Painful sensations after treatment of pulpitis may be normal or a consequence of complications. In order to differentiate these conditions and determine whether it is worth seeing a doctor immediately, it is important to assess the nature of the pain, the time during which it persists, and general well-being.
It is worth noting that in most cases, one of the most important stages in the treatment of pulpitis is the removal of the pulp or neurovascular bundle of the tooth. Many patients wonder: can a tooth hurt after treating pulpitis with this method? Despite the absence of a “nerve”, pain may be observed, this is a natural reaction to the intervention - removal of the pulp, treatment and filling of the root canals. It is important to know when it is normal and when pain is caused by a complication.
Natural pain after pulpitis treatment
Why does a tooth hurt after pulpitis treatment if there are no complications?
After the anesthesia wears off, pain may appear in the area of the causative tooth, and normally this condition is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the pain gradually subsides - an unpleasant sensation of a certain degree of severity may persist for some time, but it does not intensify;
- already 1–3 days after the procedure, the pain noticeably subsides;
- there are no other symptoms - bleeding, severe swelling and redness of the gums, increased body temperature, general weakness.
It is difficult to predict how much a tooth hurts after treatment for pulpitis; it depends on the individual characteristics, the specific tooth and the complexity of the root system, the presence or absence of concomitant diseases. The norm is that moderate pain persists for up to 7 days. Important: the intensity of pain becomes less over time.
It is difficult to talk about the norm if there are such “indicators” of complications as fever, swelling, too much pain, including increasing pain. There are several possible complications of endodontic treatment of pulpitis.
Prevention of complications
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups, contact your dentist immediately if your tooth hurts after root canal cleaning;
- consult a doctor immediately if there are signs of an allergy to the filling material, increased pain, fever, swelling of the gums or face;
- follow the doctor’s recommendations after endodontic treatment regarding oral care and medications;
- do not self-medicate.
Author of the article Voznyuk Vladimir Aleksandrovich Maxillofacial surgeon-implantologist of the highest category
Work experience: 28 years.
Removing the filling material beyond the root apex
If, after treatment of pulpitis, the tooth hurts when pressed, perhaps we are talking about the removal of the filling material beyond the root of the tooth, into the adjacent tissues. The intensity of the sensation depends on how much material has gone beyond the apex of the root. Despite the fact that today a doctor has ample opportunities to control the accuracy of canal filling, as well as the use of high-quality materials, this can happen. It is worth noting that X-ray monitoring of treatment is intended to prevent the development of such a consequence - after the filling is completed, an image should be taken in which, in the event of a re-filling, the doctor will be able to notice excess material and choose the tactics for further action. Re-filling or removal of filling material beyond the root apex in itself does not pose a particular threat.
The exit of the filling material beyond the root apex can cause long-term pain immediately after the anesthetic wears off and persists for a long time - up to several months. This is a natural reaction of tissues to foreign material. Removal of material may be due to the following reasons:
- difficulties in determining the length of channels;
- incorrect selection of a pin from materials for the canal;
- lack of apical stop, etc.
However, this is not the only possible treatment difficulty that provokes pain.
Insufficient canal filling
The opposite situation, in which a tooth may hurt after treatment of pulpitis, is insufficient filling of the root canals, the formation of voids at the apex of the root. In this case, often unpleasant sensations do not occur immediately, but as the inflammatory process develops - this can happen either after 1-2 weeks or after a longer period of time.
Here, painful sensations are associated with the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms in the voids. This process leads to one of the diseases:
- periodontitis - inflammation of the peri-root tissues;
- tooth root apex cyst;
- granuloma.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, pain may appear immediately or make itself felt when the cyst or granuloma has reached an impressive size. Its intensity is often low, minor pain is more often observed when biting after treatment of pulpitis, and in the absence of mechanical impact on the tooth there is no discomfort at all.
What is it – tooth pulpitis?
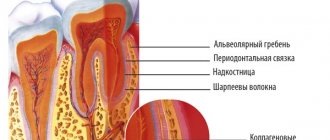
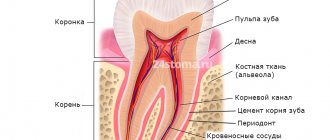
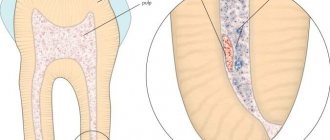
Pulpitis is a dental term that refers to an inflammatory process that affects the nerve bundle inside the tooth - the pulp. Colloquially, the pulp is often called the nerve of the tooth. Strictly speaking, the pulp is not only nerves, but also small blood vessels, thanks to which a living tooth receives nutrients and necessary microelements. If the pulp is removed (and this often happens during the treatment of pulpitis), the tooth becomes dead and fragile because it does not receive the nutrition necessary for its full functioning and healthy condition.
