Gum inflammation
Recommended Articles
- Causes of gum inflammation
- Types of inflammation
- Main manifestations and symptoms
- Diagnostic features
- Treatment methods
- Prevention methods
Gum inflammation is a general concept that includes both superficial and deep inflammatory processes. Everyone faces this problem to one degree or another, and in the absence of proper attention to the condition of the oral cavity, inflammation can lead to serious consequences, including the loss of healthy teeth. It is important to recognize in time not only the onset of inflammation, but also to assess the depth of its spread, receive qualified dental care and prevent complications.
Consequences of periodontal disease
Periodontal disease requires urgent treatment, as it can lead to serious consequences:
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis;
- intoxication of the body with pus;
- loss of teeth;
- cancerous tumors;
- impossibility of prosthetics;
- pulpitis;
- serious problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
Specialists of the 32 Dent clinic network specialize in the treatment of all types and forms of periodontal disease. Every day, doctors help patients once and for all get rid of a problem that brings internal discomfort and unaesthetic changes.
Gingivitis
This is the first and reversible stage of periodontitis. Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums. This disease is very dangerous during pregnancy - due to changes in the hormonal levels of the pregnant woman, the disease progresses faster than usual, can lead not only to the loss of teeth in the pregnant woman herself, but also cause dental problems in the future in the child, and even provoke premature birth.
If you notice the following signs, then most likely these are symptoms of developing gingivitis:
gum inflammation, bleeding,
bright red gum color,
pain and swelling in the gum area,
bad breath, quickly forming plaque and stones.
Signs of periodontal disease
- the size of the partitions between the teeth decreases;
- gums bleed profusely;
- food constantly gets stuck between teeth;
- ulcers and ulcers form on the surface of the gums;
- temperature rises;
- itching of the gums increases with the progression of the disease;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, noticeable by the patient himself and those around him;
- the necks of the teeth are exposed;
- the gums peel away from the teeth;
- gum tissue acquires a light shade;
- there is a feeling when “all your teeth” hurt (in fact, the pain is localized in the gums);
- teeth gradually become loose until they fall out completely;
- It is not possible to chew food, immunity decreases.
Depending on the level of spread of the lesion, there are:
- the initial stage of periodontal disease - symptoms are almost completely absent, but changes in the periodontium are already occurring, the patient feels mild itching, periodic pain;
- the second stage is when the size of the partitions between the teeth decreases. Food often gets stuck, there is heavy bleeding, there is a feeling when “all your teeth hurt”;
- advanced periodontal disease - the periodontal tissues are severely destroyed, ulcerative lesions can form on the gums, teeth become loose and fall out.
Forms of dental disease:
- acute periodontal disease – with this form the patient feels pain, itching, and general discomfort;
- chronic periodontal disease is a more complex form, which is characterized by outbreaks of pain, the formation of abscesses (purulent periodontal disease), and exposure of the roots.
Antibiotics after tooth extraction
One of the surgical operations in dentistry is the removal of wisdom teeth. Antibiotics in the preoperative period are prescribed for prophylactic purposes to patients with glomerulonephritis, endocarditis, diabetes mellitus, and those with weakened immune systems. Prevention is possible with planned removal, which is carried out in case of atypical position and mobility of the unit, in case of chronic cysts and periodontitis, in case of mechanical damage without the possibility of recovery after sanitation of the oral cavity.
An antibiotic is also prescribed after tooth extraction if the operation is performed as an emergency. More often, Ciprofloxacin. What antibiotics to take after tooth extraction is prescribed by the dentist, taking into account the specifics of the microflora. The main indications for such removal are acute purulent inflammatory diseases localized to bone tissue, abscesses, lymphadenitis, and phlegmon. Antibiotics are used for tooth extraction if it is not subject to conservative treatment, including filling, due to extensive destruction and loss of functionality.
Antibiotics for wisdom tooth removal are prescribed if the integrity of bone or soft tissue was damaged during the procedure, which in the future can provoke infection, inflammation, and the formation of gumboil. Antibiotics after wisdom tooth removal are prescribed for the following complications:
- Alveolitis. It develops 3-4 days after surgery and is characterized by a dry gray lump with a whitish coating. The pathology is characterized by an unpleasant odor, pain, swelling of the cheek, and an increase in temperature to 38-39 °C.
