ICD - deposits (growths) on teeth:
- K03.6 - deposits (growths) on teeth
- K03.60 - pigmented coating (black, green, orange)
- K03.61 - due to the habit of using tobacco
- K03.62 - due to the habit of chewing betel nut
- K03.63 - other extensive soft deposits (white deposits)
- K03.64 - supragingival calculus
- K03.65 - subgingival calculus
- K03.66 - dental plaque
- K03.68 - other specified deposits on teeth
- K03.69 - deposits on teeth, unspecified
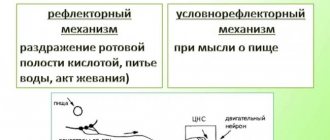
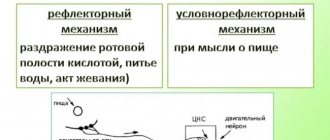
Mechanism of plaque formation
Plaque formation on teeth begins 2 hours after brushing.
Dental plaque has the following formation mechanisms:7
1.
The surface of the tooth is coated with saliva; it contains proteins to which microorganisms attach more easily.
2. The number of microorganisms gradually increases, they produce acids and polysaccharides - high molecular weight carbohydrates that serve as food for acid-producing bacteria.
3. Subsequently, the number of bacteria increases, and the plaque structure becomes stronger. And acids destroy tooth and gum tissue.
Local immunity
Local immunity provides local protection of the body from the penetration of foreign agents. Barrier functions are provided by the skin and mucous membranes. Any microtrauma to the skin and damage to the mucous membranes contribute to the unhindered penetration of harmful viruses and bacteria, which leads to the development of diseases.
Local mucosal immunity
provided by epithelial cells and the lymphoid apparatus of subepithelial spaces. Lymphoid cells secrete secretory immunoglobulins types A, G and M.
Local immunity of the oral cavity
Every day it resists the attack of pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the oral cavity, therefore it is the most vulnerable place that should be given special attention.
How does local immunity differ from general immunity?
General immunity is the entire human immune system, which protects the body from foreign agents. It includes internal protective mechanisms: immune cells of various organs, lymph nodes, cerebrospinal fluid barrier, etc.
Local immunity is the first barrier of the body's immune defense, preventing further penetration of microorganisms, ensuring their death or cessation of vital activity. This is the main function of local immunity and its distinctive feature.
Methods for detecting plaque
To determine the quality of home hygiene, you can use solutions of dyes: erythrosine, basic fuchsin, bismarck brown fluorescent sodium. These dyes do not have a pathological effect on the enamel or the oral mucosa. Special tablets are widely used.6
Directions for use: Chew 1 tablet thoroughly and then rinse your mouth with water. What is colored is plaque on the teeth.
It is recommended to use the tablets for children over 6 years of age.5
Contraindication for use is individual intolerance to the constituent components of tablets or solutions.
The most common diseases of teeth and gums
- Caries.
This is a common problem that affects almost every person at different ages. At the first stage of development, spots appear on the enamel, and as a result of development, hard tissues are destroyed;
- Gingivitis.
An inflammatory process that causes swelling and tenderness of the soft tissues. If treatment is not treated in a timely manner, the problem worsens and becomes chronic;
- Periodontitis.
A popular problem in which the initial stage is asymptomatic. Pain and discomfort appears after damage to bone and soft tissue;
- Periodontal disease
is expressed in periodontal damage, which can lead to tooth loss. Therefore, it is important to start treatment in a timely manner.
The influence of dental plaque on the development of periodontal diseases
Periodontal tissue is the tissue that holds the tooth in the jaw. If you remove at least one of them, the mobility of the tooth increases, which ultimately leads to its loss.
In 80% of cases, the leading role in the occurrence of periodontal pathology belongs to dental plaque. Of course, there are a number of factors (iatrogenic effects on the periodontium, for example, braces; occlusal trauma, malocclusion; malnutrition; stress; chronic diseases of organs and systems) that contribute to the occurrence of periodontal diseases.2
Plaque microorganisms and their toxins damage the epithelium and cause irritation, which leads to connective epithelial damage and inflammation.
Endotoxins (waste products of gram-negative bacteria) are aggressive; they increase capillary permeability, disrupt cell metabolism, which leads to necrosis. In response to this, the body produces many antibodies (proteins to destroy dangerous cells and viruses) and enzymes that destroy periodontal tissue. And due to the high amount of antibodies, periodontal tissue weakens its protective functions, which allows bacteria to easily destroy them.
