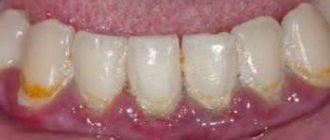
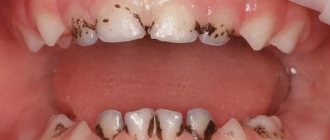
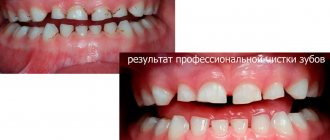
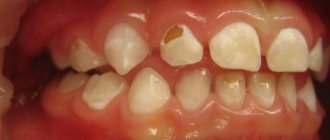
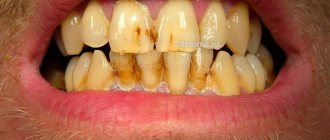
In most cases, dental plaque is the cause of insufficient oral hygiene. But it also happens that people who are very sensitive to hygiene issues develop black plaque on their teeth.
The reasons for its appearance in adults and children differ : if in the former it is a consequence of drinking large amounts of tea and coffee, as well as smoking, then in the latter it may be associated with the activity of certain bacteria, the use of mouthwashes and the use of chewable vitamins.
Types of plaque
Plaque on teeth is divided into two large groups:
- the occurrence of which is associated with external contamination of the tooth;
- appearing due to the deposition of pigments.
If oral hygiene is not maintained, plaque may appear on the teeth:
- soft microbial;
- mineralized;
- hard, often called tartar.
If everything is in order with hygiene, then black plaque is a consequence of:
- regular consumption of tea, coffee and nicotine;
- use of medications with high iron content;
- vital activity of chromogenic bacteria;
- use of certain types of rinses and antiseptics.
Bacterial plaque on teeth: causes
Soft or, as it is also called, bacterial plaque has a soft consistency, so it is easy to get rid of it with the help of an ordinary toothbrush. The main place of its accumulation is the neck of the teeth.
Harder plaque that cannot be removed with a brush is called tartar. It occurs during the mineralization of soft plaque with phosphorus and calcium salts present in saliva.
Why does plaque form?
There are constantly a huge number of bacteria in the mouth, which, firstly , multiply, and secondly , leave behind waste products. Even if you brush your teeth regularly, plaque cannot be avoided: within 6 hours after thorough brushing, you can easily notice, without resorting to the use of specialized equipment, a bacterial mass on the surface of the tooth enamel. A surge in microbial activity is observed immediately after eating: leftover food in the mouth forces bacteria to begin intensive processing.
At the same time, even small pieces of food that are invisible to the human eye are enough for microorganisms: they can feed on a film consisting of carbohydrates and proteins that invariably remains on the surface of the teeth after eating, and on food debris that gets into the spaces between the teeth. In this regard, it is imperative to brush your teeth for 15 minutes after each meal, since the mass of bacterial plaque can increase several times in volume in 1-2 hours. Plaque accumulates especially intensely on the necks of teeth in people who like to snack on a bun or something sweet between main meals.
Almost immediately after the soft plaque appears, the process of mineralization begins, as a result of which it gradually hardens. The period of primary mineralization (i.e., when the plaque, in simple terms, “sets” but still remains loose) is 10-15 hours. When the plaque finally hardens, its surface becomes ideal for the formation of deposits.
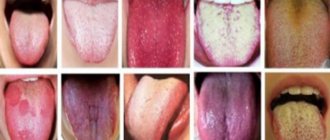
Plaque on the tongue. Causes
The tongue of a healthy person should have a pale pink color. The formation of a certain amount of light plaque on the surface of the tongue is allowed; it should be loose and the texture should be visible through it. Plaque on the tongue is thin or dense deposits, most often white or grayish in color, which completely or partially cover the surface and thereby change its color.
What it consists of:
- Saliva, epithelium, food debris.
- Bacteria and fungi that feed on the components from the first point.
- Leukocytes that eat fungi and bacteria.
Color and reasons
The causes of plaque on the tongue may vary depending on its color. We will not talk about situations where the tongue changes color due to the use of coloring products - this is not at all dangerous and quickly goes away on its own, but we will touch on different colors of plaque caused by more serious reasons.
