From this article you will learn:
- what is periodontitis - symptoms, photos,
- anti-inflammatory therapy regimen,
- modern methods of treating periodontitis.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
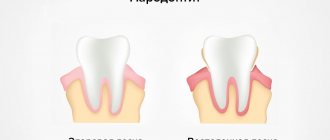
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the gums, which is accompanied by increasing destruction of the attachment of teeth to the bone tissue and soft tissues of the gums, which over time leads to tooth mobility. Periodontitis can appear in the area of only 1-2 teeth - in this case it is called localized, or it can be generalized (in the area of most teeth).
Most often, patients consult doctors with chronic generalized periodontitis, in which the gums of almost all teeth are inflamed. As a rule, most of these patients have a long history of self-medication of sore and bleeding gums (ie, symptoms of catarrhal gingivitis). Moreover, it is ineffective treatment or no treatment at all for gingivitis that leads to its gradual transformation into generalized periodontitis.
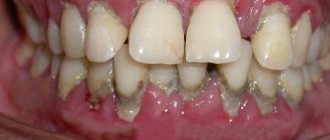
Periodontitis: generalized (Fig. 1) and localized (Fig. 2-3)
The causes of the localized form of periodontitis are local traumatic factors. This could be an overhanging edge of a filling or an artificial crown that injures the gums in the interdental space. The reason may also be “premature contacts” between the upper and lower teeth, which can appear either from natural causes or if the filling on the chewing surface or the crown is made a little higher than necessary.
Another common reason is when a dentist, when restoring a damaged tooth with a filling, incorrectly forms a contact point between the teeth in the interdental space. The lack of tight contact leads to constant food getting stuck in the interdental space and the development of inflammation. In the localized form (as opposed to the generalized form), symptoms of periodontitis occur only in teeth exposed to the traumatic factor.
What is periodontitis?
Periodontitis, or, as it is popularly called, dental periodontitis, is an inflammatory disease of the periodontal tissues that surround the tooth (gums, dental ligament and surrounding jaw bone). In professional terms, periodontitis is an inflammation of the ligaments of the tooth.
Periodontitis can be localized, that is, spread to the area of one or two teeth, or generalized, that is, affect most of the dentition. If a patient has periodontitis, it is usually chronic. Therefore, the main task of a specialist is to identify the cause of the disease, prescribe the correct treatment and, most importantly, prevent subsequent exacerbations and complications.
Treatment with folk remedies
Methods known to our grandmothers help strengthen the gums and relieve inflammation, especially at the initial stage of the disease.
The main thing to remember: alternative treatment must be agreed with the attending physician and carried out under his supervision.
The most effective means for treating gums are:
- Massage the gums using circular movements of the pads of the thumbs. You need to do it in the morning and evening for 5-10 minutes. To make the effect more noticeable, simultaneously with the massage, it is worth rubbing honey, sea buckthorn or fir oil into the soft periodontal tissues.
- Rinse. They are performed immediately after brushing your teeth with comfortable-temperature decoctions and tinctures diluted with water. To make them, they use calendula flowers, oak bark, string, celandine and pine needles.
- Applications. For them you can use honey, beeswax, sea buckthorn oil, Kalanchoe juice.
What are the signs of periodontitis?
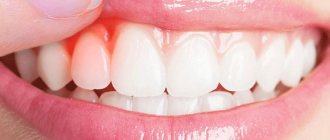
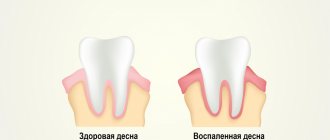
The initial signs of periodontitis are bleeding gums when pressing on them or when brushing teeth, bluish or red gums, and bad breath. Already in the later stages of the disease, tooth mobility and visible exposure of their roots appear, which indicates a severe and advanced form of the inflammatory process. When periodontitis becomes chronic, the tissues surrounding the tooth are “reabsorbed” and pathological gum and bone pockets are formed. As a result, the tooth gradually becomes loose and falls out.