- Apical periodontitis. Periodontal inflammation of an infectious, traumatic or medicinal nature is treated comprehensively. It is necessary to ensure the outflow of exudate, prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics, antiseptic treatment, and filling the canals.
- Osteomyelitis. A purulent-necrotic process caused by pyogenic bacteria and mycobacteria. With this pathology, hospitalization is necessary. How and what antibiotics to take for this pathology after tooth extraction will be prescribed by the leading doctor.
Cost of periodontal disease treatment
The price of periodontal disease treatment depends on the following factors:
- volume of lesion;
- type of periodontal disease;
- forms of the disease;
- general condition of the oral cavity;
- chosen type of treatment.
On average, periodontal treatment in a good clinic costs from 1000 rubles per tooth. The total price of therapy is calculated individually. To find out the cost of effective treatment in a particular case, sign up for a consultation with a 32 Dent dentist.
Types of inflammatory and dystrophic gum diseases
Inflammatory manifestations include:
- Gingivitis
- Periodontitis
Dystrophic manifestations include:
Gingivitis: signs, causes and treatment
Gingivitis is the first stage of inflammation, in which the integrity of the periodontal junction has not yet been compromised. This disease can be identified by the following signs:
- Swelling of the gums.
- Blood while brushing teeth.
- Pain when eating cold, hot or solid foods.
Improper brushing of teeth, errors during fillings and dentures, improper bite – all this can cause gingivitis. By the way, this is one of the most popular problems that pediatric dentists encounter.
Treatment of gingivitis involves a set of procedures carried out in a dental clinic and at home. If there is dental plaque, it is necessary to carry out ultrasonic cleaning. In addition, you should pay more attention to hygiene: brush your teeth properly and use antibacterial agents.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a pathology that occurs as a result of advanced gingivitis. In this case, the swelling of the gums becomes even stronger, they begin to bleed frequently. If left untreated, infection and pus may form. As a result, the bone tissue begins to atrophy, and this leads to increased sensitivity of the teeth, their mobility, and sometimes even loss.
Treatment of periodontitis is prescribed taking into account the course of the disease. At first, procedures such as removing plaque from the enamel and regular brushing of teeth with antiseptic agents may be sufficient. In more serious situations, when the infection has penetrated deep into the bone tissue, surgery may be necessary:
- Partial gum excision.
- Cleaning periodontal pockets.
- Implantation of bone tissue substitutes.
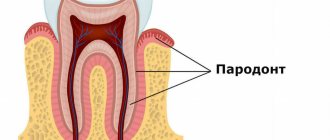
Periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is a systemic disease. As a rule, it is typical for elderly patients. Inflammatory-dystrophic manifestations in this case are concentrated in the periodontal tissue.
Periodontal disease develops at a leisurely pace, gradually erasing tooth enamel. The presence of this disease can be determined by exposed tooth roots and cervical chips of tooth enamel. In most cases, no pain occurs, but if you ignore the problem, you can “lose” your teeth.
To eliminate periodontal disease, it is necessary not only to observe and treat the dentist, but also to related specialists.
Treatment of inflammation at home
The course of treatment of teeth and gums is always selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the disease:
- A type of inflammatory process.
- Neglect of pathology.
- Patient's age.
For example, in adult patients, inflammatory processes most often occur due to chronic diseases. To eliminate the problem, as a rule, pharmaceutical products are required - antiseptics, gels, ointments, antibiotics, toothpastes. If a child’s gums become inflamed, this is almost always associated with teething and herbal medicine, that is, rinsing with herbal decoctions and using other methods of traditional medicine, is sufficient for treatment.
Whatever the situation, adequate treatment is only possible after consultation and diagnosis by a qualified doctor. Remember that the wrong choice of procedures can not only fail to produce results, but also cause painful complications.
Antiseptics
Rinsing with antiseptic agents is the most important step in the fight against inflammatory processes. Let's name well-proven drugs that can be purchased at the pharmacy:
- Malavit - reduces inflammation and prevents its development, but does not eliminate pain effectively enough.