White
White color is almost harmless. Many people experience a thin white film in the morning. It is easily removed when brushing your teeth with a toothbrush. This is quite normal - overnight in the absence of oxygen, bacteria actively multiply, which forms plaque on the teeth and mucous membranes.
Grey
Why can plaque on the tongue be gray? Usually this is the next stage of white, that is, a sign of the development of thrush, gastritis or tonsillitis. Sometimes gray deposits also appear with long-term use of antibiotics, due to disruption of the natural flora of the oral cavity.
Yellow
In this case, there are several reasons for the yellow plaque:
• ARVI. Usually accompanied by high fever and general malaise; • Problems with the digestive tract, such as gastritis or ulcers; • Long-term use of antibiotics or vitamins. No treatment is required; • Jaundice. In this case, the lower part of the tongue is affected rather than the upper part, and it is not easy to detect.
Green
This is a very rare phenomenon and occurs due to exposure to certain types of fungi. Sometimes the cause may be excessive load on the liver, that is, eating large amounts of fatty and fried foods. In very rare cases, green deposits are caused by antibiotics.
Brown
There may be several reasons for a brown coating on the tongue:
- Improper functioning of the gallbladder, formation of stones in it;
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. Accompanied by sharp pain and diarrhea;
- Alcoholism;
- Liver diseases;
- Regular consumption of dark drinks, especially coffee and strong tea. The teeth also suffer and become yellowish or brown.
Blue
Why is the coating on the tongue such an unusual color, like blue? A sign of anemia, a lack of vitamin B12, iron and folic acid in the body. Sometimes the tongue turns blue in people who smoke for a very long time.
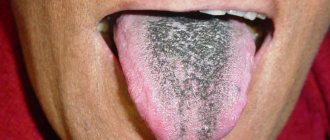
Black
If the tongue is not gray, but rather black, this is a very bad sign. Most often, he talks about serious disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. Spots and cracks indicate stagnation of bile, that is, problems with the pancreas and liver. At the same time, there is always a bitter taste in the mouth. If the organ is covered with black dots, this is a signal of lead poisoning. If both the mucous membrane and tooth enamel darken, this indicates the proliferation of a chromogenic fungus in the oral cavity.
In conclusion, I would like to advise you to get into the good habit of inspecting your tongue every morning during hygiene procedures. If something seems doubtful to you, consult a doctor for advice. Be attentive to your health!
Using materials from https://topdent.ru/articles/nalet-na-yazyke.html https://netnaleta.ru/u-vzroslyh/o-chem-govorit-nalet-na-yazyke-u-vzroslogo/ https: //yandex.ru/turbo/anzub.ru/s/novosti/nalet-na-yazyke-norma-ili-otklonenie/?utm_source=turbo_turbo https://stom.32top.ru/stat/782/
Pigmented dark plaque on teeth
The main reason for the appearance of such plaque in adults is smoking, drinking coffee and tea. Maintaining hygiene guarantees the absence of bacterial plaque and tartar, but if you neglect it, black plaque will not take long to appear. Pigments adhere very well to enamel covered with bacterial plaque formed as a result of infrequent brushing of teeth.
Types of pigment plaque include:
- brown coating that occurs from regular consumption of tea and coffee in large quantities;
- accumulation of nicotine deposits;
- darkening of the enamel as a result of taking medications containing iron;
- proliferation of bacteria that form dyes (they are called chromogenic);
- change in enamel color after using antibiotics;
- blackening due to diseases of internal organs.
If plaque is caused by bacterial factors, then regular thorough brushing of teeth, the use of rinses and floss reduce the likelihood of its occurrence to a minimum. However, if the reason for the appearance of plaque lies in the influence of dyes, maintaining hygiene to prevent it will not help.
Black plaque on children's teeth , the causes of which are associated with the activity of chromogenic anaerobic bacteria, appears in the form of spots localized in the neck area. Actinomycete bacteria produce hydrogen sulfite, which reacts with iron (found in saliva and red blood cells). As a result, a form of black iron that cannot be cleaned off with a regular brush is deposited on the surface of the teeth. Chromogenic coloration can also be orange, green and brown.
