Plaque on the tongue itself is not a disease, it is a symptom that reflects what is happening in the body. There are types of plaque on the tongue that indicate a disorder in the functioning of internal organs. These types of plaque are called pathological.
Author:
- Sadykhov Rahim Agalarovich
ENT pathology expert
3.64 (Votes: 14)
Plaque on the tongue itself is not a disease, it is a symptom that reflects what is happening in the body. In this regard, the statement that language is a mirror of our health is quite true. A slight transparent or whitish coating is normal for a healthy adult. It is usually noticeable after sleep and can be easily cleaned with a toothbrush. However, there are other types of plaque that are not so harmless and indicate a disorder in the functioning of internal organs. These are pathological types.
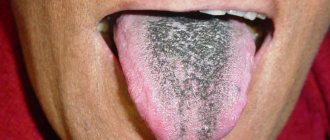
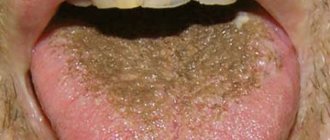
Pathological plaque can be different: the color ranges from thick white to black, dense and sticky in consistency, and has a bad odor. The structure of the language itself may also change. This is the first signal about the onset of the disease, so if you notice uncharacteristic changes in the appearance of your tongue, consult a doctor for a correct diagnosis. Indeed, in this case it is necessary to identify the root cause of this unpleasant manifestation and quickly begin to treat the underlying disease.
What can cause pathological plaque?
The main reason is a malfunction of the internal organs. However, there are two other possibilities: smoking and improper oral hygiene. For active smokers, a yellowish coating is a constant companion, which may not indicate anything bad about health other than the presence of a bad habit. If you don't brush your mouth properly, your tongue will be completely ignored. It is wrong to brush your teeth alone. Bacteria accumulate on the surface of the tongue; they also need to be removed. To clean the tongue, many toothbrush manufacturers make a special brush on the other side. There are also scrapers for the surface of the tongue.
If a person does not smoke and maintains proper hygiene, but there is still plaque, then this may be an indicator of the following diseases:
- Diseases of the digestive system (the most common cause) are ulcers, gastritis, diseases of the gallbladder, pancreas, and liver. Usually in such cases the plaque is accompanied by a persistent unpleasant odor that does not go away even after cleaning.
- Diseases of the respiratory system - tuberculosis, bronchitis, asthma.
- Infectious diseases - influenza, sore throat, ARVI, acute respiratory infections.
- Reduced immunity.
- Diseases of teeth and gums.
- Changes in acid-base balance due to medications.
Comments
At what age do people usually get Günther Müller's glossitis?
Vladimir (01/30/2021 at 11:57 pm) Reply to comment
- This type of glossitis, in fact, like all others, can develop in patients of any age, but people who have chronic diseases, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, and smokers are always at risk.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (02/05/2021 at 09:16) Reply to comment
It turns out that our tongue can say a lot about the body, it’s not for nothing that doctors always ask to see it, even if they just came for a medical examination. Can any age have these diseases or older people?
Maria (02/05/2021 at 07:32) Reply to comment
I wonder what is better to eat to avoid such serious problems? It seems to me that a lot depends on food. Against the backdrop of abundance, you begin to not understand what is useful and what is not.
Marina (02/05/2021 at 08:20) Reply to comment
I once had glossitis, about five years ago. Although I don’t smoke, don’t drink, I lead a healthy lifestyle. Before this I had a sore throat. What folk remedies do you recommend that are the most effective?
Irina Frolova (02/05/2021 at 09:40) Reply to comment
Hello. I developed glossitis due to candidiasis. The tastes are very dull. Everything seems to have been cured, but I don’t feel the same brightness from food. Please tell me, can something be done about this or is it forever?
Vera (03/04/2021 at 10:56 am) Reply to comment
Since childhood, all doctors have told me “geographical language.” It has some stains and a yellow-green coating. Is this a disease or not? It just doesn't bother me the way it feels. But it's not very easy to clean.
