Most people aged 17-27 years old face problems caused by the appearance of a wisdom tooth (the so-called third molar or eight). Sometimes it can erupt at a later period. Almost 10% of people do not have them at all, and in a third, they remain in the jaw all their lives in the form of embryonic anlages, never appearing.
However, this process is not always accompanied by pain, discomfort and other problems. Quite often they erupt successfully and retain their chewing function for many years without showing any signs of carious lesions.
What to do if teething still causes discomfort: treat it or is it better to resort to removal? These and other questions will be discussed later in the article.
Causes of high blood pressure
High blood pressure is divided into 2 types:
- primary (essential) hypertension (or hypertension) is the most common type of high blood pressure, often has no cause, develops over many years, the risk increases with age;
- secondary hypertension occurs against the background of the development of any disease (kidneys, endocrine system organs, sleep apnea) or taking certain medications.
Causes of high blood pressure include:
- old age (the older a person is, the higher the likelihood of developing hypertension);
- family history of the disease (high blood pressure in parents or other close relatives);
- unhealthy diet - diet high in salt and fat;
- lack of physical activity;
- overweight, obesity;
- sleep disorders;
- chronic diseases (chronic kidney disease, endocrine disorders, diabetes, high cholesterol);
- race (eg, African Americans have a higher risk);
- gender (in middle age, high blood pressure develops more often in men, in old age - in women; women who had high blood pressure during pregnancy are more prone to arterial hypertension in old age);
- certain medications (contraceptives, decongestants, NSAIDs, antidepressants);
- stress;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- non-compliance with sleep schedule, night shift work.
High blood pressure is often called the “silent killer” due to its lack of noticeable symptoms. In some cases (especially when blood pressure levels reach dangerously high levels), a person may complain of headache, nosebleeds, and shortness of breath. Many people do not associate these symptoms with abnormal blood pressure readings because they are not in the habit of periodically monitoring their blood pressure with a doctor or at home.
Pain mistaken for toothache
Diseases and conditions in which pain can be mistaken for dental pain . These are mainly diseases of related areas (paranasal sinuses, organs of vision and hearing, pharynx, cervical vertebrae, brain); The cause may also be diseases of the heart and blood vessels, the musculoskeletal system (spine), the nervous system, as well as mental disorders.
Trigeminal neuralgia. The trigeminal nerve is responsible for sensation in the face and mouth. When it is affected, the pain is very severe and similar to a toothache. Unfortunately, many patients with neuralgia have undergone numerous depulpations and tooth extractions, but continue to experience pain. Despite the patient’s confidence that the cause of the pain is the tooth, the dentist needs to correct the diagnosis and refer the patient to a neurologist. Another option is postherpetic neuralgia, which occurs in people who have had herpes zoster (shingles). Therefore, it is important to inform your dentist if itchy blisters have appeared on the skin and mucous membranes for some time, or this diagnosis has been made.
Cluster headache is a syndrome of unknown origin, characterized by acute, paroxysmal pain. Perhaps this is a form of migraine. Cluster headaches are more common in men aged 30-60 years. Many patients report pain after drinking alcohol.
In classic cases, there is unilateral pain in the upper jaw, maxillary sinus and behind the orbit. Cluster headache is often mistaken for acute pulpitis or periodontitis of the chewing teeth of the upper jaw.
Inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media) is a common disease, especially in children, caused by streptococci. It is well known that with diseases of the chewing teeth, pain can radiate to the ear area. Conversely, with inflammation of the middle ear, the symptoms shift to the back of the upper and lower jaws. After diagnosis, the patient is referred to an otolaryngologist.
Acute maxillary sinusitis (sinusitis). The roots of the teeth of the upper jaw are adjacent to the bottom of the sinus, so inflammation often imitates toothache. Most forms of sinusitis are allergic and are characterized by dull pain in the zygomatic region and alveolar process of the upper jaw.
In acute sinusitis, the pain can be stabbing, pressing, pulsating. Often it radiates to the infraorbital region, to the area of the upper jaw teeth. In this case, the pain is felt not in any one tooth, but in several. It is recommended to contact an ENT specialist.
Diseases of the paranasal sinuses are often chronic and allergic. They tend to be seasonal, because for most people allergens are seeds and pollen of various plants. In countries with a northern climate, the incidence of sinusitis increases in spring and autumn. The patient should be referred to an ENT specialist and an allergist.
Heart diseases. Angina is pain behind the sternum, which can radiate to the left shoulder and along the arm. The pain usually occurs after physical activity. These symptoms are extremely important, since angina pectoris is a harbinger of acute myocardial infarction. Sometimes the pain is felt only in the left shoulder and arm, and even less often in the left corner of the lower jaw.