The inflammatory process in the pulp never occurs on its own - there are always reasons that trigger it. Knowing the reasons why pulpitis appears is necessary and useful; this will make it possible to carry out effective prevention of this dental disease.
Take a short test and calculate the cost of treatment!
Take a short test
One of the root canals was not processed
This is one of the rarest complications, since before starting endodontic treatment the doctor will definitely prescribe an x-ray diagnosis. It allows you to reliably determine the number of channels and evaluate their structure. But there are cases of abnormal location of root canals or their extremely small sizes, which makes them unnoticed in the image.
This leads to the following situation: the doctor removes the pulp in each canal, but one remains unattended - the inflamed pulp continues to hurt, and pathogenic bacteria continue to multiply. Such pain is difficult to confuse with other complications - the patient simply does not receive relief after treatment, and the pain characteristic of pulpitis itself remains. The sensations are pulsating in nature, the pain intensifies when eating, exposure to temperature on the tooth, and becomes unbearable at night.
The same symptoms can be observed with incomplete removal of the pulp in the diagnosed canal. In both cases, other symptoms may be observed:
- headache, sensations “radiate” to the ear, temple - depending on the specific tooth;
- increased body temperature;
- symptoms of general malaise.
Most complications are related to the complexity of the canal structure, and the following is no exception.
Instrument breakage in the root canal
After treatment of pulpitis, the tooth may also hurt due to a broken instrument. Part of it remains in the root canal, and unpleasant sensations occur immediately or a few days after the visit to the dental office.
The nature of the pain may vary depending on the size of the fragment and other conditions.
It is worth noting that this complication is quite rare. This is explained by the fact that a good dental clinic uses modern, high-quality instruments from reliable manufacturers that are sufficiently durable. In addition, the rules for their use must be strictly observed, including multiplicity, force during exposure, etc. And finally, the doctor will notice the presence of a foreign body in the tooth on a control image, which he will prescribe after treatment.
Complications in the treatment of acute pulpitis
In some cases, as a result of treatment of acute pulpitis, the patient develops complications. Severe pain or increased sensitivity occurs when:
- biting hard food, chewing rough food;
- pressing on the tooth;
- exposure to cold water.
In such cases, the doctor prescribes treatment of the tooth with an anesthetic solution or a course of physiotherapy in the form of obtaining fluctuating currents. In case of relapses, it is recommended to replace the medication that was placed in the dental cavity during treatment. If such procedures are not effective, the affected tooth may be removed.
If treatment of acute pulpitis is required, the price depends on a number of factors. The final cost is influenced by the quality of the consumables used, medications, types of material for filling, as well as the equipment used. Dental clinics have a standard price list that indicates how much each procedure costs.
Root perforation
Perforation is the creation of an artificial root hole. As a rule, in this case, the pain is sharp, unbearable and makes itself felt immediately after the anesthetic stops working. This can happen during instrumental processing of canals - preparing them for filling.
As in most other cases, the structure of the root system plays an important role here. Narrow, curved canals are a common cause of perforation. In this case, the tool does not move along the canal, but into the root wall.
If a tooth hurts for this reason after treatment of pulpitis, the symptom may be accompanied by bleeding. In addition, some patients report pain even with current anesthesia - subjectively it is perceived as the feeling of an injection into the gums. If the tooth was filled after perforation, the filling material may leak beyond the root. Severe pain persists for up to 3 weeks, and the main complication of this phenomenon is the inflammatory process.
What are the causes of pain
The occurrence of pain after treatment of pulpitis after removing nerves and cleaning root canals can be caused by two main reasons. The first is damage to the tissues of the apex of the tooth root, the second is poor-quality filling.
The first reason is quite understandable: when instruments intervene in the internal areas of the tooth, part of the nerve is torn off, and until this place heals, some time must pass. If the tooth itself was treated efficiently, then in a maximum of 3 days the wound inside will heal and the pain will disappear.
But with the second option the situation is more complicated.
There are several options for poor-quality filling of a tooth with pulpitis:
- The dental canal is not completely sealed;
- The canal is sealed too deeply;
- The filling material has gone beyond the root;
- When filling, a piece of the instrument remained inside;
- During the procedure, a perforation of the root canal occurred during cleaning.