The most common microorganisms found in dental plaque are Actinomyces, Actinobacillus, Bacteroides, Eikinella corrodens, Fusobacterium, Vielonella recta, Treponema denticola, Capnocytophaga.8
Reasons for color change
A yellow tint may appear due to smoking. Tar and tobacco smoke stain the mucous membrane, settling on the surface. A yellow coating appears. Due to vascular contraction and changes in blood composition, blood supply is disrupted. With a lack of oxygen, the mucous membrane turns pale and yellow.
The causes of yellowing of the palate are diseases of the oral cavity and body. This is also caused by age-related changes due to metabolic disorders and blood microcirculation.
Tartar
Tartar is mineralized plaque on teeth.
More often it is located on the crown of the tooth, i.e. above the gum. But if the periodontal tissue is destroyed and the gum moves away from the tooth, the root is exposed and the tartar is already below the gum.
It is assumed that subgingival calculus is formed from components of blood serum, since it does not have contact with saliva.2
The different topography of these types of tartar suggests a different mechanism for their removal.
- Supragingival calculus is removed using hand instruments and scalers
- Subgingival calculus is often removed surgically to allow better visualization of the approach.
Oral Care Tips
We have collected the top 5 tips from dentists that must be followed to keep your teeth beautiful and healthy.
- Don't go to bed with unclean teeth. Otherwise, the microbes will secrete lactic acid, which causes caries.
- Learn proper teeth brushing techniques. For example, clean them with smooth circular movements without strong pressure, hold the brush at an angle of 45 degrees, treat not only the outer, but also the inner and chewing surfaces of the teeth.
- Clean your tongue at the end of each brushing of your teeth, as plaque, consisting of dead mucous cells, food particles and microorganisms, is regularly deposited on it.
- Eat more fruits and vegetables. Plant foods contain dietary fiber that helps remove plaque from your teeth and tongue. In addition, fruits are excellent sources of vitamins to maintain oral health.
- Limit your consumption of starchy and sweet foods. The fast carbohydrates they contain stimulate the growth of cariogenic bacteria.
Individual oral hygiene
Individual oral hygiene is the removal of plaque by the patient himself at home using various hygiene products; in other words, it is home brushing of teeth. Home hygiene does not always remove all dental deposits, but proper hygiene will reduce the amount of plaque and bacteria.
Toothbrush
The toothbrush should be soft.
For many, this is surprising, because most are accustomed to using a brush of high and medium hardness - but this is wrong. Using a soft brush will initially seem like poor hygiene, but there are benefits to it as more time will be spent brushing and hygiene will be done properly.
Thanks to a soft toothbrush, the risk of injury to enamel and gums is reduced. The toothbrush should have smooth, thick bristles.3,13
Mono-tuft toothbrush
Allows you to thoroughly clean the gingival sulcus area.
The mono-beam cleans areas that are inaccessible to a regular brush. A mono-beam brush is convenient to use when the gag reflex is pronounced. This brush is a must-have hygiene product; you can use it to clean your teeth without using toothpaste.3,14
Rules for using a mono-beam brush:
- Hold the monotuft brush vertically
- Place the brush so that the bristles are around the gum line
- We move the beam from one tooth to another along the gum line with soft stroking movements.
- We don't put pressure
- We repeat the same steps on the inner surface of the teeth.
Dental floss
Dental floss should be safe and not injure the gums when used correctly.
Dental floss can be classified by color, thickness and fiber structure. Classification of dental floss:
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | Shape:3 | a comment: |
Superfloss - threads with different thicknesses (used in children with braces, and in adults with implants). |
| classification: | By processing: | a comment: |
|
| classification: | According to the presence of impregnations: | a comment: |
|
| classification: | Based on holder availability: | a comment: | Flosssticks are dental floss with holders. Disadvantages of floss sticks:
Dental floss should be used after every meal to prevent food from getting stuck in the teeth.10 |
Rules for using dental floss:
1. It is necessary to unwind about 40 cm of thread from the roll and cut it using the built-in cutter.
2. The ends of the thread are wound around the middle fingers.
3. The middle part of the thread is clamped with the index finger and thumb so that 5 cm remains
4. The thread is threaded between the teeth and moved with sawing movements without strong pressure.
5. The tooth is grasped from all sides and gently brushed from top to bottom.
6. The used piece of thread is wound around the middle finger (can be washed with water), the next gap is cleaned with a clean piece
7. The floss is threaded through the same gap to clean the adjacent tooth.
When should you start flossing?
- Up to 2 years of age, floss is not used - until baby teeth completely erupt. The exception is when the child has tight contacts between the front incisors.
- 2.5-6 years – the period of “contact caries”. Its occurrence is associated with densification of the dentition. A toothbrush cannot fully clean the interdental spaces. It is necessary to use dental floss. Closer to 6 years, you can use a ribbon thread or an irrigator.
