Tooth extraction is a complex and traumatic dental operation, after which the patient must follow certain recommendations to prevent postoperative inflammatory processes and complications. It is very important to maintain oral hygiene to prevent the proliferation of bacterial flora and infection of the soft and hard tissues of the teeth. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed a combination of therapeutic and prophylactic therapy using antibacterial and antimicrobial drugs (for example, Metronidazole) and disinfectant solutions for local treatment.
Removal of a tooth
One of the safest, most effective and affordable disinfectants is Chlorhexidine. This is a combined agent that destroys representatives of fungal, microbial and bacterial flora, providing sanitation of teeth and mucous membranes after surgical procedures to extract a tooth from the bone alveolus. It can be used by patients of any age. If necessary, Chlorhexidine can be used to prevent complications after extraction in children and pregnant women.
Rinse after tooth extraction with Chlorhexidine
What is Chlorhexidine?
"Chlorhexidine" is a clear liquid with a characteristic odor of ethyl alcohol, which has antimicrobial and antibacterial effects. The drug is used for antiseptic treatment of the skin and mucous membranes after surgical operations, for accidental injuries and injuries accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the skin: scratches, cuts, abrasions. The product can be used to disinfect hands if it is not possible to provide standard hygienic treatment with water and soap.
The mechanism of action of the drug on the bacterial cell
The active ingredient of the antiseptic is chlorhexidine in the form of bigluconate. The drug is available in several dosage forms for local and external treatment:
- spray;
- solution;
- vaginal suppositories (suppositories).
In dentistry, Chlorhexidine is used in the form of a spray and solution. It is used to treat hands, medical instruments, and is also used to disinfect the oral cavity after dental treatment using surgical methods. The effect of the drug lasts up to four hours after use.
"Chlorhexidine"
The active substance is active against most pathogenic microorganisms, which include gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, various groups of viruses, yeast-like fungi, and dermatophytes. Chlorhexidine is especially effective for the prevention of dental infections caused by chlamydia and trichomonas.
"Chlorhexidine" after tooth extraction
Why do you need Chlorhexidine: properties and action
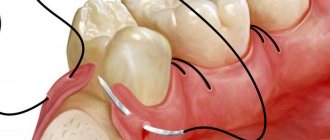
After a tooth is removed, an open wound remains in the gum and fills with blood. A blood clot forms in the hole, protecting the open area of the periosteum from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and microbes. If the clot does not adhere tightly to the socket or is accidentally damaged during eating, the risk of infection of the bone tissue and the development of osteomyelitis of the jaw increases - a purulent-inflammatory pathology, which, if not treated in a timely manner, can lead to the death of bone structures (osteonecrosis).
And this is how a blood clot may look in real life - it is very important not to wash it out when rinsing your mouth
To avoid damaging the clot, the following recommendations must be followed:
- in the first 1-2 days after removal, you should not drink through a straw, spit saliva, or perform other actions that create a vacuum in the mouth;
- You can chew on the side on which the removal took place 72 hours after surgery;
- You need to rinse your mouth carefully, trying not to make too active movements;
- Do not touch the clot with your tongue or try to remove it from the hole.
Another common complication after tooth extraction is alveolitis. This is a disease in which inflammation of the socket occurs. The pathology is accompanied by fever, severe pain, which can radiate to the ear, eye area, jaw and cervical and submandibular lymph nodes. The gums at the extraction site swell, and severe swelling and redness appear.
- How to rinse your mouth with Chlorhexidine for gum inflammation
Development of alveolitis in the socket after tooth extraction
The main cause of alveolitis is non-compliance with the hygiene regime and an increase in the number of pathogenic flora in the oral cavity. Pathogenic microorganisms entering the alveoli cause inflammation of soft tissues and the development of a pathological process. To prevent alveolitis and other possible complications, the patient is prescribed local treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions, one of which is Chlorhexidine. The use of this drug ensures disinfection of the mucous membranes and hard tissues of the tooth and prevents the development of infectious and inflammatory processes.
Tooth extraction is a full-fledged surgical operation.
Video - “Chlorhexidine”: application and effectiveness
Chlorhexidine for oral diseases
The drug solution is often prescribed for certain dental diseases:
- stomatitis;
- gingivitis and periodontitis.
Stomatitis
For the aphthous form of the disease, rinsing with a chlorhexidine solution is effective. The product also helps with candidiasis of the oral cavity. Treatment usually does not take longer than 10 days.
Gingivitis and periodontitis
Diseases caused by the formation of accumulation of bacteria in subgingival pockets lead to bleeding gums and tooth mobility. In such a situation, rinsing alone is not sufficiently effective. Chlorhexidine is used comprehensively for the treatment of these diseases:
- treat the surface with the solution during cleaning;
- an antiseptic-based drug is placed in the pockets on the gums;
- rinsing with a chlorhexidine-based solution.
