- What is keratoplasty?
- Corneal pathology
- Causes of corneal diseases
- History of corneal transplantation
- How do you prepare for the operation?
- What types of keratoplasty are there?
- Postoperative period
Every day in our practice we see that every fourth patient comes to an appointment with a corneal disease. More than 10 million people worldwide suffer from corneal diseases. Pathology of the cornea is one of the main causes of decreased vision, blindness and low vision.
Indications
The list of indications includes pathologies that are not amenable to conservative therapy. Keratoplasty is indicated for patients with:
- corneal dystrophy (including those with minimal thickness);
- keratoconus (both in the early stages and in the late stages, including progressive ones);
- keratoglobus;
- Fuchs' dystrophy;
- the presence of scars on the surface of the cornea;
- damage to the cornea of various types;
- ulcers (wounds) of the cornea of any origin;
- eyesores of various natures, affecting visual acuity;
- bullous keratopathy associated with cataract surgery;
- congenital or acquired anomalies of the structure of the eye;
- defects of a traumatic nature.
Each indication for surgery for a particular patient is determined by the doctor.
Corneal pathology
The cornea is a unique optically transparent lens, the first to encounter an aggressive environment, conducts and refracts rays in a special way, and participates in maintaining the shape of the eyeball. Despite the high regenerative potential of corneal epithelial cells, it is an absolutely transparent structure, which is achieved by passive nutrition of this organ, which does not have its own vessels.
It is this amazing organ that is often susceptible to a huge range of diseases, risks and dangers associated with the loss of this unprecedented transparency: here is a wide variety of hereditary forms of corneal dystrophies, senile degenerations, injuries, burns, post-inflammatory changes, consequences of iatrogenic interventions, keratoconus, etc. The result of the listed diseases and their consequences is a violation of transparency, and, as a consequence, a persistent decrease in visual functions with absolutely healthy other optical environments and a well-functioning retina.
When keratoplasty is contraindicated
The list of contraindications includes:
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- inflammatory lesions of different parts of the eye (such as the cornea, sclera, conjunctiva) of an infectious nature: uveitis, keratitis, scleritis;
- ingrowth of blood vessels into the cornea (in normal conditions, the cornea of the eye and all its tissues are deprived of blood supply);
- chronic diseases in acute stages (complete remission should be expected);
- acute infections (you need to wait one to two weeks after the patient has completely recovered);
- autoimmune diseases.
Important! All contraindications and possible complications are identified during diagnosis.
Varieties
There are the following types of keratoplasty:
- End-to-end (penetrating) operation
. In this type, all layers of the patient's cornea are replaced, including the epithelium, stroma, and endothelium (the back layer of the epithelium adjacent to the chamber of the eye). Penetrating keratoplasty is indicated for pathological processes affecting cells of all tissues of the cornea. - Layered
. With the layer-by-layer technique, only individual sections of the cornea are transplanted. Not the entire tissue is transplanted, but a separate layer or two (unlike penetrating keratoplasty, in which the cornea is separated completely).
There are two types of lamellar keratoplasty:
- Front
. Layered anterior keratoplasty involves cutting and subsequent transplantation of the upper epithelium (the first layer), as well as in some cases the main layer - the stroma. The posterior lining epithelial membrane usually remains intact. - Posterior with excision of the posterior endothelium
. The method is more complex, but has fewer complications.
Depending on the purpose of the procedure, the following types of keratoplasty are distinguished:
- Therapeutic surgery is necessary to restore the structure and improve the condition of the cornea, often performed in conjunction with other interventions (for example, lens replacement).
- Refractive (optical), necessary to restore the functions of the patient’s cornea and to normalize refraction - the natural refraction of light rays passing through the cornea of the eye.
- Plastic transplantation allows you to restore the cornea locally or completely if there are defects on it, but while maintaining its function and structure.
