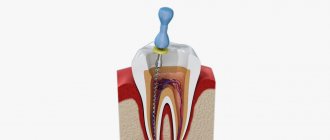
If caries is not treated in time, serious complications can develop. Periodontitis is one of the most common. This is an inflammation of the connective tissue surrounding the root of the tooth. It is accompanied by acute toothache that cannot be tolerated. Symptoms also include bad breath, mobility of teeth, swelling of the gums, and a cyst at the apex of the root. The disease must be quickly eliminated, otherwise you may lose the tooth.
Does your tooth hurt for a long time after periodontitis treatment? Find out what this might be related to. We tell you in what cases you need the help of a specialist and where to go in Moscow.
Pain after CARIES treatment.
Normally, slight pain may occur when pressing on the filling.
, when a hard piece of food gets on the tooth while eating, or when running a fingernail or toothpick over the filling. Painful sensations more often occur after treatment of deep caries: the bottom of the carious cavity is close to the “nerve” of the tooth, and the placed filling, when pressed on it, transfers pressure to the tooth pulp. Over time, these pain sensations will decrease, because... The tooth pulp will develop a protective layer of dentin and “fence itself off” from the filling. However, this takes some time, and the discomfort when biting on a tooth can last up to several months.
Slight dull pain
in a tooth it can also be quite normal. In some patients, this is an individual reaction of the tooth to the doctor’s intervention (mechanical treatment of the tooth with burs, medicinal treatment with antiseptics, “exposure” of the filling with a halogen lamp, etc.). Such pain should not persist for more than 7–14 days.
Acute pain is not considered normal
, spontaneous (causeless) attacks of aching pain, especially at night. If you experience similar sensations after caries treatment, you should consult a doctor for an examination and, possibly, additional procedures.
If the filling is located in the cervical part of the tooth (near the gum), then the tooth may react to temperature stimuli
. In this case, it is important to pay attention to whether there is an overhanging edge of the filling in the gum area (i.e., a step or gap between the edge of the filling and the tooth). If such an unevenness exists, it can injure the edge of the gum, the gum can become inflamed and expose the root of the tooth. And, as you know, the root of the tooth is not covered with enamel and is very sensitive to any irritants. Therefore, if you notice that after treatment of cervical caries or wedge-shaped defect, the gums of the tooth become inflamed, and the tooth reacts to cold or sweet foods, then consult a doctor immediately.
Insidious periodontitis: crept up unnoticed, left without a tooth
Periodontitis is the next stage of inflammation after pulpitis. The infection is localized at the apex of the tooth root and surrounding tissues. The disease is often asymptomatic, but without timely help it leads to tooth loss.
Causes:
- Untreated pulpitis. If a tooth hurts and then stops, it means that the inflammation has entered a chronic stage. Chronic pulpitis will slowly spread throughout the tooth and turn into periodontitis.
- Pulpitis treated using outdated methods. Before the advent of the apex locator, there was nothing to measure the length of the root canal, and the doctor acted blindly. If the canal is not completely treated and particles of infected pulp remain in it, complications arise. To avoid this, the doctor may have overdone it and brought the dental material beyond the root apex. Over the years, a focus of infection sometimes develops around a lump of paste.
- Tooth injury. A common problem in active children. Due to injury (the incisors are often affected), the pulp dies, and periodontitis develops after this. In fact, the reason is the same pulpitis that was not noticed and not treated in time.
Types of periodontitis
| Form | View | How it hurts |
| Spicy | Serous | Mild aching pain in the tooth area. |
| Purulent | Throbbing pain. Tooth mobility may increase. Possible swelling of the cheek, weakness, fever, flux. | |
| Chronic | Fibrous | No symptoms or slight darkening, dull color of the crown of the tooth. |
| Granulating | Mild pain when biting eventually turns into pain from heat, chewing, or pressure. The gums become red and swollen. | |
| Granulomatous | No symptoms. A fistula appears to drain the discharge, but the patient cannot always see it. |
The most aggressive is granulating periodontitis, which very quickly spreads to neighboring tissues. With this diagnosis, most often the tooth cannot be saved.
