Stomatitis in a child is a very common phenomenon caused by an inflammatory process of the oral mucosa, which also occurs in newborns. We can say that raising a child and not knowing what stomatitis looks like in children is almost impossible. Quite often, the symptoms of the disease initially resemble those of a respiratory infection with a characteristic fever, stuffy nose and poor appetite. But after a short time, parents notice the appearance of blisters and ulcers on the gums, cheeks and inner lips, which can be caused by various pathogens. The child behaves anxiously, capriciously, sleeps poorly... Even for an adult, it is very difficult to endure the painful sensations that arise from stomatitis, not to mention children, who cannot always clearly explain what is tormenting them. Parents, of course, are concerned about the question of what causes stomatitis in children and whether the occurrence of such a disease can be prevented. Let's try to understand this thoroughly.
Blue for stomatitis: methods and features of use
The name stomatitis comes from the Greek language. Stoma means mouth. Symptoms of this disease may be:
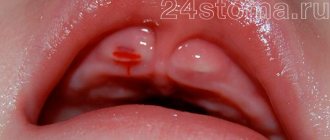
- the mucous membrane is swollen, covered with a white or yellow coating;
- white ulcers of varying sizes form in the mouth;
- body temperature is high, it is difficult to bring it down with medications;
- Gums may bleed;
- a pronounced unpleasant odor appears.
Very often, the doctor tells the patient that bluing will help with stomatitis. But what is it? Are we really talking about the blue that grandmothers added to white paint when whitewashing ceilings? Of course not.
This is not household blue, but methylene blue or iodide starch. We are talking about a strong antiseptic that neutralizes pathogenic foci.
Blue for stomatitis is not the only drug that helps fight the disease, but it is rightfully considered the most effective.
In addition to bluing, pain-relieving applications for ulcers, rinses or antibiotics (if the condition is advanced) may be prescribed.
Since this disease causes a high temperature, the doctor prescribes antipyretics. But this is not a treatment for stomatitis, but general safety measures for the body. But blue for stomatitis is prescribed for treatment.
The instructions for which indicate that an adult patient should repeatedly treat the affected area of the mucous membrane. Processing is carried out up to 15 times a day
Please note: oral cavity treatment is carried out with a 1% aqueous solution
Do not confuse it with alcoholic methylene blue.
Blue for stomatitis in children is used differently than in adults. Let's start with the fact that children should not treat ulcers so often. This is done 4 times a day, after meals.
If stomatitis is caused by herpes, then the oral cavity can be treated up to 5 times. Only an aqueous solution can be used on mucous membranes.
In the mid-twentieth century, an experiment was conducted at one of the medical institutes in Russia. A group of 86 children from one and a half to ten years old was identified. The children had severe signs of stomatitis. 56 people had the aphthous form, 13 had the ulcerative form, and in 17 patients stomatitis arose as an allergy to medication.
The children were fully examined, and the causative agents of stomatitis were identified using laboratory tests. They all received topical treatment with methylene blue, but in different forms.
The younger group, which included children over one and a half years old, received a spray based on starch iodide. The middle group, aged two years and older, received treatment in the form of applications. Treatment was carried out daily, the first day in a medical facility, then at home.
At the same time, doctors observed a group of children who were prescribed antibiotic treatment for stomatitis at the clinic. The babies recovered on 9-10 days.
And they look at inexpensive medicines from their mothers’ youth with distrust. Another thing that makes the drug less popular is the fact that it must be prepared in special pharmacies, while new drugs can simply be bought at any pharmacy outlet.
The drug is intended for both external and internal use.
When treating the skin with the drug, the injured areas and adjacent healthy areas are treated. Contact of liquid with mucous membranes should be avoided.
