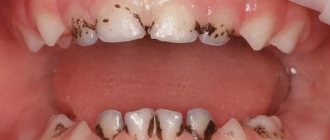
The problem occurs several weeks before the eruption of a baby or permanent tooth. The appearance of a cyst is indicated by a bluish-purple spot (hematoma). This is due to difficulty in tooth eruption.
An eruption cyst is a type of soft tissue benign tumor that appears when a tooth has already begun to erupt through the gum. Scientists and doctors have not agreed on why it occurs. The most likely causes: infection, trauma, improper development of teeth, which causes a lack of space for the “newbie”. In addition, it may be a consequence of caries and improper care.
Eruption cysts occur during the growth of baby teeth or, more often, at 6–9 years of age, when permanent teeth emerge. The fact is that, due to its anatomical structure and location, the chewing group of teeth is the most difficult to erupt.
If you notice a large formation in your baby’s mouth, in the place where a tooth should appear, consult a doctor. Do not resort to self-medication under any circumstances. Infusions, rinses and even strong antibiotics most likely will not help, but ruining a child’s health in this way will cause serious harm.
If you contact a specialist, treatment can follow one of two scenarios. In the most favorable option, the doctor will advise giving the child toys, special teethers, crackers - everything that the baby can chew. This will help break through the mucous membrane.
In difficult situations, surgery may be necessary. Then the surgeon will cut the gum under local anesthesia. This will make teething easier.
It is forbidden to try to cut or tear the mucous membrane on your own; you can cause a serious infection or injure your baby.
Causes of Teething Cysts in Children
During teething, a hematoma is formed; it occurs due to the fact that the tooth cannot break through the mucous membrane and thereby injures the gums and ruptures blood vessels. The longer the formation is in the oral cavity, the larger its size; in addition, the amount of swelling will depend on the group affiliation of the tooth.
The main causes of the tumor:
- pulpitis;
- caries;
- periodontitis;
- improper tooth treatment or lack thereof;
- eruption injuries.
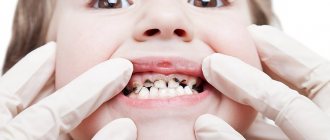
The baby’s body tries to limit the source of infection, which is why a dense protective capsule is formed, which eventually develops into a cyst. The occurrence of such formations is quite common. An infection caused by carelessness, an unsuccessful attempt to chew hard food, a fall that led to a tooth injury - all this can serve as a starting point for gum inflammation and further development of a cyst.
Another fairly common mistake parents make, which can lead to the appearance of a tumor during teething, is negligence in caring for baby teeth.
It is generally believed that you should take serious care of your dental health after changing them. Since there is no point in treating non-permanent baby teeth - they will soon fall out. In fact, not taking things seriously leads to many problems. Any gum diseases and oral infections should be eliminated in a timely manner, regardless of how many teeth the baby has and whether they are permanent or not.
Hematoma during the eruption of primary teeth, normal or pathological?
Teething is a physiological process, which, however, can cause a lot of trouble for the baby and sleepless nights for parents.
For some lucky people, teeth pop up like mushrooms after rain, quickly and imperceptibly; to the delight of mom and dad, grandparents. Just a couple of days and your baby is smiling happily, proudly showing off his new tooth! But more often than not, the eruption of a baby tooth causes discomfort for the baby and anxiety for parents. Suddenly, the smiling baby begins to act up for no apparent reason, and may even develop a fever. Temperatures can vary from 37 to 38 degrees and above. The parents' concern is understandable; what if the little one gets sick? It is natural to want to help a child and alleviate suffering. What to do in such a situation?
Our recommendations.
- Examine the child's oral cavity. You may immediately see an area of swollen gum mucosa or an already erupting tooth.
- Assess your baby's salivation. The already increased salivation in a 1-2 year old child at the time of the eruption of a new tooth intensifies even more. Transparent nozzles may appear. If drool flows like a river, then this is another confirmation that the cause of the whims lies in the new tooth!
- The absence of ARVI symptoms, improvement in the child’s condition and mood after taking an anesthetic also confirms that the “culprit” of the trouble is a new tooth.