In the granulomatous type of the disease, the inflammation site has a hard shell, and inside it is filled with pus. Depending on the size, these neoplasms are called granuloma (up to 5 mm), cystogranuloma or radicular cyst (more than 1 cm).
Thus, granuloma and tooth root cyst are manifestations of chronic periodontitis.
Diagnostics
Do not confuse fistula with stomatitis. The fistula looks like a pimple, is located on the gum near the roots of the tooth, and does not hurt when pressed. If a fistula appears, contact your dentist as soon as possible.
The doctor can suspect a problem before the formation of a fistula or gumboil based on complaints. It is very important that the patient describes all the symptoms and does not hesitate to complain about mild, unexpressed, occasional pain and discomfort.
X-rays help to accurately establish the diagnosis. Periodontitis is visible even on a small targeted photograph. Next, to plan treatment, the dentist will suggest taking a panoramic image (all teeth in one frame) or a computer tomogram (a three-dimensional image of the dental system).
CT - 3D computer tomogram
allows you to see the type of periodontitis, the location and size of cystogranuloma, and give a prognosis for treatment.
Positive dynamics
visible on a repeat tomogram 2 years later
From all sides
The advantage of CT is the ability to examine the tooth and the tissue around it from different angles
Treatment
Depending on the stage and form of the disease, the doctor will select the optimal method.
1. Therapeutic treatment. Typically, three visits to the dental office are required.
- Urgent Care. The dentist will remove the source of inflammation: clean and disinfect the canals using medications and laser sterilization. If necessary, the doctor will install a drainage to drain the pus.
- Treatment of tooth canals and installation of a temporary filling. If there are doubts that the immune system will cope with the remaining microorganisms, the dentist may prescribe antibiotics, physiotherapy, rinses and medicinal baths.
- Tooth restoration. At the last visit, the dentist will take an x-ray to make sure that the inflammation has been removed. After this, you can begin filling and restoring the aesthetics and chewing function of the tooth.
- Observation. We can talk about the positive dynamics of the tissues surrounding the tooth after 1-2 years based on the results of an x-ray examination.
2. Tooth-preserving operations. Sometimes conservative methods are not enough. A dental surgeon can perform a cystectomy (removal of the cyst) or apex resection (cutting off part of the tooth along with the cyst).
3. Tooth extraction. In advanced stages, it will not be possible to completely defeat foci of infection. Attempts to save a tooth will lead to large financial expenses and jeopardize neighboring teeth. The best solution would be to install an implant in place of the affected tooth.
If a tooth is left without treatment, it will be removed prematurely. The inflammation will grow and go into an acute stage, and at the most unfortunate moment.
Doctors call chronic periodontitis a ticking time bomb. Exacerbation is provoked by stress, exertion, hypothermia or climate change. That is, it will happen on a long-awaited trip to the sea, while working on an important project, before an exam, or during an infectious disease.
Periodontitis in children
In a child, periodontal inflammation can develop on both milk and permanent teeth. Features of childhood periodontitis:
- high flow rate,
- severe symptoms (temperature, pain, swelling, possible suppuration),
- increased risk of complications. If urgent measures are not taken, the rudiments of permanent teeth will suffer.
Treatment follows the same scheme as for adults. If there is less than a year left before a baby tooth falls out or the roots have already resolved, the pediatric dentist will suggest removing the tooth.
Prevention
Simple and inexpensive measures will reduce the risks of periodontitis and tooth loss.
- Maintain good oral hygiene.
- Eat right. Excess carbohydrate foods provoke the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Contact a specialist for dental treatment in a timely manner. Come for a routine examination every six months, even if nothing hurts. Voice all complaints.
- Treat with understanding the doctor’s suggestion to undergo a panoramic radiography or computed tomography. Complete information will allow you to notice and cure the disease.
For expert assistance in writing the article and providing examples of work, we thank dentist-therapist Olga Yuryevna Yuryeva.
Pain after REMOVAL of a “NERVE” from a tooth (after treatment for PULPTIS).
Quite often, so-called “post-filling” pain occurs after tooth depulpation. Mild pain when pressing on a tooth is considered normal.
and tapping on it, lasting no longer than 4–8 weeks. This is due to the fact that during the treatment process the doctor performs mechanical treatment of the root canals with metal instruments and rinses the canals with powerful antiseptics. All this can irritate the tissue surrounding the root. The reaction to such influences is different for all patients.
