, and the appearance of complexes (overgrown mucous membrane can completely cover the crown part of the tooth, which looks extremely unaesthetic), so dentists recommend cauterizing them in a timely manner.
Therapy for hypertrophic gingivitis
The disease is one of the most common in dentistry - it occurs with equal frequency in both adults and children. It is characterized by the proliferation of soft interdental tissues, which, if left untreated, can overlap the crowns of the teeth. The appearance of pathology is provoked not only by poor oral hygiene and hormonal imbalance in the body, but also by chewing hard pieces of food that injure the interdental spaces, and improper use of personal hygiene items (threads to remove plaque, brushes, etc.).
In complex therapy (taking anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy, gingivectomy) to treat the disease, dentists recommend using a method such as coagulation.
Coagulation of the gingival papilla
The procedure is quite in demand due to the careless attitude of most people towards their own health. Due to limited time or fear of dentists, many simply do not treat diseases of the gums and teeth, such as gingivitis, caries, etc.
As a result, the lesion site becomes overgrown with pathological gum tissue. This disease requires medical intervention, namely coagulation of the gingival papilla.
Inflamed gingival papilla
Cauterization is performed under local anesthesia and during the procedure the patient feels only mild discomfort. Thanks to the use of an electrocoagulator, healthy tissues are not affected by the instrument.
Oral care after the procedure
The postoperative period is quite unpleasant and painful, since, in essence, a part of the living mucous tissue, albeit of a pathological nature, was surgically removed. The pain syndrome will accompany the patient for two days after the operation, after which it will gradually recede. To alleviate the condition, the doctor may prescribe analgesics.
Rinsing with herbal decoctions or chewing propolis will help relieve pain.
The recovery period after surgery takes on average from 2 to 10 weeks . This is exactly how much tissue needs to fully regenerate. During this time, the patient must regularly visit the attending physician’s office to monitor the condition.
The doctor may prescribe rinsing with an antiseptic solution of Chlorhexidine or Furacilin and the use of anti-inflammatory ointments. It is very important to prevent infection from entering the treated tissue areas.
Furacilin
Depending on the nature of the disease, the doctor may prescribe antibiotic medications in order to completely destroy the pathogenic microflora and prevent re-complications.
Other situations when the procedure is performed
Such a modern treatment method as coagulation is often used in dentistry for the following purposes:
- removal of formations on the mucous membrane: malignant and benign,
- removal of any granulation tissue,
- correction and plastic surgery of gums to give an aesthetic smile,
- treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease (only in complex therapy): in particular, the procedure can be carried out to cauterize and treat inflamed gingival papillae that have grown during the course of the disease. And also for removing granulations and pathological tissues from periodontal pockets - at the end of the procedure, the periodontal pockets remain completely sterile, the tissues fit tightly to the tooth, which prevents plaque, bacteria and food particles from getting inside,
- cauterization of inflamed gingival papillae: pathology can occur not only against the background of periodontal tissue diseases, but also due to trauma to the mucous membrane, malocclusion, hormonal disorders in the body, incorrectly performed dental treatment, chipped fillings and the presence of uncomfortable prosthetic structures,
- removal of papillomas, fibroids: they may look harmless, but sometimes they grow greatly, causing inconvenience, and become dangerous to health.
What are the benefits of using a rubber dam?
The rubber dam makes the doctor's work easier. It provides good access and visibility, protects the tooth from the ingress of liquids (saliva, blood), and, consequently, from contamination of the “working field” by microorganisms that can cause complications in the future in the form of relapse of caries or pain in the teeth where root canals were treated. Also, if biological fluids enter, the adhesion (gluing) of the filling to the tooth may decrease. Even moisture released during breathing can cause the short life of the restoration.
Who should not undergo the procedure?
Despite the fact that the described technique has a number of advantages (in comparison with traditional methods of surgical interventions), there are also some contraindications to the operation. Coagulation is not performed if the following problems have been diagnosed:
- intolerance to low-frequency electric currents: in this case, it is permissible to use only a laser,
- exacerbated infectious diseases,
- disorders of the cardiovascular system: there is a high probability of increased blood pressure,
- disruption of the hemostasis system: the risk of bleeding increases,
- chronic diseases: for example, diabetes.
Also, the use of “hot” instruments is unacceptable during the active change from primary to permanent occlusion in children, which occurs between the ages of 6-8 and 12 years.
Important! If the patient has the above conditions, the operation should be performed only under the supervision of a highly qualified specialist, and also provided that the likely harm from the development of the disease outweighs the risks of complications after coagulation.
What is gum coagulation
Gum coagulation is the surgical excision of mucous tissue using a hot instrument. This is plastic surgery of gum tissue performed using electric current.
Despite the frightening description, the procedure is as painless and comfortable as possible for the patient. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Unlike classical surgery, the patient does not lose a drop of blood during the procedure.
The method is used to remove various types of tumors and to treat diseases such as:
- periodontitis;
- periodontal disease;
- inflammation of gum pockets;
- fibroma;
- hemangioma;
- tissue hyperplasia, etc.
Periodontal diseases
Coagulation methods
There are several options for treating the affected mucosa. Depending on which device is used, the following methods are distinguished:
- cauterization with a metal instrument with a hot tip: the instrument is considered obsolete and is rarely used nowadays - the procedure using it is quite traumatic, and the subsequent rehabilitation period is quite long,
- excision with an electrocoagulator: here, with the help of a device, electrical energy is converted into thermal energy. High-frequency alternating electric currents supplied through the tool “dry” and destroy damaged areas,
- treatment with a laser device: damaged tissues are “burned out” with a beam of intense light.