So, if there are complaints of pain in the posterior part of the lower jaw on the left and there are no objective reasons from the teeth, we can assume the cardiac nature of the pain. In this case, the dentist will refer the patient for a consultation with a cardiologist or therapist.
Salivary stone disease develops in the duct of one of the salivary glands. For a long time, the only symptom was dry mouth. When the stone reaches a critical size, it clogs the salivary duct; toothache appears. Swelling may occur in the submandibular area. To make a diagnosis, several x-rays are taken. The treatment is carried out by a dental surgeon, it consists of making an incision in the duct and removing the stone under local anesthesia.
Pain of musculoskeletal origin can be caused by injury or dysfunction of the muscles of the neck, head, and jaws. Pain can be noted in the area of the teeth, cheek, temple, side of the neck, and back of the head. This group also includes diseases of the temporomandibular joint and the cervical spine. Other joint diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, gout, psoriasis; collagen diseases, or collagenoses) can cause pain in the maxillofacial area.
With internal dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, complaints of toothache often arise. Joint dysfunction is caused by displacement of the articular disc, the formation of adhesions or due to various forms of arthritis, injuries, yawning, and prolonged opening of the mouth. Manifestations: the mouth does not open completely, when opening the lower jaw moves to the side, clicking or creaking in the joint, as well as pain in front of the tragus of the ear.
The pain is long-lasting, dull, muffled, but can become more acute when opening the mouth wide or chewing. In some cases, the pain radiates to the temple, cheek, and distal parts of the upper and lower jaws. In such cases, the patient may believe that he is experiencing toothache.
Tumors. Pain is rarely a symptom of malignant tumors in the jaw area. In typical cases, there are complaints of tingling or decreased sensitivity (numbness). Most tumors affect not only sensory but also motor nerves.
Atypical pain conditions masquerading as toothache are a group of syndromes that do not correspond to any specific disease. In this case, the patient is usually convinced that the cause of the pain is the teeth” and insists on their treatment or removal. Although the cause is unknown, many experts suggest the nervous system is involved. Atypical pain is usually chronic, aching; patients feel it deep inside the bone and have difficulty localizing it. Sometimes the pain seems to move from one area to another, and there may be complaints of pain throughout the body. The examination should include psychological screening and behavioral tests that assess depressive, anxious, and hostile behavior. It is possible that the primary cause of atypical pain is a psychological disorder. Consultation with a psychologist or psychiatrist is indicated.
Blood pressure readings
- Normal pressure is from 90/60 mm Hg. Art. up to <120/80 mmHg Art.
- Prehypertension (risk factor for the development of arterial hypertension) - 120–129 mm Hg. Art. / <80 mmHg Art.
- Arterial hypertension 1st degree - 130–139 mm Hg. Art. or 80–89 mm Hg. Art.
- Arterial hypertension 2 degrees - ≥140 mm Hg. Art. or ≥90 mm Hg. Art.*
*American Heart Association classification.
Online blood pressure calculator on the NHS website.
American College of Cardiology online cardiovascular risk (stroke, heart attack and other diseases) calculator (risk of complications for patients with high blood pressure over the next 10 years and beyond).
From tooth decay to heart disease
12.Mar.2021
Valeria, proper care and timely sanitation of the oral cavity will help you avoid many diseases. Heart and teeth - is there a connection?
– If a person treats his oral health carelessly, considers it something insignificant, and does not see a doctor for a long time, this can lead to serious diseases that will last a lifetime. The relationship is more obvious than it might seem at first glance. When there is a focus of inflammation, in an affected tooth or gum, ulcers, for example, bacteria multiply in these places. Normally, every person has them, and thanks to their protective functions, balance is maintained. However, if the affected area is not treated, the body begins to spend a lot of energy fighting and becomes exhausted. Bacteria enter the blood and there is a danger of their penetration into the heart. The most common pathology is infective endocarditis, when the structure of the valves is destroyed.
Is the heart so fragile?
– Normally, the heart is well protected from the entry of bacteria. They can only penetrate through the blood and the flow must be large so that pathogens can gain a foothold there. With multiple forms of caries, as a rule, a decrease in immunity occurs, which leads to the entry of microorganisms into the bloodstream. In this situation, the heart becomes a target for infection.
How long will it take from the time the infection enters the hearts until symptoms appear?
– If an infection develops on a heart valve, it can destroy it in just two weeks.
Valeria, what symptoms are we talking about?
