The color of tooth enamel is individual for everyone, even white has various shades, which must be taken into account when making prosthetics or installing a filling. To determine the natural tone as accurately as possible, dentists use the Vita scale. This is a special standard designed to select the tone of materials in accordance with the natural color of tooth enamel.
The Vitascale scale is a special standard, made in the form of a compact palette with fixed samples made of cardboard or plastic. It is used to compare the results obtained during the whitening procedure, making crowns, veneers, and to select the shade of the filling.
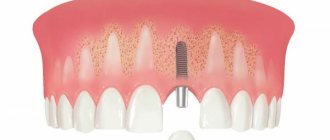
Indications for installing a dental bridge
Dental bridge, bridge-like prosthesis are the names of a design for permanent wear for the purpose of functional replacement of lost dental units.
They are installed in the absence of 1-4 teeth located in a row. A classic of the genre is a bridge consisting of three crowns, the most popular among patients. Gaps in the dentition cause several problems at once. This includes disruption of the digestive tract, accelerated loss (resorption) of bone, and deformation of the jaw, changing the oval of the face.
All of these issues are resolved with the help of dentures, and in particular, bridges. The patient is offered several options for prosthetics, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. The financial issue is of no small importance, since the price of high-quality structures is quite high.
Important! Most clients of dental clinics are concerned about the aesthetic factor, which also largely depends on the material and type of the future bridge.
Installation of dental bridges is possible in the absence of both chewing teeth and front incisors. They fully restore both the appearance of lost teeth and their functionality.
You should know that for prosthetic bridge construction, abutment teeth are required. If there are no teeth, or they are quite badly damaged, then removable dentures or dentures on implants can replace the bridge.
Implants previously implanted in the jaw are fitted with a removable or conditionally removable structure. This approach is a good solution if the patient does not want to grind his teeth for a bridge.
Dental bridge: what it looks like and how it works
Dental bridges are non-removable prosthetics, which means you cannot remove them yourself, without the help of a doctor. Dentures are fixed on the supporting teeth, replacing missing units in the middle part.
The main parts of the design are artificial teeth - more precisely, their crown parts - and retainers, through which the dental bridge is securely attached to the oral cavity.
Fixing bridge fastenings can be represented directly by dental crowns placed on the supporting teeth, inlays and clasps - iron brackets. In some cases, the design is supplemented with an element that imitates gum tissue.
For reference: A dental bridge received its name for its visual resemblance to a building structure.
The bridge can “sit” on the prosthetic bed in different ways and connect to the gums with varying degrees of density. There are 3 types of connections:
- lavage (temporal). There remains a slight gap between the dental bridge and the gums, which is not noticeable, but makes cleaning much easier. In addition, food debris does not get stuck under the denture;
- tangent. The prosthesis touches the gums, as if passing along one tangent line. This type of dental bridge is relevant in the smile area, since it does not interfere with normal conversation, can be cleaned with a toothbrush and looks good in appearance;
- saddle-shaped The bridge fits very tightly to the gums.
For reference: The saddle-shaped type of prosthesis, which sags in the middle, still causes a lot of controversy among dentists. B. Bynin in the middle of the last century considered its use advisable only in removable bridge structures due to the risk of the formation of bedsores on the mucous membrane.
Recently, in connection with the massive introduction of metal-ceramics, supporters of the use of saddle-shaped bridges in metal-ceramic dentures have appeared.
In any case, the type of dental bridge is selected by the doctor providing orthopedic treatment, with the active participation of the patient.
Types of dental bridges
Dental bridges are classified according to material and production technology. The starting materials for bridges can be:
- metal;
- metal ceramics;
- ceramics;
- zirconium dioxide;
- polymers.
Depending on the manufacturing technology, dental bridges are classified into the following types:
- adhesive, which are used mainly for prosthetics of 1 dental unit. This type of bridge has a frame made of fiberglass arch with a crown located on it. The adhesive structure is placed on halves or even quarters of crowns and fixed to the supporting teeth with special glue;
- classic, when the supporting units are completely covered with crowns.
Important! Adhesive technology for fixing bridges allows you to preserve your natural teeth as much as possible.
Metal bridges, in turn, are divided into cast and stamped. The former are preferable, as they are more durable and can withstand extreme loads, have a long service life and delicate shapes.
Material and technology are factors that determine the price and quality of dental bridges. However, in recent years, implant-supported dentures have become increasingly popular. And patients (not without reason) begin to doubt that a dental bridge is the only right solution.
Basic properties of dental porcelain
Physical properties: Dental porcelains are close to glass, their structure is isotropic. They are supercooled liquids and, due to their high viscosity, can maintain a glassy isotropic state upon cooling without noticeable crystallization.
Dental porcelains can transition when softening or hardening from a solid to a liquid state (and vice versa) without forming a new phase.
