Healthy teeth and gums, like other tissues of the human body, require a whole range of useful substances. These include not only minerals (calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, etc.), but also vitamins, which are catalysts for metabolic processes occurring in the body. With prolonged vitamin deficiency, quite serious negative consequences can develop. To exclude them, it is important to promptly notice signs of vitamin deficiency, and also, if possible, maintain an optimal balance of essential substances in the diet.
The most important vitamins for the health of teeth, gums and other oral tissues are:
The best material for bridges
Feldspar ceramics on a zirconium oxide framework or E.max on a zirconium oxide framework. Metal-ceramic dentures, having the same strength, look a little less natural, but when combined with removable clasp locking prosthetics, they come out on top.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays an important role in maintaining dental health. It participates in the metabolic processes of minerals - phosphorus and calcium. Without vitamin D, these microelements are not absorbed, resulting in an uncontrolled release of minerals. This significantly increases the likelihood of caries and leads to tooth decay.
The main signs and consequences of vitamin D deficiency:
- metallic taste in the mouth and a general change in taste sensations;
- dryness, numbness, burning and pain in the mouth;
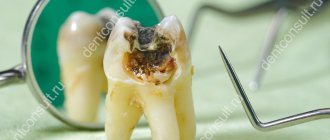
- caries, increased tooth fragility;
- weakening of the ligamentous apparatus of the teeth, which in an advanced stage can lead to loosening and loss of teeth.
Vitamin D Rich Foods:
- fish of different breeds;
- eggs;
- Cod liver;
- milk, etc.
We should not forget that in addition to foods, our body is capable of producing vitamin D on its own. To get the daily requirement of this substance, it is enough to be in the sun for only 15 minutes.
Dentistry
The effect of vitamin D on gums and teeth
Because vitamin D has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects, patients with low vitamin D levels have been shown to be more susceptible to developing gum and periodontal disease. Due to the vitamin's positive effects on bone metabolism, periodontitis patients with low vitamin D levels also showed a poor response to periodontal surgery. Studies have shown that patients with plasma vitamin D deficiency have poorer outcomes (ie, lower levels of tissue attachment and changes in probing depth) after periodontal surgery. To improve postoperative results, it is recommended to check the patient's vitamin D blood level before starting treatment and, if necessary, administer supplements.
Vitamin D deficiency can lead to decreased bone mineral density, osteoporosis, bone fractures, progression of periodontal disease, and loss of dental implants. Adequate intake of vitamin D may reduce the risk of developing gingivitis and chronic periodontitis as it has been shown to have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effects.
In addition, vitamin D is important for bone metabolism, alveolar bone resorption, preventing tooth loss, and promoting bone formation around dental implants. Patients who demonstrate poor wound healing response after dental treatment, including post-implant healing, should undergo evaluation. If there is a lack of vitamins, medications are prescribed that increase the level of essential substances to the required level.
The effect of vitamin D on the healing of dental implants
Vitamin D deficiency can impair the immune response to infections, increasing the risk of oral inflammation after surgery, including dental implants. The synthesis of antimicrobial proteins by immune and epithelial cells, as well as nonspecific immune responses, are activated by vitamin D. In bones, vitamin D stimulates the activity of osteoclasts and increases the production of extracellular matrix proteins by osteoblasts. Vitamin D deficiency is correlated with low bone density, pathological fractures, and poor bone healing.
Since osseointegration of dental implants depends on bone turnover, there is a possibility that low levels of vitamin D in the blood may negatively affect the healing processes and formation of new bone on the implant surface. Most studies indicate that adequate serum vitamin D levels can promote peri-implant bone healing.
Modern research shows that when a normal level of vitamin D in the blood is achieved, the condition of bone tissue and implants comes to a stable state. Taking excess doses does not have any harmful effects, the substance is eliminated from the body without harm to health. When planning treatment, the level of vitamin D, as well as other vital parameters, should be monitored by a specialist; repeated diagnostic sessions should be discussed in advance by the doctor and the patient.
Yandex Zen: How does vitamin D affect the condition of teeth and the healing of implants?
The best material for crowns
E.max (Imax) or feldspathic ceramics on a zirconium oxide frame. Metal-ceramics are inferior to them in aesthetics, but are in no way inferior in strength - for chewing teeth this is an equally reliable, but less expensive choice. Metal-ceramics on a cobalt-chromium alloy, when manufactured with high quality, are no worse than metal-ceramic crowns on a gold or gold-platinum alloy.
The best anesthetic
The best local anesthetic not only in dentistry, but also in medicine in general today is articaine.
It is mainly used in conjunction with adrenaline. This increases the depth and duration of pain relief. The most effective is a solution with a 4% concentration of articaine and an adrenaline ratio of 1:100,000. Of the commercial products presented on the Russian market, Ubistezin Forte is the leader. Other worthy drugs: Ultracaine, Septanest. For more information, see What is the best anesthesia in dentistry?