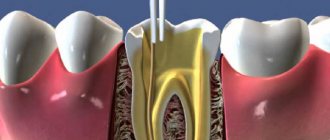
One of the most important problems of medical institutions is nosocomial infections. Infection can occur during treatment and diagnostic procedures, as well as naturally - through household contact or airborne droplets. We do not undertake to estimate the frequency and volume of nosocomial infections, but we can talk in detail about those disinfectants that are used in modern medical practice.
In order to prevent the spread of nosocomial infections, modern chemical agents are used to disinfect hospitals based on chlorine, hydrogen peroxide, alcohols, aldehydes and other disinfectants. Their active use for disinfection of premises, medical instruments, and equipment reduces the risk of infection to almost zero. However, the very concept of “disinfection” is somewhat broader than a list of disinfectants and methods of their use. There are other methods of disinfection other than chemical disinfection.
Disinfection methods
Disinfection is a list of chemical, mechanical, and physical manipulations specifically designed to destroy pathogenic agents that cause various diseases in humans and animals.
Disinfection is carried out using the following methods:
- boiling;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- air ozonation;
- steam, air sterilization;
- treatment with chemical disinfectants.
Depending on the time and place of disinfection, disinfection is divided into:
- Preventive disinfection - carried out if the exact source of infection cannot be identified or does not exist, to protect against possible infection.
- Focal disinfection - performed when the source of infection is identified.
Focal disinfection includes: current treatment, which is carried out in the presence of the patient, and final treatment, which is carried out after the patient leaves (discharge or death) to eliminate foci of the pathogen.
All medical instruments, equipment, surfaces and objects with which the patient has been in contact are subject to chemical disinfection or another disinfection method. Disinfection of surgical instruments followed by sterilization is mandatory.
Disinfectants
Disinfectants used in medicine are classified according to their composition and purpose. They have varying degrees of antimicrobial activity, toxicity, and influence on the object they treat. The following modern disinfectants are officially approved for use in medical institutions:
- Based on chlorine: Chlormisept economy. These products are used to disinfect medical instruments made of plastic, rubber, and glass. Chlorine-containing preparations have low toxicity, but cause corrosion of metals. Among the disadvantages is the presence of the smell of chlorine.
- Hydrogen peroxide solutions: Alphadez oxy. They have low toxicity, are odorless, and are used to disinfect instruments made of rubber, plastic, and glass. Does not have a fixing effect on organic matter.
- Aldehydes: Alfadez forte, Alfadez ortho. They are used for disinfecting endoscopes and related instruments, as well as for cleaning premises and washing equipment. They have high activity against many pathogenic microbes. Aldehyde agents are often used for HLD and chemical sterilization, but they have a fixing effect and therefore require careful pre-cleaning and disinfection.
- Alcohol-containing antiseptics: Miroseptic, Ecobriz antiseptic, Estilodez antiseptic. Used as an antiseptic for treating the skin before injection, for disinfecting the skin and surgical fields.
All objects in contact with blood and in contact with the wound surface are subject to mandatory disinfection. Sterilization of medical instruments is carried out after their preliminary disinfection using chemical solutions or steam sterilization.
Disinfection in dentistry
Disinfection in dentistry.
One of the most important activities in dental practice is high-quality disinfection.
surfaces, equipment, materials and tools. This is the main component of the complex of measures for
preventing the spread of diseases.
According to statistics, a large number of infections occur in the dentist's chair. This is where you take a risk
get not only standard nosocomial infections, but also more serious diseases: HIV, hepatitis,
tuberculosis Failure to comply with sanitary standards can lead to infection not only of patients, but also of everyone
clinic staff, as well as members of their families.
Disinfection of surfaces.
Disinfection of surfaces in the dental office is an extremely important part of prevention.
nosocomial infection. When working with high-speed turbines and drills in the air
a suspension appears consisting of microscopic drops of water and pathogenic microorganisms. Aerosols
remain in the air for up to 30 minutes and spread over a distance of up to 80 cm. and when using water
cooling, the diameter of the aerosol cloud reaches 2 meters. All this settles on surfaces and tools.
Treatment and disinfection are aimed at reducing bacterial contamination of all surfaces, including
equipment, tables, armrests, door handles and faucets and should be performed after each patient.
Disinfection can be carried out in the presence of the patient, therefore, according to SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-
10, the product must belong to the 4th class of low-hazard substances (for all types of effects on the body).
