Author: Brodsky Sergey Evgenievich Deputy Chief Physician, Candidate of Medical Sciences in the specialties: dentistry and medical microbiology Any person is inclined to believe that if the nerve is removed from the tooth, then it will no longer hurt. However, this opinion is not entirely true. A dead tooth can hurt, and also react to cold and hot, and this is a phenomenon called hypersthesia, increased sensitivity dental unit. These unpleasant sensations require a visit to the dentist, as they may indicate inflammation that has begun in a dead tooth or other dental problems.
Deputy Chief physician Sergey Evgenievich Brodsky
Sign up for a free consultation
+7
Why can a tooth hurt if the nerve has been removed a long time ago?
In medical practice, there are cases when a tooth that was pulpless a month, or even a year ago, suddenly begins to hurt. At first, it may be a barely noticeable discomfort, a reaction to hot or cold. However, soon the unpleasant sensations develop into acute pain, in addition, it often comes to swelling, suppuration and tumors. An unambiguous answer to the question “why does a tooth that has been healed for a long time begin to hurt?” difficult - doctors currently cite several of the most common and obvious reasons:
- Incomplete depulpation
. In other words, if for some reason the nerve was not completely removed, sooner or later it will definitely make itself felt. The process of pulp removal is very complex, requiring maximum precision and care from the doctor. In this case, experience also plays an important role - a young specialist who is thoroughly familiar with the theory is unlikely to be able to cope with this task better than a dentist seasoned by many years of medical practice. If the nerve is not completely removed, over time you will inevitably have to deal with pain and a variety of complications. By the way, if the patient has a pronounced reaction of the tooth to cold or hot, most likely it is the nerve that has not been completely removed. - Poor quality filling after depulpation.
This reason is also quite common in medical practice. For a better understanding of the situation, let us explain: the root canal of a tooth has a thickness of 0.5 to 1 mm, in an expanded form (after processing with special tools) - up to 2 mm. The shape and bends are individual for each individual channel - they can be straight, with bends, with creases. It is not always possible to see this on an x-ray, so the doctor has to work “blindly”, by touch. It is not surprising that in some cases part of the canal remains unfilled. And it is in this part that bacteria accumulate over time, causing inflammation and leading to pain. Also, the filling itself may not lie tightly, allowing access to pathogenic microorganisms. - Increased pressure on the tooth
. The tooth does not just stand in the jaw bone - it is attached to it by numerous threads of connective tissue. If during the filling process the doctor installs a filling that is too high, then the chewing load on this tooth will increase significantly, which, accordingly, will increase the load on the ligaments. Over time, the increased pressure will turn into a constant aching pain, especially evident when pressed. - Infection
. If we assume that the nerve has been completely removed and all the canals have been thoroughly cleaned and securely sealed, there is only one option left - the activity of pathogenic bacteria that entered the root canals and then into the jaw tissue during the treatment of caries or pulpitis. - Insufficient hygiene
. After high-quality depulpation, the patient needs high-quality regular oral hygiene. Even under the most reliable filling, bacteria can accumulate over time if you do not brush your teeth in a timely manner. Some patients believe that dental plaque does not accumulate on the filling material and is not afraid of tartar. In fact, this is not so - bacteria have an equally destructive effect on both tooth enamel and artificial fillings. The infection can get to the root of the tooth and from the gums - this is especially true for people suffering from periodontal diseases. - In fact, one of the neighboring “living” teeth hurts
.
Naturally, it takes time for bacteria to accumulate in an unfilled canal or for an infection to make itself felt. It is likely that a tooth can get sick in a year or after 5 years - it all depends on the degree of neglect of the problem, as well as on the individual characteristics of the body (people with strong immunity tolerate inflammation much easier, so they may not notice alarming manifestations for longer).
In any of the above cases, the tooth will have to be re-treated - the filling will have to be removed, the canals will have to be cleaned and filled again. In addition, a number of additional disinfection measures will have to be carried out.
Why do teeth react to heat?
There are many causes of hyperesthesia, and not all of them are obvious upon a quick examination.
- Caries. Indeed, it can become the culprit of pain. But, as a rule, in this case we are not talking about a superficial lesion, but about large carious cavities hidden under the gum, in the area of the neck of the tooth. Sometimes a dental examination is not enough to detect them; the problem can only be identified with the help of an x-ray.