– Shortness of breath and fatigue, swelling of the legs, the appearance of low-grade fever (from 37 to 38 degrees) a week or two after the viral infection. The symptoms described indicate that the heart may not be working at full capacity. This is a reason to see a doctor.
Can you give an example?
– In our practice, there are few cases where the heart was damaged due to foci of infection in the oral cavity. But you need to understand. That everything in the human body is interconnected. An inflamed carious tooth against a background of weakened immunity can become a trigger. One day, a 36-year-old young man with heart failure was admitted to the clinic. Before admission to the hospital, the man played sports, led an active lifestyle, worked and did not experience any health problems. Before hospitalization, he noted a slight increase in temperature for several days. Echocardiography, in other words, ultrasound of the heart, showed the presence of vegetations, bacterial lumps, on the heart valves. The aortic valve, which allows blood into the systemic circulation, was half destroyed. The patient was hospitalized.
Valeria, has the cause of the infection been established?
– According to the man, shortly before hospitalization he received dental prosthetics services. Perhaps his body had not fully recovered and was susceptible to infection, perhaps the patient did not complete the course of antibiotics. However, we did not find other objective causes of endocarditis.
What is the treatment?
– Infectious endocarditis requires powerful and long-term antibiotic therapy - it is difficult to remove bacteria from the blood. In case of severe infectious lesions of the heart valve apparatus, the only way out is implantation of an artificial prosthesis to replace the damaged one and lifelong use of medications that reduce blood clotting.
Who is at risk?
– Infectious lesions of the heart occur absolutely equally among both men and women. People with weakened immune systems or autoimmune diseases are at risk.
Valeria, what would you wish to our readers?
– It is necessary to be attentive to your health at any age and understand that there are no small things in our body. You need to take care of yourself - undergo regular preventive examinations, lead an active lifestyle, eat healthy food, and do not smoke. To prevent oral diseases, it is necessary to visit a dentist at least once a year.
How often should you check your blood pressure readings?
Blood pressure is usually measured when visiting a doctor (for example, a therapist). There is no need to specifically visit a specialist for this; it is enough to ensure that the pressure is measured at least once every 2 to 5 years, starting from the age of 18 (with normal blood pressure and no increased risk of cardiovascular diseases).
People over 40 years of age, and people 18–40 years of age at risk of high blood pressure, should have their blood pressure checked at a healthcare facility at least once a year. If a diagnosis of arterial hypertension has been established or a person has other risk factors for developing cardiovascular diseases, it is recommended to measure blood pressure more often and not neglect monitoring at home. Your doctor will help you choose a device for measuring blood pressure (tonometer).
For children 3 years of age and older, blood pressure is measured regularly during annual routine examinations.
Caution: The American Heart Association does not recommend the use of wrist- or finger-worn blood pressure monitors, which are less accurate.
If recommended, measure blood pressure at home twice a day on the left and right arm: in the morning before breakfast (but not immediately after waking up) and before taking any medications, and in the evening, preferably at the same time. In each case, you need to measure the pressure 2-3 times (at short intervals, 1-3 minutes) for a confident, accurate result. 30 minutes before, do not smoke, do not eat, do not drink coffee (and alcohol), do not exercise, and empty your bladder. During the measurement, you must sit in a comfortable position, leaning back in a chair or armchair, do not cross your legs and ankles, and do not talk. The arm on which the cuff is worn must be freed from clothing and held at heart level; it is most convenient to place it on a table or armrest of a chair. Don't forget to write down your measurement results.
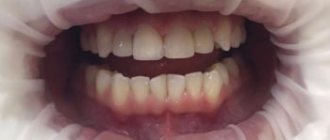
What are wisdom teeth?
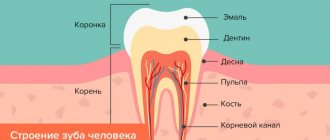
Dentists and scientists call them a vestigial organ, the need for which disappeared when people learned to heat food. Eights, like all other human teeth, consist of roots, a neck and a crown, but despite this they have certain anatomical features.
Here are the main differences:
- they are only indigenous and do not come in milk;
- their eruption is often accompanied by pain;
- have a larger number of roots - from 2 to 5;
- bent and twisted roots.
Is it possible to normalize high blood pressure and what to do?
Yes, with the help of lifestyle modification (influencing modifiable factors), treating the underlying disease, taking medications that normalize blood pressure.
Lifestyle modifications include proper nutrition, including avoiding fatty foods and reducing salt intake (the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) eating plan recommended by the US National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute is preferred); weight normalization; quitting smoking and alcohol; regular physical activity; stress management (for example, mastering relaxation techniques).
