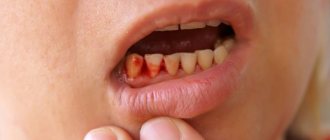
Every person has had an inflamed gum at least once in their life. This usually occurs due to brushing too aggressively, using a hard toothbrush, putting too much pressure on the soft tissue of the floss, or eating very hard foods. If the causative factor is eliminated, the gums quickly heal and the inflammation goes away. But there are situations when the gums near the crown of the tooth become inflamed, but there were no obvious reasons provoking this condition. In this case, you need the help of a dentist.
Causes of bleeding gums
If you notice your gums are bleeding, before you panic, first consider whether you might:
- mechanically damage the interdental spaces when using floss (dental floss). In this case, it is worth treating the oral cavity with an antiseptic solution of chlorhexidine 2-3 times a day, rinsing with calendula decoction
- replace a regular toothbrush with an electric one. Bleeding is normal the first few times you use an electric toothbrush. This usually goes away completely within 2-3 days. If not, contact your dentist, start rinsing with an antiseptic, and stop using the power brush until you receive further instructions from your doctor.
- Using an oral irrigator incorrectly. Often new owners of such an indispensable device as an irrigator immediately begin to treat the oral cavity with a high-pressure stream of water instead of allowing the tissues to adapt. In this case, it is worth temporarily filling the irrigator container with chlorhexidine, either pure or mixed with water, and cleaning at the minimum power level. Typically, symptoms should completely disappear within a couple of days.
Also, bleeding gums are not a rare occurrence in pregnant women as a result of powerful hormonal changes. During this period, you need to treat your teeth with increased attention and care.
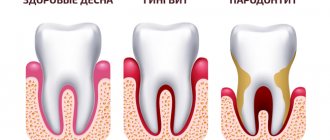
None of the above? Then there is a high probability of an inflammatory process in the tissues. In the early stages, you may notice slight bleeding and slight swelling - signs of gingivitis. Ignoring the symptoms can lead to the development of pain and the onset of suppuration, which will indicate the transition of the disease to a dangerous stage of periodontitis.
Why do my gums bleed when brushing my teeth?
Hormonal background
Hormonal changes (mostly affecting pregnant women and teenagers) are one of the many causes of bleeding gums. Dentists note: hormonal changes in the body are accompanied by changes in the chemical composition of saliva, which leads to rapid mineralization of plaque on the teeth.
Lack of vitamins
A deficiency of vitamins C or K also causes blood to appear on the gums. An insufficient amount of vitamin C (especially during seasonal vitamin deficiency, a decrease in general immunity) leads to rapid wear of blood vessels and bleeding gums, and the lack of vitamin K, responsible for blood clotting, depletes the gums and makes them extremely sensitive and loose.
Microflora
Bacteria inhabiting the oral cavity are responsible for the accumulation of dental plaque, which can, over time, with poor hygiene, become tartar, causing inflammation and bleeding.
Changes in the composition of saliva in the body against the background of periodontitis and gingivitis directly affect both the respiratory tract and the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Methods for treating bleeding gums
The treatment that's right for you depends on the cause of your symptoms.
As we have already mentioned, if you notice bleeding as a result of careless manipulations with floss when performing oral hygiene, changed your toothbrush, started using an irrigator, or are pregnant, you can fix the problem yourself. It is enough to rinse with antiseptic compounds and temporarily reduce the load.
In case of gingivitis, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible. The doctor will examine your teeth for tartar and plaque. Perhaps the problem will be solved after professional cleaning and removal of unwanted deposits in which bacteria multiply. Additionally, local anti-inflammatory drugs (Metrogil Denta, Cholisal) and chlorhexidine rinses may be prescribed.
If the gums are very inflamed and painful, more radical actions may be required:
- Surgical cleaning of periodontal pockets. This technique is called “curettage” and provides a closed type of treatment (without cutting the gums) if the pockets are not deep and an open one (with cutting the gums) if the closed one does not produce results.
- Gum plastic surgery. The procedure is used in advanced, especially severe cases of periodontitis. The doctor either removes excess tissue or, on the contrary, builds up the gum. The operation is low-traumatic and quite effective, especially in combination with treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs and (if necessary) antibiotics
Why does the gums around the crown become inflamed?
In addition to mechanical damage, the gums can react with swelling due to the irritating effect on it of chemicals contained in oral hygiene products - toothpaste, rinses.
However, swelling of the gums near the tooth under the crown can be caused by more serious reasons. For example, swelling may be a sign of:
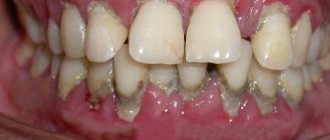
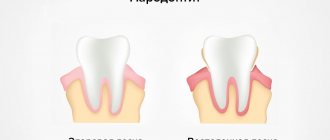
- Gingivitis or periodontitis. It usually appears due to poor oral hygiene, the presence of dental plaque, malocclusion, poorly fitting crowns, as well as hypovitaminosis and endocrine disruptions. At first, the gums swell and bleed, darkening of the gums around the tooth at the crown may be observed, and later suppuration and tooth mobility occur.
- Flux, or periostitis. This disease affects the hard periodontal tissues and, in particular, the periosteum of the jaw. Very often, tooth flux under the crown is a consequence of asymptomatic pulpitis or periodontitis. If the flux is not treated, there are two possible options for the development of the disease - involution of the flux and its spontaneous opening. In the second case, a fistula forms on the gum (tooth under the crown), through which purulent contents flow. In this case, the pain subsides, but the inflammatory process itself continues and without appropriate treatment, osteomyelitis of the jaw can form.