- Newly installed filling. If your tooth begins to react to heat for the first time after visiting the dentist, there is no need to sound the alarm. Normally, after a few days, the gum microtraumas will heal and the tooth enamel will be restored.
- Other dental interventions. Increased tooth sensitivity for several days after cleaning or whitening is an absolute norm and does not require dental intervention. A reaction to heat will definitely occur after tooth preparation, for example, before installing veneers or crowns. Unpleasant sensations from hot tea are guaranteed in the first days after the removal of a gum pocket over a wisdom tooth or any other procedure that traumatized the gums. In 83% of cases, the tooth aches due to a non-carious lesion, for example, a wedge-shaped defect or pathological abrasion of the enamel. Such conditions progress quickly, but are difficult to treat. That is why, given the prevalence of the problem, at the first cases of discomfort caused by hot food, you should urgently consult a dentist.
- Increased tooth wear. Normally, the process of enamel abrasion is almost invisible. With pathology, by the age of 35-40, the length of the visible part of the tooth can decrease by 30-50%. Moreover, the process, as a rule, affects all teeth, without exception. There are several reasons for increased abrasion: bruxism, prolonged and frequent chewing of solid foods, straight bite, exposure to chemicals. For example, for workers involved in the production of inorganic acids, increased enamel abrasion is an inevitable occupational disease.
- Cervical wedge-shaped defect. In adulthood and old age, more often, a kind of step may form at the neck of the canines and premolars. It is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance. At first, the defect will make itself felt only by a slight reaction to hot foods, but later it can lead to chipping of the entire coronal part. The cause of the disease is not completely clear, but many dentists are convinced that the whole issue is due to many years of improper oral care, namely, too harsh brushing of teeth.
- Erosion of enamel. This type of non-carious tooth damage is more common among young patients under the age of 30-35 years. At first, the enamel is covered with whitish spots, which over time acquire a yellow and then a brown tint.
Erosion can be caused by:
- external factors: excessive consumption of sweets, juices, carbonated drinks, addiction to aggressive whitening agents, wearing braces;
- internal causes: reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus due to reflux disease, regular induction of vomiting with anorexia, and even banal heartburn, which recurs too often.
At least 10% of all cases of hyperesthesia are caused by other dental pathologies. The dentist can identify them during a conversation with the patient and during an examination.
- Microcracks in enamel. In the most advanced cases, even the patient himself in the mirror can see longitudinal stripes crossing the entire surface of the tooth. At the initial stage, digital transillumination will help detect the problem. In a darkened room exposed to ultraviolet rays, healthy enamel emits a blue glow, while the affected areas remain darkened. Microcracks appear as a result of the habit of cracking seeds, love of hard nuts and candies.
- Recession (recession) of the gums. This is a pathology in which the gum gradually drops below the enamel-cementum border, exposing the neck of the tooth. The latter remains absolutely defenseless against any influences, including hot food. Sometimes recession develops as an independent disease due to the congenital thin gum biotype or age. But more often, prolapse is a consequence of periodontal disease.
- Sometimes, during an examination, the doctor does not detect any dental problem, but the patient cannot even eat a spoonful of hot soup without pain. In this case, the problem will have to be looked for by involving doctors of other profiles: a neurologist and endocrinologist, a gynecologist and gastroenterologist, a pediatrician and an immunologist. It is these specialists who are able to identify the cause of hyperesthesia caused by systemic disorders in the body.
- Pregnancy. While expecting a baby, many women face the problem of increased tooth sensitivity. In this case, it is likely that the dentist will not detect any pathological changes in the enamel or gum disease. Healthy teeth hurt due to a hormonal storm in the body, and a woman can only do one thing: be patient and wait. As a rule, 12-18 months after birth, hyperesthesia goes away on its own.
- Endocrine disorders. Any problems in the hormonal system can increase acidity in the oral cavity. And this in turn entails an increase in the sensitivity of the enamel.
- Lack of vitamins and minerals. A lack of calcium, magnesium and phosphorus is especially destructive to gums and tooth enamel. For better absorption, they should be taken together with vitamins: phosphorus and calcium with vitamin D, magnesium - in the form of a chelate or gluconate in combination with vitamins B6, C and D.