Two-week treatment allows you to relieve the main symptoms and reduce the concentration of microbes in the oral cavity several times. Chlorhexidine is also used as a prophylactic against gingivitis and periodontitis. This is especially true after oral surgery or when it is impossible to maintain proper hygiene. Removable prosthetic structures can be soaked in the drug solution to disinfect and prevent gum inflammation.
Chlorhexidine solution is the most effective antiseptic for the oral cavity; it has a unique property - when rinsing, a thin protective film is formed on the mucous membrane, which continues to act for several more hours after rinsing.
How to rinse your mouth?
To rinse the mouth, only an aqueous solution is used - this point should be taken into account when purchasing the drug at the pharmacy. The concentration of the drug is 0.05%. Some, trying to achieve the maximum therapeutic effect, begin to rinse their mouth too often - up to 6-10 times a day. This approach is completely unjustified and can harm a person, since rinsing too often can cause irritation of the mucous membranes and dislodge the blood clot, which protects the exposed bone from the penetration of microbes.
"Chlorhexidine" in the form of a solution
To ensure therapeutic and prophylactic results, it is enough to perform the procedure 2 times a day after morning and evening brushing of teeth. If your gums are prone to bleeding, you can add one more rinse, but the total number of procedures per day should not exceed three.
Video: How to rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine
How to rinse your mouth correctly
Mouth rinsing with Chlorhexidine is carried out according to the following scheme:
- brush your teeth;
- after an hour, rinse your mouth and throat with boiled water at room temperature to remove dirt and food debris;
- take a small amount of the drug into your mouth and hold for 2-3 minutes;
- Carefully spit out the product, avoiding swallowing.
The duration of treatment is from 7 to 12 days.
You just need to keep the product in your mouth
Important! "Chlorhexidine" after tooth extraction can only be used for oral baths. The product must be kept in the mouth, it is allowed to tilt the head slightly to the sides, but you cannot move the cheeks and tongue, as this creates a vacuum in the mouth and can lead to the loss of a blood clot.
Precautions and tips for use
During the procedure, you should avoid getting the product into the digestive tract - this can lead to irritation of the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines and cause inflammation of the surface layer of the gastrointestinal tract. Also, you should not use the drug for longer than the permissible period. Too long use of products based on chlorhexidine digluconate can lead to the destruction of beneficial oral flora and the development of dysbacteriosis.
Antiseptic "Chlorhexidine"
Dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity is accompanied by an unpleasant odor from the mouth, a dense coating on the inner surface of the cheeks and tongue, and other symptoms. Pathology is the main cause of stomatitis - inflammation of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, most often of an infectious nature.
- Rinse after tooth extraction to heal gums
Before rinsing, it is important to maintain an hour's interval with hygiene measures, since the active ingredient "Chlorhexidine" is incompatible with some types of chemicals that may be included in toothpastes, powders and rinses. These include:
- colloids;
- alkaline compounds;
- carboxymethylcellulose;
- soap;
- gum arabic, etc.
"Chlorhexidine" is one of the most effective and popular antiseptics
Note! After rinsing your mouth with Chlorhexidine, you should not eat or drink for 1-1.5 hours. Eating foods earlier will reduce the effectiveness of the procedure.
Visiting the dentist
Helpful information
There are several points to consider when treating:
- When treating gum inflammation, chlorhexidine should be used in combination and only after removing plaque. You should not hope that rinsing with an antiseptic in this case will have a sufficient effect. The drug may partially relieve symptoms, but not completely eliminate inflammation. In advanced cases, teeth become mobile and are at risk of removal.
- The course of rinsing with the drug prescribed by the doctor should not last longer than 12 days. Otherwise, you can develop dysbiosis in the oral cavity, which, in turn, can provoke a fungal disease. To avoid candidiasis, after 10-12 days of treatment with chlorhexidine, it is necessary to switch to rinses with other auxiliary components.
Chlorhexidine kills microorganisms associated with various throat infections, as well as all general oral flora, including Candida Albicans, which causes thrush and oral infections, and bacteria that can cause mouth ulcers.
Possible contraindications and side effects
"Chlorhexidine" has practically no contraindications, with the exception of various groups of dermatitis. The manufacturer warns about possible intolerance to the drug and allergic reactions to the components of the solution, but practice shows that allergies to the drug are very rare - less than 1% of patients.
Contraindications and side effects
Side effects during use are rare. Patients may experience increased dryness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, tingling, burning and itching. These phenomena are of moderate intensity and do not require discontinuation of the drug or cessation of treatment.