Glasses do not have their own melting point, but are characterized by a softening range. Porcelain is formed as a result of a complex physical and chemical process of interaction between the components of the porcelain mass at high temperature. Thus, at a temperature of 1100-1300°C, potassium spar turns into potassium feldspathic glass. Kaolin and quartz have a higher melting point than feldspar. However, in the feldspathic glass melt, kaolin and quartz interact with the glass. In this case, kaolin forms needle-shaped mullite crystals that penetrate the entire mass of porcelain. The quartz particles melt, lose their needle-like shape, and a small amount of them goes into the glass melt.
Numerous microscopic studies have established the following main structural elements of porcelain
:
1.vitreous isotropic mass consisting of feldspathic glass with varying degrees of saturation;
2. melted quartz particles that have not dissolved in the glass;
3. mullite crystals distributed in the melt of silica-feldspathic glass;
4.pores.
The glassy isotropic mass in modern dental porcelains constitutes their bulk. It determines their qualities and properties. The amount of glass phase increases with increasing melting temperature and increasing melting time. The ratio of crystalline and glassy phases determines the physical
properties of porcelain. The content of the glass phase in porcelain masses ensures their shine and transparency. Excessive firing temperatures lead to the appearance of excessive shine and small bubbles on the surface of the product. If the glass phase increases excessively, the strength of porcelain decreases.
Quartz particles undissolved in feldspathic glass, together with mullite and alumina crystals, form the skeleton of porcelain. Pores are an important factor in the structure of porcelain. The material has the greatest porosity (35-45%) before sintering begins.
As the glassy phase forms, the porosity decreases. At the same time, the density of the material increases and, accordingly, the dimensions of the product are reduced. The complete destruction of pores is prevented by the gas bubbles enclosed in them, formed as a result of the physicochemical interaction of individual components of the mass. The high viscosity of feldspathic glass prevents the removal of gas bubbles from the porcelain material, which causes the formation of closed pores. Modern dental porcelain is classified according to firing temperature as refractory (1300-1370°C), medium-melting (1090-1260°C) and low-melting (870-1065°C).
Composition of refractory, medium-melting and low-melting porcelain (%)
| feldspar | quartz | kaolin |
| Refractory | ||
| Medium melting | ||
| Low melting point |
Refractory porcelain
Typically used for the factory production of artificial teeth for fixed dentures.
Medium and low melting porcelains
used for the manufacture of crowns, inlays and bridges. The use of low-melting and medium-melting porcelains made it possible to use kilns with nichrome and other heaters.
The optical properties of porcelain are one of the main advantages of artificial teeth. The crown of a natural tooth is translucent, but not transparent like glass. This is explained by the fact that, along with light absorption, transparency is expressed by the ratio of diffusely scattered and transmitted light. Light, consisting of waves of different lengths, hitting the surface of the tooth can be absorbed, reflected and refracted.
Short waves are reflected from the enamel of the cutting edge of the tooth, creating a bluish tint. Long waves, passing through the middle part of the tooth, which contains the bulk of hard tissue, are reflected and refracted, forming many color shades from yellow-orange to blue. In the cervical part, the enamel becomes sharply thinner. This area ranges in color from yellow-orange to brown. Dental porcelain is also a structurally heterogeneous material.
The optical effect of porcelain is close to that of natural teeth in cases where it is possible to find the correct ratio between the glass phase and porcelain opacifiers. This is usually hampered by a large number of air pores and the clouding effect of crystals. A decrease in crystalline inclusions leads to increased deformation of the product during firing and a decrease in the strength of porcelain. This path to increasing transparency has a certain limit.
The second way to increase the transparency of dental porcelain is to reduce the size and number of gas pores. Before firing, the total volume of air inclusions in the condensed porcelain slurry is 20-45%.
To reduce gas pores, 4 methods have been proposed
:
1. Firing porcelain in a vacuum. With this method, air is removed before it has time to linger in the molten mass.
2. Firing porcelain in diffuse gas (hydrogen, helium), when the normal atmosphere of the kiln is filled with a gas capable of diffusion (the method is unsuitable in practice).
3. Firing porcelain under pressure of 10 atm. If molten porcelain is cooled under pressure, the air bubbles may decrease in volume and their light refractive effect is significantly weakened. The pressure is maintained until the porcelain is completely cooled. This method is also used in some factories for the production of artificial teeth. The disadvantage of this method is the impossibility of reheating and glazing under atmospheric pressure, because gas bubbles are restored to their original sizes.
4. In atmospheric firing, coarse-grained material is used to increase the transparency of porcelain. When such porcelain is fired, larger pores are formed, but their number is significantly less than in fine-grained materials.