Permissible concentrations of methylene blue
| Disease | Permissible concentration |
| Skin lesions | Wash wounds with a 1 - 3% alcohol solution. |
| Bursitis | Inject a 2% solution into the wounds at the rate of 0.01% per 1 kg of chicken weight. |
| Urinary tract infections | Rinse with 0.02% aqueous solution. |
| Infectious gastrointestinal tract | Give with liquid in a ratio of 1:5000. |
| Poisoning by poisons | Give intravenously 0.1-0.25 ml of 1% solution per 1 kg of chicken weight. |
| Poisoning with cyanide, hydrocyanic acid or hydrogen sulfide | Give intravenously at the rate of 0.5 ml of 1% solution per 1 kg of chicken weight. |
As can be seen from the table, the main areas of use of the drug are the fight against infections and poisoning, as well as the treatment of wounds.
Mode of application
When washing, which is carried out for cystitis or urethritis, a Methylene blue aqueous solution is prescribed. According to the recipe, the solution ratio should be 1:5000. The procedures are carried out 1-2 times a day, their duration is determined by the doctor.
Internal use of methylene blue for adults – 0.1 g 3-4 times a day. For children, the dose is calculated based on the child’s age, the approximate dosage is 0.005-0.01 g for 1 year.
Poisoning caused by cyanide or hydrogen sulfide requires intravenous use of the drug. To do this, prescribe 50-100 ml of a 1% aqueous solution or a 1% solution with 25% glucose. In case of intoxication with nitrates or aniline, the dosage should not exceed 0.1-0.15 ml/kg of a 1% solution.
During the treatment of stomatitis, an aqueous solution of blue is used. Since an alcohol solution can harm the mucous membrane, cause burns, and poisoning in children. For stomatitis, use a cotton swab to treat all ulcers and wounds. The procedure is carried out 3 times a day, after each meal.
Preparation and rules for using rinse solution
To rinse the mouth, prepare a blue solution in a ratio of 1:5000. To prepare the preparation for rinsing, take an aqueous solution of blue. Rinsing is done after eating.
To increase the effectiveness of the drug, it is also recommended to treat the aphthae with essential oils before rinsing.
Repeat this procedure 3 times a day for ordinary stomatitis. If a person has herpetic stomatitis, the number of rinses can be increased to 5 times a day. Read more about how to rinse your mouth for stomatitis here.
It should be remembered that blue is a dye. It is recommended to work with it only with gloves so as not to stain the skin.
Release form and indications for use
With the help of blue, you can cure various types of stomatitis, from mild forms to advanced ones. The earlier the course of treatment for stomatitis was started, the higher the likelihood of rapid healing without the development of serious complications. Stomatitis requires an integrated approach to therapy, along with bluing, patients are prescribed antipyretic, antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs.
Despite the fact that blue is the most harmless remedy, it has certain contraindications. The very first and main thing is individual intolerance to the components. It is expressed in the form of headaches, general psychological discomfort and allergies.
Often, side symptoms from the use of the drug manifest themselves in the form of indigestion, vomiting, and general weakness. There are also unpleasant sensations in the area of the bladder and kidneys. If such symptoms are detected, stop treatment with the drug.
In addition, blueing during the treatment of stomatitis can stain the teeth and lips in a characteristic color. So during the treatment process, the patient must be prepared for the fact that the aesthetic appearance is impaired.
Methylene blue is classified as an antiseptic. In veterinary medicine it is widely used for the prevention and treatment of the following diseases:
- fungal diseases of fish;
- rheumatic diseases of horses;
- infectious diarrhea of sheep and goats.
It also demonstrated excellent performance in the treatment of bird diseases caused by various infections.
| Appearance | Crystal granules |
| Solubility | Diluted in water in a ratio of 1:30, slightly soluble in alcohol. |
| Storage conditions | In a tightly closed container, in a dark place at a temperature from 150˚C to 250˚C. |
| Release form | Powder and ampoules containing 20 and 50 ml of 1% solution of methylene blue in 25% glucose solution; alcohol solution: in glass bottles of 10 ml. |
| Best before date |
|
| Compound | 10 ml alcohol solution:
|
The principle of action of blue is the ability of the active substance to form compounds with proteins of the pest cell, which helps destroy harmful bacteria.
