How long does it take for flux to last after tooth extraction?
Swelling of the gums after tooth extraction continues for varying periods of time. The duration depends on the chosen method of surgery, the condition of the oral cavity and the immune abilities of the patient’s body. On average, swelling subsides in 3-4 days, sometimes lasting up to 7 days. Complications are indicated by persistence of flux for more than a week. Swelling appears 2-3 hours after the operation; along with it, the anesthesia wears off and pain may occur. Sometimes the cessation of anesthesia is accompanied by a slight increase in temperature. Therefore, the dentists at Dr. Fedorov’s clinic prescribe painkillers.
Maximum swelling is observed on the third or fourth day. By the seventh day it should completely go away. It's not just the gums that can become swollen. If your cheek is inflamed after tooth extraction, most likely the process began to develop before the operation.
What to do if your gums are swollen after tooth extraction
Monitor your body's condition throughout the week. It is recommended to make an appointment with a doctor if:
- On the fourth day after surgery, the swelling did not decrease, but rather increased.
- A sharp throbbing pain occurs in the jaw, gum or cheek area - not to be confused with the aching pain that appears after the anesthesia wears off.
- The temperature rose to 38℃ and did not subside throughout the day.
- There is a feeling of persistent weakness and general malaise of the body.
- There is pain in the throat when swallowing.
If your gums are simply swollen after tooth extraction and there are no complications listed above, follow the recommendations received from your dentist. The swelling will completely go away within a week.
On the second day after tooth extraction, my cheek became swollen
The cheek does not always swell immediately after the patient’s gum is cut. Swelling may occur the next day - this is also natural. There may be no swelling of the cheek at all; often only the gums suffer. Moreover, everything is normal if postoperative recovery proceeds with the following introductory notes:
- body temperature on the second day is normal - not elevated;
- no sharp, throbbing pain in the gums;
- a day after the onset of swelling began to gradually decrease.
Forecast
If the patient strictly adheres to all recommendations and carefully monitors hygiene, then there is no need to fear relapses.
If treatment was started already in the acute stage of flux or interrupted in the middle, then the prognosis becomes less pleasant. Flux can become chronic, which increases the risk of re-development several times. If the patient does not seek qualified help on time, then the flux can even cause blood poisoning, which leads to death.
It is very important to use only proven treatment methods and consult with experienced specialists, since some consequences of self-medication can be even more unpleasant than the disease itself.
Reasons why the cheek swells after tooth extraction
Swelling appears due to the inflammatory process occurring in the mucosa and pulp after surgery. This is a non-infectious inflammation. If operations are carried out correctly and the surgeon’s instructions are followed, the swelling goes away painlessly and without the need to take antibiotics. The integrity of the oral mucosa is disrupted during doctor intervention. The more swollen the gums are after tooth extraction, the more the integrity of the mucous membrane is damaged.
Severe swelling most often appears in patients who have had their wisdom teeth extracted - they generally have large, intertwined roots that complicate the process. The same applies to situations where inflammation began before surgery.
Cheek swelling during wisdom tooth removal
Working with outer teeth is a complex operation. Therefore, swelling always occurs after wisdom teeth removal. Doctors often resort to cutting the gums, after which they apply stitches.
For two to three days after surgery, the temperature may remain above 37℃, and opening the mouth, talking and swallowing may be accompanied by pain. The risk of infection and serious inflammation is higher than with other tooth extractions. The surgeon must prescribe baths with an antiseptic solution and antibiotics. Additionally, it is recommended to eat soft, pureed foods at room temperature, and refrain from sweets, alcohol and smoking.
Treatment in dentistry
Turnkey dental treatment is an important condition for successful therapy. A set of measures used by a specialist ensures:
- opening of an abscess;
- cleansing the pathological area of the periosteum;
- antiseptic treatment;
- installation of drainage to drain pus;
Antibiotics are also prescribed. They remove inflammation. Amoxiclav, Tsifran and other drugs are used. At the same time, vitamins and medications are taken to increase the body's defenses. When the wound is cleared of exudate, the drainage is removed. If necessary, stitches are applied and rinsing is prescribed. It is important that all pus is removed, otherwise the therapy will not be effective. It is forbidden to use warm compresses, as they will increase inflammation. Alcohol lotions are not recommended.
Most often, when an abscess is removed, the masticatory organ is preserved. The operation is painless as anesthesia is used. An anesthetic is injected into the gum, only then an incision is made to release the pus. Additional measures include iontophoresis and laser therapy. After surgery, it is forbidden to take Aspirin to prevent bleeding. Remember that opening the capsule yourself often leads to the infection spreading to the entire jaw. Don't take the risk, you should see a dentist!