- Cosmetic transplant. The operation is optional, but is performed to transplant a transparent cornea when the patient’s natural one is cloudy (this happens with complete blindness).
For your information! Separately, keratoprosthetics is distinguished. This is a transplant of a combined material made from donor tissue and rigid plastic material in the central part. Such operations are usually performed to strengthen the cornea as much as possible, for example, after previous unsuccessful keratoplasties.
Interventions are carried out in two ways: traditional surgical and more modern and laser. The first option requires high professionalism and experience of the doctor working with the instruments. The laser method is characterized by maximum precision, therefore it allows for manipulations of any complexity, cutting out areas according to the given individual parameters of the patient.
Features and benefits of keratolytics
A keratolytic is a softener for the skin of the feet based on chemical components. When applied to the skin, the product actively exfoliates keratinized particles of the epidermis, after which they can be easily removed with a nail file.
The main feature of the “liquid pedicure” is that the procedure does not require soaking your feet in water or using cutting tools. Keratolytics act effectively on dry skin, do not injure it and restore smoothness with minimal time.
Liquid pedicure helps to cope with problems such as:
- corns;
- dry calluses;
- cracks;
- rough keratinized skin;
- hyperkeratosis.
| Liquid pedicure is a safe procedure. The action of the active substances is aimed only at rough areas and does not affect healthy skin. When used correctly, keratolytics do not cause irritation or allergic reactions. But if you are individually intolerant to the components of the product and have skin damage, you should pay special attention to the procedure. |
Preparatory activities
Preparation for refractive layer-by-layer or through-and-through surgery includes examining the patient to assess the condition of his eyes and body. Indications and contraindications, the type of transplantation (end-to-end or layer-by-layer) are determined. For diagnostic purposes, the doctor prescribes specialized procedures: biomicroscopy to check all structures of the eye, pachymetry to measure thickness, scraping and biopsy of the membrane for subsequent microbiological and bacteriological studies. A blood test (general, for infections), examinations by a therapist and other specialists are also prescribed.
At the patient preparation stage, the affected areas of the cornea of the eye, their diameter, shape, volume and other parameters are also determined. This is necessary for the subsequent formation of a graft of the required size. If a patient is counting on donor tissue, he is put on a waiting list. The waiting period depends on the desired characteristics of the graft. When choosing artificial material, the wait is usually less long.
Your doctor will give you detailed recommendations for preparation. If the patient is taking blood thinners, they may be temporarily stopped or changed. You should not eat food on the day of surgery. Preliminary hospitalization in a hospital is not required.
Types of keratolytics
Heel softeners vary in the presence of active ingredients in the composition and can be:
- alkaline;
- acidic;
- with urea.
Let's take a closer look at each type.
Alkaline keratolytics
This is the most active softener that can easily cope with rough skin, old calluses, and corns on the feet. The alkali quickly dissolves the proteins and lipids that make up the epidermis, the surface of the skin becomes loose and dead particles can be easily removed with a pedicure file.
Alkaline keratolytics are quite active, so they should be used with caution and preference should be given to trusted manufacturers. Lotion for removing calluses and corns “Liquid Pedicure” from ARAVIA Professional is a product that quickly copes with foot problems, restoring the skin smoothness, softness and well-groomed appearance.
Acid keratolytics
Acid-based keratolytics
, as a rule, used for peeling.
- Fruit acid renews and moisturizes the skin.
- Salicylic acid has an antimicrobial effect.
- Dairy helps reduce the manifestations of hyperkeratosis.
But acids act only on the surface of the epidermis; they are not able to penetrate deeper layers and will not be able to cope with too rough skin.
Urea-based keratolytics
Products with urea
cause protein denaturation, that is, under the influence of the active substance, intercellular connections are broken and stretched. The stratum corneum of the epidermis softens greatly, but to remove it, you will have to make some effort by actively treating the skin with a file.
