Beautiful snow-white teeth are an important component of the image of a successful person. But for a number of reasons, the enamel becomes covered with an unaesthetic coating. This problem cannot be ignored, since soft plaque mineralizes and turns into tartar. It cannot be removed during normal oral hygiene. Deposits can only be removed by contacting the dentist.
If black plaque is not professionally removed , the patient will experience bad breath, darkening of the enamel, inflammation of the gums and the development of caries. As a result, he will have to treat the consequences that have arisen.
The process of formation of dark plaque on teeth -
As we said above, dark plaque on teeth is formed due to various pigments that are deposited on the surface of the teeth. But to be completely precise, it is thanks to chromophores (these are compounds in pigments that determine their color). Chromophores can be of organic and inorganic origin. For example, organic chromophores include the so-called polyphenolic compounds, which include “tannins”, “furfural”, etc. These compounds can be found in coffee, tea, wine and fruits.
Tobacco smoke (polyphenols, etc.) also contains a large number of dark-colored pigments of organic origin. As for inorganic chromophores, these include metal ions - primarily Fe 2+ and Fe 3+ (divalent and trivalent iron), Cu 2+ (divalent copper), as well as Mn 2+ (divalent iron). valence manganese). And I think - everyone now understands that the formation of pigmented plaque on teeth occurs due to the deposition of organic and inorganic chromophores on the surface of the teeth. A particularly interesting process will be the deposition of metal salts on the teeth of children and adults, which we will discuss in detail below.
Important: dark plaque on teeth forms much more slowly if the surface of the teeth is clean and does not have a layer of soft microbial plaque or hard tartar. But, if there is soft microbial plaque on the teeth that has not been properly removed (during oral hygiene), or there is already a tightly attached layer of partially mineralized plaque, then in this case the pigments are integrated into their structure much faster.
Those. to the bacterial film on the surface of the teeth, as well as to a rough surface (for example, fillings) - pigments will “stick” much faster than to a completely clean tooth surface. The same applies to tartar, which is dental plaque mineralized by calcium salts contained in saliva (primarily calcium phosphate). And chromophores, i.e. pigments - they can integrate perfectly even into the crystal lattice of calcium phosphate, which, together with bacteria, makes up tartar.
How is tartar formed?
The plaque accumulated on the teeth from food debris and bacteria that process them turns into tartar. In addition, plaque contains waste products from microorganisms, which bind the substance into a dense mass. If such deposits are not removed, they gradually become saturated with minerals and harden. The formed stone contains 70–90% mineral components, while the number of living microorganisms in it is significantly lower than in soft plaque. There are three stages of mineralization:
- up to 60 days: accumulation of minerals and nucleation of crystals;
- 60–700 days: growth and improvement of crystals;
- over 700 days: crystal saturation.
At the first stage, we are talking about soft dental plaque, then about tartar [1, 2].
Dark plaque on teeth from smoking, tea and coffee -
Yellow or brown plaque on teeth can most often be found in patients who smoke or drink strong coffee or tea. Below we will once again present 2 photographs in which we ask you to pay attention to the following. Both patients have plaque on their teeth (especially a lot of soft microbial plaque). We have already said above that pigments hardly adhere to clean tooth enamel, but very quickly attach to the layer of microbial plaque.
Pigment + bacterial plaque –
But if with stains from tea and coffee everything is quite simple, and they can be attributed simply to superficial pollution, then with smoking things are more complicated. On the one hand, some of the pigments contained in tobacco tar will indeed remain only on the surface of the tooth enamel, and in the future this pigment plaque can be removed without problems. But on the other hand, experienced smokers may experience a change in the physiological color of the enamel and even dentin, which is associated with prolonged penetration of the resin into the depths of the hard tissues of the tooth (this occurs through many micro-cracks on the surface of the enamel). And such pigmentation cannot be changed by professional teeth cleaning, and chemical whitening will be required.