If you have persistently high blood pressure due to a medical condition (such as diabetes) or caused by taking certain medications, it is recommended that you consult your doctor. Control of the underlying disease, refusal of drugs (or their replacement) that increase blood pressure, make it possible to stabilize the patient’s blood pressure and condition.
Nonmodifiable risk factors associated with high blood pressure include age and family history.
Symptoms and diagnosis
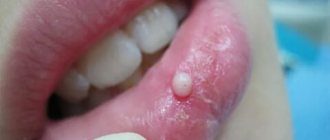
The main symptom indicating activation of third molar growth is pain that occurs when chewing. In the case of the formation of a cyst or “hood,” inflammation develops, which, in addition to pain, can be accompanied by an increase in body temperature, enlargement and soreness of the submandibular lymph nodes, and a headache due to the development of the inflammatory process.
A sign that wisdom teeth are growing abnormally is:
- acute pain in the temporomandibular joint;
- numbness of the jaw and aching pain. This may indicate improper growth inside the bone and possible trauma to the jaw nerve;
- inflammation and enlargement of lymph nodes. As a rule, such a sign indicates that an infectious process has begun;
- redness, swelling of the gums and pain when pressing on it;
- displacement of teeth in a row.
If you have such symptoms, you should immediately visit your dentist for diagnostic measures. Only a specialist can confirm or deny the presence of problems associated with the growth of the third molar.
Diagnosis of an impacted tooth, completely or partially hidden under the gum tissue, is carried out in several ways:
- Palpation and probing;
- Sight radiography - to determine the direction of growth and the number of roots;
- Orthopantomography;
- Computed tomography.
The diagnostic method is determined directly by the doctor; sometimes an examination in the dental chair is sufficient, and sometimes an x-ray is necessary to identify existing problems and predict the risk of their development in the future.
Treatment of high blood pressure
Treatment of arterial hypertension is based on lifestyle modification, constant monitoring of blood pressure, and the use of antihypertensive drugs (medicines that lower blood pressure) - one or more, based on the patient's individual situation.
Medicines prescribed for high blood pressure include: ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, beta blockers, alpha blockers, alpha beta blockers. In most cases, these medications do not cause side effects. However, you should not self-medicate; you should consult a doctor who will select an effective drug and prescribe a regimen for its administration. It is important to follow all recommendations, observe the dosage and not skip taking the drug(s).
When diagnosing arterial hypertension, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) provides an accurate idea of the patient’s blood pressure levels. ABPM also excludes the factor of chance, distortion of real blood pressure readings (the so-called “white coat” syndrome or “white coat” hypertension), and registers imperceptible changes in blood pressure (for example, during sleep). This test is recommended by the American Heart Association to confirm the diagnosis of hypertension.
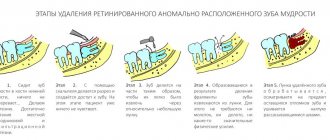
What to do: treat a wisdom tooth or remove it?
Many people are often interested in the question: is it better to use the services of a dentist at the stage of intramaxillary development and remove a rudimentary tooth so that it does not create problems later?
However, most experts agree that preventive removal of eights is unacceptable. When the tooth has erupted correctly and does not cause any discomfort, it can be preserved. The main thing is to carefully observe the rules of hygiene and visit the dentist on a regular basis to monitor and perform hygiene procedures.
Removal is resorted to in cases where conservative treatment methods cannot achieve the desired result.
Undesirable effects of other Russian vaccines
"CoviVac"
This is an inactivated vaccine. That is, a killed coronavirus is delivered to the body. This is an old and proven technology, many vaccines against viral diseases have been made using it: polio, influenza and others. Dead viruses cannot cause disease, but their entry is enough for the body to learn to recognize them. As a result, when a live virus enters from an infected person, a strong immune response is formed immediately.
To enhance the immune response, aluminum hydroxide was added to CoviVac. One dose contains up to 0.5 mg. This dose is much less than permissible.
The instructions for the drug say that the vaccine can rarely cause headaches and short-term fever. Pain and hardness at the injection site are more common.
"EpiVacCorona"
This vaccine differs from Sputnik V and CoviVac in that it is not created using viruses. It is not killed or neutralized virus particles that are introduced into the body, but artificially created proteins. Using them, the immune system is trained to recognize real viruses. This method of creation reduces the reactogenicity of the vaccine, so it is recommended for vaccination in elderly or weakened people.
In a publication in the Russian journal Infection and Immunity, the vaccine developers claim that the only adverse events were mild pain at the injection site. And the CoviVac vaccine does not cause headaches, muscle weakness and other common symptoms.