It is important to consider that when using a keratolytic with a high urea content (above 20%), the skin will quickly lose moisture and become very dry. Therefore, this product should only be applied to problem areas of the skin with severe roughness and it is better to entrust this to a professional.
Materials for transplantation
End-to-end or layer-by-layer surgery is carried out using either donor tissue or synthetic materials (artificial). The latter option began to be used relatively recently, only in the 21st century. It has a higher survival rate and minimal risk of rejection.
Tissue is collected from the donor either posthumously within 24 hours, or after brain death is determined while cardiac activity is preserved. Healthy patients without serious illnesses are eligible to receive a donor transplant. Tissues from infants and elderly people over 70 years of age are not used.
Progress of the operation
Refractive transplantation (both end-to-end and layer-by-layer) is more complex than other areas of ophthalmic surgery. The operation, which can be viewed on video, includes the following steps:
- The patient sits on a chair or lies down on a couch, fixes his head on a special holder;
- Anesthesia is administered. Local anesthetic drops are usually used, but at the patient’s request (or if there is a direct indication), the surgeon can perform the operation under general anesthesia;
- An eyelid expander is installed;
- The doctor begins the operation and begins performing manipulations. With refractive laser keratoplasty, the actions are performed with a laser beam. With the traditional surgical method, incisions are made with a thin scalpel or a special vacuum or manual trephine. Penetrating keratoplasty involves cutting through the cornea of the eye. With layer-by-layer plastic surgery, the cornea is cut into half or three-quarters, then exfoliated with a keratome;
- Then the excised area is removed, and donor or synthetic material is transplanted;
- Synthetic delicate cross-shaped continuous sutures are applied along the edges with a strong thread;
- Sometimes a special treatment lens is installed to protect the eye;
- A local antibiotic is instilled.
Duration ranges from 40-60 minutes to several hours (depending on complexity). The operation can be performed on an outpatient basis without hospitalization. In this case, after assessing the results and condition, if there are no problems (if everything went easily and without complications), the patient can go home. If the intervention was complex, the person operated on remains in the hospital for some time.
Rehabilitation
The rehabilitation period is quite difficult and long. The timing and speed of restoration of the patient’s visual functions depend on the initial pathology of the organ, the success of engraftment, the doctor’s experience, general health and other factors. Complete healing occurs within a year. The stitches are removed no earlier than six months later. In the first months, vision may deteriorate, which is gradually restored.
During rehabilitation, some restrictions apply:
- In the first 7-14 days, you should not get your eyes wet.
- Avoid any contamination.
- Mechanical influences must be excluded.
- UV protection when going outside.
- Reducing eye strain. You should read less, work on the computer, and use gadgets.
- Limit any activity in the first month, and heavy physical activity until complete healing (for a year).
- Regular visits to the doctor.
- Refusal to visit baths, swimming pools, saunas for a year.
- Refractive correction method with glasses.
The surgeon will give you more detailed and clear instructions.
Is there a possible complication?
Complications can occur, and their development is usually caused by medical errors, non-compliance with the recommendations given by the surgeon, as well as the individual characteristics of the human body.
One or more of the following complications may occur:
- rejection of the material, accompanied by pain, swelling, turbidity, discharge (occurs rarely - in 5-25% of cases, usually within the first month, less often - for six months);
- long-term healing and recovery;
- increased intraocular pressure (up to glaucoma);
- bacterial or fungal infections;
- cataract;
- keratoconus;
- failure, suture divergence;
- inflammation of different parts of the eye;
- iris prolapse, lens displacement.
If any complication occurs, you must immediately show the operated eye to the surgeon. So, in case of rejection, glucocorticosteroids should be applied topically every day, as prescribed by a doctor, several times. In case of infection, antibacterial drops are prescribed. Sometimes repeated intervention is required.
