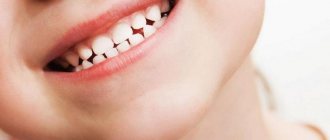
Bad teeth in a child: reasons
A child’s baby teeth rot for various reasons.
Some are impossible to influence, others can be easily eliminated by dentists and caring adults. Most often, destruction of the enamel, and subsequently the coronal part of the primary occlusion units, is facilitated by:
- Disorders of intrauterine development of a child. Developmental pathologies are formed due to maternal toxicosis, non-compliance with nutritional recommendations, and the use of potent medications.
- Early birth of the baby. Prematurity of a baby indicates incomplete formation of internal systems - in particular, weak thin enamel of baby teeth.
- Antibacterial therapy administered to a child in the first year of life.
- Poor hygiene. Lack of systematic cleaning after the first tooth erupts, improper care, and inadequate parental control.
- Unbalanced child nutrition. Predominance of flour and sweets in the menu, lack of fermented milk and dairy products, hard fruits and vegetables.
- Reduced immunity. Congenital or due to a lack of vitamins in the diet.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, dysbacteriosis.
- Diseases of the endocrine system - diabetes mellitus.
- Previous infections - ARVI, chicken pox, scarlet fever.
- Pathogenic microflora entering the baby’s mouth from the outside. If family members have the habit of licking the baby’s spoon or pacifier, or kissing the baby on the lips.
- Poor ecology is a significant external factor that negatively affects the condition of the child’s teeth and general well-being.
- Heredity - parents or grandparents have bad teeth.
- Mechanical injuries, external damage to tooth enamel - cracks, small chips.
Effective prevention of caries
What else can be done if a child has bad baby teeth? Engage in prevention. It is very important to teach your baby to rinse his mouth after every meal in order to remove sources of bacteria from the oral cavity as often as possible. A child should brush their teeth under the supervision of an adult, and even better if mom or dad does this for a while.
It would be a good idea to remove candies, toffees and other sweets from the diet, and instead introduce your baby to cottage cheese, hard cheese, fish, sour cream, and eggs. The child should spend enough time in the air and get his portion of sunlight - a source of vitamin D. All this together will help protect the teeth from further destruction.
How to determine if a child has bad baby teeth
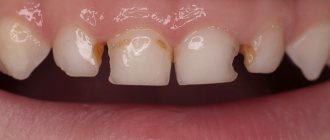
A child's rotten front teeth are immediately visible. These are dark or yellow spots of enamel, reddened gums, and damaged edges. But sometimes decay begins on the distant teeth - molars, premolars, and then you need to focus on indirect signs.
The fact that a child is growing bad teeth is indicated by:
- complaints of pain and discomfort - reaction to toothpaste, hot or cold foods;
- unpleasant odor from the baby’s mouth - putrid, pungent;
- change in enamel color - the appearance of dark stripes, yellow or dark spots;
- development of dental diseases - caries, pulpitis.
Any of the listed factors indicates the need for consultation with a pediatric dentist - a full diagnosis and timely treatment.
Caries on the front milk teeth - what to do?
On the front milk teeth, caries occurs almost as often as on the lateral ones. What should the child’s parents do in such cases? Be sure to take him to the dentist, regardless of the stage of the disease. Even if you notice a white spot on your baby’s front teeth, do not delay visiting the doctor to avoid further development of caries, its complications and other unpleasant consequences that pose a threat to the health of the child’s future permanent teeth.
Stages of decay of children's milk teeth
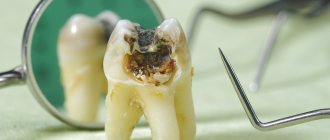
A child’s bad teeth almost always mean caries. The disease is distinguished by the type and depth of tissue damage. Dentists highlight:
- Initial and superficial caries is the primary destruction of the enamel, manifested as white spots.
- Visible carious lesions are medium and deep caries. Teeth rot quickly and stains develop into cavities. The child begins to experience pain. An unpleasant odor appears from the mouth.
- Circular caries is the circular destruction of enamel and dentin near the gums. If left untreated, the tooth breaks and rots further to the root.