Of the four methods mentioned above, vacuum firing has become the most widespread, which is currently used both for the manufacture of dentures in dental laboratories and in factories for the production of artificial teeth. Porcelain fired in a vacuum has 60 times fewer pores than with atmospheric firing.
When firing porcelain masses, shrinkage is 20-40%. The reasons for this shrinkage are:
· insufficient compaction (condensation) of particles of ceramic mass;
loss of liquid necessary for preparing porcelain paste;
·burnout of organic additives (dextrin, sugar, starch, aniline dyes).
The direction of shrinkage is of great practical importance. Shrinkage can be:
· in the direction of greater heat;
· in the direction of gravity;
in the direction of the larger mass.
In the first and second cases, the shrinkage is insignificant, because In modern ovens, even heat distribution is guaranteed and gravity is low. Shrinkage in the direction of large masses is significantly higher. The mass in the melt, due to surface tension and the connection between particles, tends to take the shape of a drop. At the same time, it is pulled from the peripheral areas (i.e. from the neck of the crown, for example) to the central part of the crown (towards the larger mass of porcelain), which can ultimately lead to the appearance of a gap between the artificial porcelain crown and the ledge of the prepared tooth model.
The strength of porcelain depends on the formulation (composition of components) of the porcelain mass and production technology. The main indicators of porcelain strength are:
· tensile strength;
·compressive strength;
· bending strength.
The method of condensation of porcelain particles has a great influence on strength.
There are four condensation methods:
electromechanical vibration;
· coronal brush;
·gravity method (without condensation);
· grooved tool.
Most researchers believe that the best compaction of the porcelain mass can be achieved with a grooved tool followed by the application of pressure with filter paper during suction.
liquid.
Among the technological conditions that significantly affect strength indicators, the following should be noted:
·necessary compaction of the material, i.e. condensation of porcelain particles;
good drying of the mass before firing;
·optimal (usually no more than 3-4) number of firings;
· firing at an adequate temperature for a given mass;
· firing time;
· method of using vacuum during firing;
· glazing the surface of the prosthesis.
The best varieties of dental porcelain, subject to optimal manufacturing conditions, have a bending strength of 600-700 kg/cm2. This strength of the dental material is insufficient. Therefore, we can conditionally distinguish at least two main directions in the search for ways to increase the strength of porcelain
:
1. through new firing technologies, including the development of appropriate equipment and tools;
2. by changing the composition of the porcelain mass.
For example, the introduction into glass or porcelain of crystalline particles of high strength and elasticity, having the same coefficient of thermal expansion as glass or porcelain, leads to a significant increase in strength. In this case, its increase occurs in proportion to the growth of the crystalline phase. Quartz is added to porcelain as a crystalline phase dye. Quartz particles combine well with the glass of the main substance, but their coefficient of thermal expansion is different. When cooling, stress zones appear around the quartz crystals, which are clearly visible under a polarizing microscope. Cracks in quartz-reinforced porcelain follow stress zones, bypassing the crystals.
Adding aluminum oxide particles to some types of porcelain, e.g. the use of alumina (aluminum oxide) porcelain leads to an increase in the mechanical strength of the fused aluminum oxide equal to 2000°C. The firing temperature of alumina porcelain is 1650-1750°C. Reducing the firing temperature is achieved by introducing other mineral substances into aluminum oxide.
\/III. Standard artificial teeth
Standard artificial porcelain teeth are one of the main elements of complete and partial plate and clasp dentures.
Their main advantage over metal and polymer artificial teeth is their high imitation ability. The reflective qualities of porcelain generally resemble those of natural teeth. The color fastness of porcelain is also unrivaled. In addition, porcelain is very indifferent to the human body and is absolutely indicated for people with hypersensitivity to polymers.
Among the disadvantages of porcelain teeth, one should note their fragility, insufficiently strong connection with the prosthesis base, low abrasion, and technological qualities that are worse than those of polymer teeth. Insufficient strength of the teeth in the area of attachment of the crampons (in crampon teeth) and the hollow part (in diatoric teeth) appears with unfavorable articulatory relationships.
CRAMPON is a fixing wire element, mainly for anterior artificial porcelain teeth. Crampons can be straight, curved, or with button ends.
Plastic teeth do not have this drawback, and they are preferred in case of deep bite and deformation of the dentition. In addition, grinding porcelain teeth due to the hardness of porcelain and the presence of crampons is a more labor-intensive process that requires a lot of attention and time from the dental technician, and sometimes from the doctor, where articulation and other errors should not be allowed.
This involves the use of fine-grained diamond or other abrasive tools, which must be constantly moistened due to the potential for overheating. Overheating of a porcelain tooth during its fitting process leads to the chipping of part of the crown or the formation of a crack.
Artificial teeth are divided into:
1.according to location in the dentition on the front and lateral teeth.