It is necessary to distinguish the exposure of roots during periodontitis from the so-called gum recession - a decrease in the height of the gingival margin, as a result of which the root of the tooth is exposed, in other words, “sliding” or gum atrophy. Unlike periodontitis, recession is not caused by inflammation and does not entail the formation of pathological pockets and loosening of teeth. Additionally, in most cases, gum recession can be successfully treated.
Symptoms
- Inflammation of the gums;
- hyperemia (redness) of the mucous membrane, swelling, reaction to temperature stimuli;
- sore gums;
- discomfort, bleeding gums when chewing, oral hygiene;
- detachment of the gum from the tooth wall;
- formation of periodontal pockets;
- abundant plaque and tartar around the tooth;
- pus from the gums;
- loosening of the gum edge;
- exposure of tooth roots;
- tooth mobility;
- inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes
Symptoms of periodontitis vary depending on the extent of the inflammatory process. The more severe the stage of the disease, the more pronounced the symptoms. The disease does not occur suddenly; the early stage of periodontitis is catarrhal gingivitis - inflammation of the gums, not accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane.
What are the causes of periodontitis?
Understanding the causes of the disease is a very important point, which helps the doctor correctly determine how to treat gum periodontitis. The disease can be triggered by both general and local factors. Common causes include diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diseases associated with pathology of the endocrine system, some gynecological and urological diseases, sexually transmitted infections, and a weakened immune system. Local, or local, factors are missing teeth, malocclusion, incorrectly installed fillings or crowns, which mechanically irritate the gums and create conditions for the accumulation of bacterial plaque. A significant role is played by the specific microbial flora of the oral cavity, which occurs in some patients and causes periodontitis. But the main factor in the development of periodontitis is poor oral hygiene.
Causes of periodontitis
A decisive role in the development of the disease is played by pathogenic microorganisms in dental plaque, which contribute to gum inflammation. The accumulating bacterial plaque hardens. Tartar builds up and penetrates deep into the gums, causing the mucous membrane to begin to peel off from the tooth, creating a free space that is gradually filled with pathogenic bacteria. Gingivitis develops, which without proper treatment quickly transforms into acute periodontitis.
Factors that provoke the development of periodontitis also include:
- regular injury to the gums due to incorrectly installed dentures and orthodontic systems;
- incorrect occlusion;
- accumulation of food particles and plaque under prosthetic and orthodontic structures;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- decreased immunity;
- physical trauma to teeth (impact);
- bruxism.
The development of chronic periodontitis can be influenced by problems with the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine disorders, blood diseases, vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorders, insufficient chewing load (the predominance of soft foods in the diet), autoimmune pathologies, and allergies to certain medications.
How is periodontitis diagnosed?
It is possible to determine whether a patient has periodontitis or not already at the first appointment, focusing on his complaints and the condition of the oral cavity. Moreover, when diagnosing the disease, special tests are used, the most popular of which is the Parma index. It works as follows: a special Schiller solution is applied to the gums, which reacts to unhealthy tissues and colors them in a bright color, revealing the source of inflammation. There is also an index that determines the level of bleeding, and a Russell test that reveals the condition of not only the gums, but also the bone tissue.
X-ray studies, which determine the degree of the disease that has arisen, are the main ones in the diagnosis of periodontitis. For such a study, you can use a radiovisiograph (a device for conventional targeted X-rays), or an orthopantomograph (an extraoral device that can take a picture of both jaws at once). However, the most informative method is considered to be extraoral cone-beam computed tomography, which allows layer-by-layer examination of each piece of the jaw and tooth in three-dimensional format.
Currently, the Florida probe computer diagnostic technique has appeared, which allows you to most accurately determine and record the depth of periodontal pockets - the main pathological manifestation of periodontitis. The examination is easily tolerated by patients and helps the doctor prescribe appropriate treatment.
For periodontitis, a microbiological study is also carried out, with which you can study the microflora of the oral cavity and determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics for a more accurate selection of drug treatment.