- Kamistad – recommended in the presence of severe pain. It also copes well with swelling.
- Chlorhexidine is a suitable treatment for gingivitis in children. Daily rinsing after meals is recommended.
- Listerine is a good drug for eliminating swelling. Suitable for all types of gum inflammation.
- Stomatophyte is an antiseptic made from natural raw materials: chamomile flowers, oak bark and sage leaves.
- Furacilin is an excellent antimicrobial agent. Penetrates inside the microbial cell, preventing its division.
- Miramistin is an anti-inflammatory drug with a pronounced antimicrobial effect.
Gels and ointments
Therapeutic gels and ointments are applied to the inflamed gums after rinsing with antiseptic agents. They provide effective protection to the mucous membrane, preventing infection from entering wounds and helping to cope with pain.
List of the most effective gels and ointments:
- Metrogyl Denta is a powerful antiseptic gel. It has pronounced anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties.
- Cholisal is one of the best options for combating inflammation that occurs due to internal reasons. Relieves pain well.
- Kamistad - suitable for both preventing gingivitis and combating complications (severe swelling, pain).
- Gengigel is an excellent healing agent. Improves blood supply, promoting rapid healing of wounds in the oral cavity.
- Stomatophyte A – recommended for severe and prolonged pain.
- Asepta - contains propolis, which provides accelerated tissue regeneration and reduces inflammation.
- Solcoseryl is a healing agent with a pronounced anesthetic effect.
Metronidazole
Gastrointestinal disorders: epigastric pain. nausea, vomiting. diarrhea, glossitis, stomatitis, “metallic” taste in the mouth, decreased appetite, anorexia, dry oral mucosa. constipation, pancreatitis (reversible cases), discoloration of the tongue, coated tongue" (due to the proliferation of fungal microflora).
Immune system disorders: angioedema, anaphylactic shock.
Nervous system disorders: peripheral sensory neuropathy, headache, convulsions, dizziness, the development of encephalopathy and subacute cerebellar syndrome (impaired coordination and synergism of movements, ataxia, dysarthria, gait disturbances, nystagmus, tremor) has been reported, which are reversible after discontinuation of metronidazole , aseptic meningitis.
Mental disorders: psychotic disorders, including confusion, hallucinations; depression, insomnia, irritability, increased excitability.
Visual disturbances: transient visual disturbances such as diplopia, myopia, blurred contours of objects, decreased visual acuity, impaired color perception: neuropathy/optic neuritis.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: agranulocytosis, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract: increased activity of liver enzymes (aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase), development of cholestatic or mixed hepatitis and hepatocellular liver damage, sometimes accompanied by jaundice; In patients treated with metronidazole in combination with other antibacterial agents, cases of liver failure requiring liver transplantation were observed.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: rash, itching, skin flushing, urticaria, pustular skin rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome. toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Disorders of the kidneys and urinary tract: staining of urine in a brownish-reddish color, caused by the presence of a water-soluble metabolite of metronidazole in the urine, dysuria, polyuria. cystitis, urinary incontinence, candidiasis.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site: fever, nasal congestion, arthralgia, weakness.
Laboratory and instrumental data: flattening of the T wave on the electrocardiogram.
Description
Compound
active ingredients: metronidazole benzoate, chlorhexidine digluconate
1 g of gel contains metronidazole benzoate in terms of metronidazole 10 mg, chlorhexidine digluconate solution 20% in terms of chlorhexidine digluconate 0.5 mg
excipients: carbomer, propylene glycol, sodium saccharin, trilon B (trilon B), triethanolamine, peppermint oil, purified water.
Dosage form
Basic physical and chemical properties:
gel is white or almost white in color with a specific odor. It should be uniform in appearance.
Pharmacological group
Products for use in dentistry . Antimicrobial and antiseptic agents for topical use in dentistry.
Pharmacological properties
Antimicrobial combination drug for the complex treatment and prevention of certain infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
The effectiveness of the drug is due to the presence of two antibacterial components - metronidazole and chlorhexidine.
Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole derivative that has antiprotozoal and antibacterial effects. Active against anaerobic bacteria that cause periodontal diseases: Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, Prevotella denticola, Fusobacterium fusiformis, Wolinella recta, Eikenella corrodens, Borrelia vincenti, Bacteroides melaninogenicus, Selenomonas spp.
Chlorhexidine is a bactericidal antiseptic. Active against a wide range of vegetative forms of gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms, as well as yeast, dermatophytes and lipophilic viruses.
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC50) of metronidazole for anaerobic bacteria is below 1 μg/ml. When applied topically (applied to the gums), the concentration of metronidazole in the gum area is significantly higher than when the drug is administered orally, and the level of systemic absorption of metronidazole when applied topically is significantly lower than when administered orally. The main route of excretion of metronidazole and its metabolites is the kidneys. Reduced renal function does not alter the pharmacokinetics of a single dose of metronidazole.
If excess chlorhexidine is ingested, when applied topically as part of a dental gel, about 1% of the dose that enters the stomach is absorbed from the digestive tract. Chlorhexidine does not accumulate in the body and is minimally metabolized.
Metrogyl Denta - composition and release form of the drug
The drug is available in the form of a white or almost white gel. Active ingredients : metronidazole benzoate, chlorhexidine gluconate.
1 gram of gel contains: metronidazole benzoate - 16 mg (in terms of metronidazole 10 mg); chlorhexidine gluconate solution (20%) (2.5 mg, based on chlorhexidine gluconate 0.5 mg).
Excipients : saccharin, sodium hydroxide, disodium edetate, levomenthol, propylene glycol, carbomeric homopolymer (type C), purified water.
Dosage regimen
The gel is intended for topical use in dentistry only.
For adults and children over 6 years of age with gum inflammation (gingivitis), Metrogyl Denta ® is applied to the gum area in a thin layer with a finger or with a cotton swab 2 times a day. After applying the gel, you should refrain from drinking and eating for 30 minutes. It is not recommended to wash off the gel. The duration of treatment is on average 7-10 days.
In case of periodontitis, after removing dental deposits, periodontal pockets are treated with Metrogyl Denta ® gel and the gel is applied to the gum area. Exposure time - 30 minutes. The number of procedures depends on the severity of the disease. In the future, the patient can apply the gel independently:
- Metrogyl Denta ® is applied to the gum area 2 times a day for 7-10 days.
For aphthous stomatitis, Metrogyl Denta ® is applied to the affected area of the oral mucosa 2 times a day for 7-10 days.
To prevent exacerbations of chronic gingivitis and periodontitis, Metrogyl Denta ® gel is applied to the gum area 2 times a day for 7-10 days. Preventive courses of treatment are carried out 2-3 times a year.
To prevent post-extraction alveolitis after tooth extraction, the hole is treated with Metrogyl Denta ® gel, then the gel is applied 2-3 times a day for 7-10 days.
Treatment of periodontal disease - effective techniques
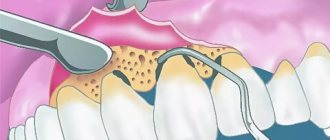
- removal of dental plaque by professional cleaning (air flow, laser, ultrasonic, mechanical);
- drug treatment (taking immunomodulatory, hormonal drugs, antibiotics);
- local therapy (rinses with antiseptic solutions, applications using anti-inflammatory gel);
- injections into the gums, when vitamins, antitoxic serums, and antibiotic-containing compounds are injected;
- physiotherapy (darsonvalization, laser treatment, electrophoresis, use of vacuum), aimed at actively supplying the gums with oxygen.
Metroxidine denta
- Description
- Quality control
Dosage form
Composition per 1 g
Active ingredients:
- Metronidazole benzoate – 16.0 mg
- Equivalent to metronidazole – 10.0 mg
- Chlorhexidine digluconate solution 20% – 2.5 mg
- Equivalent to chlorhexidine bigluconate – 0.5 mg
Excipients:
propylene glycol – 50.0 mg, carbomer-980 – 15.0 mg, disodium edetate – 0.5 mg, saccharin – 1.0 mg, levomenthol – 5.0 mg, sodium hydroxide – 4.0 g, purified water – up to 1 year