Do you want to have healthy teeth and a beautiful smile? Monitor the condition of your gums. Soft tissues perform many important functions, so they must be protected. Proper nutrition, careful grooming and regular dental checkups significantly reduce the risk of developing gum disease.
However, gingivitis, periodontitis and other diseases are not the only causes of gum inflammation. This disorder can also be a consequence of a tooth bruise. Let's look at what leads to injuries and what complications can arise.
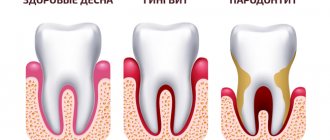
Dental periodontitis - what is it?
Periodontium refers to the whole complex of tissues responsible for tooth retention: connective fibers, blood vessels, periodontium, gums, canals and jaw bone. Periodontitis is an inflammation of the gum tissue, which quickly affects the rest of the complex. As a result, the dentogingival connection is disrupted and the tooth falls out. Periodontitis is a very common disease that affects more than 95% of the world's inhabitants in various stages: from the rudimentary form of periodontitis to advanced, untreatable.
It is believed that most often the pathology manifests itself in men and women aged 30 to 40 years and in adolescents 16-18 years old. However, the disease can affect anyone, regardless of gender and age, if you do not monitor the condition of your oral cavity and postpone a visit to the dentist. Periodontitis can be treated only in the early stages; when it becomes chronic, no dentist, even the most modern, can cope with it, since the tissues have undergone irreversible changes.
Mechanical damage to the gums: how to treat
Damage to the gums is a serious problem, which in some cases requires the intervention of a specialist. It is better not to self-treat gum damage. But you can familiarize yourself with general recommendations on how to behave immediately after an injury:
- Use an antiseptic solution and rinse your mouth twice a day
- Take painkillers
- Eat on the other side so as not to provoke an attack of pain
- If possible, consult a dentist as soon as possible to avoid suppuration and other complications.
Etiology of periodontitis
Periodontitis can be caused by various factors.
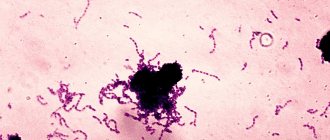
- Microbes.
The oral cavity of any person is inhabited by pathogenic microorganisms that do not cause harm if proper nutrition and hygiene are observed. But, if the patient constantly consumes carbohydrates and neglects to use dental floss, bacteria actively develop and gradually affect the enamel, dentin and reach the periodontal tissues. - Genetic predisposition.
If for many generations all family members have suffered from this disease, there is a high probability of adopting this predisposition. Heredity plays a big role in the development of gum periodontitis, even if a person carefully monitors hygiene and eats right. - Mechanical damage to the gums.
Tissue bruise due to negligence, an incorrect bite, in which increased pressure is applied to a specific area of the gum, or an oversized filling, due to which the tooth puts increased pressure on the gum and damages it. - Systemic diseases.
Dental diseases and periodontitis can cause pathologies not related to the oral cavity, such as vegetative-vascular dystonia, HIV, diabetes mellitus, hypertension and gastrointestinal diseases. - Autoimmune diseases.
Reduced immunity, disruption of the endocrine system, hormonal imbalances during pregnancy. - Poor quality dentist work.
Tissue damage during treatment, an unsuitable crown, incorrectly installed braces and other tissue injuries due to the fault of the doctor can provoke periodontitis.
Among the given factors are microbial causes of the development of periodontitis, and microbes are known to be transmitted from one person to another. So is periodontitis contagious? No, directly, for example, by airborne droplets or through saliva, it is impossible to become infected with the pathology, and every person has microbes that provoke the disease - even if periodontitis bacteria are transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person, the microbes will not develop without additional favorable circumstances: poor oral hygiene, gum injuries, predisposition or concomitant diseases.
Acute and chronic injuries
Acute gum injuries include injuries resulting from soft tissue injury:
- Too hard bristles of a toothbrush
- Fish bone
- toothpick
Bruised gums are possible from falls and fights. Thermal burns are also possible if you consume too hot food or drink.
Chronic injuries include those that a person receives as a result of prolonged exposure to irritating agents on soft tissue:
- Food constantly stuck between teeth
- Poor quality filling that extends beyond the tooth
- Orthodontic devices (braces, plates)
- Poorly fitted clasp on a prosthesis
- Edges of a crown on a tooth
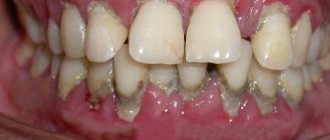
Mechanical injuries may be accompanied by slight bleeding. And with chemical and thermal injuries, erosion forms at the site of damage. With chronic injuries, purulent discharge may form on the gums. In advanced cases, surgery may be required. But more often local treatment is enough. Minor injuries can be treated with special healing balms prescribed by the dentist.
Symptoms of periodontitis in adults and children
Typically, the signs of periodontitis vary depending on the stage of development of the disease, but there are also general symptoms characteristic of the entire period of pathology:
- unpleasant constant bad breath, plaque and tartar are associated with the active activity of bacteria;
- bleeding and brighter gum color due to tissue inflammation;
- increased sensitivity of teeth, pain when chewing;
- thick viscous saliva;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- headache, weakness and lethargy.
Stages of periodontitis
With each stage, dental periodontitis develops more strongly. Unfortunately, most often patients consult a doctor already with a severe form of the disease.
Mild periodontitis
There is bleeding of the gums when brushing teeth, small periodontal pockets up to 3 mm deep, slight swelling of the gums and discoloration - the tissues look loose and slightly blue. The initial stage is almost painless and can be treated in just a couple of visits to the dentist.