Another mandatory test is a blood test. It allows you to identify the cause of the disease, which may be either the initial stage of diabetes or a chronic infectious process in other organs and systems, as well as disorders associated with hormonal levels and metabolism.
In the process of diagnosing periodontitis, consultation with related specialists is often required to identify and treat concomitant diseases.
Diagnostics
- Taking anamnesis;
- dental examination with measurement of the depth of periodontal pockets (periodontogram);
- orthopantomogram (OPTG), CT;
- rheoparodontography (assess the tone of blood vessels);
- Schiller-Pisarev test;
- microbiological studies (PCR);
- blood tests (general, sugar).
Differential diagnosis of periodontitis is carried out with gingivitis, eosinophilic granuloma of the jaw, periodontal changes in Lefebvre-Papillon syndrome. What examination methods will be required depends on the form and severity of the disease.
How is periodontitis treated?
Successful treatment of periodontitis can only be achieved in a well-coordinated team of “doctor plus patient”. Much depends on the doctor, but even more depends on the patient himself. The doctor is responsible for the treatment, and the patient is responsible for maintaining the result, because periodontitis is a chronic disease.
Treatment methods for periodontitis are divided into medicinal and surgical. In case of minor inflammation caused by dental plaque, the doctor thoroughly cleans the teeth, eliminates conditions that contribute to the retention of microbial plaque, polishes the surfaces of the teeth and applies a therapeutic bandage with medication to the inflamed area. If a deep periodontal pocket forms and severe pain occurs, the patient may be prescribed antibiotics. When treating severe periodontitis, it is necessary to resort to more serious (surgical) procedures, such as curettage and flap operations. But in any case, periodontitis requires complex treatment, including professional hygiene, drugs for local and internal use, and, if necessary, surgical procedures.
There is also a hardware method for treating periodontitis - Vector. The method involves using ultrasound in combination with medications aimed at fighting microbes and stimulating healing. The Vector device is used both as an independent technique and in combination with surgical treatment.
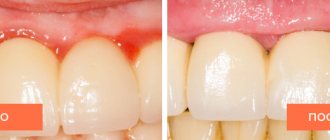
Is it possible to restore gums?
Periodontitis is a disease that greatly impairs the aesthetics of a smile. That is why dentistry has long and successfully used a surgical method of gum restoration - gingivoplasty. With its help, you can change the height of the gum, improve its structural condition, restore atrophied tissue or, conversely, remove excess.
Contraindications to the operation are: diabetes mellitus, cancer, decreased blood clotting, and inability to use anesthesia.
In other cases, after carrying out anti-inflammatory procedures and achieving stable remission, you can safely start a conversation with your doctor about gingivoplasty.
What are the surgical treatments for periodontitis?
Surgical treatment of periodontitis is important in the later stages of the disease with severe tooth mobility and deep periodontal pockets. This is, first of all, a curettage procedure, which involves removing dental plaque and pathological granulation tissue from under the gums. If the depth of the periodontal pocket is up to 4 mm, closed curettage is performed without opening the gum; if it is more, open or flap surgery is performed, when it is necessary to detach the periosteal flap, fold it back and clean out the pocket. This procedure is always performed with pain relief and is well tolerated by patients.
In addition to the procedures described above, splinting is performed for periodontitis, which secures loose teeth.
Classification
Periodontitis is classified according to location, nature of the course, and severity.
According to the nature of the flow
There are acute and chronic forms. In the first situation, the signs of periodontitis are pronounced, the gums are loose, bleed, and hurt. If the patient does not consult a doctor or ineffective treatment is prescribed, the disease takes a chronic course. In the chronic form, the symptoms are smoothed out, there are no acute signs of inflammation, but the consequences are more severe. Chronic pathology is characterized by periodic exacerbations, when the symptoms become pronounced.