- Chronic stress. With prolonged emotional overload, the nerve endings, including those in the dental pulp, become so sensitive that they react to the slightest discomfort.
- Exposure to chemicals. Moreover, medications and increased levels of aggressive substances in drinking water, air, and food can be detrimental to tooth enamel.
Medications that can cause hyperesthesia include:
- aspirin;
- tetracycline;
- oral contraceptives;
- other hormonal drugs;
- diuretics;
- cough syrups.
Only one tooth or all of them may experience discomfort when eating hot food. And this fact often suggests the cause of the pain. So, a problem with one tooth is more likely to indicate a mechanical injury. Damage to several teeth located next to or symmetrically to each other indicates increased abrasion. In a generalized form of hyperesthesia, when the entire oral cavity is affected, we can almost certainly talk about systemic problems in the body: hormonal imbalance, metabolism, problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Why do teeth hurt from sweets, hot and cold?
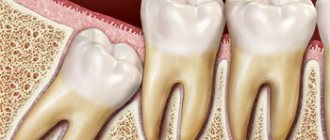
Only at first glance the tooth looks like a monolithic bone formation. In fact, hidden under the strong enamel is porous dentin and a soft, sensitive pulp, penetrated by a network of nerve fibers. Under the influence of negative factors, tooth enamel becomes thinner, exposing more sensitive tissues. Now, when there is a temperature difference, the enamel is no longer a reliable protection: the dentin tubules quickly and unevenly expand from hot and just as quickly narrow from cold. These impulses are immediately picked up by the nerve endings of the pulp. And they react painfully.
Sensitivity to sweets is explained by the fact that sugar is the best breeding ground for bacteria. When processing sugar, they release acids into the oral cavity. And if you treat yourself to chocolate day after day, your tooth enamel will gradually become thinner. And since dentin is very sensitive to chemical irritants, very soon every lollipop or eclair will feel unbearable pain.
With receding gums and periodontal diseases, the situation is even more serious. In this case, the teeth become clogged because the bacteria have already damaged the not very strong dental cement covering the neck of the tooth. And if you don’t see a dentist in time, you may soon lose your tooth.
Why can a tooth hurt immediately after nerve removal?
It also happens that immediately after the end of the anesthesia (and the procedure for removing nerves is invariably accompanied by the use of local anesthetics), the patient begins to experience acute pain in the dead tooth. There may be several reasons for this:
- The filling material got from the root of the tooth onto the soft gum tissue . This situation can occur if the material is fed into the root canals under very high pressure. In addition, this often occurs due to incorrect measurement of the channel length. To avoid this problem, it is necessary to take pictures before and after depulpation, and if defects are detected, immediately remove the filling, remove excess paste and reseal the canals.
- Remains of dental instruments in the canal . The needles for widening the canals and removing nerves are very thin. Even though modern instruments are made from high-quality materials, there is a small chance that a small piece of needle will remain in the canal, causing discomfort and pain.
- Damage to the tooth root . During the process of cleaning canals and removing nerves, there is a possibility of drilling through the root of the tooth, resulting in an open cavity leading directly into the jawbone (which, by the way, can also be damaged due to drilling too deep).
- The body's reaction to filling material . Or simply an allergy. Anyone can encounter this, especially if the patient has not previously had to deal with dental intervention. In this case, it is necessary to urgently remove the filling and repeat the procedure using a different material.
All of the above causes of tooth pain after nerve removal are pathological and require urgent medical intervention.
It is important to understand that immediately after treatment, a tooth with a removed nerve may hurt for some time for a number of reasons:
- Depulpation is a process of violating the integrity of nerve tissue, which cannot be completely painless. After the local anesthesia wears off, the patient still feels discomfort and aching pain for some time, which can be relieved with toothache tablets.
- A reaction to cold and hot things in the first couple of days after nerve removal is normal. Due to the violation of the integrity of the tooth tissue, its sensitivity also increases, which goes away after complete healing.
In order for the recovery period to pass quickly and painlessly, it is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations of the attending physician - do not drink or eat for 2 hours after the operation, observe the rules of hygiene, take anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
When should you see a doctor?