2. According to the method of fastening in the base, porcelain teeth are divided into crampon and diatoric. Porcelain anterior teeth are most often equipped with crampons, but they can also be perforated (diatoric). The lateral teeth are always made with holes. The cavities or rims in porcelain teeth are designed to be mechanically attached to metal or plastic. Crampons can be
made from alloys of various metals. The best alloys are those whose coefficient of thermal expansion approaches that of the porcelain mass during firing. In our country, a silver-palladium alloy is used for this purpose.
Artificial teeth made from factory-made porcelain are fired according to a special regime. Raw materials made from various components for porcelain masses are called batch. By introducing low-melting additives (fluxes) into the mixture, which include boric acid, lithium carbonate, magnesium oxide and sodium carbonate, the melting temperature is regulated.
The process of burning the charge is called fritting (melting), and the product obtained during sintering is called frit. From the frit, by adding plasticizers (starch paste, dyes, etc.), a molding mass is prepared for the production of artificial teeth from porcelain in a factory. In recent years, vacuum firing of porcelain teeth has been used at the plant.
It should be noted that porcelain teeth are available in various styles and colors:
·the front top and bottom have 8 styles, and the side top and bottom have 4 styles;
·there are 9 color shades that correspond to the color scale of porcelain teeth.
Porcelain front teeth are produced
:
· sets of 12 teeth (6 upper and 6 lower);
· sets of 6 upper teeth or 6 lower teeth separately;
·incomplete set of 4 teeth (2 upper and 2 lower fangs on the right and left sides).
Porcelain lateral teeth are produced:
· sets of 16 teeth (8 upper teeth and 8 lower teeth, consisting of 4 molars and 4 premolars, 2 each on the right and left sides);
·incomplete set of 8 teeth (upper and lower), or 4 upper and 4 lower molars or 4 upper and 4 lower premolars on the right and left sides.
Porcelain teeth can be produced in sets for toothless jaws, 28 teeth each (6 anterior upper, 6 anterior lower and 16 lateral upper and lower).
An album of porcelain teeth is used as a standard when selecting styles and colors of anatomically shaped teeth. In addition, to select the color, a porcelain teeth color scale is used, which is presented in the form of central incisors in 9 color shades (from No. 1 to No. 9).
Abroad, many companies produce artificial porcelain teeth for removable dentures. For example,
(Liechtenstein) produces sets of anterior porcelain teeth Vivoperl-PE and sets of lateral teeth Vivoperl-PE-Orthotype.
Porcelain teeth (Germany) are widely known in Russia. Biodent supplies porcelain teeth in sets of 6 front teeth (USA).
Bridge VS implant
It should be noted that among all possible options for fixed prosthetics, dental bridges undoubtedly occupy a leading position. But now the choice has become wider, and doctors definitely offer installation of implants for consideration.
Let us say right away that if prosthetics is possible without implantation, then the latter cannot do without the manufacture of prostheses. The implant is implanted into the bone tissue and is essentially an iron rod protruding from the gum. Therefore, a crown, dental bridge or removable denture must be placed on it.
There are very few disadvantages of implants, and they can only be called disadvantages conditionally. First of all, this is the high price of treatment, since it includes the installation of implants and the production of prostheses.
For reference: In the process of prosthetics according to the “implant + dental bridge” scheme, at least two doctors are involved - an implant surgeon and an orthopedist.
Another disadvantage of prosthetics on implants is the duration of treatment, if you do not take into account simultaneous or one-stage implantation. Classic surgery most often involves a bone graft or sinus lift, after which a break of several months is required. Only after osseointegration of the bone tissue is completed is it possible to install a dental bridge and other types of prostheses.
Pros of implantation:
- the integrity of the supporting teeth, since they do not need to be ground;
- reliability of fixation of titanium dental roots due to the strong “rooting” of the implant in the oral cavity;
- the comfort of using the bridge is comparable to using your own teeth;
- durability of prostheses, service life has no restrictions.
It is worth noting that implantation treatment has contraindications, although very few. However, if they are present, you will have to return to installing a dental bridge in the classical way or choose removable prosthetics.
Porcelain crowns are the best option for tooth replacement in terms of aesthetics
Article navigation
- Porcelain: material features
- Indications and contraindications
- Types of porcelain crowns
- Advantages and disadvantages of the material
- Porcelain crowns: the process of creation and installation
- How to fix the product
- Care rules for long-term use of dentures
- Life time
- Comparison of porcelain with other materials
- Price issue
Question for a specialist
Teeth are one of the strongest parts of our body, but, nevertheless, they are not immune from the negative effects of the food we eat, the lifestyle we lead, and the environment. They grow twice, in the milk and permanent dentition, and if we fail to maintain their original shape, color, functionality, then we have to find ways to correct the situation. Fortunately, today prosthetic technology is experiencing its heyday, and restoring damaged or destroyed teeth is not a problem. Today, attractive porcelain crowns, for example, are in increasing demand. Let's look at the features of this material and the stages of manufacturing structures based on it in detail.
