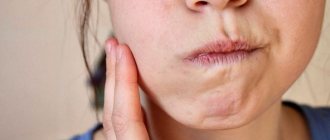
- Causes of gum sensitivity Vigorously brushing teeth
- Changes in hormone levels
- Irritation from dental plaque
- Gingivitis
- Toothpastes
When inflammatory processes occur, the gums become red, itchy, and swollen.
Many people believe that these symptoms will go away over time and think that everything is fine. But if you start the problem of gum sensitivity, you can face more serious consequences. We tell you how to deal with sensitive gums at home, when to go to the dentist and what to choose for daily care.
Use of Chlorhexidine in dentistry
Upon contact with the mucous membrane, it forms a thin protective film. The effect lasts after the procedure for 24 hours.
Shown:
- with gingivitis;
- in case of development of periodontitis;
- against the background of treatment of stomatitis;
- in case of inflammation of the socket after tooth extraction;
- for inflammation caused by semi-impacted wisdom teeth;
- for disinfection of removable dentures;
- for root canal treatment;
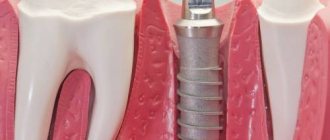
- after installation of dental implants.
An alcohol-based chlorhexidine is used to treat the hands of a dental surgeon.
The antiseptic enhances the effect of surface anesthesia, therefore it is often prescribed together with Lidocaine. This reduces the number of bacteria at the injection site. Able to fight pathogenic microorganisms after removing stone and plaque.
Taking medications after tooth extraction
Experienced specialists recommend taking antihistamines. They will help avoid swelling of the cheeks, because in addition to working on allergic reactions, antihistamines also have an anti-edematous effect.
You should not overdo it with medications if the pain is tolerable and tooth extraction was a procedure of ordinary complexity. A little trick that can be remembered for the future is to take an analgesic even before the patient stops feeling the anesthesia administered by the doctor.
As for antibiotics, it is strictly not recommended to take them without a corresponding prescription from the attending physician. In what cases does the surgeon issue a referral for the purchase of necessary medications:
- for difficult removal;
- with the development of the inflammatory process;
- in case of concomitant diseases such as stomatitis or candidiasis.
What solution to use for rinsing the mouth after implantation
It is recommended to use an aqueous 0.05% solution. It is effective even with large blood clots after extraction and promotes rapid wound healing. Rinses are prescribed in courses as prescribed by the dentist. You cannot use the drug for longer than the recommended period due to the risk of severe irritation of the mucous membrane.
Smokers and people with diabetes can use alcohol-based Chlorhexidine rinses. This composition ensures high safety and stabilization of the drug. Local treatment with an alcohol-containing drug significantly reduces the formation of plaque in the oral cavity, especially after implantation.
What symptoms indicate inflammatory processes?
We have looked at the main reasons why gums become inflamed and bleed. But how to deal with the symptoms? What exactly indicates the disease until the gums begin to bleed and become swollen?
In addition to insufficient oral hygiene, inflammation can be caused by untimely treatment of pulpitis, the formation of tartar along the gum line, as well as fillings and crowns with an overhanging edge.
Symptoms include:
- pain when pressed or touched;
- bad breath;
- itching and redness around the tooth;
- discomfort when biting food;
- loosening of teeth.
How to do mouth baths correctly
At the beginning of the rehabilitation stage, it is difficult to perform hygiene procedures. Therefore, the patient is prescribed rinses with antiseptics. For the first few days, it is recommended to apply a bandage or cotton swab soaked in a 0.1% solution. Then proceed to direct rinsing, which must be done carefully .
Until the wound has completely healed, rinsing is replaced with oral baths.
«
You can use the drug up to 6 times a day, 10 ml. Rinsing takes 1-2 minutes. You cannot brush your teeth or eat food for half an hour after the procedure.
Rinsing is a good prevention of gum suppuration under the implant, eliminating the risk of bacteria entering the wound. To enhance the effect, during the first 2-3 days you can alternate with Betadine every other time.
General recommendations
The most important rule in such a sensitive issue will be timely assistance from a qualified specialist. Therefore, if your tooth suddenly starts to hurt badly, this is not a reason to just take a pill and forget about this unpleasant moment, this is a good reason to go to a dental clinic, where you will be given first aid.
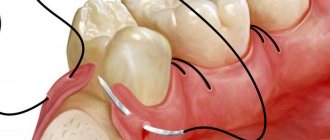
With any removal, complex or ordinary, there are a number of rules that must be followed to speed up the healing of the wound, as well as avoid abscesses and other negative consequences.
- Removing the gauze compress. The doctor leaves cotton wool or gauze after tooth extraction. A maximum of one hour after arriving from the dentist, you must carefully remove the protective swab. If it has dried out and stuck to the gum, do not remove it until you soak the area with chlorhexidine, since careless movement can damage or even remove the clot hiding the wound.