By localization
According to the distribution of the pathological process, periodontitis is divided into:
- Localized
(focal) - occurs in a small area, in the area of 1 or several teeth. - Generalized
periodontitis is inflammation of all or most teeth in a row.
The symptoms of localized and generalized forms of the disease are no different, the only difference is in the number of teeth around which the pathological process has spread.
Degrees of periodontitis
- Mild
– fiber disintegration of the compact plate, reduction of the interalveolar septum to 1/3 of the length of the tooth root, signs of osteoporosis, slight tooth mobility, periodontal pockets of 2.5-3.5 mm. - Medium
– the depth of periodontal pockets increases to 5 mm, moderate tooth mobility is observed (grades I-II), bone atrophy around the teeth reaches 1/2 of the roots. Exposure of the necks and roots of the teeth or inflammatory growth of the gums occurs, abscesses (abscesses in the gums) can form. The teeth begin to “diverge” under chewing pressure, and the gingival margin becomes deformed. This is especially noticeable in the area of the front incisors. The gums bleed when chewing or brushing teeth, the necks of the teeth are exposed, and react painfully to temperature stimuli. - Severe
– symptoms increase, exacerbations of chronic periodontitis in adults are accompanied by the formation of abscesses, severe swelling of the gums, and pain. The depth of periodontal pockets reaches 6 mm, right up to the root apex. The interdental spaces increase, there is strong tooth mobility (II-III degrees), bone resorption, up to complete resorption of the alveolar septum.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, the disease progresses differently. Aggressive forms of periodontitis are characterized by rapid, almost rapid destruction of periodontal tissue, loosening of teeth, and their painless loss. In another part of patients, the disease progresses slowly, with occasional exacerbations, and long remission.
The most severe form is necrotizing periodontitis.
, in which the gum tissue stops receiving nutrition, blood circulation in them stops, and necrosis of the periodontium, periodontal ligaments, and alveolar bone occurs. This form of the disease occurs in patients with severe immunodeficiency conditions (AIDS, DiGeorge syndrome, SCID, etc.).
Is it possible to eliminate periodontitis with a laser?
Laser treatment of periodontitis is one of the most effective and minimally invasive ways to combat the disease, which is one of the stages of complex treatment. The laser has cleansing and antibacterial properties. During the procedure, each periodontal pocket is treated for a certain time, sufficient for the laser light beam to destroy pathogenic bacteria. The procedure is bloodless and virtually painless. However, a good effect can only be obtained with an integrated approach to the treatment of periodontitis.
What contributes to the development of periodontal disease?
Factors contributing to the development of the disease:
- vascular disease and a tendency to form plaques;
- hormonal disorders;
- weakened immunity;
- side effects of medications;
- smoking;
- lack of vitamins;
- structural features of the gums and jaw.
Symptoms to watch out for:
- Unexplained pale gums
- Redness
- Visible lengthening of the tooth due to the opening of the neck
- Increased sensitivity to hot and cold
- Periodic bleeding.
- Unexplained itching in the gums
- Loosening of teeth that begins with slight mobility.
Any of the above symptoms is a reason to consult a dentist. He will make a diagnosis and develop a treatment plan for periodontal disease. Whether it will be carried out entirely at home or with mandatory visits and medical procedures depends on the actual stage of the disease.
Is it true that periodontitis can be cured with implantation?
Implantation is a method of combating not periodontitis itself, but its consequences. At a later stage of the disease, teeth become loose and fall out, so they have to be replaced with implants. It should be understood that dental implantation for periodontitis has its own difficulties and limitations, since bone tissue is absorbed in this disease. Its sufficient volume is the main condition for successful installation of implants. If periodontitis is in an advanced stage, implantation can be very difficult or even impossible due to a lack of bone volume. That is why patients should begin treatment as early as possible in order to do everything possible to preserve their teeth, and if they are lost, do not miss the opportunity to restore them with implants.
In any case, before installing implants, it is necessary to transfer periodontitis to the stage of remission (stabilization) or, if possible, eliminate the cause of its occurrence.