Dental bridges made of polymers
This is another type of dental bridge from a low price category. At first glance, they may seem very attractive, even visually, and you won’t have to pay much for dentures.
However, plastic dental bridges have even more disadvantages than metal ones. The only advantage is the price.
Disadvantages of plastic dental bridges:
- poor aesthetics - artificial teeth do not have the transparency and pearlescent luster characteristic of natural teeth;
- susceptibility to chips, cracks and other damage beyond repair. A broken part will have to be replaced with a new one, which certainly does not reduce the cost of dental prosthetics;
- hyperallergenicity;
- short service life of a dental bridge - over time, the plastic darkens or turns yellow under the influence of the alkaline environment of the oral cavity and quickly wears out.
For reference: The average lifespan of plastic dental bridges is 4 years. After this period, new artificial teeth need to be installed.
It is advisable to install a denture made of polymer material as a temporary structure when a permanent bridge is in the process of production. It is especially in demand when the front teeth are lost, since in this case the gaps cause not only physical, but also moral inconvenience.
Types of porcelain crowns
The types of porcelain dentures are determined by their location in the oral cavity - in the front (frontal smile zone) or on the side. In addition, such prostheses can be made from various types of materials.
Made from classic ceramics
Such crowns are made of classic ceramics or porcelain. They are distinguished by high aesthetics and fairly good strength. They are placed mainly on the front teeth, since this is where the appearance is most important, while the chewing load is reduced to a minimum - that is, the risk of product breakage is reduced.
Made from pressed ceramic
In fact, it is lithium silicate, which today is commonly called glass ceramics. There are no pores in it, so the aesthetics of the finished product remains at the same high level, but at the same time the strength characteristics increase significantly. This category includes IPS brand materials (e.max and Empress), which are most popular in the dental market today.
On a note! Very often, ceramic crowns include products made from zirconium dioxide (or oxide). Unlike zirconium, it is not a metal, but simply an element or material that is completely incorrect to call ceramics. In general, ceramic or porcelain or zirconium dioxide crowns constitute a group of metal-free products – this is already the correct name.
Metal-ceramic dental bridges – selection criteria
A metal-ceramic dental bridge combines the best qualities of metal and ceramics, while eliminating their disadvantages - low aesthetics and strength. The beauty of this type of denture is due to the fact that the metal base is lined with a layer of special dental porcelain called ceramics. It is thanks to its application layer by layer that a shade of artificial teeth close to natural is achieved.
The minimum service life of a metal-ceramic dental bridge is 7 years, and throughout the entire period it retains its shape and color. However, it also has a number of contraindications for which prosthetics are not performed:
- pronounced deviations in bite;
- bruxism – grinding teeth during sleep;
- metal allergy;
- severe forms of periodontal inflammatory processes – periodontitis and periodontal disease;
- severe destruction of supporting teeth;
- low dental crowns at the supporting units.
Despite the almost impeccable aesthetics of the material, metal-ceramic dental bridges are not recommended to be placed in the smile area, since the dark frame can show through the ceramic layer. In the area of the anterior teeth, it is preferable to install metal-free dentures that have the best aesthetic properties.
Important! The supporting units for a metal-ceramic dental bridge can be either your own or implanted dental roots.
Porcelain: material features
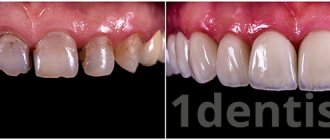
Today, porcelain, first used in prosthetics just over two centuries ago, is considered the most popular material. Crowns made from it are essentially a ceramic product without metal impurities in the composition. The product is produced by processing ceramic mass at high temperatures. The complexity of the manufacturing process of porcelain structures determines their high qualities - wear resistance, precision fit, high aesthetics. They are easy to install, hypoallergenic, and serve their owner for many years, maintaining their original color and shape.
This is interesting! It is believed that the first dentures with a porcelain component appeared about three centuries ago. Orthodontist Pierre Fauchard sharpened crowns from durable ivory, additionally strengthening them with a layer of gold. To make the structure look aesthetically pleasing, he made the top covering from a thin layer of ceramic to match the adjacent units. It was only towards the end of the 19th century that the technology of firing a porcelain crown on platinum foil appeared.
It is important to understand that porcelain and ceramics are actually the same thing. Porcelain is a type of ceramic, one of its highest quality types, since it has a snow-white color even from the inside, i.e. in cross-section, as well as high strength characteristics. But in dentistry there is no division as such into “porcelain” and “ceramics”, so crowns are generally called ceramic, even though there are varieties (pressed ceramics, regular or even with the addition of a composite).