It should be noted that the vast majority of such cases occur through the fault of the dentist. I don’t want to talk badly about doctors, but the statistics speak for themselves. In part, such misfires among doctors stem from a lack of experience; it is much worse when their poor-quality work is associated with ordinary negligence.
However, the dentist cannot be blamed if the patient’s root canals are not completely straight: in this case, even an experienced dentist, no matter how hard he tries, can accidentally damage the canal or fill it not to the top. Therefore, in such cases, it is always better to take an X-ray of the tooth.
Let's look at the most common causes of pain after pulpitis treatment.
An incompletely sealed canal
If the canal is not completely sealed, it means that there is free space left in it or the filling material is not placed tightly, and bacteria will continue to develop in this space, even if the canal itself has been well cleaned. They'll get there anyway. The development of this process often smoothly flows into periodontitis (aka abscess).
To prevent infection from entering the space surrounding the treated tooth, it needs to be treated, and, if possible, as quickly as possible.
Otherwise, this may result in tooth loss, and then either prosthetics or empty space. The first is much more expensive and takes longer than treating pulpitis, the second is constant inconvenience and not the most aesthetic appearance.
The filling material has gone beyond the root
The situation opposite to the above is not so critical. Excess filling material is less dangerous. The tooth may hurt for a long time, although not severely.
But, in any case, before retreatment, it is better to take an x-ray. If the doctor did not go too far with the filling, the pain will go away in about a month; if there is a lot of excess material, you can do a simple operation to remove it.
A piece of the instrument remained inside
The third option, a fragment of an instrument in the root canal, is practically the same as an incompletely sealed canal, only there is also a foreign body in addition. The consequences are the same as an abscess, so the tooth must be immediately treated, foreign objects removed, the canal thoroughly cleaned and properly sealed.
Root perforation during the procedure
The most dangerous of all the undesirable consequences of pulpitis treatment is root perforation. This happens mainly when the canals are severely curved, and even if the doctor works carefully, he may accidentally damage it.
The treatment is carried out with special preparations, it can be performed from the inside of the tooth and from the outside, but in general the procedure is quite complicated.
Allergy
This complication of pulpitis treatment is easier to differentiate - an allergic reaction is often accompanied by tissue swelling. If it is a consequence of material moving outside the root canal, there may be swelling of the gums around the treated tooth. In some cases, it spreads to other areas - cheek, lip, depending on the specific tooth.
When pressure is applied, the pain becomes stronger, it is difficult to relieve with painkillers, and over time it only intensifies.
Is it painful to treat pulpitis?
Treatment of pulpitis is painless, since before drilling the dentist injects the gum with an anesthetic drug. After 2-4 minutes the pain goes away, only a sensation of touch or pressure remains.
Before injecting an anesthetic, the doctor may suggest topical anesthesia, that is, lubricate the gums with a “freezing” gel so as not to feel the insertion of the needle. Another popular service that complements anesthesia is sedation. The patient inhales special sedatives, completely relaxes and even falls asleep.
For allergy sufferers, hypoallergenic drugs are chosen; in extreme cases, the dentist may suggest treatment under anesthesia. Unlike local anesthesia and sedation, anesthesia negatively affects the cardiovascular system and the entire body as a whole.
What to do?
What to do if your tooth hurts after pulpitis treatment? The most important recommendation if you suspect a complication after treatment of pulpitis is a return visit to the doctor. If this is not possible, you should contact another specialist and explain the situation.
If it is not possible to visit the clinic immediately, you can use a painkiller - give preference to the one that you have already taken, to which there have been no negative reactions. However, it is better to try to consult with a specialist, if not in person, then by phone.
It is difficult to say exactly how quickly the pain will subside in each case. However, on average, after visiting the dentist, relief comes quite quickly:
- When removing the filling material beyond the root apex: a visit to the doctor will allow the specialist to remove excess material, and after 2-3 days the discomfort will subside.
- If the filling is insufficient: the doctor will choose a tactic for further treatment; it is quite possible that several visits will be needed to eliminate the inflammatory process - for larger cysts or granulomas, surgical treatment is also required. This complication requires refilling to prevent recurrent complications.
- If the pulp or part of it is intact: the doctor will remove the remaining pulp and repeat the manipulations that were required to treat pulpitis. The pain in this case goes away within a few days after all measures are completed.
- If an instrument breaks off: the doctor will perform an X-ray diagnostic and, if the presence of a broken instrument is confirmed, will remove it. In rare cases, resection of the root apex is performed.