But yellow plaque on teeth can form not only among lovers of tobacco, strong tea or coffee. Pay attention to the photo of the lower teeth below. This patient does not smoke, does not abuse coffee or tea, but in this patient, in the area of the necks of the teeth, a layer of partially mineralized dental plaque is clearly visible, which is already tightly attached to the tooth enamel and can no longer be cleaned off with a regular toothbrush. Those. The problem here, again, is not related to excessive consumption of coffee or tea, but, first of all, to insufficient oral hygiene. As a result of this, the completely soft microbial plaque that has not been removed begins to mineralize and at the same time turns a little yellow.
Partially mineralized dental plaque –
Important: drinks and food products that contain a large amount of pigments - dark-colored carbonated drinks, beets, wine, tea or coffee, spices, berries and some fruits (24stoma.ru). If the tooth enamel is not covered with a layer of microbial plaque, then such products can only temporarily change the color of the tooth enamel (for example, many people notice that immediately after drinking wine their teeth turn blue for a short time). But in the presence of dental plaque, pigments penetrate into the structure of the latter, remaining in it for a long time.
Other causes of darkening of teeth -
Some ingredients in oral care products can stain your teeth. First of all, we are talking about such a common antiseptic as chlorhexidine, which is included in many toothpastes and mouth rinses. The same effect can be caused by the antiseptic benzalkonium chloride, which can be included not only in some mouth rinses, but also in some dental gels (an example is Kamistad gel).
Long-term use of rinses and toothpastes containing essential oils can also lead to darkening of your teeth, because the latter are also polyphenolic compounds (eg Listerine mouthwash). But here it should be noted that black plaque on teeth as a result of the use of antiseptics and essential oils does not appear in all patients. The fact is that darkening occurs only on those surfaces of the teeth on which there is a layer of microbial plaque. And it is possible that while this coating was light, you simply did not notice it. But in any case, such darkening will be reversible.
Dark plaque after using chlorhexidine -
Another common ingredient in hygiene products that can lead to darkening of teeth is stannous fluoride (SnF2), which is included in some toothpastes as an anti-caries component. There is a scientific paper about this at the link above. The fact is that pigments (chromophores) can also be formed by chemical processes of initially colorless compounds. In addition, stannous fluoride can react with volatile sulfur compounds produced by oral bacteria to form tin sulfide (SnS2). This can cause plaque-covered tooth surfaces or demineralized areas of enamel to turn yellowish.
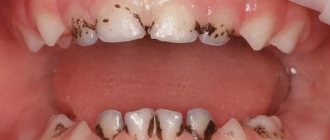
But! Dark plaque on teeth can occur even with good oral hygiene, and even if you do not smoke or drink strong tea or coffee. This formation mechanism is associated with the vital activity of chromogenic bacteria in the oral cavity, which primarily includes actinomycetes. Most often, the formation of such plaque occurs in children, but adults are no exception (see photo below).
Black plaque produced by chromogenic bacteria -
Black plaque on a child’s teeth –
As we said above, the mechanism of deposition of insoluble metal salts on teeth will work not only in children, but also in some adults. The fact is that in the oral cavity there are bacteria called actinomycetes. They are anaerobic bacteria and are often called chromogenic bacteria. It is these bacteria that are responsible for the appearance of black or tightly attached plaque, located circularly in the area of the necks of the teeth (Fig. 10-12). Sometimes such plaque may have a brown or greenish tint.
Black plaque in a child -
According to various statistics, the formation of dark plaque occurs in 1 to 20% of all children, and the process itself occurs as follows... Actinomycetes, in the course of their life activity, release hydrogen sulfite, which enters into a chemical reaction with iron compounds contained in saliva. As a result, an insoluble form of iron is formed (with impurities of calcium and phosphorus), which is deposited on the teeth in the form of a black plaque. Moreover, this happens even in patients with high-quality regular oral hygiene.
Scientific studies have shown that the deposition of black plaque in the form of insoluble iron salts is associated with 2 main factors. Firstly, we are talking about the species composition of the microflora of the oral cavity, i.e. The higher the content of actinomycetes in the oral cavity, the higher the risk of black plaque formation. Thus, one of the scientific studies showed that in children aged 6-12 years with black spots, actinomycetes were sown in 70% of cases, and in children without black spots - only in 20% of cases. And this shows an obvious dependence.