Coagulation techniques and its types
Removal of inflamed tissue can be done using different techniques. Each of them differs in the way the current is supplied. There are two types of coagulation. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Monopolar method and its features
The doctor uses an instrument that looks like a scalpel. But the effect on tissue is carried out not mechanically, but with the help of an electrode built into the scalpel handle, through which current is passed. In this case, electrical impulses (weak charges of safe alternating voltage) pass through the entire human body, and the safety of the process is ensured by a special return plate with which the tool is equipped. The presence of this element is mandatory, because it is responsible for the process of closing the electrical circuit.
The method is effective when performing coagulation to remove large tumors.
On a note! If cutting is performed with a faulty device or by an unqualified specialist, consequences such as injury and burns to the mucous membrane may occur during the procedure. The method is considered quite outdated these days, so doctors rarely resort to it.
Bipolar method and its features
The main difference between this method of coagulation is that the current passes only through the affected areas of the tissue (the doctor acts on them pointwise), so a return plate is not needed for its implementation. The operation is performed with an instrument with a forked tip, which grips and clamps the gum so that the electrical circuit is closed directly in the area of the procedure.
Types of coagulation (cauterization) of gums
Monopolar technology
A special return plate is placed on the patient’s body, which is responsible for closing the electrical circuit. A weak electrical impulse is passed through the patient's entire body and through the surgical instrument. With this procedure, you can get rid of even large neoplasms and tumors located in the deep layers of tissue. Due to its effectiveness, this method is used more often than others.
Bipolar technology
An electrical discharge is passed locally, only through the part of the body in which the tumor or inflammation is located. Therefore, the end plate is not used. This method is effective for the treatment of mild dental diseases.
The gum cauterization method is widely used in dental practice and shows good results in the treatment of periodontal diseases.
Before performing the operation, the doctor examines the patient’s oral cavity for injuries to the mucous tissues, since their presence can cause complications.
Bipolar gum coagulation technology
Upon completion of the operation, the patient is given a list of recommendations and a prescription for medications. For each patient, recommendations are made individually, depending on the disease and its severity.
How to prepare for the procedure
There is no need for special preparation before coagulation, but you should do the following:
- visit different specialists: before the procedure, if necessary, the doctor may refer you for a consultation with other specialized specialists (infectious disease specialist, oncologist, periodontist),
- Avoid drinking alcohol several days before the procedure, as well as on the day of coagulation: it negatively affects blood clotting and the effect of medications and anesthetics used during the procedure,
- have a snack before the procedure: the snack should not be heavy, but you should not completely refuse food, because After the operation, you will not be able to eat for at least another 1-2 hours.
Preparing for surgery
Coagulation does not require special preparation . As before any other dental operation, the patient needs to undergo professional cleaning of the oral cavity and get rid of tartar. If the appearance of a neoplasm is accompanied by any diseases of the teeth or gums, the patient must first visit the offices of a periodontist and dentist to receive advice and eliminate the problems.
Patients are advised to eat and drink well before the procedure. This will ensure you feel good and give you enough energy to survive several hours without food after the procedure.
The day before the procedure, you should avoid drinking alcohol and smoking, as they have a bad effect on blood clotting.
How is the procedure performed?
The operation is performed only by an experienced dental surgeon. First, the doctor will sanitize the oral cavity and administer anesthesia (in the case of using a laser, it is often possible to confine oneself to local “freezing” in the form of gels and sprays, since the procedure causes virtually no pain to the patient). Next, the specialist works with an instrument designed for coagulation and performs the necessary manipulations.
Important! The patient should relax in the dentist's chair and not make sudden movements. Otherwise, the hand of even the most experienced specialist may tremble, and the instrument will damage healthy areas.
The duration of the operation directly depends on the degree of complexity of the actions performed, but on average coagulation takes no more than 20 minutes.
How does the procedure work?
The operation is performed by a dental surgeon. Since the procedure is practically painless, it is performed under local anesthesia, which uses an anesthetic gel.
While sitting in the dental chair, the patient should try to relax as much as possible and not move . Due to sudden movements, the instrument in the hands of a specialist can shake and damage healthy tissue.
Using a laser beam, the doctor excises the inflamed areas of tissue or completely removes the tumor. In total, this type of operation takes a quarter of an hour. It may take more or less time depending on the patient's specific problem.
The main thing for the patient is not to move
For several hours after the operation, you should refrain from eating food so as not to damage the tissues that have become especially sensitive after the procedure and not to cause an infection. It is necessary to take special care to keep your mouth clean and rinse after every meal. Outside the home, you can chew gum or use dental floss.
To speed up regeneration and relieve discomfort, you can rinse your mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs ( chamomile , oak bark , calendula , etc.).
In order to make sure that the operation will be successful and will not cause any complications, the dental surgeon can refer the patient to an oncologist, infectious disease specialist and periodontist for additional examination and health monitoring.
Advantages of the method
In comparison with the long-familiar, classical methods of surgical interventions, coagulation allows you to gently and painlessly target pathological areas of tissue, as well as destroy pathogenic bacteria. In addition, the gums do not bleed after coagulation, heal faster and look attractive. Therefore, you should not delay your visit to the doctor for fear of unpleasant sensations. Timely assistance will be the key to the health of your oral cavity and the beauty of your smile.
What complications may arise after surgery?
Many patients note that their gums hurt in the first few days after coagulation. This phenomenon is considered a completely natural consequence of the intervention. To reduce discomfort, you can take painkillers that you usually use and keep in your medicine cabinet.
If the pain does not disappear after some time, and additional alarming symptoms appear (inflammation and redness of the mucous membrane, the appearance of bad breath, discharge of pus), then be sure to visit a doctor. The specialist will tell you what to do to make the gums suppurate go away: for these purposes, antibiotics that destroy pathogenic microflora and treatment of the mucous membrane with antiseptics are most often prescribed.