- What is the best way to help your baby survive this stage? Firstly, these are special gels and teethers. You shouldn’t get carried away with gels; they don’t have the most beneficial composition for a developing body. The gel alleviates the condition for a very short period of time, thanks to a component that has a local anesthetic effect. Secondly, painkillers and antipyretics (for example, Nurofen (suppositories or syrup), again if necessary, no more than once every 6-8 hours. Do not forget that children tolerate fever much easier than adults.
The most important thing in alleviating the symptoms of teething is the patience and care of the family around the baby, the ability to distract and entertain the child.
Even a eruption hematoma (as in the photo),
There is no reason to panic and visit the dentist in person, especially now, during the COVID-19 pandemic.
All you have to do is take a photo and send it to us by email. We will remotely provide individual recommendations and reassure parents. According to observational statistics, only 0.05% of cases require dental intervention. The hematoma does not need to be smeared with anything (it will not help), or opened (at home there is a risk of infection, in the office it is at least useless). Just calm down and be patient, as soon as the tooth erupts, the hematoma will go away (like an ordinary bruise). May 21, 2022
Complications with cyst growth
Tooth trauma, advanced caries, nasopharyngeal or periodontal disease, dental malformations - one or more of these factors can lead to the development of a cyst. The danger is that the cyst grows unnoticed. It usually does not hurt and at the initial stage does not cause discomfort or reaction of the lymph nodes. With further development, suppuration and various unpleasant sensations may appear. But even if there is no pus, the cyst is very dangerous. Therefore, do not delay treatment.
A cyst can lead to intoxication of the body due to the fact that waste products of harmful microorganisms enter the blood. The consequence of this can be headaches, high fever and, in the worst case, sepsis.
In addition, complications are caused by local problems - phlegmon, abscesses, osteomyelitis. These complications are inflammatory in nature and often occur when the cyst suppurates. The spread of pus can lead to destruction of the jaw bones, damage to the internal organs of the digestive system, liver, and heart.
It is impossible to avoid the appearance of a cyst, but if you properly care for baby and permanent teeth and treat infections in a timely manner, you can reduce the likelihood of its occurrence. In addition, periodic visits to the dentist will allow you to notice the problem at an early stage, when treatment will be as simple and easy as possible for the body.
Main reasons
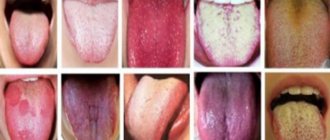
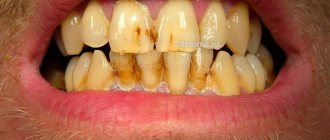
Why can one or more teeth turn blue? There may be several reasons for this; sometimes there is nothing dangerous to health in this process, and sometimes this is a reason to urgently seek advice from a dentist. A change in shade is possible due to poor quality nutrition or adherence to a strict diet. This can also happen if you eat a lot of fresh berries, such as blueberries, blueberries or blackberries.
Newly installed fillings may differ in color from natural tissues. A pulpless, that is, dead tooth can also change its color. This is explained by the fact that when the pulp is removed, nutrients stop flowing to the tissues.
If a seemingly healthy tooth begins to turn blue, this may indicate that there are problems with the root system. This is usually preceded by serious dental diseases. In addition, the cause of blue enamel may lie in the patient’s body; this phenomenon may be caused by the presence of chronic diseases or problems with the digestive system. Another common reason is the use of low-quality water with high levels of iron.
Cyst treatment
A dental cyst is treated either with therapeutic methods or with surgical intervention. The first ones are used in simple cases.
Surgery involves two types of operations - cystotomy and cystectomy. In both cases, local anesthesia is used. With cystomy, only the anterior wall of the cyst is removed. This is a less traumatic option, as it allows you to preserve the rudiments of permanent teeth during surgery on milk teeth.
Cystectomy is performed if the size of the cyst does not exceed 1.5 cm. This operation is more difficult, but postoperative recovery is much faster.