Black plaque on a child’s teeth can also form for other reasons . It appears due to:
- the use of antiseptics that contain chlorhexidine, benzaclonium chloride, as well as essential oils (the latter are found in the popular Listerine product);
- consumption of foods rich in iron, as well as vitamins with a high content of iron.
Medical Internet conferences
The influence of chlorhexidine on the microbial composition of the bottom of a prepared carious cavity
Tverskova V.Yu.
Scientific supervisor: candidate of medical sciences, assistant Kazakova L.N.
GBOU VPO Saratov State Medical University named after. IN AND. Razumovsky Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation
Department of Pediatric Dentistry and Orthodontics
Relevance of the problem. Among oral diseases, caries ranks first in prevalence. Currently, caries is diagnosed in children under 2 years of age in 36% of cases, and in 3-year-old children in 53% of cases[1]. The incidence of deep caries in children is 23% of the total number of caries diseases. According to many authors, caries can be classified as an infectious disease [2], the leading factor in which is Streptococcus mutans. Str. mutans attaches to the smooth surfaces of teeth, participates in the formation of dental plaque, and this action is mediated by the synthesis of glucose polymers from sucrose present in food. Glucan formation causes intercellular aggregation of Str. mutans and other bacteria present in the plaque. The sticky glucan matrix of dental plaque prevents the diffusion of large amounts of acid produced by microorganisms, which prolongs its residence on the surface of the teeth and leads to demineralization of the enamel, causing dental caries. The emerging focus of demineralization of the surface layer of enamel is the “entry gate” for further infection of deeper located hard tissues and dental pulp, this is especially true immediately after eruption, at the first stage of secondary mineralization. The special structure of hard tissues, characterized by less mineralization at this stage of tooth development, creates a number of difficulties in the treatment of acute deep caries with a favorable outcome. Since it is impossible to create conditions close to sterile at the border with the pulp using standard irrigation of the prepared cavity.
Goals and objectives of the study. The purpose of our work was to study the effect of chlorhexidine bigluconate, used in different forms, on the qualitative microbial composition of the prepared carious cavity in acute deep caries.
Materials and methods of research. During the study, a group of children (20 people) was identified with a diagnosis of acute deep caries of permanent teeth at the stage of ascending development. To determine the microbiocinosis of the bottom of the carious cavity, a bacteriological study was carried out.
Acute deep caries was treated conservatively only in children with a good level of oral hygiene and with a compensated form of caries in two visits.
On the first visit, rational anesthesia was carried out, the carious cavity was prepared under a bath of the same antiseptic, this was done carefully, but with extreme caution. After the final preparation of the carious cavity with a sterile bur, a section of dentin was taken from the bottom and a bacteriological examination was carried out. Then the children were blindly divided into 2 groups of 10 people. In the first group of patients, a tampon moistened with 0.05% chlorhexidine was placed on the bottom of the carious cavity under a temporary dressing. In the second group, a “patch” of self-adhesive film “Diplen Denta” containing chlorhexidine bigluconate 0.01-0.03 mg/cm² was applied to the bottom of the carious cavity under a temporary dressing. Further research was carried out after 48 hours.
On the second visit, having previously isolated the tooth from saliva, a temporary bandage and a tampon with an antiseptic were removed in the first group; in the second group, the self-adhesive film dissolved on its own, and in both cases, a sterile spherical bur without pressure was taken from the bottom of the cavity for bacteriological examination. In patients, a calcium-containing preparation was applied to the bottom of the carious cavity, and the cavity was filled with permanent filling material “Vitremer”.
Further bacteriological examination was carried out in accordance with generally accepted rules of clinical microbiology.
Results. Microbiological examination of the bottom of the carious cavity in patients after complete preparation of the carious cavity revealed a significant degree of its contamination with pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microflora. Streptococci, enterococci and yeast of the genus Candida were sown (Table No. 1). In the group of patients, when using 0.05% chlorhexidine during re-seeding from the bottom of the carious cavity, a decrease in the number of streptococci was observed, the effect of 0.05% chlorhexidine on enterococci was insignificant, the growth of yeast of the genus Candida was not detected (Table No. 1).