Vladimir (03/04/2021 at 11:38 am) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
What color is the pathological plaque?
By the color of the coating on the tongue, you can determine which organ malfunction caused it:
| White | A light whitish coating that can be easily cleaned with hygiene procedures is the norm for an adult. A cause for concern is if the white coating is dense or has a cheesy structure and is not cleaned. This may be a sign of a fungal infection. Other reasons include: monotonous diet, lack of vitamins, poor hygiene, smoking, intoxication, wearing dentures, taking medications. |
| Grey | Sometimes the tongue becomes covered with a gray coating when taking antibiotics for a long time. Also accompanies diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. |
| Yellow | Often indicates liver disease (in such cases a bitter taste is felt in the mouth). It can also occur with diseases of other organs of the digestive tract, with viral diseases, with an excess of bile in the body. |
| Green | This is a rare occurrence. Most often it is an indicator of liver problems. |
| Brown | Occurs with disorders of the digestive tract, alcoholism and smoking, and abuse of brown foods (chocolate, coffee, black tea). |
| Orange | It occurs mainly with gastritis, due to the fact that gastric juice enters the oral cavity in large quantities. |
| Blue | It may appear due to problems in the cardiovascular system, kidneys, due to a lack of folic acid, iron, Vit C, Vit B12. It can also appear due to mercury and heavy metal poisoning. |
| Black | Appears in cases of liver dysfunction, lead poisoning, acute infections, Crohn's disease, acidosis. |
Surface type
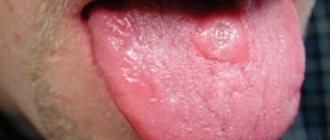
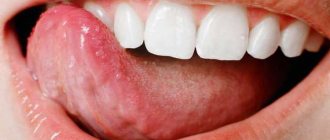
In general, the disease can affect different areas of the mucous membrane, but the superficial variety affects only its upper layer. Superficial glossitis of the tongue can be seen in the photo.
The photo shows superficial glossitis of the tongue
It all starts small - the catarrhal stage of the disease. First, the mucous membrane becomes swollen, and upon visual inspection it is noticeable that it is covered with a dense coating. If treatment is not started during this period or the pathology is not completely cured, then an ulcerative form develops - small painful aphthae appear on the mucous membrane, which can bleed.
What is glossitis of the tongue? This is a disease that, like many other dental pathologies, can occur in acute and chronic stages. It can have pronounced symptoms or a sluggish inflammatory process that will go unnoticed for a long time, undermining your health. That is why it is so important to undergo timely preventive examinations with a dentist and therapist.
Diagnostics
To establish a complete picture of the state of the body, the doctor determines the color of the tongue, its structure, position, motor functions, and possible other pathologies in the oral cavity. Among the laboratory and instrumental research methods aimed at clarifying the characteristics of plaque and the reasons for its appearance, the following may be prescribed:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- sowing on flora from the surface of the tongue;
- determination of antibodies to the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- scatological research.
If you are concerned about the condition of your tongue, plaque on it, pain, unpleasant odor, contact the ENT doctors of our clinic. High-precision equipment and the experience of our specialists allow us to quickly make correct diagnoses and prescribe treatment.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Glossitis is an external manifestation of diseases of internal organs caused by a deficiency of certain vitamins. Key development factors:
- Pernicious anemia is caused by a reduced level of vitamin B12 and folic acid. A decrease in the absorption of substances occurs as a result of long-term drug therapy, gastrointestinal disorders, oncological diseases of the digestive organs, autoimmune diseases, and congenital metabolic pathologies. Vegetarians, nutritional deficiencies, or alcoholism may have mild deficiencies.
- Pellagra is a disease that develops due to deficiency of nicotinic acid (B3, PP). Patients with nutritional deficiencies are susceptible. Provoke the development of stomach diseases, UV irradiation, antibiotic therapy.
- Sprue – manifested by gastrointestinal dysfunction. Identified in patients who visited endemically unfavorable areas.