Ceramic dental bridges
Ceramic dental bridges are an ideal solution for dental prosthetics in the smile area. Dental porcelain, which is a ceramic material, allows light to pass through, resulting in the translucent effect of natural tooth enamel.
Therefore, ceramic dentures have an appearance that is as close to natural as possible, and sometimes it is difficult to distinguish them from your own teeth even at close range. This type of bridge has excellent aesthetics, but is inferior in strength to another type of ceramic - zirconium dioxide.
Dental bridges from zirconium began to be made relatively recently, and they have not yet found widespread use. But this is only a matter of time, since this material is superior to ceramics in strength and is not inferior to it in aesthetics. Plus, it's as durable as metal.
Zirconium dental prostheses have such high mechanical strength that they can be used to make a dental bridge even for 6 units missing in the oral cavity! And the durability of such bridges is evidenced by an average service life of 17 years.
Advantages and disadvantages of the material
It is no coincidence that Europeans call special dental porcelain an enamel substitute. Prostheses made from it not only perfectly replicate the anatomical features and shade of the original units, but they are also smooth, translucent, and have a mirror-like shine. Exactly like enamel. Porcelain teeth, if they are truly made with high quality, cannot be distinguished from natural ones. Therefore, the material is often chosen for prosthetics of the front teeth - those that are located and clearly visible in the “smile zone”.
Complex on 4 OSSTEM implants with delayed loading - from RUB 170,000.
Complex implantation Osstem (South Korea) with delayed loading after 4-6 months.
Guarantee for the doctor’s work - unlimited Call now or order a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
In addition, they are quite durable and resistant to chips, and perfectly retain their original shade even when exposed to coloring pigments from food. With proper installation and high-quality oral care (regular hygiene, professional cleanings, avoiding combining hot and cold foods), porcelain products will delight you with their shine, stable shade and shape for about 10-15 years.
And if you have long dreamed of a flawless smile, then porcelain crowns are a great way to achieve it. Installation is quick, the designs are well suited for allergy sufferers who may react to polymers or metal. Products made from pressed ceramics are very light, and you get used to them quickly.
However, this modern aesthetic material has its drawbacks. Due to its fragility, the material does not allow the manufacture of bridge structures. Only single restorations are made from it. And the production of porcelain dentures itself is expensive, which affects the final cost of the product. Especially if the choice fell on modern pressed ceramics.
Interesting! The very first known dentures, as archaeologists testify, were allegedly made from the teeth of wolves and other wild animals. The artifacts were found in Mexico and date back to 2500 BC. Later, dentures were made from the shells of sea creatures and were fixed in the mouth with gold rings. Until the middle of the 18th century, dentures were made from ivory and the teeth of various animals.
CAD/CAM Innovation
The price of dental bridges made of pressed ceramics and zirconium depends significantly on the production technology. Today, CAD/CAM technology, which translates to “computer modeling/manufacturing on a robotic milling machine,” is increasingly becoming the choice of doctors and patients.
The innovative CAD/CAM bridge manufacturing technique involves the use of a 3D scanner, software to create a three-dimensional model of the patient’s entire dentofacial apparatus, and a milling machine on which an orthopedic model of future teeth is created.
This technology practically does not require human participation and allows you to avoid many errors and errors in the execution of the prosthesis. At the end, the dental bridge has an ideal anatomical match with the patient’s specified parameters (direction, inclination of teeth, etc.), which ensures maximum wearing comfort and durability.
Thus, the advantages of ceramic dental bridges are:
- hypoallergenic - both porcelain and zirconium almost never cause allergies, because the materials have a significant similarity in structure to real teeth;
- impeccable aesthetics of the bridge;
- bending stability and maintaining the original shape throughout the entire service life;
- slight tendency to accumulate food plaque in the bridge;
- low maintenance requirements.
Porcelain crowns: the process of creation and installation
The process of creating porcelain dentures is quite labor-intensive. It consists of two stages.
Preparatory stage
At this stage, the doctor determines the condition of the tooth that will need to be restored. The specialist also sanitizes the oral cavity and performs therapeutic procedures. Next, the doctor begins to work with the tooth on which a ceramic prosthesis will be installed. It is advisable to remove the nerve from it to protect it from further inflammation under the crown.
If there is nothing left from the top of the tooth, it will not be possible to fix the crown - you must first build up the tooth. For this, pins or stump inlays are used (the first option is universal, the second is individual, laboratory). If the crown remains, then it is given the shape of a cone. Pure ceramics are quite thin, so little living tissue is ground away - a layer of hard tissue will need to be removed from the prepared unit to form a ledge 0.8 to 1.5 mm wide. It is this thickness of the walls of the future porcelain crown that ensures the strength of the product. The prepared apex becomes like a cylinder or a truncated cone.