When using the film "Diplen Dent" a significant decrease in the colonization of cariogenic species Str. mutans, Str. Sanguis, Str. salivarius. The number of representatives of the resident group of bacteria - enterococci - decreased (Table No. 1).
We associate the higher efficiency of the Diplen Denta film containing chlorhexidine bigluconate in a concentration of 0.01-0.03 mg/cm² with its ability to adhere tightly to the bottom of the cavity, which ensures deeper penetration of the active component through weakly mineralized dentin and dentinal tubules.
Conclusions. Thus, the results of the study confirm that the application of chlorhexidine digluconate in the form of a film for 48 hours, as an intermediate stage in the treatment of acute deep caries in children, leads to a significant decrease in the level of streptococci, enterococci and yeast of the genus Candida in the peripulpal area.
How to remove plaque from teeth on your own
Many people do not like to visit the dentist again, especially when it comes to removing plaque, which does not cause much inconvenience. The reasons for this are clear: lack of free time and reluctance to pay for the procedure.
You can try to remove plaque from your teeth at home, but this will only work if there are no subgingival deposits and the plaque layer is thin.
The first method involves using a special toothpaste to remove plaque with abrasive substances. The label of such pastes must indicate the RDA indicator, indicating the degree of abrasiveness. In pastes that eliminate plaque, its value should exceed 100. But such pastes cannot be used on an ongoing basis. If the paste contains pyrophosphates, then it can help get rid of tartar, since they have the ability to dissolve its matrix.
The most effective of these pastes are:
- President White Plus. The abrasiveness index is 200 units; in addition, the composition contains silicon dioxide, which has abrasive and polishing properties. You should not use the paste more than once a week.
- Lacalut White. According to the abrasiveness index (RDA=120), it is more gentle than the previous sample. The composition contains pyrophosphates, which make the plaque loose.
The second method is to use a special toothbrush, which allows you to remove plaque yourself. Recommended use:
How to rinse your mouth?
To rinse the mouth, only an aqueous solution is used - this point should be taken into account when purchasing the drug at the pharmacy. The concentration of the drug is 0.05%. Some, trying to achieve the maximum therapeutic effect, begin to rinse their mouth too often - up to 6-10 times a day. This approach is completely unjustified and can harm a person, since rinsing too often can cause irritation of the mucous membranes and dislodge the blood clot, which protects the exposed bone from the penetration of microbes.
"Chlorhexidine" in the form of a solution
To ensure therapeutic and prophylactic results, it is enough to perform the procedure 2 times a day after morning and evening brushing of teeth. If your gums are prone to bleeding, you can add one more rinse, but the total number of procedures per day should not exceed three.
Video: How to rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine
How to rinse your mouth correctly
Mouth rinsing with Chlorhexidine is carried out according to the following scheme:
- brush your teeth;
- after an hour, rinse your mouth and throat with boiled water at room temperature to remove dirt and food debris;
- take a small amount of the drug into your mouth and hold for 2-3 minutes;
- Carefully spit out the product, avoiding swallowing.
The duration of treatment is from 7 to 12 days.
You just need to keep the product in your mouth
Important! "Chlorhexidine" after tooth extraction can only be used for oral baths. The product must be kept in the mouth, it is allowed to tilt the head slightly to the sides, but you cannot move the cheeks and tongue, as this creates a vacuum in the mouth and can lead to the loss of a blood clot.
Plaque on a child’s teeth: treatment
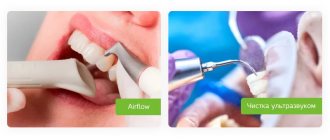
Removing bacterial and chromogenic plaque in a child will be no different from a similar procedure recommended for an adult: ultrasonic cleaning and AirFlow are used in the same way.
However, chromogenic staining of teeth may return over time. The only possible solution to the problem is regular professional cleaning by a dentist. To make visits to the dentist as rare as possible, your child should be taught to use an electric toothbrush, the pulsating circular movements of the head of which perfectly break up plaque.
Accelerated formation of deposits is promoted by blood in the oral cavity, so the child’s gingivitis must be treated. The use of chlorhexidine and antiseptics based on it should be abandoned.