If the pain when biting on a tooth is sharp, severe, there is a feeling of an “overgrown” tooth, swelling of the gums or cheeks around the tooth appears, general health worsens or body temperature rises - this is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. Complications of endodontic treatment may have arisen that need to be addressed.
Main causes
Dental treatment can be therapeutic or surgical, and pain can appear after any type of intervention. In most cases, mild or moderate pain is a physiological reaction of tissues to the manipulation, can be easily eliminated by taking anti-inflammatory or painkillers and lasts several days after a visit to the dentist.
Also, pain after dental treatment appears due to complications and violations of the technique of performing medical manipulations. Pain is most often observed after:
- dental fillings;
- root canal treatment;
- removal of a diseased tooth, cyst or granuloma.
The dentist must advise the patient about how the recovery process will occur after treatment and for what symptoms it is necessary to come for another appointment. Also, for comfortable well-being after treatment, anti-inflammatory and, in some cases, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. If, despite following all the doctor’s recommendations, the pain continues to bother you, then it is best to undergo another examination by a specialist.
Pain after treatment of PERIODONTITIS.
Sometimes it happens that the tooth never hurt, but the doctor diagnosed periodontitis and treated it, after which the tooth began to bother. In such a situation, do not rush to blame the doctor and believe that he provided poor-quality treatment.
Treatment of periodontitis is a very complex process that cannot promise guaranteed success. After all, periodontitis is an accumulation of microbes outside the tooth root (in the bone tissue). If before treatment microbes moved freely from the oral cavity to the tooth root and back, then after filling the canals, the bacteria remaining in the bone tissue are “immured.” Normally, this manipulation allows you to localize the source of infection, after which it is easier for the body to cope with it and “defeat” the microbes.
However, with a weakened immune system, due to the individual characteristics of the body, inflammation and a pain reaction may occur in response to sealing of the channels. Even if the tooth did not bother you before, now it can react to pressure and touching it; there may be pain when biting, throbbing, or a slight aching pain in the tooth.
Abnormalities include sharp, paroxysmal pain, the inability to close teeth due to pain, swelling of the gums or cheeks around the tooth, the appearance of tooth mobility, deterioration in general health, or a significant increase in body temperature.
In any case, if pain occurs, it is better to consult a doctor. Additional manipulations or the prescription of certain medications may be required. However, don't panic! Sometimes this kind of pain goes away on its own after some time.
When should you see a doctor?
Have you recently had a root canal treatment? Does your tooth hurt a lot after periodontitis treatment? Do the unpleasant sensations persist? Make an appointment with your dentist. The specialist will conduct a diagnosis and determine the exact cause of the pain syndrome. If errors were made during treatment, the canals will have to be re-processed and filled.
You should also consult your doctor:
- if the tooth loosens easily,
- When closing the jaws and chewing, there is a sharp pain,
- the gums are very swollen, the lip or cheek is swollen,
- body temperature rises to 38-39 degrees,
- health deteriorates significantly.
You should not endure toothache and drown it out with pills. It may indicate pathological processes occurring inside the tooth. You need to see a doctor and get medical help as soon as possible.
Root perforation
Perforation is the creation of an artificial root hole. As a rule, in this case, the pain is sharp, unbearable and makes itself felt immediately after the anesthetic stops working. This can happen during instrumental processing of canals - preparing them for filling.
As in most other cases, the structure of the root system plays an important role here. Narrow, curved canals are a common cause of perforation. In this case, the tool does not move along the canal, but into the root wall.
If a tooth hurts for this reason after treatment of pulpitis, the symptom may be accompanied by bleeding. In addition, some patients report pain even with current anesthesia - subjectively it is perceived as the feeling of an injection into the gums. If the tooth was filled after perforation, the filling material may leak beyond the root. Severe pain persists for up to 3 weeks, and the main complication of this phenomenon is the inflammatory process.