In particularly advanced situations, damage covers an increasingly larger volume of tissue, leading to serious pain and loss of the milk unit.
Maybe you shouldn’t treat the tooth, but just remove it?
It will be easier to persuade a child to treat a tooth than to remove it. Even under the influence of modern anesthesia, the patient does not lose tactile sensitivity (no pain occurs, but there is rocking and pressure). Children can perceive such sensations as pain. Medical manipulations during dental treatment are much more gentle. Also, with the early loss of one tooth (and especially several), it can cause problems with speech and malocclusion. Do not forget also about the psychological aspect: very often children who do not have front teeth begin to be teased by their peers.
Bad teeth in a child: how to treat
Decay of baby teeth can be stopped. Especially if the parents quickly assessed the threat and brought the child to the children's dental clinic. Treatment options are different:
Remineralization of tooth enamel
The doctor will apply a special gel to the baby teeth, which contains minerals to strengthen the teeth. Usually it is calcium, phosphorus, fluorine. The substances will restore the enamel structure at an early stage of destruction, but if the teeth are already rotting, the dentist will select a different treatment.
Sealing
Cleaning out carious cavities and then installing a filling. The preparation method is selected according to the patient’s age. Modern dental clinics treat teeth without a drill - using the ICON method, as well as using classical methods.
Ozonation of teeth
A method of disinfecting destroyed cavities followed by filling, when ozone is used to eliminate pathogenic microflora. The treatment has proven itself to work with children's rotten teeth, but is only suitable for moderate decay.
Laser therapy
The disinfectant effect of a laser beam is an excellent way to disinfect a small cavity and remove bacterial microorganisms in the mouth of a young patient. Suitable for the treatment of moderate caries of primary teeth.
Removal
A radical method of dealing with rotten teeth of a child. Used when it is impossible to carry out therapy and save teeth.
Rodikova Tatyana
When parents are interested in why their child has bad teeth, I first of all ask about nutrition. Almost all children today eat sweets, chips, and drink soda without restrictions. Of course, this negatively affects the teeth. The second common reason is heredity. Congenital diseases and medications are less likely to damage teeth.
Caries of primary teeth and its ENT complications
Sometimes parents unsuccessfully try to understand why their child often suffers from colds, complains of ear pain, and suffers from a chronic runny nose. And few people realize that the reason for weakened immunity lies in the baby’s untreated teeth. How can this be? It turns out that it’s all about pathogens! Caries develops under the influence of pathogenic bacteria, which can also cause diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system of the child. Therefore, timely treatment of caries is important, including for maintaining the normal functioning of other organs of the baby.
Why treat baby teeth?
Rotten baby teeth do not always attract the attention of parents. Especially if the pathological processes are painless and do not bother the child. Adults think that when the bite changes, the bad teeth will disappear by themselves, and instead of rotten teeth, normal molars will grow. Dentists warn about the fallacy of such a misconception.
Rotten milk teeth are:
- damage or destruction of tooth germs - a high risk that the root units will grow sick or not appear at all;
- early loss of primary occlusion units - leads to displacement of existing teeth, the appearance of crowding, and the formation of a pathologically abnormal bite;
- an ugly smile, an unaesthetic appearance - the appearance of complexes due to appearance in young children, decreased contact with peers, uncertainty, isolation;
- deterioration of diction - rotten, breaking teeth interfere with the correct movements of the tongue during speech, leading to a lisp, burr;
- gradual spread of infection - damage not only to the surface of the teeth, but also to the pulp, development of pulpitis, the appearance of an abscess, as well as a tendency to ENT diseases and gastrointestinal diseases.
Is it true that baby teeth don’t have nerves and don’t hurt?
Baby teeth are no different from permanent teeth. They have both nerves and roots (by the time they are replaced with permanent teeth, they resolve on their own). Of course, this is why it is very important to treat them with anesthesia. True, baby teeth, even with significant destruction, may actually not hurt for a long time, this is due to the peculiarities of their structure. But over time, they too can get sick. Therefore, in no case should you wait for this, since it is always more difficult to treat a child with acute pain - he is under stress, and there is absolutely no time to adapt. It is possible that the tooth will hardly be cured; it will have to be removed.