Important! Most patients tolerate Chlorhexidine well, but in very rare cases, adverse reactions may occur. Extremely rarely, intolerance can manifest itself as a pinpoint, pale pink rash on the surface of the tongue, gums and inner surface of the cheeks. If this symptom appears, you should consult a doctor.
"Chlorhexidine" is sold in all pharmacies
Advantages and disadvantages of the drug
Positive properties of the drug:
- kills pathogenic microorganisms (antimicrobial activity is higher than that of Miramistin);
- maintains a long-lasting antiseptic effect even upon contact with bloody and purulent secretions;
- used in low concentrations, which protects the oral mucosa from irritation;
- impossibility of overdose;
- affordable price.
Negative points include:
- weak or zero effect in the treatment of viral diseases, especially like herpes;
- bitter, unpleasant taste causes discomfort;
- Regular use leads to darkening of the enamel and surface of the tongue.
Can children rinse their mouths with Chlorhexidine?
Tooth extraction may also be required in childhood. Typically, this measure is required when baby teeth are loose, but in case of severe carious lesions, molars may also need to be removed. Preventive treatment with antiseptics in childhood is especially necessary. This is due to several factors:
- insufficient activity of the immune system to suppress the growth of pathogenic microorganisms;
- poor hand hygiene and non-compliance with sanitary standards;
- increased sensitivity of the gums and soft tissues surrounding the tooth to the effects of pathogenic bacteria and inflammatory processes.
Can children rinse their mouths with Chlorhexidine?
If necessary, Chlorhexidine can be used in childhood, but the rules of use will differ from the preventive treatment of adult patients. For children, it is recommended to dilute the drug with boiled water in a ratio of 2:1 (2 parts Chlorhexidine - 1 part water). You should rinse your mouth strictly under adult supervision and only if the child knows how to spit out the product and does not swallow it.
The number of procedures is also slightly reduced. The maximum permissible number of rinses in childhood is 2 times a day. The course of prevention depends on the age of the child. Approximate norms are presented in the table below, but they may vary depending on the condition of the oral cavity, the complexity of removal and other individual characteristics of the child.
Treatment of a child with the drug is allowed
Table. The duration of the course of use depends on the age of the child.
| Child's age | Course of use after tooth extraction |
| 2-5 years | 3 days |
| 5-8 years | 5 days |
| 8-14 years | 7 days |
What to do if the drug is accidentally swallowed?
During the procedure, it is necessary to avoid getting Chlorhexidine into the stomach, but if this happens, there is no need to panic. The need to take any measures depends on the amount of the drug that enters the stomach. If the volume does not exceed one sip, you can do nothing, but at the same time carefully monitor how you feel.
- What medicine is put into the hole after tooth extraction?
If pain or cramping occurs in the abdomen, it is necessary to rinse the stomach with warm soda or saline solution, and then take any sorbent drug, for example:
- "Neosmectin";
- "Smectu";
- "Filtrum-sti";
- Activated carbon;
- "Polysorb".
Activated carbon
The same steps must be performed if the amount of medicine swallowed is more than 10 ml. If you feel unwell, have intestinal or stomach cramps or signs of intoxication, you should consult a doctor.
"Chlorhexidine" is one of the most famous and affordable antiseptics used in dental practice. It allows for disinfection of the oral cavity after surgery and prevents pathogenic bacteria from entering the socket of the extracted tooth. If you use Chlorhexidine according to the regimen prescribed by your doctor, you can avoid serious complications, for example, purulent-infectious lesions of the periosteum or alveolitis. During use, it is important to follow the precautions described in the official instructions for the drug.
Type of gum after removal (normal) –
How can you determine that your gums are healing normally after tooth extraction? First, open your mouth wide in front of the mirror and see if the hole of the extracted tooth is covered with a blood clot. In the photo below you can see what the holes should look like immediately after removal and after different times.
Under no circumstances should the hole be empty. The latter may indicate that the blood clot has either already fallen out or has not formed at all (this is possible if the doctor used anesthetic solutions with a high vasoconstrictor content during anesthesia). In this case, you need to immediately consult a doctor again. Please note that normally the socket of each tooth will be covered with a dense blood clot (Fig. 5-6).
At first, the surface of the blood clot will be bright red, but within a few days it will become covered with a whitish or yellowish coating (this is fibrin). This is completely normal and does not indicate the development of inflammation. Next, gradual epithelization of the surface of the blood clot will occur (Fig. 7), until the usual gum mucosa appears on its surface. But if the hole is empty, there are food remains in it, there is pain and an unpleasant odor - these are signals of the development of inflammation. We hope that our article was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Higher prof. the author’s education in surgical dentistry, 2. Based on personal experience as a dental surgeon, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Outpatient surgical dentistry” (Bezrukov V.), 5. “Propaedeutics of surgical dentistry” (Soloviev M. .).