Dentists themselves recommend not delaying a visit to the clinic if the slightest alarming symptoms occur:
- Acute throbbing pain in the first hours after depulpation.
- The presence of edema, a swollen cheek or gum, the formation of an abscess under a tooth without a nerve.
- Manifestation of tooth reaction to cold and hot long after dental intervention.
- The pain after the operation does not subside, but on the contrary, it becomes stronger.
- An increase in body temperature (indicates the presence of an inflammatory process).
- Pain when pressing on a tooth or chewing.
If you contact an experienced doctor in a timely manner, any problems can be solved as soon as possible.
What to do if a dead tooth hurts
At the first appearance of pain, you should contact your dentist. Since in most cases pain is a consequence of the inflammatory process, the doctor must carry out a diagnosis.
It is imperative to assess the condition of the gums, diagnose (or exclude) diseases such as periodontal disease, periodontitis, etc. Gum disease is difficult to treat, and timely diagnosis will help to prescribe the right treatment in time.
After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment aimed at eliminating the causes of pain:
- If inflammation is detected, anti-inflammatory drugs or antibiotics may be prescribed.
- The old filling is removed, the canals are cleaned, and the filling is performed again.
- The darkened crown of the dead tooth is additionally whitened to restore the aesthetics of the smile.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
A specific treatment plan is prescribed individually, based on the results of the examination and the general condition of the patient’s teeth and gums. Sometimes pain in a dead tooth is a consequence of a whole range of dental problems.
Why does a tooth hurt when pressed?
If the tooth does not bother you until you start chewing or pressing on it, most likely the reason lies in problems with the ligaments that “attach” the tooth to the jawbone, or due to slight swelling that will subside in a few days.
However, there are other reasons:
- A fragment of a dental needle remained in the canal.
- Excess filling material has gone beyond the root of the tooth and landed on the jaw bone.
- The nerve was not completely removed (in this case the tooth hurts even with light tapping).
- During the treatment of caries, an infection got into the root canals.
If you feel a sharp pain when pressing, it hurts to chew and even speak, you must urgently go to the clinic, take an x-ray and repeat the operation to clean and fill the canals, having previously eliminated possible foci of inflammation.
We correct other people's mistakes. Dental retreatment with a 10% discount
Moscow
What complications may arise?
Pain is one of our body's defense mechanisms. If there is pain, it means one of the systems is not working correctly, and there is a certain pathology. If you do not pay attention to these signals for help in time, you may encounter serious complications:
- Inflammation under the tooth
. At first it will be concentrated in one place. But in the absence of proper treatment, it will spread to nearby tissues, and then, through the bloodstream, throughout the body. - Infection of adjacent teeth
. If the cause of the pain is the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, it is likely that the infection will spread to the soft tissue of the gums and then spread throughout the entire oral cavity.
If, after removing a nerve, a wisdom tooth hurts, then, contrary to popular belief, it is not necessary to remove it - if it is possible to repeat the treatment, eliminating the source of infection and inflammation, the doctor will definitely do everything in his power to save the tooth.
In the most advanced cases, the doctor usually decides to remove the filled tooth.
How to relieve pain?
The process of treating a damaged tooth is very complex and time-consuming. It often takes several visits to the doctor to completely eliminate the cause of the pain. At the same time, in order to somewhat reduce pain, it is quite acceptable to use painkillers, especially considering the fact that most of them also have an anti-inflammatory effect:
- Ibuprofen.
- Aertal.
- Ketanov.
- Nimesil.
- Nise.
- Paracetamol (may help with moderate pain).
In addition, you can numb an open tooth using special lidocaine-based sprays.
Don’t forget: pain relief is just a means to eliminate discomfort, but unfortunately, no pill, even the strongest and highest quality, can cope with the source of the disease.
Indications for root canal treatment
Acute throbbing pain in a tooth is a marker of inflammation. Against this background, the following symptoms should alert you:
- swelling of the gums and cheeks;
- flux formation;
- reaction to temperature stimuli;
- fever, chills;
- increased pain when biting.
Clinical manifestations are a reason to return to the dentist, otherwise there is a high risk of losing a dental unit. If defects are detected, repeated radiography, removal of the filling, cleaning and obturation of the canal are necessary.