There are 3 zones with different levels of hygiene:
1 zone:
Treatment area where the highest level of hygiene must be maintained. The basis of work in the 1st zone should be
lie principles:
Sterility (dental instruments);
Disposables (disposable items);
Individuals (gloves);
2 zone:
The boundary of the treatment area, including the surface of the manipulation table, armrests, dental unit,
emptyers, individual cups (sippy cups), spatulas and cups for mixing impression material, etc.
Treatment and disinfection of surfaces in these areas is carried out after each patient, at the end of the shift and as needed.
pollution.
Zone 3 : The rest of the office: furniture, equipment, door handles, taps and sinks, bactericidal lamps,
lamps, walls and floor. In this area, routine cleaning is carried out daily, at least 2 times a day with
using disinfectants.
They are used as disinfectants and pre-sterilization cleaning agents.
only chemicals approved in accordance with the established procedure in the Russian Federation,
applied strictly in accordance with approved guidelines
Department of State Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance of the Russian Ministry of Health.
Criteria for choosing a disinfectant.
When choosing a particular disinfectant, it is necessary to clearly define the requirements for the disinfectant
means.
This:
- wide spectrum of action;
- no toxicity;
- no influence on processed objects;
- fast action;
- resistance to environmental factors;
- residual antimicrobial effect;
- ease of use;
- no odor;
- efficiency;
- good solubility;
- stability;
- cleaning properties.
Properties of objects to be disinfected.
In dental practice, medical devices of various designs and compositions are used.
instruments and medical products that require careful selection of products for the most complete
disinfection and maximum care. For example, we need a means to process
instruments, accordingly, selection is carried out among drugs whose guidelines indicate their
possibility of using disinfection for this object. Preference is given to disinfectants
with a non-corrosive washing effect. This criterion significantly narrows the choice
drug.
The breadth and spectrum of the antimicrobial action of the disinfectant.
Disinfectants can affect the following types of infections: viral, bacterial,
fungal and sporicidal. Not all drugs affect all types of infections, you need to know
what effect can be expected and what level of disinfection is required.
The ability to combine stages of processing medical products.
Nowadays there are a large number of broad-spectrum products on the market. This is a combination sink
and disinfection, disinfection and sterilization, pre-sterilization cleaning and disinfection in one process.
There are universal means that can be used to disinfect medical
instruments, and for disinfection of surfaces, premises, furniture, medical equipment, utensils,
linen, sanitary and technical equipment, cleaning equipment. Disinfectants with
additional features, such as disinfection of surfaces with a deodorizing effect and the presence
The cleaning effect of the drug gives greater freedom of choice and creates a favorable atmosphere for work.
Terms of use of working solutions and the possibility of their repeated use.
This criterion is necessary when calculating economic benefits. But it must be taken into account that with large
the volume of instruments processed, the disinfectant will become unusable earlier than possible
the suitability of working solutions; therefore, its use is not always profitable. Some remedies can be
apply only during one work shift, others within 36 days. Range of disinfectants by duration
The suitability of working solutions is quite wide and you can choose the most optimal option for each
specific dental institution.
Convenience of using disinfectants.
The very concept of “ease of use” is a collective term and includes the following
aspects of working with the drug:
- solubility;
- release form;
- operating temperature of the disinfectant;
- smell;
- cooking conditions;
- storage stability;
- performance.
As is known, chlorine-containing substances lose their biocidal activity over time, especially in the light, which
creates certain inconveniences, because It is constantly necessary to check the presence of active chlorine in the preparation before
application. Compliance with temperature conditions, i.e. maintaining a certain temperature value
solution during disinfection and chemical sterilization greatly complicates the work with data
disinfectants. The container in which the drug is produced and the volume of this product, as well as the preparation conditions
working solution - everything must be taken into account when choosing a disinfectant.
Degree of toxicity.
The degree of toxicity in humans may be manifested as an inhalation hazard, possible
poisoning when the disinfectant enters the gastrointestinal tract and possible effects on the skin. The most important is undoubtedly
is the inhalation effect on humans, because this poisoning occurs much more often than
accidental ingestion of disinfectant into the stomach. Inhalation Hazard Classification
disinfectants contains four classes in accordance with the size of the acute toxic zone
actions.
In dentistry, it is allowed to use drugs belonging to the third and fourth hazard classes.