How to restore teeth with severe periodontitis
In severe cases of the disease, the risk of losing a tooth or an entire row of teeth is very high. Tooth extraction for periodontitis is indicated in cases of excessive mobility, when the unit is barely held in the bone and moves in all directions around its axis. If it is impossible to save the tooth, orthopedic treatment is carried out - prosthetics supported by natural teeth or implants.
For single defects or restoration of a tooth segment, two-stage implantation with delayed loading is used. Implants are implanted after a course of gum treatment and restoration of bone volume. Bone parameters are restored through osteoplastic surgery. After new bone tissue is formed (after 6 months), implants are implanted, the prosthetic system is fixed after they have fused with the jaw bone ( after 3-6 months
). Treatment may take about a year.
In case of complete edentia, one-stage implantation methods with immediate loading demonstrate high efficiency. The ability to install implants in deep bone layers that are not subject to inflammation allows you to avoid osteoplasty and sinus lifting. Treatment will take no more than a week.
What consequences can untreated periodontitis lead to?
Loss of teeth
The advanced stage of the disease destroys the soft and hard tissues around the teeth, which leads to their loss.
Deterioration of conditions for implantation
As mentioned earlier, with severe periodontitis, the volume of the jaw bone is significantly reduced, which makes it difficult to install implants, requiring preliminary bone growth, and in extremely severe cases makes implantation impossible.
The occurrence of other diseases
Periodontitis contributes to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diseases of the lungs, heart and even the formation of blood clots.
Types of periodontitis
By place of development:
- localized - a small lesion affecting only one tooth; often results from mechanical damage to tissue;
- generalized - damage to several teeth also affecting the gingival and bone tissue.
According to the nature of the course:
- acute - characterized by sudden pain attacks and rapid development of symptoms;
- chronic periodontitis is the transition of untreated acute periodontitis to a chronic form, in which pain and other symptoms practically disappear, but the disease progresses and deforms the tissue.
How to avoid further exacerbation of the disease?
This is where the patient becomes the main member of a well-coordinated doctor-patient team. To maintain the results obtained after treatment of periodontitis, you should brush your teeth correctly and regularly, following all the recommendations of the treating dentist, since with periodontitis, individual oral hygiene differs from usual. In particular, along with a regular brush and paste, there is a need to connect additional hygiene products: dental floss, various brushes for teeth, an irrigator, etc.
In addition, it is necessary to come to the dentist for professional cleaning at least once every six months, and for people with chronic periodontitis even more often - once every three months. Good hygiene is an excellent prevention of periodontitis and the only way to maintain the results of treatment.
Prevention of periodontitis
The best prevention of periodontitis is proper oral care. You need to brush your teeth at least 2 times a day: before breakfast and before bed. Moreover, the procedure should take at least 3 minutes, and the main movement when cleaning is from the root to the cutting edge of the tooth. Don't ignore dental floss. They perfectly clean the interdental spaces and prevent the development of pathogenic bacteria.
If the disease has already manifested itself, pay attention to your toothbrush. Her stubble should be stiff. And even if at first brushing your teeth with its help seems uncomfortable, over time your gums will get used to it. You need to change your toothbrush every 1.5 months.
Author: Maria Kozodaeva Candidate of Medical Sciences. Dentist-therapist, endodontist, periodontist, implant surgeon. Work experience more than 11 years.
The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
How much does it cost to cure periodontitis? What does the cost consist of?
The price for periodontitis treatment depends on the complexity of the disease, whether surgical procedures will be performed and to what extent.
Important!
Folk remedies in the form of all kinds of herbal infusions do not help with periodontitis. They can bring temporary relief and mask the problem, but mouth rinses cannot radically solve it. Neither home treatment nor the miraculous toothpaste from TV commercials will help get rid of periodontitis. Rinses and toothpastes are just one of the auxiliary components in complex treatment. If you have periodontitis or suspect it, contact the dentist for timely diagnosis, since it is in the early stages of the disease that doctors have a lot of opportunities to help you!
