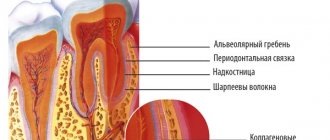
Why did gumboil appear after dental treatment?
Swelling of the gums indicates the occurrence of an inflammatory process, which caused the complication. If painful sensations are observed against the background of the tumor, the main reasons for this may be:
- Periodontal inflammation. The tumor is observed on both cheeks, but pronounced swelling occurs only on the infected side.
- Neglected teeth, improper placement of fillings. Before swelling occurs, pain occurs. After 2-3 days, a flux with pus may form.
- Incorrect development of wisdom teeth. A hood forms from the mucous membrane, in which food particles accumulate and become inflamed.
- Removal of a tooth. Due to mechanical damage to the tissue, swelling can be considered normal.
- Cyst. The inflammatory process lasts for 1.5-2 years and injures the periosteum. The pathology occurs against a background of severe pain.
Attention! Swelling of the cheek after dental treatment can develop due to infection in the socket, which not only causes discomfort and swelling, but can also lead to more serious consequences.
If there is no pain during swelling, the reasons for this are as follows:
- allergic reaction to anesthesia, dental materials (swelling sometimes affects the entire face);
- removal of the nerve: part of the nerve may remain in the canals; after installation of the filling, flux appears;
- dissection of the gums, extracted tooth (in these cases, swelling is normal);
- infectious inflammation of the lymph in children, accompanied by aches and fever;
- neurological diseases accompanied by swelling, congestion in the ears, sore throat, weakness.
Important! In the case of severe pathologies of internal organs, the drainage of fluid is often disrupted; as a result, it accumulates in the nose, cheeks, neck, cheekbones and near the eyes.
Diseases and complications that lead to severe swelling
- Alveolitis.
Inflammation of the socket is a fairly common occurrence after tooth extraction. The so-called dry socket occurs due to various factors that prevent the formation of a blood clot after extraction (improper removal, general diseases, mechanical stress, bad habits, and so on). The swelling in this case is not so pronounced and occurs in the area of inflammation. The main symptom is shooting pain, an unpleasant odor and a gray coating. If left untreated, advanced alveolitis can develop into phlegmon and osteomyelitis. - Difficult tooth extraction.
In the presence of retention, dystopia and other pathologies, tooth extraction will always be more traumatic, which leads to quite pronounced swelling after surgery. This also includes the removal of third molars. In complex cases of extraction, the doctor should inform how long it takes for the swelling to subside after tooth extraction (approximate time frame). If the procedure was carried out correctly and the patient complied with the instructions, there is no need to worry. - Mistakes during tooth extraction.
During the extraction process, the doctor did not remove the root, interroot septum, fragments, or introduced an infection into the hole. Another rather rare, but still possible reason is when, after tooth extraction, a cyst remains that was not detected. Its growth contributes to the occurrence of edema. - Systemic diseases of the body.
Problems with the cardiovascular system, diabetes, hypertension, pathologies of the circulatory system, poor immunity - all this negatively affects the body’s ability to recover after surgical interventions.
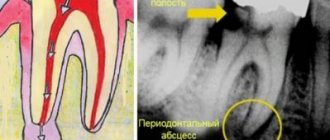
What does flux look like?
It is of infectious origin, the process occurs against the background of inflammation of the body of the jaw or in the periosteum. Flux is formed not only after dental surgery, but also after furunculosis or tonsillitis. If the cheek and gums are swollen, there is throbbing or mild pain, in advanced stages pus may appear and the temperature may rise. On the upper jaw, the flux covers the lip, cheek, gum and nasolabial area. In addition to the face, the infection often spreads to the neck.
Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are used for treatment. After using topical medications, you should not eat or drink liquids for 2 hours.
Reasons for the development of abscesses after an injection
Any intramuscular injection is an invasive procedure. Such an intervention violates the integrity of the skin and triggers a whole chain of pathological changes. As a rule, the cause of an abscess is incorrect administration of injections in violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis. Often such complications occur if the injection was given at home.
Predisposing factors for the development of an abscess are decreased immunity and a sharp weakening of the body.