- Pain relief. Any discomfort after tooth extraction is a normal process for which you need to be prepared. Ice or any cool item from the refrigerator will help relieve discomfort. The selected item is wrapped in a towel and applied to the sore cheek. In addition to relieving pain, this action will help reduce the chances of swelling. However, this action also has its limitations: ice can be applied several times, making sure to take a break of 5-7 minutes.
- Eating. In the first few hours after tooth extraction, be it a molar or a chewing tooth, you should not eat any food, even if you are very hungry. Over the next 24 hours, the temperature of the food should only be at room temperature. Food should not be too spicy or salty, this can cause additional irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Limit alcohol and smoking. On the first day after tooth extraction, you should refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages. Even a small dose of alcohol can cause blood vessels to dilate, which will ultimately lead to bleeding from the wound. Smoking is permissible, but again at least 2-3 hours after the operation.
- Applying and removing sutures. If sutures were placed at the dental clinic after tooth extraction, the patient is usually invited for a follow-up appointment in a week. In some cases, the sutures dissolve on their own within two weeks.
- Dental treatment. For those who are now closely involved in treating the entire oral cavity, a reasonable question arises: when can the procedures be continued? If the removal was not difficult, then it will be possible to resume meetings with your doctor after 7 days.
The use of Chlorhexidine for swelling of the gums
The drug is indicated for relieving inflammation of local gum swelling after implantation or tooth extraction. Its antimicrobial properties help avoid suppuration and infection of the wound. Helps reduce swelling and irritation of the mucous membrane.
On average, the course is 1 week. To perform oral baths, liquid is drawn into the mouth, held for 1-2 minutes and spit out. If the procedure is performed after brushing your teeth, you must thoroughly rinse off any remaining toothpaste. The components in its composition can sharply reduce the effectiveness of Chlorhexidine.
Important restrictions after tooth extraction
Each patient, in addition to recommendations, should also know what not to do:
- Visit the bathhouse, sauna or swimming pools. Experts also recommend limiting yourself to a short period of time by taking a shower rather than a hot bath.
- Go to the gym and take on heavy physical activity;
- Experiencing stress, which, oddly enough, can seriously affect the wound and even contribute to the opening of bleeding;
- Get into the mouth, in the wound area with dirty hands;
- Touch the site of tooth extraction, be it the tongue or fingers, because this will certainly lead to damage to the clot;
- Brush the removal area with a toothbrush;
- Actively rinse your mouth, because any aggressive external actions can lead to clot disruption and the development of alveolitis.
It is worth noting that representatives of the fair half of humanity are not recommended to remove teeth during the menstrual cycle, because this will only provoke bleeding from the resulting wound.
Advantages and disadvantages of the drug
Positive properties of the drug:
- kills pathogenic microorganisms (antimicrobial activity is higher than that of Miramistin);
- maintains a long-lasting antiseptic effect even upon contact with bloody and purulent secretions;
- used in low concentrations, which protects the oral mucosa from irritation;
- impossibility of overdose;
- affordable price.
Negative points include:
- weak or zero effect in the treatment of viral diseases, especially like herpes;
- bitter, unpleasant taste causes discomfort;
- Regular use leads to darkening of the enamel and surface of the tongue.
Side effects
Any drug has limitations in use and may have side effects. Chlorhexidine is a safe antiseptic; however, an allergic reaction to it is possible. In addition, it can stain the enamel yellowish, cause a burning sensation and temporary loss of taste. During use of the product, a slight feeling of numbness and a feeling of bitterness may occur. The listed side effects are minor and are fully compensated by the high efficiency and availability of chlorhexidine.
Use of the drug in children and pregnant women
Attention! If there are no wounds in the patient's mouth, chlorhexidine can be used by pregnant and lactating women. It does not penetrate into the blood or breast milk, but acts only on the surface. A 10-day course of treatment is safe for such patients, according to studies.
When treating children, the course of use of the drug should also not exceed 10 days. For the youngest patients, it is preferable to use chlorhexidine in the form of a spray, which does not require rinsing skills. The spray is easy to use and can be applied to any area of the oral mucosa. Children under 3 years of age should not use the drug to irrigate the tonsils. Despite the safety of the drug, if the drug is used by pregnant women or pediatric patients, it is recommended to first consult with your doctor.
Chlorhexidine bigluconate solution 0.5 mg/ml 100 ml
Name
Chlorhexidine bigluconate.
Description
Transparent, colorless or slightly yellowish liquid, odorless.
Main active ingredient
Release form
Solution for external use.
Dosage
0.05% 100 ml.
pharmachologic effect
An antiseptic with a pronounced bactericidal effect against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria (does not affect acid-fast forms of the latter): Treponema pallidum, Chlamidia spp., Ureaplasma spp., Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Gardnerella vaginalis, Bacteroides fragilis, protozoa (Trichomonas vaginalis), microbial spores , viruses, fungi; has little effect on some species of Proteus and Pseudomonas. Chlorhexidine bigluconate is also active against treponemas, gonococci, and trichomonas. Retains activity (slightly reduced) in the presence of blood and pus. Cleanses and disinfects the skin without causing damage.