Diagnosis of the disease
The main diagnostic method for suspected periodontal disease is measuring the depth of the gap between the gum and tooth. In a healthy person it does not exceed 1-2 millimeters. The procedure is carried out using a periodontal probe, a thin instrument with millimeter notches.
If the process is generalized, the doctor measures the periodontal pockets of each tooth, records the obtained indicators and draws up a periodontogram. In the future, it will make it possible to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment or, conversely, to detect the progression of the disease in time.
X-ray examination is important for diagnosing periodontitis: panoramic X-ray or layer-by-layer scanning. It allows you to identify loss of bone tissue and its sclerotic changes.
In very severe cases, the doctor may refer the patient for further examination: measure the degree of hypoxia in the gums, determine the quality of the periodontal microvasculature, examine bone tissue for density.
Treatment of gums at home
How to treat inflammation? There are many ways to treat gum inflammation at home. Dentists usually recommend antiseptic drugs with anti-inflammatory effects. The optimal treatment regimen is prescribed by the dentist after diagnosis. Let's consider the most effective treatment options.
Rinse with solutions
Rinsing with special solutions helps to quickly get rid of pain and stop inflammatory processes occurring in soft tissues. The compositions of the solutions disinfect the surface of the gums, destroying pathogenic bacteria. It is necessary to rinse your gums after every meal, 2 to 4 times a day. Some drugs in this group are used in pure form, others must be diluted in water.
To treat inflamed gums, dentists usually prescribe the following solutions:
- Furacilin;
- Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin;
- Rotokan;
- Stomatophyte;
- Malavit;
- Listerine;
- Chlorophyllipt.
The listed drugs are usually used to prevent diseases of the oral cavity, reduce pain and reduce inflammation, but do not apply to independent means of treatment. Therefore, rinsing is usually prescribed in combination with other procedures.
Teeth in danger: how to recognize the disease
Thanks to advertising, even children know about caries. But periodontal diseases are still a closely guarded mystery. Let's eliminate this gap. Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the tissue around the tooth and gums. As a result, loose teeth and other unpleasant “bonuses” appear.
Periodontitis - symptoms:
- gums bleed, especially under stress (chewing hard food, brushing);
- sensations of itching and pulsation under the gums;
- bad breath even after hygiene procedures;
- the mucous membrane around the teeth changes color;
- dark hard deposits on the enamel;
- periodontal pockets and tooth mobility appear.
Signs of the chronic form:
- inflammation and swelling of the gums;
- the mucous membrane becomes bright red;
- discharge of pus from periodontal pockets;
- throbbing severe pain;
- weakness, general malaise, possible fever.
We continue to understand the features of the disease: to understand whether you belong to the “risk group”, you need to know where gum inflammation comes from.
Periodontitis - causes:
Insufficient oral hygiene is the most common reason. Residues of food, falling under the gums, provoke the formation of microbes and the development of inflammation.
Food poor in vitamins and microelements.
- The predominance of soft food on the menu. The gums do not receive the necessary “massage” and there is insufficient blood flow.
- Complications of gingivitis and stomatitis.
- Weakened immunity, chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus).
- Very tight fit of teeth to each other (crowding).
- Allergies to medications and chemicals.
It’s simply amazing when some patients want to get rid of an illness that takes years to develop in a few days. People ask how to treat periodontitis with folk remedies and sincerely believe that this is a panacea. We responsibly declare that “grandmother’s spells”, miraculous rinses and ointments will at most ease the pain, but will not stop the development of the disease.
Professional dentistry involves complex treatment of periodontitis - more complex and lengthy, but effective.
- Consultation with a periodontist is the first step. The doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and determine a further treatment plan. After the x-ray diagnosis, the specialist will be able to answer the questions: is it possible to save the teeth or will some have to be parted with;
- will tell you how to treat periodontitis , how much the procedure will cost;
- coordinates treatment and prosthetic options;
- will determine the sequence of methods in the clinic.