Other causes of cheek swelling
If you have a tooth removed and your gums are swollen, the cause does not necessarily lie in soft tissue damage. Swelling is possible due to the following:
- performing an operation if the patient has a flux;
- complex course of the operation - due to tooth growth in the wrong direction, strong inclination, removal of large teeth with large, intertwined roots;
- inflammation and infection of soft tissues or tooth roots before surgery;
- allergies or other forms of individual intolerance to anesthesia and medications used during removal - therefore it is important to know exactly what components you are allergic to before removal;
- poor antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity and mistakes made by the doctor during tooth extraction;
- chronic diseases leading to complicated recovery - neuralgia, hypertension, as well as a general decline in the body’s immune functions;
- ignoring prescriptions received from the dentist - for example, independently adjusting the dosage or deciding not to take antibiotics.
Most often, patients' swelling does not subside after tooth extraction due to lack of normal care - skipping medications, complete absence or insufficiently frequent disinfection treatment.
Possible complications
Patients face complications due to incorrect care, complex or incorrect removal. Dentistry distinguishes 5 types of complications:
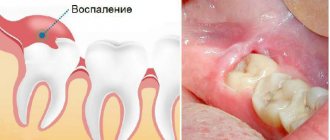
- Alveolitis - to put it simply, this is dryness of the socket. A blood clot always forms in the latter. It does not need to be removed, since the clot protects soft tissues from the penetration of bacteria and infection. If it is accidentally removed, the mucous membrane becomes susceptible to the pathogenic influence of bacteria, and suppuration may develop. Sometimes the inflammation shifts and spreads - a large area of the jaw, cheekbones and eyes become inflamed.
- Osteomyelitis is bone inflammation. With osteomyelitis, acute pain is felt in the upper and lower jaw, and swelling only increases.
- An abscess is suppuration inside the gum. Can move, leading to loosening of the tooth root.
- Flux is a severe inflammation of the jaw, in which the temperature rises and acute pain appears in the area of the jaw and temples.
- Neuritis is an inflammation in which the motor activity of the facial nerve is disrupted. Neuritis is indicated by swelling of the cheek, palate, tongue and larynx.
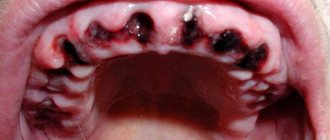
Briefly about the disease
Periostitis is an inflammatory disease with purulent contents that causes infection. Pathogenic microorganisms often enter the pulp from carious cavities. An abscess forms at the root apex. Pus penetrates into the gum tissue, they become inflamed, and swelling develops. The sore spot looks like a lump on the outside. Cause of infection:
- Cyst;
- Untreated caries;
- Inflammation in the gum pocket;
- Jaw injuries;
- Periodontitis or pulpitis;
- Poor installation of fillings or crowns;
The clinical picture of the disease is clearly expressed. The acute phase of periostitis has the following symptoms:
- The patient experiences severe pain in the head, neck, and jaws. Discomfort intensifies during chewing.
- The temperature rises.
- The gum tissue turns red.
- A tumor forms on the cheek. It can spread to the nose, lips, eyelids.
- Malaise and general weakness appear.
- The lymph nodes located under the lower jaw become enlarged.
An alarming symptom is the rapid growth of a lump, increasing throbbing pain. The capsule with pus may burst, then the patient feels relief. The chronic form lasts several months. The disease will not go away on its own. The disease is eliminated by the dentist.
How to eliminate cheek swelling
It is impossible to get rid of edema 100% before the inflammatory process stops. To reduce discomfort and pain, you can apply cooling compresses for 7-10 minutes with a break of 30-40 minutes. Taking painkillers, baths and rinsing with soothing solutions at room temperature helps.
How to remove cheek swelling after tooth extraction at home
- Avoid contact with the hole. It should not be touched with the tongue, brushed, or allowed to get in contact with food.
- Adhere to dietary restrictions. You should not eat or drink for 4 hours after removal. In the next week, food should be soft, at room temperature, not hot or spicy. Eating sweets is not advisable.
- In the first 3-4 hours after removal, apply cooling compresses to the cheek. It is optimal to keep the compress for 3-5 minutes, maximum – 10-15. The compress can only be done on the first day.
- Rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution. The main thing is to follow all the dentist’s instructions.
Symptoms
Such an abscess cannot be confused with anything else, as it has characteristic symptoms.
Compaction, suppuration, redness of the tumor and pain when pressed often indicate a burst flux.
The pathology is treated with anti-inflammatory, antihistamine, painkillers and antibiotics.
The first thing you should pay attention to is the ¾ seal on the gum. If the inflammatory process has begun recently, then the compaction will not cause much discomfort, pain appears only when pressure is applied, and the tumor has a pronounced red color.
During the period between the discovery of flux and a visit to the dentist, smoking and chewing tobacco are prohibited.
Dentist
Novikova Olga Alexandrovna
8 years of experience
As pus accumulates inside the abscess, it will increase in size and change its color to white. In this case, the pain will become constant, its character is sharp and aching.
Further, the tumor continues to develop, pronounced swelling appears on the face, the tissues on the abscess are stretched until a rupture occurs. As the disease progresses, pus can penetrate deeper into the periosteum and then spread even to soft tissue. This outcome is possible if treatment is not started in time or if dubious traditional methods are used.