How to prepare your child for an orthodontic appointment
The initial appointment with an orthodontist takes place without any preparation. The child just needs to brush his teeth and eat beforehand. The latter is desirable, as it will help reduce salivation and facilitate the examination procedure. The child should also be told about the doctor’s specialization. In simple words, explain who this pediatric orthodontist is and what he treats.
An orthodontic examination is a painless procedure. It does not cause fear or discomfort in the baby, but it helps to identify deviations in the development of the dentition as early as possible.
Soldatenkova Alina
Typically, the removal of decayed milk teeth involves the extraction of several units at once. At Azabuka, we recommend performing this procedure under anesthesia or sedation. It is completely safe for the child, and most importantly, it does not leave traumatic, unpleasant memories in the child’s memory.
Why did the child develop caries, after all, he brushes his teeth every day?
No matter how independent a child is, until the age of six he cannot brush his teeth on his own, because at this age fine motor skills and coordination are not sufficiently developed. Try to remember how difficult it is for preschool children and even first-graders to write sticks, circles and letters in copybooks. Therefore, parents should help children under 6 years of age to brush and floss.
Carious lesion is a multifactorial disease, its occurrence and severity depend on the local immunity of the oral cavity, the structure of tooth enamel, diet, saliva composition and level of hygiene. To be able to assess the risk of developing caries and try to reduce its intensity, you need to regularly (preferably once a quarter) go to the pediatric dentist. The doctor will select the necessary procedures (therapeutic and preventive) depending on the specific case and will correct them at regular examinations.
Other causes of enamel darkening in children
Rotten baby teeth in a child look different in the photo. Usually these are black spots, lumpy enamel, deformed crowns - unpleasant, ugly, even creepy. But an unaesthetic appearance does not always indicate rotting. Sometimes the reasons lie in other diagnoses or pathologies:
- black plaque;
- enamel hypoplasia;
- abnormalities in tooth shape.
Black plaque - stains on baby teeth
Dark spots on teeth are not always tooth decay. It could also be:
- Priestley's plaque - appears due to the increased activity of certain bacteria that secrete a black pigment. The defect is aesthetic, but dentists advise cleaning the enamel from plaque, since it can prevent caries or other dental diseases.
- Dark deposits due to taking iron supplements are an aesthetic problem, which professional cleaning helps to cope with.
Dark pigmentation is also caused by dysbiosis, lack of calcium, and taking antibiotics. Plaque is removed using gentle dental cleaning methods, returning the enamel to its natural whiteness.
Enamel hypoplasia and tooth shape abnormalities
Hypoplasia manifests itself as a change in the structure and color of the enamel and is not a carious lesion. Is it congenital or acquired? In the case of systemic hypoplasia, the shape of the dentition units may also be affected. Externally, the pathology manifests itself as:
- an altered line of the tooth edge is a natural deformation, and not due to rotten teeth;
- barrel-shaped crowns, cone-shaped - due to changes in the tooth at the dentin level;
- spots on the tooth surface of different sizes and shades - altered enamel thickness, insufficiently developed tissues.
For isolated manifestations, hypoplasia is not treated. In case of severe defects in baby teeth, the doctor will suggest remineralization and filling of the affected areas.
Do baby teeth hurt due to caries?
Painful sensations when the surface of the teeth comes into contact with sweet, sour or salty food irritants is one of the first signs of incipient caries on baby teeth. Further, the discomfort in the affected teeth will only intensify, and when caries affects the pulp, the teeth begin to hurt like adults. In addition to acute pain, this stage of the disease is characterized by a high risk of premature removal of a baby tooth.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
How to protect your child's teeth
Among the main preventive measures for the preservation of teeth in children of any age are:
- Maintaining oral hygiene to prevent plaque formation - timely care, selection of toothbrushes and toothpastes according to age, professional cleaning using gentle methods.
- Good nutrition - creating a varied menu that will include yoghurts, kefir, cheeses, vegetables and fruits.
- Selection of a vitamin complex according to age - independently or after consultation with a pediatrician.