In addition to actinomycetes, bacteria of the genus Prevotella, for example, P.gingivalis and P.intermedia, can also lead to the deposition of insoluble iron salts. But they show such activity only if a child or adult has concomitant gum inflammation, manifested by bleeding. Those. These bacteria extract iron from red blood cells that enter the mouth during gum disease, turning it into black plaque. Thus, the presence of gingivitis in the patient is another risk factor.
The connection between black plaque and drinking water –
Scientific studies show that drinking unfiltered tap water, as well as water purified by osmosis, increases the risk of deposition of insoluble iron salts in the form of black plaque by 13 times (you can read the clinical study at this link). How to remove such plaque - read at the very end of the article.
Laser cleaning
This is an innovative, gentle and painless method of cleaning teeth from plaque of any color (black, yellow, etc.). During the procedure, the enamel is not damaged, and there is virtually no gum bleeding. Although this method of dealing with deposits is expensive, the investment is completely justified.
Benefits of laser teeth cleaning:
- removal of plaque and tartar, regardless of location;
- low level of pain, and therefore local anesthesia is not required;
- the ability to regulate the intensity of the impact;
- absence of noise and vibration, which is important for patients with dental phobia;
- non-contact - the device does not come into contact with tissues;
- safety of the procedure - the formation of enamel microcracks is excluded;
- no gum bleeding - even if tissue is damaged, the blood immediately coagulates under the influence of the laser;
- minimal risk of complications - the beam has a disinfecting effect, so during the procedure all pathogenic microorganisms are killed;
- rapid tissue restoration - due to stimulation of trophism and reparative processes;
- lightening the enamel by 1-3 tones;
- long-term effect - no plaque on the teeth for a year, provided proper care of the teeth and the oral cavity.
Laser deposit removal can only be performed by adults (over 18 years of age). It is not given to pregnant and lactating women if the patient has inflammation of the oral mucosa, severe heart pathologies or infectious diseases. Also contraindications are AIDS, HIV, bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis.
How to remove black plaque on teeth -
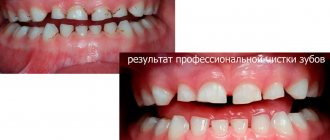
If you only have a not too pronounced dark plaque on your teeth (in the absence of tartar or a thick layer of pigmented plaque), its amount can be reduced using an Oral-b electric brush and a special toothpaste with increased abrasiveness. We'll cover this method below, but keep in mind that this will only work on a thin layer of plaque.
How to remove plaque on teeth if a thick layer of plaque has formed or there is already tartar - in this case, you should immediately contact your dentist for professional teeth cleaning. Professional cleaning will completely remove all external contaminants from your teeth, but if you are an experienced smoker and pigmentation of the hard tooth tissues themselves (enamel and dentin) has already occurred, then chemical bleaching may also be required.
Dentists' advice on oral hygiene at home
Doctors remind that the process of plaque formation does not stop for a minute, so home care and some nutritional rules are mandatory.
Experts recommend quitting smoking and reducing consumption of foods and drinks containing large amounts of food coloring. It is also necessary to increase the amount of solid food in the diet and promptly treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Recommendations for hygienic care:
- Teeth should be brushed at least twice a day;
- After eating or drinking, you should rinse your mouth;
- For effective cleansing, you need to use not only a toothbrush and toothpaste, but also floss and an irrigator.
Note: doctors say a firm “No” to the use of hydrogen peroxide and soda. This can cause burns to the mucous membrane and accelerated abrasion of the enamel.
The dental network offers services for diagnosing and removing plaque on teeth. Our specialists are highly qualified and regularly improve their skills in leading clinics in Russia and Europe. We have a system of family and cumulative discounts.
You can contact any of the branches of our center in Moscow, located within walking distance from metro stations:
- Art. Alekseevskaya (VDNKh district, etc. Mira), address: st. 3rd Mytishchiskaya house 3, building 2;
- Art. Shelepikha, address: Shelepikhinskaya embankment, address: building 34, building 1.
Entrust the health of your teeth to professionals; we will be able to reliably protect you from dental and periodontal diseases. Remember that prevention is the best defense! We are waiting for you every day, seven days a week.