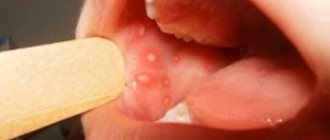
Medicines for the treatment of viral diseases of the oral mucosa
I. Pain relievers
First of all, to treat a child suffering from acute and recurrent herpetic stomatitis, in order to relieve or weaken painful symptoms in the oral cavity, an affordable and very effective anesthetic is used - anesthetic ointment to lubricate the oral mucosa before eating and treating the oral cavity.
II. Specific antiviral agents for local therapy
- Bonaftone ointment
- 0.5%. Antiviral activity is manifested in its influence on the processes of HSV reproduction. Lubricate the oral mucosa 3-4 times a day after meals. - Tebrofen ointment
- 0.25 and 0.5%. It has an antiviral effect due to the ability to suppress the growth of viruses. The ointment is effective in the treatment of acute and recurrent herpetic stomatitis, and also acts against the influenza virus and adenovirus infection. It is recommended to lubricate the mucous membrane 3-4 times a day.
- Florenal ointment
— 0.5%. Provides high neutralizing activity against HSV. Does not have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane; lubricate the mucous membrane 2-4 times a day.
- Adimal ointment —
0.5%. Has high neutralizing activity against influenza virus and HSV.
- DNase —
A 1% solution that has the ability to prevent the intracellular proliferation of DNA-containing viruses. Available in bottles of 25-50 mg. The contents must be dissolved before use in 5 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution.
- Oxolinic ointment
- 0.25%. The most widely used ointment with antiviral effect. The virucidal effect of the ointment is especially evident in relation to the influenza virus, adenovirus, and, to a lesser extent, to HSV.
- Riodoxol ointment
- 0.25 and 0.5%. It has antiviral and antifungal effects, and has virus-neutralizing activity against influenza and herpes viruses. In case of possible side effects (burning, hyperemia of the mucous membrane), the drug is discontinued. Lubricate the mucous membrane with a thin layer 1-3 times a day.
- Alpizorin ointment
— 2.5%; alpisarin liniment - 5%. It has high activity against DNA-containing viruses. To treat affected areas of the skin, 5% alpisarin ointment is used; for damage to the oral mucosa, 2% ointment is applied 4-6 times a day. The drug is characterized by good absorption, anti-inflammatory effect, and a high chemotherapeutic index. It has immunostimulating properties regarding cellular immunity. Compared to bonaftone, alpizarin is less toxic.
- Gossypol
— 3% liniment. Has an antiviral effect, weakly active against gram-positive microorganisms. Gossypol liniment is available in 20 g jars. The drug is well tolerated.
- Megosin ointment
- 5%. It is a drug synthesized from gossypol, has virucidal activity against HSV, an interferon inducer, the drug has proven itself in the treatment of recurrent herpetic stomatitis.
Interferon preparations. Interferon in ampoules of 500 U/ml actively suppresses the reproduction of most known viruses, which prevents the development of the infectious process. It is characterized by harmlessness, absence of side effects and allergic reactions. It is used in the treatment and prevention of acute and recurrent herpetic stomatitis, viral warts in children.
- An aqueous solution of leukocyte human interferon for instillation into the nasal and oral cavity - 3-5 drops per day after meals.
- Interferon ointment based on vinylin is prepared according to the recipe: interferon - 2.0 x 10 IU/g; anesthesin - 0.1; vinylin - 10.0. Stir thoroughly before use. Indications for the use of interferon ointment are all forms of viral infection in children.
- Zovirax (acyclovir)
acts selectively on cells infected with HSV and on viral DNA polymerase. Has low toxicity to cells not infected with the virus. It has immunostimulating properties and has an anti-relapse effect. It is used for herpetic stomatitis, ophthalmic herpes in the form of a 3% ointment on a soft paraffin base, and for herpes of the lips in the form of a 5% cream on a white aqueous creamy base. The drug is applied 5 times a day for 5 days. Treatment is recommended to begin in the prodromal period.