Treatment of a dead tooth in dentistry
During the first visit to the dentist, the patient is usually sent for an x-ray, which will help determine the possible causes of pain in the pulpless tooth. Next, the doctor acts based on the current clinical situation:
- The dead tooth is opened and the remaining filling is removed from the canals.
- If there are remnants of nerve endings in the pulp, complete depulpation is performed.
- The root canals are thoroughly disinfected.
- Finishing the channels, cleaning and polishing them.
- Filling of root canals. If there is a one-stage treatment, the doctor uses a filling paste. If there is a need to eliminate the source of infection and inflammation, the dentist will install a temporary filling, which will be replaced with a permanent one in 2-3 weeks.
- Restoring the final shape of the tooth. Restoration work is no less complex a process than canal filling. If the permanent filling turns out to be higher than it should be, an additional chewing load will be placed on the tooth, which may cause discomfort and pain to arise again over time.
It may seem that treating a dead tooth is much easier than depulping a live one. In fact, the opposite is true - finding and eliminating an existing defect is much more difficult than doing all the work on treating a tooth “from scratch.”
The main causes of pain immediately after depulpation
A feeling of mild pain in a pulpless tooth is acceptable for two to three days after the intervention. A natural reaction is increased sensitivity to temperature stimuli. Such symptoms are caused by traumatization of mucosal tissues and nerve fibers, as well as the formation of a hematoma (local hemorrhage).
Dentists identify several main causes of pain immediately after depulpation:
- Contact of filling material with gum tissue. The situation occurs frequently and occurs due to incorrect determination of the channel length or excessive pressure when feeding the composite.
- During treatment, the doctor uses very thin needles. Despite their strength, when passing curved areas, there is a high probability that a fragment of the tool may break off.
- Allergic reaction of the patient's body to the composite. The condition is dangerous for people seeking dental care for the first time. In this case, the pain syndrome is accompanied by swelling and redness of the oral mucosa, an increase in body temperature, and urticaria and itching are characteristic.
If the pain increases or occurs suddenly a few days after surgery, then this is an obvious reason to visit a doctor.
Prevention
If for some reason you had to depulpate a tooth, you should not think that now it will never bother you again - without proper preventive measures, the likelihood of pain is very high. To avoid complications, follow simple rules:
- Do not eat or drink for 2 hours after surgery - this will reduce the risk of infection under the filling. Smoking and drinking alcohol are not recommended for at least 24 hours after treatment.
- Take anti-inflammatory pain medications as recommended by your dentist.
- At first, try to reduce the chewing load on the pulpless tooth.
- Regular hygiene. Immediately after treatment, buy a toothpaste to reduce tooth sensitivity. In the future, brush your teeth 2 times a day, do not neglect dental floss and mouth rinses.
- Professional hygiene. Visit your dentist at least once every six months. Make an appointment for a professional plaque and tartar cleaning once a year. To protect your teeth from adverse external influences, go through the procedure of fissure sealing, and to strengthen the enamel - remineralization or fluoridation.
And remember - everything in our body is interconnected. Don’t wait for pain – at the first signs of discomfort after dental treatment, contact your doctor immediately.
Author: Elena Kopylova Dentist-therapist, endodontist, pediatric dentist. Work experience more than 7 years. The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Prevention of tooth sensitivity
To prevent manifestations of hyperesthesia, it is enough to review some habits:
- stop cracking seeds with your teeth;
- never subject the enamel to excessive stress: do not open bottles with your teeth, do not try to peel nuts with them;
- drink carbonated drinks and juices only through a straw.
Women experience symptoms of hyperesthesia almost 2 times more often than representatives of the stronger sex. This is because the fair half of humanity is more prone to worries and depression. And stress worsens the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, disrupts metabolism and changes the acidity in the mouth. Therefore, to avoid hyperesthesia, it is useful to reconsider your outlook on life and learn to think positively.
Hygiene plays an important role in preventing tooth sensitivity. Oddly enough, but sometimes it turns out to be excessive. Hard brushes, rinses containing ethyl alcohol, love for whitening pastes - all this is better left in the past. But fluoride-containing pastes and brushes of medium hardness will not only effectively remove plaque, but will not damage tooth enamel.
Category Miscellaneous Published by Mister dentist