The presence of a third class of hazard (for example, if it enters the stomach) in the instructions for use of the drug,
implies its relation to moderately dangerous drugs that are prohibited from being used in the presence
patients. In accordance with SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements
organizations carrying out medical activities”, only drugs of the fourth class are allowed
use in the presence of people. This is a very important point when choosing a product for routine cleaning and
disinfection of the dental office. Wiping the surfaces of the border of the treatment area can be carried out in
presence of the patient.
Influences on processed objects.
Dentistry uses complex and expensive equipment that wears out quickly when
using “aggressive” disinfectants. The best means for disinfecting products
compositions based on QAS and cationic surfactants are considered for medical purposes, since, having a wide range
actions, they have the most gentle effect on product materials and do not interfere with their functionality
properties and have a cleaning effect, which allows them to be used for combined disinfection and
pre-sterilization cleaning.
Personnel training.
An important point affecting the quality of disinfection is the training of personnel.
It is necessary to have detailed instructions for both routine and general cleaning, taking into account
the disinfectant used, as well as the procedure for treating surfaces in the office.
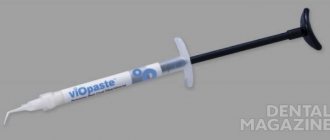
Disinfectant "Defect-Forward"
specially developed for use in dentistry.
The drug was created to replace expensive disinfectants
foreign production to more affordable - Russian, without loss of quality.
"Defect-Forward" is an analogue in its properties, and in some respects
indicators superior to disinfectants from well-known manufacturers: Johnson and
Johnson, Schulke and Mayer.
The main advantages of disinfectants from the “Defect” line.
- They have high cleaning properties, do not spoil the objects being processed, do not discolor fabrics, do not fix organic contaminants and biosubstrates, and do not cause corrosion;
- Do not contain phosphates, aldehydes, acids, active chlorine and oxygen;
- According to the parameters of acute toxicity, in accordance with GOST 12.1.007-76, they belong to the 4th class of low-hazard substances (for all types of effects on the body);
- In accordance with SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10, they are approved for use in the presence of people;
- They have a balanced synergistic composition and a high degree of stability: with a minimum amount of active ingredients (from 2.6 to 9%) they have a wide spectrum of action and powerful disinfecting ability;
- Destroy foreign odors of various origins;
- They have a prolonged antimicrobial effect;
- They do not lose their physicochemical properties and biocidal activity during freezing and subsequent thawing.
- In accordance with GOST 194330-81, they are not dangerous goods, fire- and explosion-proof;
- Working solutions do not have a cumulative or allergenic effect, are biologically degradable, and environmentally safe. During disposal, no additional dilution with water is required.
- They have a pH level close to neutral;
- The shelf life of the products is 5 years. Working solutions remain effective for 36 days and can be used repeatedly.
- Do not cause resistance in microorganisms;
- Universal in use: can be used by wiping, irrigation, spraying, immersion, aerosolization, foam generation;
- Active in hard water, in the presence of organic contaminants;
- Have all the necessary permits for use at all sites;
Cleaning and disinfection of conventional medical instruments
The use of Dezefect-Forward for the disinfection of medical products
purposes, including combined with pre-sterilization cleaning.
Medical products must be completely immersed in the working solution immediately after
their application, ensuring immediate removal of visible surface contaminants from products using
cloth napkins. Used wipes are placed in a separate container, disinfected, then
disposed of.
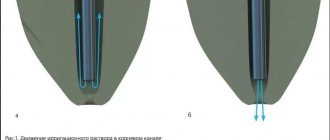
The channels and cavities present in the products are filled with a solution, avoiding the formation of air pockets. Through
the channels alternately pump the product solution and remove air using a syringe or other device.
The procedure is repeated several times until biological contaminants are completely removed.
Detachable products are immersed in the solution in disassembled form. Products with locking parts are immersed
opened, having previously made several working movements for better penetration of the solution into
hard-to-reach areas of products in the locking area. The thickness of the product layer above the products should not be
less than 1 cm.
Disinfection of dental equipment with Dezefect-Forward.
Impressions, denture blanks and other dental materials are pre-washed with 0.05%
solution of the “Defect-Forward” product. They are disinfected by immersing them in the working solution according to the following modes:
(given in the instructions). At the end of disinfection, dental materials are washed with running water.
water, after which they are dried in air. The product for processing impressions is used repeatedly,
processing no more than 50 prints. When the first signs of a change in the appearance of the solution appear
it should be replaced.