Agents that stimulate interferon formation in the body. One of the simplest methods is ultraviolet radiation.
- Poludan
has the ability to stimulate the production of endogenous interferon and has an antiviral effect. Used as eye drops. The contents of the ampoule (0.0002 g) must be dissolved in 2 ml of distilled water and instilled 6-8 times a day.
III. Medicines with local symptomatic action
Antiseptic treatment of the oral mucosa is indicated for advanced and severe forms of the disease and precedes the use of antiviral drugs. In dentistry, antimicrobial agents are widely used for antiseptic treatment. These include: 1% solution of sanviritrin; 0.5% etonium solution; 0.5% solution of sodium mefenaminate, etc. New aerosol preparations have antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic effects. However, their use in children is not always desirable due to the freon content, the cooling effect, possible allergic reactions, and also because of the fear that they often cause in children.
- Ambassador
The composition includes propolis, which has anti-inflammatory, disinfectant, analgesic and antiviral properties. Should be used if you are not allergic to bee products.
- Kameton
- an aerosol combination preparation containing chlorobutanol hydrate, camphor, menthol, eucalyptus, vaseline oils and freon.
- Devovinisol
consists of chloramphenicol, vinylin, linetol, citral and ethyl alcohol. It has the properties of a broad spectrum antibiotic - chloramphenicol and the anti-inflammatory properties of its components. Contraindicated in case of intolerance to chloramphenicol and microflora resistance to it.
- Libyan
- an anti-inflammatory, disinfectant and keratoplasty drug having a combined composition (linetol, anesthesin, etc.).
IV. Proteolytic enzymes
They have pronounced antiseptic and proteolytic properties. In addition to the main necrolytic effect, enzymes enhance and restore the phagocytic activity of neutrophilic leukocytes and fibroblasts, which contributes to the rapid course of regeneration processes. To effectively cleanse the affected mucous membrane of necrotic masses, trypsin, chymotrypsin, chymopsin, solutions of DNase, ronidase, terrilitin, hygrolitin are used.
- Trypsin
- a proteolytic enzyme that has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. Available in ampoules containing 0.01 and 0.005 g of trypsin. The contents of the ampoule are dissolved in 5 ml of distilled water before use.
- Chymotrypsin
- proteolytic enzyme of the pancreas. Its action is similar to trypsin and has the same indications for use. Available in ampoules of 0.01 and 0.005 g. The contents of the ampoule are dissolved in 5 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution.
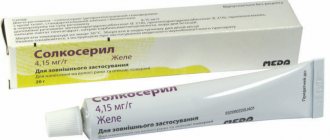
V. Keratoplasty agents
During the period of epithelization, keratoplastic substances are prescribed to accelerate the healing processes of the lesion elements. Symptomatic agents that promote epithelialization include a 1% oil solution of citral, rosehip oil, aloe ointment, carotoline, an oil solution of vitamin A, solcoseryl (jelly and ointment), as well as alazol and inosol aerosols. All drugs are used in the form of applications 3-4 times a day.
- Solcoseryl
- a combined preparation consisting of solcoseryl, polidocanol and ointment base. The action of the ointment is based on the ability to activate fibrinolysin, accelerate the growth of fibroblasts, increase energy exchange in tissues and reduce swelling. Available in the form of ointment and jelly to lubricate the mucous membrane.
- Rosehip oil, sea buckthorn oil, carotoline and vitamin A oil solution are used for applications and lubricating the mucous membrane.
VI. General therapy drugs General specific and nonspecific antiviral and immune therapy drugs.
- Bonafton
- tablets of 0.1 and 0.25 g; taken orally, without chewing, an hour after meals, 1 (0.25 g) tablet. 5 times a day; course of treatment is 5 days. The drug is most effective when used in combination with local antiviral agents. Possible side effects: headache, dyspepsia.