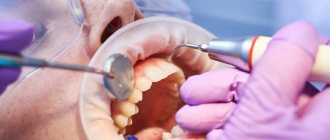
Removing dental plaque at the dentist -
Depending on the amount of plaque and tartar, as well as the equipment of the dental office, the dentist can use the following methods or a combination of them:
- ultrasonic cleaning + conventional mechanical polishing (carried out using a polishing brush and paste),
- ultrasonic cleaning + Air-Flow,
- Air-Flow only.
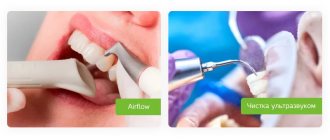
a) Cleaning dental plaque using Air Flow –
The Air-Flow method is something like sandblasting. From a special tip under high pressure, a water-air mixture with particles of an abrasive-polishing substance is supplied to the tooth surface. This method works great if your layer of pigmented plaque is not too thick and there are no massive hard dental deposits. But if they do exist, then the dentist will first remove the massive deposits with ultrasound and, using Air-flow, polish your teeth, removing all the smallest irregularities and plaque residues.
How to get rid of plaque using Air-flow –
b) Removal of dental plaque using ultrasound –
Ultrasound cleaning of plaque is the most common and most versatile method. Its advantage is that with the help of ultrasonic cleaning devices (scalers) you can remove pigmented plaque of any severity, as well as the most massive hard dental deposits. The cost of the procedure averages from 150 to 200 rubles per 1 tooth, but there are clinics where this service can cost even 400-500 rubles (per 1 tooth).
A nozzle is inserted into the tip of the ultrasonic scaler, the tip of which oscillates at ultrasonic frequency during the procedure, and during the oscillation process water is supplied generously to the tip of the nozzle. As a result of mechanical contact of the nozzle with dental plaque, the attachment of the latter to the tooth is destroyed. The cavitation mechanism also works in parallel. It lies in the fact that the propagation of ultrasonic waves in an aqueous environment leads to the formation of many air bubbles, which burst with the occurrence of hydrodynamic impacts (this leads to cleansing of the tooth surface).
Removing plaque using ultrasound (video) –
After ultrasonic cleaning, tiny particles of plaque (irregularities) always remain on the surface, which must be removed. This can be done either using Air-flow, or using traditional teeth polishing using a rotating polishing brush with bristles and a special polishing paste. If polishing is not done, the tooth surface will remain rough, which will lead to the rapid adhesion of new portions of microbial and pigmented plaque to the teeth.
What to do?
Many people want to clean their teeth from plaque at home. To do this, they use special bleaching pastes, soda, activated carbon, 3% hydrogen peroxide solution, and lemon juice. Sometimes, with slight darkening of the enamel, these methods give the desired effect.
But if you abuse such bleaching, as well as in case of increased sensitivity of the enamel, you can only harm yourself. Therefore, if you want to return your teeth to a snow-white shade, you need to start with a visit to a specialist. The dentist will assess the condition of the enamel, identify diseases of the oral cavity (if any) and recommend the best option for cleaning teeth from plaque.
In a clinical setting, there are several ways to get rid of deposits. Let's consider them in as much detail as possible. This will allow you to go for a consultation with a “theoretical savvy” specialist.
How to remove plaque from teeth at home -
You can remove plaque from your teeth at home using a combination: an Oral-b electric brush + a special teeth polisher.
As the latter, you can use, for example, PRESIDENT White Plus toothpaste, which has an abrasiveness of RDA 200. But the best option is to buy a special dental polishing paste that the dentist uses. The best option for such polishing pastes is Detartrine or Detartrine Z (the latter is better, but more expensive). Oral-b toothbrush and Detartrine series toothpastes:
You can use the Oral-b electric toothbrush every day, and in fact, these brushes are made exactly like a dentist's tool for polishing teeth from plaque. But the special tooth polishing pastes mentioned above are not intended for daily use, but only for periodic processing. Such pastes are capable (even without the use of ultrasonic cleaning) of removing not only moderate pigmentation plaque, but even small tartar.