- In case of perforation: the dentist will treat the canals without affecting the hole. Using modern osteoplastic materials, he will close it, which will save the tooth. If a purulent process occurs, several visits will be required to eliminate the inflammation.
- In case of gum injury: contacting a doctor will allow you to receive recommendations regarding antiseptic and healing agents for treatment at home. Relief occurs on average within 1–3 days.
- In case of an allergic reaction: it will be necessary to refill the root canals using other materials. The doctor will perform the necessary manipulations and also prescribe decongestants that will quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Pulpitis
4604 19 October
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Pulpitis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition _
The term “pulpitis” refers to the inflammatory process in the pulp of the tooth. The pulp is a complex connective tissue structure rich in nerve fibers and blood vessels. According to statistics, among dental diseases, pulpitis ranks second after caries, of which it is a complication.
Causes of pulpitis
The most common reason for the formation of pulpitis is advanced caries. As dentin is destroyed, the carious cavity increases; the pathogenic microorganisms present in it (streptococci, staphylococci, diplococci, enterococci, gram-positive rods, etc.) penetrate through the dentinal tubules into the pulp chamber and trigger the pathological process.
Another cause of pulpitis is sinusitis, periodontal disease, periodontitis of the nearest tooth, osteomyelitis, sepsis, when the infection enters the pulp in a retrograde manner with blood and lymph flow through the apical opening of the root.
It is impossible not to mention such a reason as a medical error - we are talking about an insufficiently carefully sealed tooth canal during the treatment of deep caries, as a result of which an infectious process begins to develop under the filling.
In rare cases, the inflammatory process in the pulp becomes a consequence of tooth trauma, deep cracks and chips of the enamel.
Classification of the disease
There are several classifications of pulpitis. In Russia, the classification proposed by the Moscow Medical Dental Institute (1989) is more often used.
Acute pulpitis:
- focal,
- diffuse.
Chronic pulpitis:
- fibrous,
- hypertrophic,
- gangrenous.
Exacerbation of chronic pulpitis:
- fibrous pulpitis,
- gangrenous pulpitis.
In addition, pulpitis is distinguished by the condition of the pulp:
- intact non-inflamed pulp,
- atrophic pulp,
- reversible pulpitis,
- irreversible pulpitis,
- pulp necrosis.
Symptoms of pulpitis
Acute focal pulpitis is manifested by sharp paroxysmal pain: at first it is insignificant, but as the inflammatory process progresses it becomes unbearable.
Often the pain is especially bothersome at night.
In advanced cases (with diffuse pulpitis), the pain radiates to neighboring teeth, and sometimes the patient cannot even determine exactly where it hurts. In the case of focal pulpitis, the affected tooth may react to cold and hot food, and the pain subsides for quite a long time. With diffuse pulpitis, hot food increases the pain, and cold food brings relief for a while.
Chronic fibrous pulpitis reminds itself of itself with aching pain, and there is a reaction to hot and solid foods. Upon examination, the enamel of a diseased tooth may be darker and dull compared to others.
Hypertrophic pulpitis is characterized by the presence of pain, as well as bleeding of the gums when eating solid foods. Patients complain of bad breath (halitosis), which occurs as a result of poor oral hygiene due to bleeding gums.
Gangrenous pulpitis is characterized by a change in the color of the affected tooth to gray, the presence of a putrid odor from the mouth, a reaction to hot and cold food, and aching pain. The gums near the tooth may be swollen and hyperemic, and the regional lymph nodes are enlarged.
Chronic pulpitis in the acute stage is diagnosed in cases where exacerbations take a severe form: the patient experiences very severe pain after a long period of “calm”. Thus, this form of the disease often combines the symptoms of acute and chronic pulpitis.
Diagnosis of pulpitis
Diagnostic measures begin with collecting an anamnesis, during which the doctor determines the presence or absence of complaints of unmotivated pain, pain from exposure to various irritants.
In the absence of obvious pain, it is clarified whether the patient experiences discomfort in the area of the affected tooth (tingling, feeling of heaviness, fullness).
During a visual examination, the doctor performs palpation, percussion, determines tooth mobility, examines periodontal tissue, pays attention to swelling and hyperemia of the gums, and palpates regional lymph nodes.
For accurate diagnosis, the following studies are used:
- radiography - to assess the degree of destruction of tooth tissue and the size of the carious cavity;
- thermal test - to determine the reaction of a diseased tooth to thermal stimuli;
- electroodontodiagnostics - to determine the sensitivity of the nerve when an electric current is passed through it.