Suction systems in dentistry are disinfected using a working solution of a product concentration
1.5%. 1 l, pass through the suction system of the installation for 2 minutes. Then a 1.5% solution of the product
leave it in it to act for 30 minutes (during this time the suction system is not used). Procedure
carried out 1-2 times a day, including at the end of the work shift.
Disinfection of air in a dental office using Dezefect-Forward.
Air disinfection is carried out using technical installations by spraying working solutions
products with a concentration of 0.6% with an exposure of 30 minutes or 0.8% with an exposure of 15 minutes, at the consumption rate
50-100 ml/m3. Surfaces are first disinfected, windows and doors are closed, and the air supply is turned off.
exhaust ventilation. After the disinfection period, the remainder of the working solution, if necessary,
remove from surfaces with a dry cloth, and ventilate the room for 10-15 minutes.
The disinfectant "Defect-Forward" has antimicrobial activity against
various gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms, including pathogens of purulent
septic and other nosocomial infections (escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococci and others
known pathogens of nosocomial infections), pathogens of particularly dangerous infections - plague, cholera, mycobacterium tuberculosis,
fungi of the genus Candida, trichophyton (the product is effective for the prevention of candidiasis and dermatophytosis), molds,
fungal spores, viruses (in relation to all known human pathogenic viruses, including enteric viruses
and parenteral hepatitis (including hepatitis A, B and C), HIV, polio, adenoviruses, enteroviruses,
rotaviruses, SARS viruses, bird flu H5N1, swine flu A/H1N1, influenza
human, herpes. The product is characterized by a residual antimicrobial effect.
"Defect-Forward" contains as active ingredients a complex of 2 quaternary ammonium
compounds - alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride, dimethyldidecylammonium chloride, as well as fragrance, dye,
water.
Disinfection Center produces premium disinfectants to protect your health.
Documents regulating disinfection and sterilization activities
in dental institutions
1. OST 42-21-2-85 “Sterilization and disinfection of medical devices. Methods, means, modes";
2. Order of the USSR Ministry of Health dated July 12, 1989 No. 408 “On measures to reduce the incidence of viral hepatitis
in the country";
3. Order of the USSR Ministry of Health dated September 3, 1991 No. 254 “On the development of disinfection in the country”;
4. Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated August 18, 1997 No. 170 “On measures to improve the prevention and treatment of HIV
infections in the Russian Federation";
5. Guidelines for disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization of medical products
appointments (MU-287-113 dated December 30, 1998), approved by the Department of State Sanitary and Epidemiological Monitoring of the Ministry of Health of Russia;
6. “Concept for the prevention of nosocomial infections”, approved by the measured deputy
Minister of Health of the Russian Federation G.A. Onishchenko 06.12.1999;
7. Guide “Use of ultraviolet bactericidal radiation for air disinfection and
surfaces in premises" (R 3.1.683-98, approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation);
8. Sanitary and epidemiological rules SP 3.5.1378-03 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the organization and implementation of disinfection activities”;
9. Sanitary and epidemiological rules SP 1.1.1058-01 “Organization and conduct of production control
for compliance with sanitary rules and implementation of sanitary and anti-epidemic (preventive)
events";
10. Guidelines MUK 4.2.1035-01 dated May 23, 2001 “Control methods. Biological and microbiological
factors. Control of disinfection chambers";
11. Manual “Organization of disinfection and sterilization regimes in dental institutions and offices”
(L.A. Ponomareva, Moscow disinfection station No. 7, 1998);
12. Methodological recommendations “On organizing and conducting anti-epidemic measures in institutions
dental service" (candidate of medical sciences P.S. Oparin, Irkutsk disinfection station, magazine "Siberia-Vostok",
April 2000);
13. Methodological letter of the Central State Sanitary and Epidemiological Service in Moscow dated March 21, 1995, No. 12/20/-208 “Organization of sanitary and hygienic
and disinfection and sterilization regimes in dental institutions”;
14. Manual on the use of disinfection and sterilization means in health care facilities and the organization of disinfection and
sterilization in endoscopy and dentistry departments.
Moscow, 1998. Instructions.
Instructions for using the disinfectant “Defect-Forward” for disinfection and pre-sterilization cleaning.
Certificates.
on state registration of disinfectant Declaration of conformity
We are in social networks: