I. V. Zelensky, chief physician of the children's dental clinic, applicant for the Department of General Dentistry and Pediatric Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "Stavropol State Medical University" of the Ministry of Health of Russia
B. B. Sysuev Ph.D. Sc., Associate Professor, Department of Pharmacology, Pyatigorsk Medical and Pharmaceutical Institute, Volgograd State Medical University, Ministry of Health of Russia
V. A. Zelensky , Doctor of Medicine, Professor, Head of the Department of General and Pediatric Dentistry, Stavropol State Medical University, Ministry of Health of Russia
A. A. Dolgalev Doctor of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of General Dentistry and Pediatric Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "Stavropol State Medical University" of the Ministry of Health of Russia
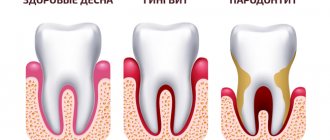
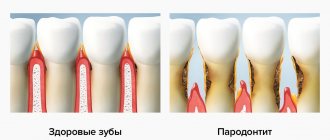
Periodontal pathology and dental caries are the most common dental diseases. The clinical course of periodontopathy has characteristic features: a latent period of development in the initial stage, then an acute course, but more often chronic with regular exacerbations. In the initial stage, periodontal pathology is difficult to diagnose, since the symptoms are not clearly expressed, and in the chronic course of the process, stopping it is associated with certain difficulties. Severe forms of periodontitis, leading to tooth loss, are observed in 15–20% of middle-aged people (35–44 years).
The basic stage of treatment of periodontal diseases is therapeutic treatment without the use of surgical methods. A significant place is given to drug therapy, in particular local, using antiseptic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and desensitizing drugs. Medicines that normalize microcirculation and tissue metabolism, enhance regeneration, immunomodulation, have sorbent and antioxidant activity, etc. are also widely used. The clinic of periodontal diseases - features of etiology and pathogenesis, anatomical and physiological structure of tissues and the course of the pathological process - determines the choice of dosage forms and bioactive components to optimize treatment. The permanent search for auxiliary substances that can increase the effectiveness of treatment of periodontal pathology is very relevant.
Purpose of the study: to conduct a scientific analysis of the features of the use of existing dosage forms, medications and medical devices used in the treatment of periodontal diseases.
Introduction
The information world is very huge. Each of us is haunted by a million points of view
for any problem in any field of knowledge, you just need to ask a search query. The same thing happens in medical circles on the Internet - discussions of health problems are widely represented by both patients and doctors and often reach the point of absurdity:
For example, in questions:
- loosening of the tooth,
- exposure of the neck of the tooth,
- why are my gums and teeth exposed?
that is, in situations where the gums on a tooth have receded, patients are always confused: they have periodontal disease
, then suddenly it changed to
periodontitis
, then periodontal disease returned again. And the search for an answer to the question becomes endless.
The problem of “how to treat periodontal disease” is picked up by doctors who only add fuel to the fire by recommending medications and even folk remedies for periodontal disease, without having sufficient competence to do so.
Let's consider these points of view professionally, and try to convey one simple truth, which for the vast majority of patients (and even some doctors) will be a revelation: the diagnosis of periodontal disease of the gums
» —
does not exist
.
An expert point of view is expressed by the famous periodontist, Doctor of Medical Sciences Laura Mikhailovna Tebloeva:
As a rule, for patients who come to me and say: “I have periodontal disease,” I always clarify - did you make this diagnosis yourself or did you see a doctor? Often patients answer that they have this information from their doctor. It turns out that the patient did not read somewhere and determine the diagnosis of “periodontal disease” for himself, but, unfortunately, such a diagnosis was made by a doctor.
What to do if your denture rubs your gums
Discomfort, burning, and pain should not be tolerated; you should immediately contact an orthopedist. Inflammation of the gums under the prosthesis causes improper fitting, unreliable fastening, periodontal disease, as well as:
- Poor hygiene.
Whether it is a complete denture or a partial one, care for the oral cavity and the product itself must be thorough so that pathogenic microflora does not provoke disease. - Refusal to sanitation
of the oral cavity and dental treatment before prosthetics. Plaque and carious cavities are breeding grounds for microbes, so professional cleaning and treatment are prerequisites for a positive result. - Allergic reactions
. If acrylic is used in the design, then the symptoms may be a manifestation of an allergy to the monomers that are part of it.
First you need to eliminate the cause, and only then adjust the prosthesis; only an orthopedic doctor can do this professionally.
Always treat gum problems
When a patient comes to the doctor, he complains about something. What symptoms does he see a doctor with before receiving a diagnosis of periodontal disease? What worries him?
Literally, patients tell the doctor this: my gums have sagged, my gums have become exposed, my lower gums have receded. And for some reason the symptom of gum subsidence automatically means that the patient has the so-called. periodontal disease.
More experienced patients, who have already heard a lot of professional terms, who delve into the professional colloquial language of doctors, say this: “The necks of the teeth have become exposed a little, the teeth have become a little higher.” But, according to statistics, most patients complain about sagging gums.
And so, when patients come to the doctor with complaints about the problem of exposed tooth necks, the doctor diagnoses them with periodontal disease. Of course, he begins to treat them. And to treat it specifically for periodontal disease.
But time passes, money also goes away, and the question of why the gums recede and the necks of the teeth become exposed, why the gums recede, has not been resolved. And the patient still has periodontal disease.
Causes of periodontal disease
Most often, there are several reasons for the appearance of the disease, one of which is a violation of metabolic processes in the patient’s body. In addition, there are a number of reasons that usually go in parallel with periodontal disease:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- hormonal imbalance, disruption of the endocrine system;
- bite pathology;
- the presence of bad habits such as smoking cigarettes and excessive alcohol consumption;
- decreased immunity;
- lack of vitamins and nutrients;
- atherosclerosis, high blood pressure;
- a history of diabetes mellitus;
- hereditary factor;
- the presence of plaque of natural origin.
Symptoms of periodontal disease
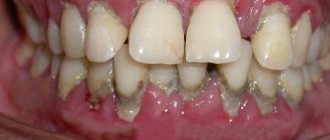
According to statistics, patients do not know about the onset of the disease, since at first it goes unnoticed. But during a dental examination, patients complain of:
- painful reaction to hot, cold, sour;
- constant bleeding gums, bloody taste throughout the day;
- swelling and soreness of the gums;
- a putrid odor from the mouth is noticed immediately after brushing;
- emerging tooth mobility.
What tactics are used to treat periodontal disease?
I want to start with the fact that patients who come with a diagnosis of periodontal disease, they need, every single one, treatment... not from the periodontist to whom they initially turned.
If we talk about the tactics of managing patients with the so-called. periodontal disease, which then come to me again, it’s a shame to voice this, but the treatment of periodontal disease was carried out right up to injections of Lincomycin into the exposed gum.
According to statistics, almost always the treatment of periodontal disease in adults with medications is burdened with a course of some antibiotics and physical therapy.
And most importantly, the task of all these manipulations is completely unclear: what do doctors want to achieve in this way, to destroy some kind of flora or to stop some destructive processes in the gums? It is very difficult for me to say what happens to the competence of a doctor who injects antibiotics for the so-called. periodontal disease, but this is absolute blasphemy. Is it possible to cure periodontal disease by destroying the flora? As a result, the gums will never recover.
Treatment of gum periodontal disease reaches the point of absurdity
I would like to note the widest range of drugs and folk remedies that patients use to attempt self-treatment of periodontal disease at home. Among the folk remedies, one can note the treatment of periodontal disease with hydrogen peroxide, and even treatment with soda:
What about the use of various toothpastes for periodontal disease? What goals do patients have? The purpose of toothpaste is preventative, not curative. And no toothpaste will eliminate inflammation, because there is no such inflammation in periodontal disease.
It is not difficult to guess that in these combinations of procedures the question of how to cure periodontal disease remains open.
Choosing a toothpaste for gums – summary
If the main symptom of gum inflammation is bleeding, it is better to use pastes of the Lacalut and President brands, because they contain components such as aluminum lactate and zinc lactate. The latter very quickly reduce bleeding gums, but keep in mind that such toothpastes (as well as toothpastes with the antiseptic chlorhexidine) are ideally undesirable to use for more than 2 weeks. And after this period, it is worth switching to toothpaste without antiseptics and antibiotics, for example, Paradontax toothpaste.
But precisely during the period of acute manifestations, in order to quickly relieve inflammation in the gums, special gum rinses can be a good addition to anti-inflammatory toothpaste. Many of them contain high concentrations of anti-inflammatory components, which can eliminate bleeding gums even faster (than if you use only one toothpaste). Such rinses are also divided into those that can be used for a short course, and those that can be used on an ongoing basis.
Important: next, a very important point for patients who are going to use anti-inflammatory toothpaste for gums - in parallel with antiseptic mouth rinses with chlorhexidine solution. Clinical studies (source) have shown that chlorhexidine can be inactivated by the oral hygiene component sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), which is present in most toothpastes.
This is of great importance because... rinsing the mouth with chlorhexidine solution is usually recommended after oral hygiene (morning and evening). Studies have found that after brushing your teeth with a paste containing sodium lauryl sulfate, ideally 2 hours should pass (at least 30 minutes, but this is not enough) so that lauryl sulfate does not affect the effectiveness of chlorhexidine. Therefore, if you are going to rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine at the same time, we recommend buying toothpaste without sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS).
There is no inflammation with periodontal disease
When does the so-called periodontal disease, there is no inflammatory process in the gums. The clinical picture of “periodontal disease” differs sharply from periodontitis; it is with periodontitis of the tooth that inflammation occurs.
And injections into the gums, endless restorations of the necks of the gums - this is running in circles. Over time, again all the restoration fillings are chipped, and again these patients come to have these fillings restored again. And this happens endlessly
:
And the diagnosis of “periodontal disease” does not go away. As Desna ran away, she continues to leave. The fillings increase, that is, the teeth increase in size, because the gums sag more and more, and nothing useful happens.
When such a patient gets an appointment with me, unwinding his entire tangle of ordeals during the consultation, it becomes clear that all previously performed gum treatment consists of 3
factors:
- Lost time,
- lost money
- shattered hopes.
The diagnosis was incorrect and the treatment was appropriate for the incorrect diagnosis. What went wrong?
Patients should always go for a consultation with such a diagnosis... to an orthodontist
.
Because periodontal disease is an occlusal injury
.
What I see in these patients with signs of periodontal disease is a completely different diagnosis. This is an occlusal injury that can only be corrected by an orthodontist.
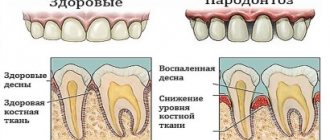
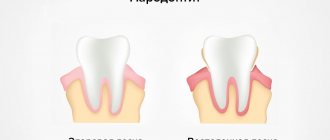
Periodontal disease is a degenerative process of periodontal tissue due to deterioration of blood supply
The reason for the development of periodontal disease is a lack of blood supply to the periodontium, sometimes combined with cardiovascular and endocrine diseases. Blood delivers nutrients to all organs, therefore, with a lack of blood supply, the process of tissue degeneration begins.
with periodontal disease, bone decreases throughout the entire jaw, in contrast to periodontitis, which can also be local in nature
Periodontal disease develops very slowly and causes almost no trouble. The gums are pale, tightly cover the teeth and do not bleed; over time, the roots gradually become exposed, but the teeth can remain stable for quite a long time. Teeth are rarely affected by caries, and non-carious lesions (wedge-shaped defects and enamel erosion) are more common.
What is occlusal injury
Occlusal trauma is when a tooth experiences excessive stress due to:
- the tooth is not in the dentition,
- the tooth is not in the correct position,
- the tooth has not grown physiologically,
- the tooth is tilted, at the wrong angle.
The occlusion of the teeth is impaired. That is, when chewing in a patient with impaired occlusion, a destructive force of chewing pressure is created, and the bone tissue in the area of these above teeth begins to decrease.
What is chewing from a physiological point of view?
It's teeth hitting teeth. The strongest blow, since the masticatory muscles are the strongest in the body.
In simple words, in a patient, from such a hyper-impact, hyper-contraction of the masticatory muscles, which develops during chewing, from this beating of teeth against each other, the bone begins to contract. Bone tissue shrinks. And after the bone, the gum also contracts, because the bone and gum are tightly connected. The gum descends, following the bone. And here we answered the main question - why gums recede.
Let's now begin to form an understanding of the answer to the next question: what to do if your gums have receded.
Instructions for use
Although different gels have individual application characteristics (permissible frequency of application, number of repeated applications), they are all used for the same purpose, in the same way. A small amount of gel is distributed over the surface of the gums, from which the child’s new teeth are erupting.
As you can see, this procedure is very simple, but even so, recommendations for the use of a particular gel for various symptoms should be taken into account. For example, using an anesthetic gel during teething, if there is no fever, is not always necessary, but this is necessary in the case when, in addition to fever, other symptoms, especially pain, are pronounced.
And remember, only your pediatrician can correctly prescribe a teething gel!
Orthodontics comes to the fore
Today, a huge mistake is happening both in the search for the causes of periodontal disease and in making a diagnosis, as well as in the method of effective treatment. Instead of putting the tooth into occlusion, removing it from a traumatic bite, patients are offered all these manipulations that I have previously voiced, which are not at all aimed at getting rid of these complaints, but only at the fact that patients are wasting time, the processes are getting worse.
In the treatment of the so-called periodontal disease is a big problem in the loss of time for inadequate treatment, and the loss of time for the patient is a complication of the pathology of dental occlusion, and the transition of the stage of the disease to a more advanced form.
If a patient, for example, three years ago had a loss of bone tissue of two millimeters, then due to the “treatment of periodontal disease” he has already lost five millimeters, that is, we have lost time.
And if he came to the orthodontist with a loss of bone tissue of two millimeters, then it would be easier to stop the loss of gums, it would be easier to eliminate the development of gum pathology after orthodontic treatment, when the teeth become aligned with the dentition.
We can already talk about the fact that we close all exposed necks of gum recession, thereby treating the neck of the tooth. But when patients waste time on treatments that are inadequate for the disease, sometimes closing the recession is no longer possible. Because there are also strict indications and contraindications for the treatment of gum recession.
Which gel is better to choose
To determine which teething gels help best, first of all, you need to familiarize yourself with their composition. Thus, the effectiveness of drugs containing lidocaine and other anesthetics directly depends on the amount of these components in them - the higher it is, the faster the pain relief effect occurs. And although pain relief occurs almost instantly, its return occurs just as quickly - usually 20 minutes after applying the gel. Anesthetic-based products include: Dentol, Kamistad, Kalgel and Dentinox.
«
Another type of no less effective gels for teething are preparations based on completely natural or semi-synthetic components. For example, these include: Cholisal, Baby Doctor and Pansoral. Compared to anesthetic-based gels, these products may have a less pronounced but longer-lasting analgesic effect, which is the result of not just blocking pain with plant substances, but eliminating the cause of its development - inflammation of the gum mucosa.
In general, all of the listed dental gels for newborns or teething children, in addition to their own advantages, have a common drawback - the risk of developing allergies. Therefore, when choosing a gel for teething, you should focus both on the allergic status of the baby and on the previously announced features of the action of each of the groups of drugs.
Thus, gels with an anesthetic will be more effective in a situation where a child has severe pain, which cannot be relieved by natural ingredients. And gels for infants based on plant substances are best suited for moderate deterioration in health, when natural pain relief by reducing inflammation will be sufficient.
«