Methylene blue does not irritate the skin or mucous membranes, but has a quick and long-lasting effect on the site of infection. According to the instructions for use, the drug is recommended for:
- rheumatism in horses and cattle;
- diarrhea of infectious nature in goats and sheep;
- fungal infections in aquarium fish;
- any infectious diseases in poultry.
Veterinarians praise the effectiveness of methylene blue. It is considered the most effective in its group of drugs. Methylene blue quickly dries wet wounds and speeds up their healing. It is completely safe.
The only downsides people note are the specific smell and strong soiling of the product. Despite all the positive aspects, methylene blue should be dosed exactly according to the instructions for use. Exceeding the norm when taken internally is fraught with rejection in the form of vomiting and abdominal pain. Animals may also develop swelling.
Attention! Dry powder is stored indefinitely in a dry place, liquid preparations - 3 years. Instructions for use allow for both external and internal administration of methylene blue
Standards and recommendations for the treatment and prevention of poultry diseases:
The instructions for use allow for both external and internal administration of methylene blue. Standards and recommendations for the treatment and prevention of poultry diseases:
- Wounds of any nature on the skin. Rinsing the affected and adjacent areas with an alcohol solution of 1-3%. Also use 1-2% powder.
- Bursitis. Inject a 2% alcohol solution directly into the wound. Dose – 0.01 ml/kg live weight of the bird.
- Gastrointestinal infections. Give with drink at a dosage of 1:5000.
- Diseases of the urinary tract of an infectious nature. Washing organs with a solution of 0.02%.
- Poisoning. Administer by injection 0.1-0.25 ml/kg at a time. Use a 1% aqueous solution.
- To treat fish, methylene blue is not used in a community aquarium. The dye may damage his device. First, sick individuals are placed in a separate container. Dosage – 1 ml (20 drops) per 50 liters of water.
For other animals, use liquid methylene blue 0.5-1% with drink:
- horses and cattle – 200-600 ml;
- sheep, pigs, goats – 50-160 ml;
- dogs – 10-30 ml.
An alternative is intravenous administration of a 1% solution:
- horses, cows – 100-200 ml;
- goats, pigs, sheep – 20-50 ml;
- dogs – 10-30 ml.
What disinfectants do you use for animals?
Point of view
To form a final opinion about whether it’s worth using bluing at all and how effective and safe it is for stomatitis, we recommend studying the reviews.
Read also: Analgin for toothache, method of use
Stomatitis did not spare my five-year-old child. Of course, I immediately called a doctor to my house, who, after examining me, prescribed me methylene blue.
I doubted it a little, but still decided to try. And you know, I am very grateful to our doctor, since the baby’s ulcers began to disappear literally on the 3rd day from the moment of using the product. Moreover, my son’s body temperature returned to normal.
For those who have not yet used this product, I recommend it and I want to say that the bluish is washed off very well from the body, but not from clothes, so be careful during the application process.
Alisa, 27
My wife also had this problem. The first time I saw her with a blue mouth, I laughed a lot. Of course, she couldn't help but be offended. I never found out from my wife herself why she smeared blue on her mouth (I was very offended), I decided to read it on the Internet.
It turns out that in this way she got rid of an unpleasant illness. And she learned this not from strangers, but from her grandmother, who treated her children and grandchildren in this way. After 5 days, there was not a single wound or reminder of the disease in my beloved’s mouth. He apologized for a long time.
Sergey, 30
I have suffered from stomatitis since childhood, and doctors constantly prescribed some medications, thanks to which I got rid of the disease for a very long time. But one day my mother came across an article about the beneficial properties of methylene blue. We decided to try it. The effect was amazing. Already on the 4th day I forgot to think about the disease. I recommend to everyone.
Marina, 27
The medicine should be stored in a place that is difficult for children to reach. Try to keep the product away from direct sunlight. Blue can be stored for no more than 1 year and only at a temperature that does not exceed 30 degrees.
Side symptoms
Unfortunately, even the safest medicine cannot guarantee 100% absence of side symptoms. First of all, it is important to note that a safety risk arises when severely affected areas are treated. As a result, the child may feel a strong burning sensation or redness.