No matter how small and insignificant the swelling may seem to you, contact your dentist. This will avoid complications. And the problem will be resolved more easily and in a short time. Remember that no rinses, infusions or other folk remedies can guarantee recovery.
Treatment of blue teeth
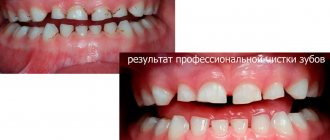
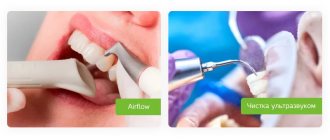
If during diagnostics it is determined that the cause of blueness of all teeth is the use of special products, the dentist or hygienist may prescribe a professional cleaning of the oral cavity. Quite often the patient requires enamel polishing; this allows for the best results.
If after such manipulations the blue discoloration does not disappear, you can try other methods.
First of all, the doctor should send the person for an X-ray examination of the jaw, this will make it possible to make a correct diagnosis, as a result of which the treatment will be as effective as possible. It may also be necessary to remove previously installed fillings and caries-infected hard tissues. If necessary, treatment of the annals and root system of the tooth will be prescribed.
There are several methods to restore the original whiteness of your teeth. One of the most common options is the installation of a composite filling, that is, direct artistic restoration of a row. A more expensive procedure is the production of an artificial crown or special onlays - veneers (indirect restoration).
How to avoid complications
To avoid missing a cyst in the early stages, check with your dentist at least once every six months, especially if your child has chronic pulpitis or periodontitis. The occurrence of cysts is most likely between the ages of 6 and 12 years, especially during the formation of the first molars in the lower jaw.
Teach your child proper and regular oral hygiene. This will reduce the likelihood of inflammation and caries in both milk and permanent teeth. For this, use high-quality children's toothpaste for a specific age. Asepta has developed Baby, Kids and Teens pastes that take into account the dental needs of children of different ages. For the little ones, specialized Asepta wet wipes designed in the form of finger pads are suitable - wipe the gums after each feeding.
It is necessary to treat infections and caries in a timely manner so that they do not lead to the formation of a cyst in the future.
Do baby teeth all change?
The child has 20 baby teeth. In an adult, the number of teeth can range from 28 to 32. Which baby teeth fall out? Everything! Normally, by the age of 14 they should change to permanent ones. Some teeth initially emerge as permanent teeth.
The order of loss corresponds to the order of appearance of baby teeth - the incisors change first, then the first and second premolars, and the canines change last.
The first molars grow permanently before the teeth change. Second molars appear in empty spaces created by jaw growth. Third molars (wisdom teeth) have lost their functionality and in many people do not grow back at all.
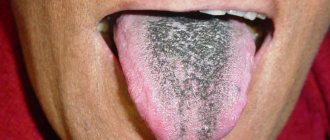
Causes of blue gums in adults
The reasons may be different, the most common include:
- problems with the cardiovascular system;
- thyroid diseases;
- kidney pathologies;
- stomatitis;
- inflammatory periodontal diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis or periodontal disease;
- caries and its complications;
- improper orthodontic treatment;
- incorrectly selected or incorrectly manufactured orthopedic design.
- a consequence of surgical intervention (blue discoloration of the periodontium can occur after tooth extraction);
- chemical (exposure to the mucous membrane of an aggressive substance used in the treatment of root canals) or thermal burn (exposure to high temperatures on the gums).
Associated symptoms
Gums can turn blue not only in the youngest patients, but also in adults. As a rule, this pathology is accompanied by many other symptoms. Most often, a person experiences noticeable pain, especially with accidental contact with tissue or with solid food, and the gums may swell and bleed.
If the cause of darkening or the appearance of age spots lies in the inflammatory process, the following symptoms can be diagnosed: severe fever and chills, itching and burning, the appearance of blood or purulent discharge, and others. In this case, immediate treatment is required in a dental clinic; traditional methods will not be effective.
If the cause of darkening of the gum or tooth is the incorrect installation of a prosthesis or crown, the patient may complain of pain even at rest, as well as slight tingling and numbness of the tissue (a sensation similar to what happens after the end of anesthesia).
previous post
How is a general examination at the dentist performed?
next entry