- Alpizarin
is available in the form of tablets of 0.1 g. The drug is well absorbed, exhibits antiviral activity due to its inhibitory effect on HSV reproduction, has a high immunotherapeutic index, and stimulates cellular immunity. The use of the drug from the first days of the disease gives a positive therapeutic effect.
Alpizarin tablets are taken orally, regardless of meals. Adults are prescribed 0.1 g, the course of treatment is 10-15 days; children - 1/2 table. 3 times a day for 7 days. Recommended for use in combination with local treatment.
- Zovirax (acyclovir)
has pronounced antiherpetic activity. Effective in patients with herpes with immune deficiency of various origins. Zovirax for internal administration is available in vials containing 250 mg of sterile acyclovir. The solution must be prepared immediately before use by adding 10 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution. The dose for children is calculated per body surface area in accordance with the instructions for use of the drug.
- Interferon
has an inhibitory effect on a wide range of viruses. The mechanism of antiviral action is its penetration into the cell followed by the synthesis of an antiviral protein, which prevents or suppresses the reproduction of viruses.
Used as an anti-relapse agent. It has no contraindications and is available in ampoules of 500 units/ml. Directions for use: intramuscularly, 1 ml every 3-4 days, course - 4-5 injections.
- Reaferon
- a domestic drug used for the treatment of various viral diseases: hepatitis B, influenza and its complications, ophthalmic herpes and genital herpes. Treatment with reaferon in children affected by the virus is carried out according to the following scheme: intramuscular injection of 500,000 units once a day. Course - 5 injections with an interval of 1-2 days. After the 1st course of therapy in case of repeated recurrence and no tendency to improve the condition within 5-6 months. a repeat course is prescribed according to the same scheme.
After treatment with Reaferon, most children experience a positive therapeutic effect. Children tolerate the drug well, no side effects or allergic reactions are observed. In case of continuously recurrent form of herpetic stomatitis in children for 1-2 months. there is a gradual decrease in the severity of symptoms of a general and local nature, until complete disappearance. Reaferon helps to interrupt the permanent course of the disease, increase remission, and in some cases lead to clinical recovery.
- Decaris (levamisole)
selectively stimulates the regulation of T-lymphocyte function, plays the role of an immunomodulator, enhancing the cellular immune response. When treating children with recurrent herpetic stomatitis, it helps prevent relapses. Children are prescribed 50 mg after meals once on the recommendation of a pediatrician. There are no side effects with a single use. Take in tablet form, 1/2 tablet. per day for 3 days with a break of 5 days between cycles. The total course of treatment is 2-3 cycles.
Where is keratoplasty performed?
The refractive correction method through keratoplasty is carried out in special ophthalmological centers located in Moscow and other Russian cities. And it is important to choose a clinic with an impeccable reputation, numerous positive reviews, and a license to carry out medical activities. The center must also be equipped with modern new equipment.
Pay attention to the choice of surgeon:
he must have a lot of experience, high qualifications and the necessary skills in keratoplasty techniques. Not all doctors perform such complex operations.
Our equipped modern clinic accepts patients with any eye diseases. We employ experienced and talented professionals. The center is equipped with all necessary equipment. You can make an appointment and receive advice, as well as qualified assistance.
Keratoplasty surgery allows you to restore the structure of the cornea of the eye or even restore vision. If you have corneal pathologies, contact the clinic: you may need a transplant.
Oral care for children
Children should follow the recommendations in this material. They should also adhere to the recommendations below.
- Use fluoride toothpaste. If your child is 2 years old or younger, consult your dentist or doctor before using fluoride toothpaste.
- If your child's teeth have not yet grown, use a terry cloth, wet wipe, or sponge to clean the gums after meals and before bed.
- If a child has a stable immune system, he should be taken to the dentist every 6 months for routine monitoring.
- Contact Child Life Services to learn how to help your child cope with pain. You can contact them at 833-675-5437 (833-MSK-KIDS).
to come back to the beginning