As a rule, such symptoms occur only in two possible cases:
- Individual intolerance, due to the specific reaction of the body.
- Failure to comply with dosage.
Also, in the course of multiple studies, it was noted that blue can cause digestive system upset if the patient suffers from severely reduced immunity. In this case, the specialist can add drugs that help restore the microflora. No other adverse symptoms were observed in any group of subjects, which may indicate the complete safety of the drug.
Treatment of blue stomatitis in children
The use of methylene blue in children is somewhat different from its use in adults. Firstly, children should not treat ulcers so often. The maximum number of uses during the day should not exceed four, and this should be done strictly after meals.
When the causative agent is a herpes infection, the number of daily repetitions can be increased to 5. When used on the mucous membrane, only an aqueous solution is indicated for children.
If stomatitis treatment is carried out for a baby, you should also take care of the mother, if the latter is nursing. A few drops of solution are also applied to her nipples - in this case, babies do not need to smear the mucous membrane with cotton swabs or disks (to avoid the risk of damaging the inside of the mouth), but the baby will still receive a certain amount of bluish.
Use of blue in the USSR
One of the medical institutions of the USSR conducted an interesting experiment in the middle of the last century. We assembled a children's group of 86 people, all of different ages - 1-10 years. The children had only one thing in common - they all suffered from stomatitis in one form or another. Thus, 56 children were infected with the aphthous type, 17 people encountered allergic stomatitis, and another 13 children had the ulcerative form.
All patients underwent a full medical examination, pathogens were detected, etc. The children were treated with bluing, but in various forms.
First, we identified a group of children whose age did not exceed 1.5 years. The affected areas were treated with iodide starch. There was also a middle group, where children under 2 years old were collected, in this case they were treated with applications. In both groups, application was carried out every day - first within the walls of the institute, and then at home.
Doctors noted that children who were experiencing the acute stage of the disease, characterized by high fever and enlargement of the lymph nodes, were on the mend already on the third day after using the blue. Complete recovery was observed after 6-7 days. Those children who were diagnosed with a milder form of the disease completely returned to normal after 3 days.
At the same time, a group was identified that was treated with antibiotics prescribed by doctors at the clinic. Interestingly, with this treatment, complete relief from the disease in the oral cavity occurred only after 9-10 days.
In other words, the experiment showed that methylene blue gives good results for stomatitis (note once again that we are talking about an aqueous solution, not an alcohol one). After this, blue was recommended for use in children's medical institutions. It is strange that even after so many years not everyone has heard of this remedy; methylene blue is unpopular completely undeservedly.
Almost all parents today strive to save their children from the disease with fashionable creams, sprays, tablets, which are not so effective and also cost many times more. It just so happens that today the effectiveness of a medicine is directly related to its price - supposedly, the more expensive it is, the better. By the way, blue is not produced in every pharmacy, but expensive products are available almost everywhere. However, to this day, methylene blue remains one of the most effective drugs for the treatment of stomatitis. It has an antifungal effect, perfectly fights viral infections, and copes with bacteria. In addition, blue has the ability to heal and relieve inflammation. Today, not every drug can boast such a set of powerful effects.
Video:
Medicines for stomatitis - TOP-11 drugs for treatment
Watch this video on YouTube
Posted by:
Work experience 32 years. Place of work: “Dentistry ECT”. Graduated from SamSMU (1985)
2018-02-24
Medical research
In the middle of the 20th century, a couple of mass experiments began on the territory of the Russian Federation. Children in the age range of 1.5 – 10 years were selected as subjects. A total of 86 applicants were selected. The group was selected so that different forms of the disease were present. Thus, 86 people, 56 had clear signs of aphthae, in 17 cases stomatitis manifested itself as an allergic response to a drug, 13 suffered from ulcerative rashes. All findings were verified by high-quality medical examination, so the likelihood of error was minimal.
During the experiment using blue, the following results were obtained:
- Within three days, the children's temperature began to drop;
- After a week, the child’s body began to actively fight and the stage of recovery began.