The correct way to administer the injection is to insert a needle into the upper outer quadrant of the buttock. It is permissible to inject the medicine into the muscle layer of the shoulder or thigh. If the syringe needle enters a large blood vessel, hemorrhage occurs into the soft tissue, which can lead to the development of an abscess. A number of drugs can have an irritating effect on tissue; when administered not into the muscle, but into the subcutaneous fat, it can also lead to the formation of an abscess.
If the wound at the injection site was scratched, this could serve as an entry point for infection and cause a suppurative process.
What symptoms do you see a surgeon for:
- Presence of hernial protrusion
- Daggering pains in the abdomen
- Bloating
- Pain in the right hypochondrium
- Bitterness in the mouth
- Nausea
- Presence of neoplasms on the skin
- Swelling and redness of the skin
- Bone fractures and bruises
- Wounds of any location
- Vomit
- Enlarged and painful lymph nodes
Swelling on the inside of the cheek
Anesthesia makes tooth extraction easier. But, if after treatment of a tooth your cheek is swollen, you should find out the origin of the pathology. You may need treatment for your gums. Discomfort appears in many patients after depulpation. Pain and swelling on the inside of the cheek can be observed from 2 hours to 7 days. If discomfort intensifies or occurs 2 days after surgery, you should immediately consult a dentist.
If, after removing the nerve, in addition to painful sensations, the gums become inflamed, purulent discharge appears, and the temperature rises, you should visit a dentist. He will find out why the cheek is swollen and how to remove the gumboil.
Attention! You cannot take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs before consulting a doctor; this will complicate the diagnosis, which will not allow you to prescribe adequate treatment.
Swollen cheek after tooth extraction: why and what to do
After tooth extraction, many people experience unpleasant symptoms: swelling or numbness of the cheek. From a medical point of view, such a reaction is normal and demonstrates the body's immune response to the operation. But in some cases, a swollen cheek can be a symptom of the development of unpleasant complications.
For what reasons does swelling occur?
Surgical intervention associated with tooth extraction causes inflammatory processes. They contribute to the appearance of soft tissue tumors.
If the doctor performed the operation correctly, and the patient followed his instructions during the recovery period, the inflammation should go away on its own, without taking medications and the risk of complications.
The duration of swelling depends on the complexity of the operation and the person’s immunity. In a normal situation, swelling subsides in three to four days, but in some cases it lasts up to seven days.
If the swelling does not subside within seven days, this may indicate a complication. In this case, you should consult a doctor.
The cheek after tooth extraction swells some time after surgery, immediately after the anesthesia wears off. Sometimes this process can be associated with a feeling of pain, as well as the release of a small amount of blood. In some patients, the temperature rises to low-grade levels. All of the above symptoms are normal and are not a cause for concern.
Analgesics can be used to relieve pain. A few days after the operation, the swelling gradually decreases and disappears within a week.
Swollen cheek after wisdom tooth removal
This type of removal is one of the most traumatic and difficult operations in dental practice. Surgical intervention ends with suturing, so inflammatory processes almost always appear. In this case, the cheek swells for a longer period and recovery after surgery causes pain to the patient.
After removal of extreme molars, patients may experience pain for several days. Additionally, there are problems with swallowing saliva and discomfort while chewing food or talking.
The appearance of painful sensations is associated with the risk of developing inflammation, therefore, after the removal of a wisdom tooth, you should follow all the doctor’s recommendations, including taking medications and rinsing with antiseptics.
Reasons for the development of edematous processes
In addition to the natural reaction processes of the immune system, the cheek may also become swollen due to:
- Carrying out surgery on a tooth with pronounced gumboil;
- Removal of a tooth complicated by its incorrect location or too large, branched root;
- Infection and tissue contamination;
- Allergies to medications;
- Intolerance to painkillers or other medications;
- Incorrectly performed extraction;
- The presence of chronic diseases in the patient’s medical history;
- Failure to comply with doctor's recommendations: refusal to take medications and perform disinfection treatment.
Frequent causes of tumors are non-compliance with oral care rules, skipping medications and preventive treatment.
Risks of complications
If the tumor does not subside within a week, but continues to grow, causing pain, this is a symptom of the development of inflammation. Along with the tumor, symptoms such as temperature above 37 degrees, general malaise, headaches, and pain in the gums may appear.