But still, it would be optimal to first undergo professional oral hygiene at the dentist, and use our recommendations as “regular maintenance therapy.” In addition, it should be taken into account that the home method of removing plaque mentioned above has special requirements for the process of carrying out this procedure, which you can read in the article at the link below.
→ Removing stone and plaque
Why is tartar dangerous?
Experts' opinions regarding the harmful effects of tartar are divided. Some believe that as they grow and move towards the root, hard deposits irritate the epithelium of the gingival sulcus and destroy the periodontal junction. According to the hypothesis of another group of researchers, the stone itself is inert, and the damage is caused by a soft coating that easily attaches to its surface. Be that as it may, tartar leads to a number of complications:
- inflammatory processes in the gums;
- exposure of roots;
- mobility and subsequent tooth loss [3].
Black plaque on a child’s teeth: treatment
Both pigmented microbial plaque and chromogenic staining of teeth due to the activity of actinomycetes bacteria are removed equally in both children and adults, but there are nuances depending on age. For example, Air-flow can be used no earlier than from 12-15 years of age (at the discretion of a specialist), ultrasonic cleaning can be used from 14 years of age. Therefore, in younger children, removal of dark plaque is carried out only with the help of a polishing brush and paste.
Removing dark plaque from a child (before and after photos) –
The main problem with removing pigment plaque caused by chromogenic staining (deposits of insoluble iron salts) is that usually the black plaque returns within 2-3 weeks. Therefore, you don’t really go to the dentist. And in order to prevent the reappearance of black plaque as much as possible, you need to follow the recommendations from the list below.
Prevention of chromogenic staining –
- solve the problem with drinking water (we already said above that drinking ordinary tap water, as well as water purified by an osmotic filter, increases the risk of stains by 13 times),
- stop taking chewable forms of vitamins,
- if you have bleeding gums, you need to see a dentist and have gingivitis treated,
- if you use pastes with stannous fluoride, switch to pastes with sodium fluoride or amino fluoride,
- use toothpastes that contain pyrophosphates, sodium citrate, polyaspartate, as well as polydone and bromelain (all these components prevent pigments from attaching to tooth enamel),
- use toothpastes with lactoferrin (this glycoprotein has the ability to bind 2 trivalent iron ions per 1 molecule),
- Buy your child an Oral-B electric toothbrush (from 3 years of age).
All this will reduce the risk of black plaque deposits, and thanks to an electric toothbrush, you can also polish your child’s teeth yourself. Here it is necessary to clarify that many models of Oral-B electric toothbrushes are for adults - in some modes they can also be used by children from 4 years old, but under the supervision of adults. By the way, you can read about how lactoferrin prevents the formation of black plaque from insoluble iron salts in an English-language study at this link.
Ultrasonic cleaning with the “Vector” device
The German “Vector” system was created specifically to rid teeth of plaque. It effectively removes soft and hard mineralized deposits on the coronal part of units, as well as in periodontal pockets. The peculiarity of the procedure is the use of a special nozzle; ultrasound is applied strictly vertically (top to bottom and bottom to top). This allows you to remove deposits carefully, comfortably and painlessly. The entire process is controlled and predictable; during the procedure, the dentist adjusts the amplitude of the waves.
Thanks to the use of a special solution with hydroxyapatite granules, high-quality polishing of the surface of the crown and root occurs; after such cleaning, the appearance of new plaque occurs several times slower. In addition, the liquid promotes rapid regeneration of inflamed tissues, reduces sensitivity during the procedure and makes breathing fresh.
Plaque removal using the Vector device can be carried out when:
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis;
- identifying periodontal pockets 4-6 mm deep;
- increased sensitivity of teeth and gums;
- atrophic processes, exposure of the necks of units.
The procedure is contraindicated in childhood, during pregnancy and lactation, in the case of deep periodontal pockets filled with pus. Also, cleaning is not carried out if there is severe mobility of the units, the presence of malignant tumors in the body, severe heart disease, or if there is a pacemaker.
After the procedure, the doctor recommends using a new soft brush and toothpaste for sensitive teeth. In addition, you should give up coloring foods and drinks and smoking for 2-3 days.