Considering these data, we can conclude that blue is an effective remedy for the treatment of stomatitis in children, with minimal or complete absence of side effects and a fairly good result.
Analogs
There are no medications with the same chemical composition.
However, this drug has a number of antiseptic analogues (drugs that have a similar effect), which can be used to treat a patient if it is not possible to use methylene blue.
The most popular of them are the following:
| Cheap, price about 20-30 rubles | Antiseptics cost from 70 to 250 rubles |
| Brilliant green (green) | Furacillin |
| Rotokan | Ingalipt |
| Chlorhexidine | Chlorophyllipt |
| Hydrogen peroxide | Miramistin (ointment or solution) |
The selection of a specific medication is carried out taking into account the characteristics of the viability of pathogenic microorganisms.
Side effects
If the recommended dose of the drug is exceeded or a person is hypersensitive to the active substance, blue in the treatment of stomatitis may cause side effects. Most often, patients in such cases experience severe irritation of the mucous membrane and redness in the mouth. Side effects from this drug disappear after stopping its use.
In persons with reduced immunity, as well as in children over one year old, an overdose of blue may experience stomach upset. If such a symptom appears, patients should immediately consult a doctor. He will prescribe medication to relieve the condition and replace the bluing with another rinse.
Properties and use for medical purposes
This drug belongs to the group of antiseptics prescribed for external use (the effect is similar to Miramistin or Chlorhexidine for stomatitis). Its active substance binds bacterial cells and stops the development of pathogenic organisms. Additionally, this product creates a protective film on the surface of the mucosa, which promotes accelerated tissue regeneration. The drug is effective against most pathogenic bacteria and, when used systematically, can treat diseases such as stomatitis in 5 days.
The active components of the presented drug do not penetrate the skin bloodstream. This eliminates the possibility of any toxic effects of the drug on the body.
Indications for use and properties
The use of methylene blue in an aquarium allows aquarists to quickly and effectively disinfect the aquatic environment in the tank. The product can be added directly to the water to prevent disease and prepare the aquarium for new residents.
The undoubted advantage of the drug is that aquarium fish tolerate methylene blue well, since it is safe and sold at a favorable price. When used, the product has the following effects on the aquatic environment:
- Improves liquid quality.
- Eliminates fungal diseases.
- Cures against single-celled parasites.
- Promotes better development of caviar.
- Reduces stress in fish when moving to a new container.
Most experienced aquarists use methylene blue as a preventive measure when transporting and moving fish to a new tank to reduce stress in their wards. In addition, the drug also eliminates the possibility of pathogenic fungi and parasites entering the aquarium.
Blue in an aquarium is also used to treat such dangerous and common ailments as:
- Aeromonosis, or abdominal dropsy - with the development of this disease, pets become lethargic and inactive. Soon the fish lose their appetite, the victims constantly lie on the bottom, the tummy swells, and large red spots form on the body.
- Branchiomycosis, or gill rot - the disease can be recognized by the following symptoms: fish lose activity and appetite, scarlet and dark stripes form on the gills. With further development of the disease, necrosis of the gills occurs, as a result of which they become dark gray in color.
- Gyrodactylosis is a disease of parasitic origin, and is provoked by fluke parasites. With the development of gyrodactylosis, the appearance of the fish undergoes dramatic changes: white mucus appears on the body and hemorrhages on the fins. Pets behave restlessly and refuse to eat.
- Tetrachymenosis - like gyrodactylosis, the disease is caused by parasites. The disease can be eliminated by using methylene blue.
Description
The drug is widely used to suppress any fungal, viral and bacterial infection that develops in the oral cavity. The main component of the drug is methylthionine chloride. The auxiliary ingredient is ultra-purified water. When treating stomatitis, a 1% aqueous solution should be used. It can be purchased at a pharmacy. Release form: bottles with a capacity of 25, 50, 100 ml.
The antiseptic methylthionine chloride is a liquid colored bright blue. The main substance, methylene, is capable of quickly penetrating into tissues, staining them upon slight contact. Therefore, it is recommended to wear gloves before handling.