The most common complications after tooth extraction are:
- Alveolitis or dry socket syndrome. The complication is associated with the disappearance of a blood clot located in the wound. Clotted blood is a natural barrier to bacteria and infection, and if it is accidentally removed, there is a risk of infection of the wound and further suppuration.
- If a swollen cheek is painful, this may indicate inflammation of the hard tissues. The swelling becomes larger and spreads along the jaw, causing pain and discomfort to the patient.
- Gum abscess is another type of purulent inflammation that can spread to other areas of the gums.
- Peritonitis or gumboil is an inflammation of the jaw, the main symptoms of which are a sharp increase in temperature and severe pain in the gum area, radiating to the temple.
- Neuritis is damage to the facial nerves, the symptoms of which are severe swelling and acute pain.
All the described complications without appropriate treatment can lead to serious consequences.
How to relieve cheek swelling
It is impossible to get rid of the tumor quickly; to do this you need to wait until the inflammatory process stops. But swelling can be reduced, along with it removing discomfort and pain. To do this, it is recommended to use cold compresses, which should be applied for 10 minutes every half hour, avoiding severe hypothermia.
Additionally, you can use analgesics and rinse your mouth with special antiseptics.
If your doctor has prescribed antibiotics, you should take them according to the instructions: they will help protect against infection and speed up the process of tissue regeneration.
Swelling is normal if it goes away within a week. In all other cases, it is better to contact a specialist.
What to do if swelling appears after treatment at the dentist
If after tooth extraction your cheek is swollen from the tooth, there is no need to worry - this is a normal reaction. You can take a pain reliever that your dentist recommends. When a pathological condition is accompanied by pain and weakness, the temperature should be measured.
Edema does not always indicate a complication; it is worth distinguishing a simple reaction of the body from a pathological condition. Don't worry if:
- the flux disappears 3 days after surgery;
- the swelling is not pronounced and does not increase in size;
- no temperature or it does not exceed 37.5 degrees;
- the pain is aching, slight, gradually goes away, eliminated with analgesics;
- in the hole there is a bloody dense clot, which is covered with fibrous tissue within 2-3 days.
On a note! Do not apply hot lotions to the injured area, release pus yourself, or massage the gums. This will provoke further development of the infection, which will lead to serious consequences.
The following symptoms indicate complications:
- the flux grows;
- there is severe pain that cannot be relieved with analgesics;
- tension together with surgery;
- temperature over 37.5-37.6 degrees;
- it hurts to swallow, speak, open your mouth;
- there is no blood clot in the hole or it is covered with a green, gray or yellow coating;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- itching, hyperemia, shortness of breath - indicate an allergic reaction.
Attention! If you have any of the symptoms, you should consult your doctor. Such signs indicate infection. If an operation was performed, the treatment is carried out by a dental surgeon or an endodontist if the root canals were cleaned.
When is it necessary to contact a specialist?
We kindly ask you not to self-medicate and not to leave things to chance. Severe swelling may be a variant of the norm, your individual reaction to the intervention, but if you are unsure about something, be sure to contact your doctor. Complications are always easier to prevent than to treat.
In rare cases, swelling may occur after implantation as a symptom of complications. Occurs with reduced immunity, wound infection, and improper care. You can read more about what to do if your face is swollen after tooth implantation and what to do in the postoperative period. If you experience the following symptoms of the disease, you should visit a doctor:
- Tissue swelling, which increases from 3-4 days after surgery.
- Throbbing pain that gets worse.
- Discharge of pus.
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- General symptoms include weakness, headache, malaise.
- Increased body temperature.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
When does swelling of the cheek go away?
How long the swelling lasts after tooth treatment depends on the degree of damage. Swelling causes injury to tissues, ligaments, and blood vessels during surgery or root removal. After such an intervention, swelling is normal. It can last from 2 hours and last for 7 days or the first day after surgery. There are no painful sensations.
Swelling after surgery on a wisdom tooth can last 4 days longer and persists for 11 days. If the surgery was serious, a bruise may form on the cheek. Pronounced swelling, increasing every day, pain is a reason to urgently consult a dentist.
A tooth after gumboil lasts for decades and saves the patient’s budget.
With proper treatment, the tooth will last for many decades. It is understood that the infection from the canals is completely removed as a result of treatment and does not pose a danger. A tooth crown destroyed by caries is either filled, or an inlay or artificial crown made of metal-ceramic or ceramic is used. After the treatment, it may be painful to bite on the tooth for some time, but this will pass.