- Alveolar process abscess is another complication of pulpitis, periodontitis or caries occurring in the tooth under the crown. With this disease, the patient will complain not only of swollen gums above the crown of the tooth, but also of severe pain in the jaw, aggravated by exposure to heat, facial asymmetry, and unilateral enlargement of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes.
- Overloading a denture with irrational prosthetics can lead to the tooth crown moving away from the gum and food starting to get clogged under it. As a result, mobility of the supporting teeth appears, and the soft tissues of the oral cavity become inflamed (gingivitis).
conclusions
Carefully monitor the health of your teeth and oral cavity. Use dental floss and irrigator carefully. In case of gum swelling, pain and bleeding, it is better to immediately seek professional help. This will allow you to stop the problem in a timely manner and prevent it from developing into periodontitis.
Don't neglect professional teeth cleaning. Remove tartar and plaque at least once a year. More often if you have dentures, implants and/or smoke.
Strictly follow your doctor's instructions, especially with regard to taking antibiotics and using medicinal ointments and solutions.
If your teeth bleed when brushing
Bleeding gums occur due to gingivitis. In itself, it does not cause major problems, but it is the first symptom of the development of such a serious disease as periodontal disease. Bleeding primarily occurs when brushing your teeth or when you have to bite something hard. It is better to deal with this symptom as early as possible, before the next stage of the disease appears - exposure of the necks of the teeth.
How does the situation develop if nothing is done?
At first, when brushing your teeth, a little blood comes out of your gums. This usually begins after gum swelling has appeared. This is the stage of gingivitis. After some time, pain, loosening of the teeth and exposure of their necks appear. A full range of symptoms of periodontitis occurs. This already causes anxiety for the patient. In the absence of adequate treatment, the final stage occurs - periodontal disease. This disease leads to complete loss of teeth
How to treat bleeding gums?
The only treatment method is to remove tartar and plaque. It is best to start by ordering a professional ultrasound tartar removal procedure from your dentist. Then you need to purchase the softest and fluffiest toothbrush possible and thoroughly brush your teeth with it in the morning and evening for at least three minutes. Instead of tooth powder, it is better to use ash and rinse your mouth with hot water - you will immediately notice how much more effectively your teeth are cleaned with this method.
Treating bleeding gums at home
- First of all, it is necessary to remove tartar. For this purpose, use grated black radish with lemon juice, chew it thoroughly and brush your teeth with it for at least 3 minutes every evening. The second most effective remedy is a decoction of walnut bark - pour 2 tablespoons of dry bark into a glass of cold water, bring to a boil and boil for 15 minutes. You also need to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth for at least 5 minutes every evening.
- The second stage is removing inflammation from the gums. A decoction of sage or oak bark works best here. Two tablespoons of sage or 2 teaspoons of bark per glass of boiling water. Boil in a water bath for 10 minutes. Rinse your mouth every four hours if possible. It should be borne in mind that oak bark somewhat darkens the color of the teeth.
- For internal prevention of the disease, you need to eat at least 400 g of cottage cheese per week and every day - something with vitamin C (kiwi, a cup of rosehip decoction with sugar, lemon, black currant, etc.).
Prevention
According to US standards, you need to have professional ultrasonic cleaning of teeth to remove tartar at least three times a year. This is mandatory, but it should be borne in mind that such cleaning is not a panacea, since if you do not brush your teeth, the stone will form again within a week. Therefore, you need to thoroughly brush your teeth twice a day with a soft toothbrush, so that it is not scary to press it hard. It is better to use ash instead of powder and rinse your mouth with hot water. After cleansing, you can use one of the following: chew a slice of fresh ginger, rinse your mouth with a homemade lactic acid product, gargle with sage, or chew grated radish. It is better to alternate the product used from time to time.
Causes of bleeding
Most often, bleeding gums are caused by mechanical trauma or an inflammatory process. In most cases, inflammation is caused by microorganisms contained in dental plaque (plaque and tartar).
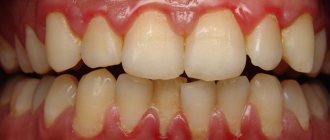
- gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, accompanied by bleeding and redness of the gums, most often occurring due to poor hygiene. Upon examination, you may see plaque and tartar in the gingival sulcus or pocket;
- Periodontitis is a gum disease that is fraught not only with bleeding and bad breath, but also with the loss of healthy teeth. With periodontitis, not only the gums are involved in the inflammatory process, but also the ligaments that hold the tooth in the bone and the bone tissue itself. In patients with periodontitis, in addition to the above symptoms, periodontal pockets, exposure of tooth roots, and tooth mobility are observed.
However, sometimes the cause of inflammation and bleeding gums can be problems not related to dentistry:
- gastrointestinal diseases - gastritis with the release of large amounts of acid, gallbladder diseases, etc.;
- problems related to blood composition. For example, anemia, hemophilia, blood clotting problems, as well as vascular fragility, which occurs for a number of different reasons;
- lack of vitamins - most often it is a lack of vitamin C;
- allergic reaction to medications, dental materials, and toothpastes.
Other causes of bleeding gums can be:
- inability to brush teeth properly;
- bad habits;
- untimely change of toothbrushes;
- overhanging edges of fillings and dentures;
- taking a number of medications.
Symptoms of diseases that cause bleeding gums
Since bleeding is associated with gingivitis and periodontitis, you should be aware of other symptoms of these diseases.
Signs of gingivitis
- Redness or bluishness of the mucous membrane
- Sore gums, especially when brushing
- Edema
- Unpleasant odor Signs of periodontitis
- All signs of gingivitis
- Loose teeth
- Exposure of necks and roots of teeth
- Fan-shaped divergence of teeth
- Suppuration from periodontal pockets