How to diagnose periodontitis
To determine periodontitis, you need to see a dentist. The doctor will collect anamnesis, conduct an examination using dental instruments, and prescribe additional diagnostics:
- Insertion of the probe into the cavity does not cause pain.
- There is no reaction to the thermal test.
- Percussion causes sharp pain.
- Electroodontodiagnostics. With periodontitis, teeth react to a current of 150 to 200 µA.
- Orthopantomography. In acute serous periodontitis, no radiological changes are observed. Later, the expansion of the periodontal fissure is determined. In an acute purulent condition, a limited abscess is detected. In case of chronic pathology in the apex area, the images show a focus of destruction surrounded by a zone of rarefaction of bone tissue.
Why is chronic periodontitis dangerous?
The anatomical structure of the teeth ensures in most cases the free outflow of serous and purulent masses from the source of inflammation. As a result, the patient may not be aware of the presence of chronic periodontal inflammation for a long time. All this time it is actively developing, exposing tissues to destruction. Sometimes this leads to the fact that it is no longer possible to save the tooth.
In addition to tooth loss, chronic periodontitis leads to the formation of skin or gingival fistulas and various types of granulomas, which require long-term (several months) complex and expensive treatment.
Granulomatous formations pose an additional danger. They can, under the influence of such unfavorable factors as stress or hypothermia, lead to the development of serious inflammatory processes, including sepsis.
Chronic periodontal inflammation can also accelerate the progression of diseases such as nephritis, arthritis and rheumatism, and provoke other health problems.
What to do?
What to do if your tooth hurts after pulpitis treatment? The most important recommendation if you suspect a complication after treatment of pulpitis is a return visit to the doctor. If this is not possible, you should contact another specialist and explain the situation.
If it is not possible to visit the clinic immediately, you can use a painkiller - give preference to the one that you have already taken, to which there have been no negative reactions. However, it is better to try to consult with a specialist, if not in person, then by phone.
It is difficult to say exactly how quickly the pain will subside in each case. However, on average, after visiting the dentist, relief comes quite quickly:
- When removing the filling material beyond the root apex: a visit to the doctor will allow the specialist to remove excess material, and after 2-3 days the discomfort will subside.
- If the filling is insufficient: the doctor will choose a tactic for further treatment; it is quite possible that several visits will be needed to eliminate the inflammatory process - for larger cysts or granulomas, surgical treatment is also required. This complication requires refilling to prevent recurrent complications.
- If the pulp or part of it is intact: the doctor will remove the remaining pulp and repeat the manipulations that were required to treat pulpitis. The pain in this case goes away within a few days after all measures are completed.
- If an instrument breaks off: the doctor will perform an X-ray diagnostic and, if the presence of a broken instrument is confirmed, will remove it. In rare cases, resection of the root apex is performed.
- In case of perforation: the dentist will treat the canals without affecting the hole. Using modern osteoplastic materials, he will close it, which will save the tooth. If a purulent process occurs, several visits will be required to eliminate the inflammation.
- In case of gum injury: contacting a doctor will allow you to receive recommendations regarding antiseptic and healing agents for treatment at home. Relief occurs on average within 1–3 days.
- In case of an allergic reaction: it will be necessary to refill the root canals using other materials. The doctor will perform the necessary manipulations and also prescribe decongestants that will quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Prevention of periodontitis
Careful oral hygiene.
You need to brush your teeth twice a day. It is recommended to periodically change your toothbrush and choose your toothpaste carefully. Cleaning should not injure the gums, otherwise an inflammatory process may develop.
Removing plaque and tartar.
The procedure for removing plaque and tartar is carried out by a dentist.
If necessary, the doctor installs fillings, polishes the teeth and advises the patient on proper oral hygiene.
Restoration of dentition.
It is not recommended to leave voids in the dentition, as this can further ruin the bite. In addition, the remaining teeth will take on excessive load, becoming vulnerable, as a result of which a chronic inflammatory process and periodontitis may develop.
Up to contents
Reasons for the development of the disease
- consequence of pulpitis: pathogenic microbes and their toxins from the inflamed pulp enter the periodontal tissue, that is, they go beyond the dental root,
- a consequence of poor treatment of pulpitis: for example, if the root canals were poorly processed, resulting in a source of infection or a foreign body remaining in them,
- injury to the jaw bone or the tooth itself upon impact: in such a situation, it may shift and pathogenic bacteria will enter the periodontal tissues from the outside,
- as a result of an overdose of certain medications that are used to expand and clean canals for pulpitis.