Conservative methods are not always effective. In this case, dental surgeons come to the rescue. The operation of resection of the apex of the tooth completely removes the source of infection and saves the tooth. Patients are usually scared by the word surgery. This intervention is not traumatic and is much more gentle than the operation of extirpating the tooth itself. The high price is associated with the delicate work of the doctor, with a higher final result of treatment. And in conclusion, let's go back to the beginning. A dentist, treating a chronically diseased tooth, sets his task not only to save this tooth. This is his narrowly professional task. But as a doctor, he solves the problem of removing the inflammatory focus, which provokes many concomitant diseases. Sensitization, glomerulonephritis, allergies, myocarditis, skin diseases such as eczema - only what comes to mind. Therapy for these diseases begins with “eliminating foci of chronic infection”
what is reliable dentistry
Everyone puts their own meaning into this concept. If someone’s teeth are simply a heavy burden that always confuses all plans, well, in 32 visits the problem can be solved inexpensively and quickly. Someone trusts Google search and is looking for inexpensive dentistry with dental implants on sale. And someone doesn’t believe anyone and studies the issues of prevention and preservation of the dental and jaw apparatus, leafing through yellowed books and finding in them the ideas and thoughts of those who created scientific, not commercial dentistry many decades ago.
Treatment of periodontitis price from 4000 rubles, anesthesia is included in the price.
You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling +7 8. Our address is Samara region, Samara, Industrial district, st. Novo-Vokzalnaya, building 269 stop Solnechnaya landmark Meteorological center, corner of Novo-Vokzalnaya and Novosadovaya streets, entrance from Novosadovaya street Opening hours: until 23 00 Reliable dentistry on duty.
How to treat gumboil on the cheek
Once a tumor develops, antibiotics are often indispensable. The dentist selects them taking into account the stage of the pathology and the characteristics of the body. Antibiotic therapy should be completed to the end, otherwise further treatment will be greatly complicated.
If surgery is required, all activities are carried out in a dental clinic. For any complication, the patient is given local or general anesthesia. The gum is incised and the accumulated pus is completely pumped out. A drainage is placed to quickly remove fluid. The patient is prescribed antibiotics to allow the soft tissues to recover faster. In case of severe damage, the gum is sutured. In the absence of complications, this is not required.
How to remove swelling from the gums through surgery:
- In case of complicated flux, urgent hospitalization in a dental clinic and an operation performed by a dental surgeon are necessary.
- If an inflammatory process is diagnosed due to dental problems, endodontic therapy (cleaning and filling the canals) or root removal will be required.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed to treat infection in many situations. In case of serious complications, combination drugs are used to treat severe swelling, selected taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogens.
- Surgical treatment - incision of the abscess (on the face and oral cavity - the incision is made in both areas), removal of purulent discharge, treatment with disinfectants, installation of drainage. In severe cases, general anesthesia is used.
- Additional therapy - analgesics to eliminate discomfort, antipyretic drugs, large amounts of fluid (if necessary, fluid is introduced into the body by infusion during hospitalization).
Chronic pathology often occurs without pronounced symptoms, pus appears gradually. In this situation, the dentist uses a therapeutic approach, both surgical and conservative. Surgery can be replaced with herbs or antibiotics, or used as an additional treatment after consultation with a specialist.
Swelling of the cheek does not always indicate the presence of a serious pathology.
A tumor after depulpation is normal and does not require serious treatment. When the gumboil gradually grows, pain is observed against this background, and the help of a dentist is required. In case of serious complications, surgical intervention while taking antibiotics is indicated. The doctor's consultation
Diagnosis and treatment
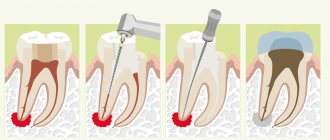
To make a diagnosis, the doctor only needs to examine the oral cavity and study an X-ray of the jaw. The flux treatment regimen is compiled individually for each patient. This may include:
- complex treatment of caries, pulpitis or periodontitis,
- taking antibacterial drugs,
- opening the abscess and draining the contents,
- rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions,
- physiotherapy - UHF, laser therapy, electrophoresis.