Which doctors should I contact
? Dental diseases are treated by dental therapists.
Treatment of pulpitis
There are two ways to treat pulpitis: conservative and surgical.
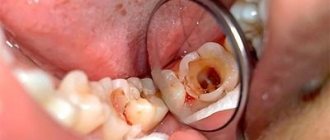
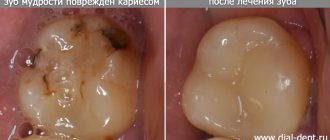
Conservative treatment is indicated in the early stages of acute pulpitis. The doctor completely cleans out the carious cavity, puts an antibiotic in it and closes it with a temporary filling. After a few days, when the medicine takes effect and the infectious process is stopped, the temporary filling is replaced with a permanent one. Conservative treatment allows you to keep the tooth alive (do not remove the nerve).
Surgical treatment (depulpation of tooth canals) is carried out in 85% of cases. The doctor cleans out the carious cavity, removes the dental nerve, fills the root canals with filling material and restores the tooth crown.
If the tooth cannot be restored, it is removed.
In case of pulpitis, all manipulations with the affected tooth are carried out under anesthesia.
Complications
In the absence of timely treatment, pulp inflammation and tooth destruction progress, as a result, surrounding tissues are involved in the process, and complications such as periodontitis, gumboil, osteomyelitis, phlegmon, abscess, and cysts develop.
In rare cases, complications can be systemic in nature - sepsis, myocarditis, brain abscess.
Prevention of pulpitis
The most reliable prevention of pulpitis is oral hygiene and timely treatment of caries.
Sources:
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocols) for the diagnosis of “dental pulp disease”. Dental Association of Russia. – 2018.
- .
- Khafizov R.G., Khafizova F.A., Azizova D.A., Shaikhutdinova D.I. Modern etiological, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of pulpitis // Uch.-method. allowance. KFU Institute of Fundamental Medicine and Biology. - Kazan. – 2015. – 74 p.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
What not to do?
If, after treatment, a tooth hurts when pressed or without mechanical action, you should under no circumstances resort to folk remedies such as heating, hot compresses, heating pads - if there is an inflammatory process, this can greatly worsen the condition. In case of allergic reactions, heat will also increase swelling.
It is also not recommended to use folk remedies for rinsing, which can cause a burn to the mucous membrane - iodine, tinctures of alcohol or vodka, liquids with the juice of “scorching” plants, etc. Even if there is no gum damage, such measures can worsen the situation.
It is also not worth taking various painkillers uncontrollably - firstly, you need to see a doctor in any case, and the effect of analgesics will not allow you to fully evaluate the clinical picture. Secondly, it can be dangerous to health.
It is important to visit a doctor at the first opportunity and perform all the necessary procedures to eliminate unpleasant consequences and improve the condition.
Why does pain occur after nerve removal?
When the procedure is performed correctly by a qualified specialist, the patient does not feel severe pain. A little discomfort and slight pain when pressing is quite normal, since there was an intervention in the structure of the tissues, part of them was removed, and the integrity of the blood vessels and nerve fibers was damaged.
But sometimes the tooth hurts after removal of the nerve for more than 2-3 days, the intensity of the pain increases. This happens for the following reasons:
- The nerve was not completely removed; part of it remained in the tooth cavity. Residual pulpitis develops, that is, repeated inflammation due to necrosis of the remnants of nervous tissue. At first, the pain is aching, but over time it becomes sharp and throbbing, as inflammation covers neighboring tissues.
- The soft tissues of the oral cavity are injured, and inflammation of the gum tissue develops.
- The pain is localized in the adjacent tooth and radiates to the treated tooth.
- Depulpation was carried out poorly. For example, the filling material is excessively extended beyond the top of the tooth or the root canal is perforated with an instrument. Sometimes a medical instrument may break, leaving a piece of it inside the canal.
If you have an allergic reaction to the components of the filling material, the pain may be accompanied by a rash and itching. If severe pain occurs when biting or pressing, this indicates trigeminal neuralgia. The rest of the time, the pain due to neuralgia is aching, and the patient experiences difficulty speaking.
Symptoms that indicate the occurrence of pathology:
- there is a constant aching pain;
- it gradually intensifies;
- the area around the tooth is red and swollen;
- there is severe pain and discomfort in the jaw and cheek;
- the pain intensifies when pressed or consumed hot or cold.
If at least one of these symptoms occurs, you should immediately consult a dentist.