Next, the orthopedist makes several impressions or impressions of the prosthetic area and the entire jaw. And selects the shade of the future artificial unit. The data obtained will be sent to the dental laboratory, where the prosthetic structure will be manufactured. Take this period up to a couple of weeks. During this period of time, the doctor will install a protective temporary plastic structure on the prepared tooth.
Laboratory stage
The technician, having received all the data from the orthopedist, begins making the crown. First, a model of the patient's jaw is cast based on the impressions. A cap made of platinum foil is placed on a specific tooth, which is filled with porcelain mass. Next, the product is double fired - inside and outside. The final stage is adjusting the size, giving the shape, the desired shade and glazing the resulting artificial tooth, final firing at a very high temperature - just under 1000°C.
On a note! Some ceramic materials (mostly pressed) are processed using CAD/CAM milling technology. That is, first a scan of the oral cavity or a finished model of the jaw is performed, the crown is created in a special program, and then turned on a robotic machine. Of course, this is more expensive for the patient, but it is more accurate, and the result is more predictable.
Adhesive dental bridges – what are they and when are they placed?
Adhesive dental bridges are also called Maryland or Manhattan bridges and are distinguished by their gentle installation, which does not require grinding or depulping the supporting teeth.
Instead of supporting teeth, a crossbar or fastener with wings is used here to secure the bridge to the teeth in the oral cavity. Dentures of this type are used only to restore the front incisors; they are too fragile for chewing units and simply will not withstand the load.
The advantages of adhesive dental bridges are:
- speed of dental prosthetics - you can close a defect in the oral cavity in just one visit;
- a gentle installation technique, for which there is no need to turn healthy supporting units into pulpless and ground ones;
- ease of care and the possibility of repair in the event of a dental bridge failure;
- affordable price, which is lower than that of ceramic and metal-ceramic bridges.
Disadvantages of orthopedic treatment using adhesive dental bridges:
- susceptibility to mechanical damage and breakdowns, low strength of bridges;
- short service life of no more than 3 years;
- accelerated loss of bone tissue due to lack of load, since the prosthesis is located above the gum;
- the danger of carious damage to the supporting teeth due to the fact that part of the load of the missing tooth is transferred to them, making access for cleaning in places of attachment difficult.
Thus, the review of the main types of dental bridges has been completed; the choice of a specific option for dental prosthetics should be entrusted to the doctor. Perhaps he will offer several methods of orthopedic treatment and will definitely explain all the nuances of installing a bridge.
Installation of dental bridges - the main stages of prosthetics
Orthopedic treatment using dental bridges always begins with an examination and assessment of the patient’s oral cavity. This is perhaps the most important stage for determining the further prosthetic treatment plan.
At stage 1, possible contraindications are excluded, and the most advantageous prosthesis from a functional point of view is selected, which will solve the problem of missing teeth as effectively as possible.
It is mandatory to take a panoramic photograph of the oral cavity, and if necessary, laboratory blood tests are prescribed. After drawing up a treatment plan, the preliminary (zero) stage ends, and work begins on preparing the teeth for prosthetics.
Prosthetics with a classic dental bridge includes several stages:
- To extend the life of a dental bridge, it is necessary to carry out sanitation of the oral cavity: treat caries, remove dental plaque and, if necessary, stop the inflammatory process of periodontal tissue.
- From the “general” they move on to the “specific” – the treatment of supporting teeth. If they are “live”, then the nerve is removed, after which preparation is carried out - in other words, turning. Tooth enamel is ground down in a circle for the best connection with the crowns of the dental bridge. Removal of the nerve is called depulpation and is done to prevent the development of pulpitis due to overheating of the pulp during grinding.
- After grinding the teeth, an impression is made and sent to the laboratory to the prosthetic technician. If the gums are severely injured during the grinding process, then taking an impression of the teeth to make a bridge is postponed to the next visit, after the tissue has healed.
- The dental bridge is ready, fitting is carried out and, if necessary, adjustment is carried out. If the prosthesis fits perfectly, without changing the bite or interfering in the oral cavity, it is “set” on cement.
The installation of a dental bridge is completed with a consultation on caring for the oral cavity in general and the prosthesis in particular.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Possible complications after installing a dental bridge
There can be complications after the installation of dental bridges, and there are many types of different errors both in treatment and in the care of the prosthesis. Most often, inflammatory processes develop at the locations of bridges - stomatitis and gingivitis.
The cause of inflammation is, as a rule, improper grinding of the teeth, when the doctor did not make a special ledge - a step on which the lower edge of the bridge crown is placed. The crown should not hang over the root or press into the gum.
The inflammatory process can also develop due to an overly massive intermediate part of the dental bridge, which puts a lot of pressure on the mucous membranes and causes cutting pain, redness and swelling near the denture.