Biting your tongue - everyone knows this
Biting the tongue, cheek or lip is accompanied by painful sensations, as damage to the mucous membrane occurs.
Obviously, the initial goal after a bite is to reduce pain. So, what should you do if you bite your tongue, what and how to relieve pain and inflammation?
The main rule is to remain calm. Calm down and try to come to terms with the pain, because tantrums and tears will not help heal the damage.
And then you should do the following:
- Be sure to stop bleeding , if any. An elementary solution would be to repeatedly rinse with cold water: it will help narrow the blood vessels and reduce bleeding activity. A worthy alternative would be a piece of ice.
- Cotton swabs soaked in 2% Lidocaine help in the fight against painful sensations . Another variation to reduce pain is eye drops with an anesthetic - Tetracaine, Alcaine.
- It is important to disinfect the entire oral cavity : brush your teeth thoroughly and rinse your mouth.
- Maintain regular rinsing : it is advisable to wash away the remains of eaten food after each meal.
- Use antiseptics such as Antiangin, Trachisan, Furacilin in the form that is optimal for you: spray, lozenge or solution.
- Avoid eating rough, cold or hot foods . During the restoration of the oral mucosa, it is advisable to create a daily menu of liquid soft foods at medium temperature: purees, soups.
- Avoid cold foods - ice cream, frozen juice and other foods with temperatures below zero - they slow down the healing process.
- Take a course of vitamins to help restore damaged areas. The optimal solution would be to include vitamin C and group B in the diet.
Do not forget to adhere to sanitary and hygienic measures: do not reach into the oral cavity with dirty hands, do not put pressure on the resulting injury.
Never pour iodine or brilliant green or peroxide into a wound: give preference to treating the environment around the injury. Antibiotics can only be used as prescribed by a doctor.
In practice, there are cases of tongue biting. In such a situation, it is important to remain cool, act quickly and in an organized manner: place the “particle” in a bag filled with ice and go to the hospital. To relieve painful sensations, it is permissible to ingest cold food: suck ice cream, frozen juice, ice, drink water.
Tongue traumatism: theory
Before you begin treatment of the tongue, you should carefully study the nature of the injury and its causes.
Mechanical impact
The first type of damage - mechanical - is the most common cause of tongue injuries. Due to mechanical damage, ulcers and superficial erosions form on the tongue.
Conditions under which mechanical injuries occur are of a domestic nature:
- damage to the integument by dental instruments - probe, bur, disc;
- the occurrence of a wound under the influence of a sharp object - a bone, a knife, a fork;
- biting the tongue while eating, epileptic seizure;
- the appearance of tongue injuries from blows to the face.
Healing of a wound caused by mechanical impact occurs depending on the depth and area of damage to the mucous membrane.
Chemical burn
Chemical injury to the tongue, as the second type of injury, occurs due to contact with the mucous membrane of a chemical substance of an acidic or alkaline nature.
Under the influence of an irritant, chemical burns occur on the tongue. The latter are characterized by the appearance of dark-colored areas, scars, blisters and blisters on the tongue (in severe cases).
Instant rinsing of the mouth with solutions with neutralizing properties is the key to rapid restoration of the integument.
For chemical burns, it is preferable to seek help from medical institutions.
Painful influence from the outside
Damage to the mucous membrane by steam, hot water, fire, electric current or ionizing radiation is called physical trauma to the tongue.
Characteristic of this type of injury is pain that gradually subsides from the moment of injury.
The main danger of physical injury is the development of acute catarrhal glossitis (inflammation). Consultation with a doctor in complex stages of injury is mandatory.
Deep damage to the tongue caused by various kinds of external irritants can be accompanied by complications: abscess or phlegmon of the tongue.
Painful swelling and accompanying difficulties with swallowing and speaking are symptoms of an abscess. In later stages, with increasing inflammation of the tongue, the abscess turns into phlegmon. The victim requires emergency hospitalization and surgical intervention.