Exacerbation of periodontitis
With exacerbation of periodontitis, the process of asymptomatic and prolonged inflammation becomes active. In this case, acute pain, swelling of the gums, and swelling of the soft tissues of the face occur. The reasons for exacerbation of periodontitis include the following.
- Damage to the membrane of the focus of purulent inflammation.
The area of inflammation in granulomatous periodontitis is limited to dense tissue, resembling a pus-filled sac. Excessive pressure on the tooth can cause rupture of this membrane and the release of infection beyond the capsule, which leads to exacerbation of inflammation.
- Impaired drainage of pus from the site of inflammation.
While pus can leave the area of inflammation through a fistula or through root canals and then into a carious cavity, the process develops almost asymptomatically and imperceptibly. But if the fistula closes or the root canals become clogged (for example, with food particles), pus begins to accumulate, pain, swelling, etc. occur.
- Decrease in the body's defenses.
As a result of decreased immunity, the factors that restrained the growth of infection in the periodontal tissue of the tooth begin to weaken. This leads to the active development of infection and exacerbation of the inflammatory process.
Up to contents
PS
In this article, we deliberately do not touch upon mistakes made by dentists that may cause pain. God forbid that a seed of doubt should be planted in you. It is very important to trust your doctor or better look for another! Any doctor will say that the most difficult patient is the patient who does not believe in his recovery. But if you have doubts about the doctor’s competence, then the best decision is to go to another for a second opinion. Take pictures before and immediately after treatment, and keep these pictures for yourself. This will help prove you are right if something goes wrong. And trust your doctor!
The situation where pain may occur is quite predictable. In such cases, the dentist always warns the patient about possible pain. And if the pain goes away after a week or two, then there is nothing to worry about.
Removing the filling material beyond the root apex
If, after treatment of pulpitis, the tooth hurts when pressed, perhaps we are talking about the removal of the filling material beyond the root of the tooth, into the adjacent tissues. The intensity of the sensation depends on how much material has gone beyond the apex of the root. Despite the fact that today a doctor has ample opportunities to control the accuracy of canal filling, as well as the use of high-quality materials, this can happen. It is worth noting that X-ray monitoring of treatment is intended to prevent the development of such a consequence - after the filling is completed, an image should be taken in which, in the event of a re-filling, the doctor will be able to notice excess material and choose the tactics for further action. Re-filling or removal of filling material beyond the root apex in itself does not pose a particular threat.
The exit of the filling material beyond the root apex can cause long-term pain immediately after the anesthetic wears off and persists for a long time - up to several months. This is a natural reaction of tissues to foreign material. Removal of material may be due to the following reasons:
- difficulties in determining the length of channels;
- incorrect selection of a pin from materials for the canal;
- lack of apical stop, etc.
However, this is not the only possible treatment difficulty that provokes pain.
Symptoms of chronic periodontitis
Chronic periodontitis is a very insidious form of the disease, since it can develop completely asymptomatically. It is extremely rare for a person to feel a slight pain when trying to bite something on a sore tooth; sometimes unpleasant sensations appear when consuming hot food and drinks.
Chronic periodontitis of the tooth is diagnosed with an x-ray, which clearly shows the process of bone destruction at the apex of the tooth root. This form of the disease has its own classification, according to which there are: fibrous, granulating and granulomatous periodontitis. With fibrous periodontitis, there is almost no pain, which is why it is most often recognized either in the acute phase or during an examination by a dentist and x-rays.
Treatment of this form of periodontitis is quite simple and is carried out in 1-2 visits to the doctor. Granulomatous chronic periodontitis most often develops asymptomatically, but under the influence of certain external factors it easily turns into an acute form. The disease has its own characteristic symptom, manifested in the formation of granulomas - capsules with pus, which separate tissues affected by inflammation from healthy ones. The treatment process for granulomatous periodontitis is long and complex, it can last for several months and even require surgical intervention!