The action of blue is based on its ability to bind bacterial cells, thereby neutralizing pathogenic microorganisms. In this case, aqueous methylene does not penetrate into the systemic circulation.
The drug should be stored in a closed bottle and a dark place, away from children. It is prohibited to use the product after its expiration date.
Composition and release form of the drug – blue or methylene blue solution
Methylene blue solution (otherwise called blue) is an antiseptic solution, the main active ingredient of which is methylthioninium chloride, the auxiliary component of the presented product is distilled water. It is available in 25 mg bottles.
The solution is a homogeneous blue liquid without precipitation. Blue is also available for sale in powder form for homemade solution, as well as a solution of blue in alcohol. The drug is available without a prescription.
To treat the oral mucosa, you need to use an aqueous solution of blue. It does not irritate the mucous membranes and is suitable even for children over one year old. Alcohol-based liquid can cause burns to the mucous membrane.
Contraindications for use
1. Wrap a gauze swab around your finger or prepare regular cotton swabs.
2. Remove the resulting plaque from the affected areas of the oral cavity using any antiseptic. Using a regular soda solution is very effective.
3. The surface of the mucous membranes must dry.
4. For bluing, take a new tampon.
5. Carefully treat all affected areas with the medicine, including adjacent healthy tissues.
We treat stomatitis with bluing from 3 to 10 times a day until the ulcers, wounds, and erosions completely disappear. After using the drug, you must refrain from eating for an hour.
The duration of treatment depends on several factors:
- stages of the disease;
- presence of pathologies;
- the patient's immune status.
Even the most harmless remedy may have its contraindications. The instructions describe factors that prevent the use of the solution in question.
The drug should not be used by patients who have an individual intolerance to the active substance of the drug. It is expressed in headaches, general psychological discomfort, and allergic reactions.
Where, what and how to lubricate?
The use of aqueous solutions is advisable for the following diseases:
- Stomatitis, caries, thrush, herpes in the oral cavity for disinfection, drying of ulcers, blisters, ulcers, accelerating the regeneration of mucous membranes.
- Follicular tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis - as a local antiseptic, spot treatment of pustules.
- Thrush - to destroy pathogenic fungi in the mouth of babies and on the cracks of the nipples of mothers' breasts. Used in the vaginal area to lubricate individual fragments of the blistering rash.
- Inside the urethral canals it is used to cleanse bacteria.
- Only in hospital settings: for diagnostic purposes - used intravenously. In case of poisoning, use according to the protocol after identifying the type of toxin.
The use of an alcohol solution is practiced to disinfect the epithelium in the following cases:
- On small surfaces there are thermal burns.
- For ulcers and blisters on the skin due to infectious lesions.
- To reduce the area of suppuration in eczema, pyoderma.
- For the purpose of disinfecting blistering rashes and boils.
- For insect and animal bites to prevent bacterial infection of wounds.
- For antiseptic treatment of skin damaged as a result of injuries (a child fell, a broken knee).
In case of a rash of unknown etiology, it is impossible to lubricate the blisters with methylene blue before examining a doctor; this will lead to a distortion of the picture of the infectious disease, inaccurate diagnosis, and, as a result, incorrect treatment.
Contraindications to the use of the drug for the treatment of stomatitis are:
- hypersensitivity to the drug;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding;
- patient age up to one year.
conclusions
- Blue is an antiseptic whose main active ingredient is methylthioninium chloride.
- The drug is used in dentistry to treat bacterial, fungal, and herpetic stomatitis.
- The main contraindications to its use are hypersensitivity to the drug, pregnancy, and the patient’s young age.
- To treat the mucous membrane, use an aqueous solution of blue. They treat the affected areas of the mouth, as well as nearby tissues. The product is also used to rinse the mouth.
- The course of treatment with blue is from 5 to 10 days. The exact duration of treatment is determined by the doctor, taking into account the patient’s condition, the type of stomatitis, as well as the presence of concomitant diseases. Rinsing can be combined with cauterization of problem areas. Read more details about how to cauterize stomatitis here.