Another reason is that there is not enough space between the dental bridge and the gum, called “flushing space.” A gap that is too narrow will cause food debris to accumulate and become lodged under the denture, causing inflammation and bad breath.
In addition, the sharp edges of dental bridges can rub the tongue, cheeks and gums, causing chronic trauma.
After fixing a dental bridge, the teeth on which it rests may become sore. There is usually only one reason – lack of timely treatment. Unnoticed caries in time can lead to inflammation and the development of pulpitis and periodontitis. Ultimately, the tooth may even be lost.
One of the causes of periodontitis may be a dental bridge that is too long or a crown that is too high, which causes overload of the tissues surrounding the tooth.
Caution: Galvanic Syndrome
It is worth mentioning separately about the so-called galvanic syndrome - the body’s reaction to the presence of metal prostheses in the mouth. These can be not only dental bridges, but also individual crowns, orthodontic appliances, inlays and even fillings with amalgam.
When interacting with saliva, which acts as an electrolyte, a potential difference occurs in the metal with the formation of galvanic currents. This complication manifests itself as a metallic taste in the mouth, dryness, burning, headaches, and sleep disturbances. The dentures themselves may darken.
The development of galvanism requires the resumption of orthopedic treatment with the replacement of a dental bridge made of a more inert metal or dental porcelain.
Important! Factors of increased risk of galvanism are initial defects in dentures, mechanical damage during operation of bridges, changes in the acid-base environment in the mouth to the acidic side due to stomatitis, periodontitis and gastrointestinal pathologies.
After installing dental bridges, other unpleasant consequences are possible. The most important and difficult stage of treatment is the preliminary stage, when planning and choosing the type of dental bridge takes place.
Complications can be caused by:
- incompletely studied data on the patient’s health in general and the oral cavity in particular;
- incorrect interpretation of x-rays;
- insufficient x-ray studies;
- inattentive approach to customer complaints and wishes.
The listed shortcomings of the doctor are a serious mistake and often lead to serious complications after orthopedic treatment with the installation of dental bridges.
What to do if the dental bridge begins to wobble
If you suddenly feel that your dental bridge is unstable, you should immediately consult a doctor. Perhaps one or both teeth on which the prosthesis rests have broken, or the bridge has been insufficiently fixed with a cementing compound.
The cause of a loose dental bridge is inflammation caused by caries, if the prosthesis is installed on living teeth, on teeth with canals that have been filled for a long time or poorly.
It will not be possible to cope with the situation on your own, and it will not be possible to correct the situation without removing the prosthesis. Diagnostics and x-rays are necessary to assess the condition of the teeth on which the dental bridge stands.
Attention! It is strictly forbidden to fix the prosthesis yourself using household adhesives or any compounds. This can lead to severe burns, inflammation and allergic reactions near the bridge.
Indications and contraindications
Porcelain structures are an excellent choice in many problematic situations. Here is a list of indications for their installation:
- allergies to plastic or metal: porcelain crowns are absolutely compatible with oral tissues, they are hypoallergenic,
- ideal restoration of the smile area: porcelain has excellent light transmission and perfectly matches the natural shade of the enamel, which allows you to make the prosthesis very aesthetic and hide its presence from others (it will not stand out against the background of neighboring teeth),
- the need to restore teeth severely damaged by caries or other dental diseases,
- the need to restore teeth that have fluorosis, hypoplasia, a wedge-shaped defect: in this case, prosthetics with crowns are resorted to if it is not possible to correct the defect by other methods (for example, whitening),
- the need to adjust the shape and position of the tooth: crowns can be used only if there is slight curvature or deviation from the norm, otherwise the patient may be recommended to wear braces.
Contraindications to the installation of these orthopedic products should also be taken into account. Limitations include serious malocclusion, bruxism, and various inflammatory processes in the oral cavity in the acute stage. First, you need to eliminate the existing problems in the doctor’s chair, and only then can you begin prosthetics.
What to do if a dental bridge falls
The answer is the same as in the previous case - go to the dentist. If the prosthesis was installed very recently, less than a year ago, then the most likely reason is tooth decay under the bridge.
A dental bridge may fall out because its service life has expired, that is, the prosthesis has worn out. In this case, the bridge must be replaced with a new one. To avoid encountering such a problem, it is recommended to regularly check the condition of the teeth and the bridge itself, as well as have professional cleaning and timely treatment of caries, especially on the teeth adjacent to the bridge.
It is important to remember that ground teeth are very vulnerable to bacteria and food plaque, so with poorly performed prosthetics they can easily be destroyed. And then the question of fixing the new dental bridge is called into question. If you are missing several teeth in a row, you will most likely need to get implants.
Pain and swelling of the teeth under the bridge are also reasons to urgently consult a doctor. Rinses and ointments will not help here, and time will be lost. As a result, inflammation will intensify and it will be more difficult to cope with it.