- Timely visits to the dentist - pediatricians recommend coming for scheduled appointments every 4-6 months. This helps to identify caries and enamel destruction at an early stage and save teeth from serious problems.
- Fissure sealing - smoothing the lumpy surfaces of molars and premolars to reduce the risk of caries and rotting of distant units.
Rodikova Tatyana
Parents often have to explain: it doesn’t matter when the child’s bad teeth appeared - at 3 years old or at 7 years old - they need to be treated. Waiting until they fall out on their own is a big risk. Fortunately, in most cases the explanations work and we begin treatment. It's nice to see how a child's face changes when he sees beautiful, even, snow-white teeth in the mirror - instead of rotten and black ones.
It is also worth carefully monitoring the mechanical integrity of the teeth, since any crack or chip is a potential threat to the child’s dental health.
The health of children is the concern of parents. Poor heredity, diseases, premature birth indicate the need for careful monitoring of the condition of teeth - timely prevention and treatment. If everything is done correctly, then the child will not have rotten teeth, but only a joyful and beautiful smile.
How to prevent tooth decay in children
The best way to combat tooth decay is prevention. To maintain the health of children's teeth, you need to follow several rules.
- Follow your diet. Reduce your consumption of sweets as much as possible. Make sure your child gets enough calcium from their diet - dairy products, nuts, legumes and sesame are especially rich in it.
- Teach your child to brush their teeth. From the first tooth that emerges (age 6–8 months), you can already use a small baby brush. Gradually accustom your child to self-care - buy tasty toothpaste, turn the process of brushing your teeth into a game, encourage your baby’s interest.
- Visit your dentist regularly. Children need to undergo preventive examinations, as well as professional hygiene procedures more often than adults - approximately once every three months. The doctor will be able to identify problems in a timely manner and give advice on the proper care of children’s teeth. In addition, visits to the doctor will become routine for the baby, and he will not be afraid of them.
Try to carefully monitor the condition of your child’s teeth and pay attention to his complaints. The sooner you see a dentist, the faster, more effective, and most importantly, painless the treatment will be. Explain to your child that dentistry is not scary. And our experienced doctors will help him make sure of this.
Causes of caries development in young children
There are two reasons contributing to the development of caries:
- plaque;
- frequent consumption of sugar (sucrose, glucose in combination with fructose, is especially dangerous).
Often children do not like to brush their teeth or do it incorrectly. As a result, plaque is deposited in areas of the teeth that do not clean themselves when chewing (in fissures, near the gums). Demineralization and softening of the enamel occurs, and subsequently caries.
Young children mainly eat liquid or pureed foods. Active chewing does not occur, and tooth surfaces are not cleaned.
In children, enamel and dentin have a structure that is unusual for adults: mineralization in the tissues is imperfect, teeth are in the process of development. Due to the low density of enamel and its insufficient mineralization, caries in young children develops frequently and is quite severe. A large number of teeth are involved in the process, and circular caries occurs - when the lesion spreads around the neck of the tooth, peeling off the crown from it.
Lack of vitamins, chronic and hereditary diseases also provoke caries in children.
Stages of disease development
At the initial stage, the manifestations of the disease may be invisible: this is what makes the disease dangerous. When the defect becomes visible to the naked eye, bottle caries is already gaining strength and affects several teeth. Therefore, it is extremely important to know about the first signs in order to stop the development of the disease in time.
- The initial stage is characterized by the appearance of white spots on the teeth. No painful sensations are observed. Many parents think that the stains are the result of an injury (for example, when a child chewed on a toy) and do not consult a doctor.
- The superficial stage begins when the baby begins to experience pain when eating sweet and sour foods. The spots turn yellow or acquire a brownish tint (for this reason they can easily be confused with plaque).
- During the middle stage, depressions with uneven edges appear on the tooth enamel (as a rule, the defect is located near the gums). The pain makes itself felt when eating cold or hot food, and sensitivity to sweets appears.
- If the disease has reached a deep stage, dental changes become visible even to a layman. The affected tooth begins to resemble an apple core, and pain occurs when pressure is applied. If treatment is not started as soon as possible, the child may lose a tooth, which will affect the ease of chewing.