Instructions for using bluing for stomatitis
A solution of methylene blue for stomatitis is approved for use by children and adults. Only a doctor should determine the method of treatment and duration of the course.
In doing so, it takes into account the following factors:
- stomatitis clinic;
- severity of the disease;
- patient's age.
Usually, during the acute and chronic stages, treatment of the entire area of the mucous membrane is prescribed. Single rashes can be applied to spots.
Instructions for using stomatitis blue for adults:
- Pre-treatment of the oral cavity involves removing white plaque. To do this, wrap your index finger with a sterile gauze pad and wipe the affected areas. The tampon must first be moistened in a soda solution (1 teaspoon per glass of water) or in sea buckthorn oil.
- If the doctor has prescribed treatment of the entire mucous membrane, then wipe it with a sterile cloth moistened with a blue solution. With the spot method, only the affected areas are lubricated with the medicine. Using cotton swabs, bluish the sores, grabbing some healthy tissue around the wounds.
- Doctors recommend that adult patients undergo procedures at least 10 times a day. In some cases, treatment of wounds with blue is prescribed every 1–1.5 hours (but no more than 15 times a day).
Stomatitis requires an integrated approach to treatment. Along with blueing, patients are prescribed antipyretics, antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs. Switching to a gentle diet will speed up recovery.
Doctors recommend eating dishes warm and with a soft consistency. Allergic foods and all irritants (spicy, sour foods) are excluded from the diet.
If you follow all the rules for using bluing, relief occurs within 3–4 days. The course of treatment for acute stomatitis is a week. And the chronic stage requires longer treatment (up to 20 days).
The instructions for treating blue stomatitis in children are somewhat different. Let's consider the algorithm of actions:
- Only a doctor should prescribe the use of the drug. First of all, the child is shown to a pediatrician or dentist. Having determined the type of pathogen, the doctor selects effective therapy. The fact is that blue itself is capable of destroying only bacterial forms of stomatitis. Viral pathogens are neutralized with appropriate drugs. In this case, blue acts as an auxiliary medicine.
- Before using the drug, it is necessary to remove white plaque from the affected areas. Do this in the same way as described above. When removing plaque, change tampons frequently. Read more about white gums in babies→
- Antiseptic liquid is applied pointwise in childhood using cotton swabs. Children under 6 years old are prescribed 2 procedures per day. Older children are allowed 4 treatments per day. Taking into account individual characteristics, the doctor may prescribe a different number of procedures.
- In infancy, treatment with cotton swabs is not recommended. It is better to apply a few drops of blue to the mother's nipple before feeding. The number of procedures per day is prescribed by the doctor.
Recovery can only be achieved with daily use of the drug. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, wound healing occurs already on the 3rd day. Full recovery occurs within 6–7 days. Chronic stages of stomatitis require longer use of blue (14–21 days).
Storage conditions and interactions with medications
Methylene blue is available without a prescription. The purchased drug must be packaged in a hermetically sealed bottle with an additional cap. It is recommended to store the solution in a dark, dry room with average air humidity. Do not expose the bottle with the active substance to direct sunlight. The average temperature at which a sealed and opened bottle is stored is from 15 to 25 degrees Celsius.
The shelf life when stored correctly is 2 years from the date of issue, which is indicated on the package. Drug interactions with other medications were not identified during the studies. Ethyl alcohol included in the product, when taken orally, can impair coordination of movement or inhibit the body’s usual reactions, therefore, after taking the drug, travel and excessive physical activity should be limited.
Methylene blue can be successfully used in the fight against many chicken diseases
Methylene Blue is an antiseptic drug.
No significant interaction with other agents has been identified.
But the following adverse reactions were observed in some patients:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Abdominal pain;
- Burns of mucous membranes;
- Allergic skin rashes.
Blue for stomatitis - methods and features of using the medicine for children and adults
Any diseases of the oral cavity are doubly difficult to endure, since they not only bring discomfort to existence, but also significantly reduce the quality of life. One of these ailments is stomatitis, which affects both adults and children.
Treatment of a disease, regardless of its type, is a rather long and painstaking process that requires care and planning.