Indications for use
The drug is used for the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, etc.). It is used for antiseptic treatment of wounds, abrasions and cracks, burns, for bacterial and fungal diseases of the skin and mucous membranes, incl. in urology, surgery, obstetrics and gynecology. In dentistry, it is used for rinsing the mouth in cases where compliance with hygiene rules is difficult, in the postoperative period after flap periodontal surgery, for washing periodontal pockets, fistulas, and abscess cavities. Since chlorhexidine bigluconate has a cytotoxic effect, the concentration of the rinse solution should not exceed 0.25 mg/ml.
Directions for use and doses
The drug is used in the form of irrigation, rinsing and application - 5-10 ml of solution is applied to the affected surface of the skin or mucous membranes with an exposure of 1-3 minutes 2-3 times a day (on a tampon or by irrigation). For the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases, the drug is effective if used no later than 2 hours after sexual intercourse. Used after urination: using a nozzle, insert into the urethra for men (2-3 ml), for women into the urethra (1-2 ml) and into the vagina (5-10 ml) and hold for 2-3 minutes. Treat the skin of the inner thighs, pubis, and genitals. After the procedure, it is not recommended to urinate for 2 hours. Complex treatment of urethritis and urethroprostatitis is carried out by injecting 2-3 ml of the drug into the urethra 1-2 times a day, the course is 10 days, procedures are prescribed every other day. The rinse solution is usually prescribed 2-3 times a day (for rinsing the mouth, the drug should be mixed with an equal amount of water).
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Use with caution in pregnant and lactating women due to the lack of data on experience with clinical use. Do not treat the surface of the mammary glands before feeding.
Precautionary measures
The bactericidal effect increases with increasing temperature. At temperatures above 100 °C, the drug is partially decomposed. Contact of hypochlorite bleaches on fabrics that have previously been in contact with chlorhexidine-containing products may cause brown stains. In patients with open traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injuries, or perforation of the eardrum, contact with the surface of the brain, meninges, and the cavity of the inner ear should be avoided. In case of contact with the mucous membranes of the eyes, they should be quickly and thoroughly rinsed with water. Concomitant use with iodine is not recommended. Use in children. The use of chlorhexidine solution (aqueous or alcoholic) in newborns as a skin antiseptic before invasive procedures is associated with a certain risk of developing a chemical burn. Based on spontaneous reporting and literature data, a higher risk of skin reactions has been identified in preterm neonates, particularly those born before 32 weeks of gestation, in whom chlorhexidine was used during the first two weeks of life. Before performing invasive procedures, it is necessary to remove all materials soaked in chlorhexidine: bandages, sheets, napkins, gowns, etc. Do not use excessive amounts of solution. The solution should not be allowed to accumulate in skin folds, under the patient’s body, or on materials that are in direct contact with the child’s skin. If an airtight dressing (occlusive dressing) is to be applied to skin that has previously been exposed to chlorhexidine, ensure that there is no excess chlorhexidine solution on the skin before applying the dressing. Use in elderly people. There are no data regarding the specifics of use in elderly patients.
Interaction with other drugs
Not compatible with detergents containing an anionic group (saponins, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium carboxymethylcellulose). Concomitant use with iodine is not recommended. The presence of soap can inactivate chlorhexidine digluconate, so before using the drug, any remaining soap must be thoroughly rinsed off. Ethanol enhances the effectiveness of the drug.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, dermatitis, viral skin diseases, age up to 12 years. It is not recommended for use on large surface wounds.
Compound
A 40 ml bottle contains: active ingredient: chlorhexidine bigluconate (in the form of dezine (chlorhexidine bigluconate 20% solution)) – 20 mg; excipient: purified water – up to 40 ml. A 100 ml bottle contains: active ingredient: chlorhexidine bigluconate (in the form of dezine (chlorhexidine bigluconate 20% solution)) – 50 mg; excipient: purified water – up to 100 ml. A 200 ml bottle contains: active ingredient: chlorhexidine digluconate (in the form of dezine (chlorhexidine digluconate 20% solution)) – 100 mg; excipient: purified water – up to 200 ml.
Overdose
Cases of overdose with external use are unknown. When ingested, the drug is practically not absorbed, so systemic effects are unlikely. However, in case of accidental ingestion, gastric lavage is necessary. If necessary, carry out symptomatic therapy.
Side effect
Possible allergic reactions (skin rash), dryness and itching of the skin, dermatitis, photosensitivity, stickiness of the skin of the hands (within 3-5 minutes), chemical burns of newborns (frequency unknown). In the treatment of gingivitis – staining of tooth enamel, tartar deposits, taste disturbance. If any adverse reactions occur, including those not listed in these instructions, you should consult a doctor.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Buy Chlorhexidine bigluconate solution 0.5 mg/ml 100 ml in the pharmacy
Price for Chlorhexidine bigluconate solution 0.5 mg/ml 100 ml
Instructions for use for Chlorhexidine bigluconate solution 0.5 mg/ml 100 ml