Moderate periodontitis
The gums bleed almost constantly, and small purulent discharge appears. Gum pockets enlarge and expose the roots of the teeth, and the interdental spaces widen. The patient feels the tooth bursting and increased pressure on the gum tissue. It is difficult to cure moderate periodontitis, but it is quite possible if you make an effort and follow the doctor’s instructions.
Severe periodontitis
The gums are completely weakened, the tissues are loose, there is no swelling. Severe tooth mobility and even tooth loss. Bone tissue with severe periodontitis becomes thinner and atrophies. The entire complex is affected - ligaments, muscles, periodontal tissues and blood vessels, and nutrition of the tooth stops. The only thing a specialist can do at this stage is to relieve gum inflammation and recommend tooth extraction for prosthetics.
Forms of periodontitis
Types of periodontitis are classified into groups according to different criteria.
By place of development:
- localized - a small lesion affecting only one tooth, and sometimes part of the tooth, for example the root; most often occurs due to mechanical damage to tissue;
- generalized - the damage spreads to a group of teeth, gum and bone tissue, so it seems that half of the jaw hurts; A common cause is the development of bacteria and reduced immunity.
According to the nature of the course:
- acute - pain during periodontitis occurs suddenly, symptoms develop rapidly;
- chronic - advanced periodontitis of the acute stage becomes chronic, pain and other symptoms practically disappear, but the disease continues to progress and destroy tissue.
Preventive measures
It is rare to avoid gum injury under certain circumstances, but there are some preventive measures you should know:
- Try to eat carefully. Without being distracted by conversations or watching movies. This will minimize the likelihood of mechanical injury or burns.
- Teeth should be treated on time. Immediately after the onset of painful sensations, you should consult a dentist.
- Prosthetic procedures take place in reliable and certified clinics.
- Do not self-medicate under any circumstances; do not take antibiotics or other serious medications without a doctor’s prescription.
- Try to brush your teeth properly. If necessary, use a soft-bristled brush.
Exacerbation of periodontitis
The disease does not occur in isolation; periodontitis affects the condition of the entire organism. Even if the pathology has passed from an acute form to a chronic one and it seems to the patient that the pain has gone away and the illness has receded, the destructive effect of the inflammatory process still continues. And the advanced chronic stage can not only worsen, but also cause severe complications of periodontitis:
- osteomyelitis - inflammation of bone tissue;
- abscess and phlegmon - the formation of abscesses and the spread of pus through the tissues;
- lung diseases - pathogenic bacteria from the oral cavity enter the lungs when breathing;
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels - a long-term inflammatory process affects the functioning of the heart.
Diagnosis of periodontitis
Diagnostics includes a visual examination to determine the presence of problems and analysis of complaints to make a preliminary diagnosis. Then the patient is sent for additional examination:
- orthopantomogram - a circular image of the entire jaw;
- X-ray - X-ray of periodontitis on a specific tooth using a targeted image;
- periodontogram - measuring the depth of periodontal pockets;
- urine and blood analysis - determination of infections and diseases in the body.
The symptoms of the disease are similar to those of other dental pathologies; the doctor’s task is to make an accurate diagnosis for effective treatment.
- With periodontal disease, there is no bleeding, swelling of the gums and periodontal pockets, there is no inflammation, since the main cause is age-related changes, diabetes mellitus and cardiac dysfunction. Read more about periodontal disease in a separate article.
- With gingivitis, periodontal pockets and tooth mobility are not observed, there is no exposure of the roots, and inflammation affects only the gum tissue. Find out about the symptoms of the disease here.
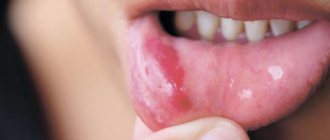
- Stomatitis is accompanied by plaque on the tongue and ulcers on the mucous membrane, bleeding and inflammation of the gums, tooth mobility and exposure of the roots are absent. About the types and signs of the disease in a separate article.
Treatment of periodontitis
Treatment of periodontitis in the early stages consists of removing plaque and tartar, cleaning periodontal pockets and drug therapy: local treatment of tissues with anti-inflammatory drugs, taking antibiotics and strengthening the immune system.
Moderate to severe disease requires complex therapy for periodontitis. In addition to sanitation of the oral cavity and taking medications, it includes splinting teeth to keep them from moving, surgery to remove pus and affected tissue, consultation with a therapist, immunologist and gastroenterologist to prevent relapse; in the case of an advanced form of the disease - examination by a prosthetist and subsequent restoration of lost teeth using crowns. Read more about the treatment of periodontitis in our article.
Dentists always aim to preserve the patient’s natural teeth, but in cases of severe periodontitis, often the only solution is tooth extraction. You shouldn’t let your oral cavity reach this state; seeing a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease gives you a 100% chance of recovery—the early stages of periodontitis can be treated quickly and without complications. And regular visits for preventive examinations completely exclude the occurrence of any dental diseases.
About gum damage in a child
Children can often damage their teeth and gums due to their active lifestyle. Parents should always pay great attention to proper teeth cleaning. Quite often, young children injure themselves with toothbrushes. In most cases, there will be a slight bruise that will go away on its own over time. If an injury occurs as a result of a blow or fall, bleeding comes from the gums, and the tooth is noticeably loose, the first thing to do is contact a pediatric dentist.
Young children are not prescribed “adult” drugs, so you should not try to cure a child by simply giving him an anti-inflammatory drug. Under no circumstances should you risk the health of children whose immune systems are not yet stable. Even if only the mucous membrane is visually damaged and the tooth is intact, this does not mean that the root or nerve of the tooth is not damaged. A doctor's examination is necessary to close any access of infection through the damaged area. Treatment of gum injuries in children begins with a visual examination and is carried out taking into account the intensity of the damage. In controversial situations, the pediatric dentist may prescribe additional tests, for example, computed tomography. Remember, regular preventive examinations for children and adults always contribute to oral health.