When treating various types of stomatitis in patients large and small, professionals often prescribe methylene blue, or simply blue. This remedy has been used for several decades with unfailing success. Therefore, the vast majority of dentists answer the question: “Is it worth using bluing for stomatitis?” They answer unequivocally: “It’s worth it!”
Pharmacokinetics of the substance
The main effect that blueing has is disinfection and restoration of an acidic environment; it perfectly conducts hydrogen ions in tissues, due to which it is periodically used as an antidote for poisoning.
In cases of local exposure, blue is not able to enter the bloodstream, therefore it is considered a safe medical product. Even if swallowed, there may be no side effects; it is eliminated through the excretory system.
Methylene blue, which enters the body through injection, is eliminated through the renal system.
Impact on microorganisms
It has an effect on certain types of gram-positive microorganisms, converting their proteins and mucopolysaccharides into ionizing compounds.
Release form
In pharmacies it is sold in the form of a 1% aqueous solution and crystalline powder with a dark green metallic sheen.
Indications for use
The scope of application of methylene blue is quite wide. This remedy is used in the treatment of various organs and areas of the body:
- Thermal injuries;
- Purulent or inflammatory diseases of the epidermis;
- Diagnostics of renal function;
- Inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary excretory system;
- Stomatitis.
Contraindications for use
Unlike most modern medications, the list of contraindications to methylene blue is small:
- Age up to 1 year;
- Hypersensitivity to the constituent components of the drug.
It is important to note that during pregnancy and lactation, a woman may be recommended to apply topical blue, since this substance does not penetrate the circulatory system and, therefore, cannot cause harm to the fetus and breastfed child
Side effects
If you carefully follow medical recommendations and follow the instructions, blueing most likely will not cause harm to your health.
But the following adverse reactions were observed in some patients:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Abdominal pain;
- Burns of mucous membranes;
- Allergic skin rashes.
Applications of methylene blue
Instructions on how to use bluing include not only its medical use, but in this article we will tell you how it works in the treatment of stomatitis.
Saliva is constantly produced in the oral cavity, which “washes” all areas. Therapy for stomatitis involves frequent treatment of affected areas to prevent the affected areas from growing.
First, remove the top layer from the ulcers. You can do this using a folded bandage, a cotton pad, a cotton swab, or any other clean material.
For adult patients, it is recommended to repeat these steps up to 15 times a day.
The use of blue in children
Dentists often prescribe blue for stomatitis in children, since this solution leads to a significant improvement in the condition already on the third day of use.
After one year of age, it is recommended to treat the breast or pacifier that the baby puts in his mouth. Sanitation is carried out up to 3 times a day.
From one to six years, the procedure is identical to adult treatment: remove plaque, blot off excess moisture, treat ulcers with methylene blue. Repeat up to 5 times a day along with additional therapy.
After age six, a healthcare professional may prescribe rinsing up to 10-12 times per day.
How to make a solution from powder
Pharmacies sell a ready-to-use 1% blue solution. The powdered substance lasts longer, so if this is the only option available, there are two ways to make a blue solution for stomatitis. You can order the solution from a pharmacist or mix it yourself. The shelf life of the diluted powder is 14 days.
Dilute 10 grams of powder in 1 liter of boiled water until the crystals are completely dissolved.
Strain the resulting solution through a fine sieve or cheesecloth in several layers (at least 6).
Now you know how to properly use bluing for stomatitis. Take care of your health and be fully armed!
Symptoms of the disease
The name of the disease comes from the Greek word for mouth. The most common manifestations are:
- Deformation of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity , the appearance of swelling.
- After the formation of a whitish coating , small ulcers appear.
- A rapid increase in temperature that is not amenable to medication.
- Gums lose their elasticity and begin to bleed.
- The presence of a specific unpleasant odor during the development of the inflammatory process.
Blue has been actively used for stomatitis in children since the 90s, so today it is widely used . However, if a child is very young and has become infected with stomatitis, it is better to first consult a specialist.
Methylene blue is a common medicine for stomatitis.