- From the age of 6 – brushing teeth with floss becomes an obligatory ritual; the child can be taught to practice independent hygiene
Dental brushes
It is advisable to use a brush every time after eating.
One procedure is enough; too sudden and repeated movements can injure the gums. Terms of use:
1. It is necessary to insert a brush between the teeth closer to the gum
2. The brush should lie at a slight angle relative to the gum
3. It is necessary to carefully move the brush so that it goes right through between the teeth.
4. Strong pressure and pressure should be avoided, the brush should pass easily
5. At the end, you can carefully remove the brush and repeat the procedure with all teeth
Dental floss removes food debris between the teeth, and dental brushes clean them of plaque. At first, it will be difficult to use dental brushes, so it is recommended to start with the smallest sizes and gradually increase them. When you first start using brushes, your gums may bleed.4
Tongue scraper
Plaque on the tongue may indicate the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria that are located in the papillae of the tongue.
These bacteria, in turn, can:
- migrate to teeth and cause caries
- cause bad breath
- accumulate on the gums, causing inflammation
- negatively affect overall oral health
- yellow coating on the tongue does not look aesthetically pleasing
We must not forget about tongue hygiene, since pathogenic microorganisms can get on the teeth and nullify the effect of brushing.
It is not recommended to brush your tongue with a toothbrush or the back of it. The best cleansing effect can be achieved using a tongue scraper. Scrapers come in metal and plastic. It is recommended to use plastic ones, as they do not injure the tongue.3
Irrigator
A device for cleaning plaque and food particles between teeth. Hygiene is carried out under the pressure of a water jet. An irrigator cannot replace dental floss. Thanks to the irrigator, hydromassage of the gums occurs and blood circulation improves.
Oral mucosa: what to pay attention to
Regular dental examinations are an important part of the prevention of not only dental and periodontal diseases, but also pathologies of the oral mucosa. They make it possible to detect cancer, leukoplakia, stomatitis and other dangerous diseases in the early stages.
Inspection algorithm
The American Dental Association recommends that your oral examination include the following steps:
- a thorough visual examination of the lips, buccal mucosa, gums, anterior part of the tongue, floor of the mouth and palate;
- examination of the throat (pharynx), including tonsils, root of the tongue;
- palpation of the jaw and neck to detect nodes, tumors, any abnormalities or abnormalities.
This procedure allows you to timely identify foci of pathological processes in the oral mucosa (OM), including erosion, ulcers, compactions, and also assess the condition of the lymph nodes.
Russian specialists adhere to a similar inspection algorithm. He suggests that the dentist should pay attention to any visible abnormalities in the structure of the face, nose, cheeks or chin. Pathological changes, taking into account their localization, are recorded using special codes. Thus, ulcerations of the mucous membranes, wounds, tissue erosions, cracks, enlarged lymph nodes and any other lesions are necessarily noted.
Oral diseases
The most common symptoms of stomatitis encountered in dental practice. Acute herpetic stomatitis accounts for 85% of all diseases of the oral mucosa; chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis is also common [1].
Aphthous stomatitis is considered a diagnostic feature of aphthous stomatitis - oval ulcerations on the oral mucosa with clear edges, with a diameter of 3-12 mm or more, surrounded by a halo of hyperemia. Herpetic stomatitis is characterized by blistering rashes not only on the surface of the mucous membrane, but also on the lips and skin around the mouth.
Data from multicenter studies in different countries of the world also indicate a high level of prevalence of other oral diseases: leukoplakia, candidiasis, lichen planus.
Leukoplakia is characterized by the presence of foci of keratosis in the form of whitish thickenings on the oral mucosa and the red border of the lips. With candidiasis, spots of white plaque with a cheesy consistency form on the mucous membrane, which are easily scraped off with a spatula. With secondary bacterial infection and erosion, the plaque may acquire a brownish tint.
The most common sign of oral lichen planus is also gray-white spots. They appear on the inner surfaces of the cheeks, tongue and gums. Due to the similarity of these manifestations with the symptoms of other diseases, in particular leukoplakia, visual diagnosis can be difficult.
Unfortunately, in recent years the number of cases of oral cancer has been increasing. The World Dental Federation attributes this to widespread smoking and alcohol consumption. Therefore, early diagnosis of cancer of the oral mucosa is becoming increasingly important. It is precisely this that makes it possible to identify precancerous and cancerous states of cells at stages when treatment can be anatomically gentle.
Experts advise paying attention to the following signs, which may be symptoms of oral cancer:
- long-term non-healing wound or irritation;
- red or white spots;
- sensation of pain, numbness, sensitive areas in the mouth or on the surface of the lips;
- tumors, thickening, roughness, erosion and other changes;
- difficulty chewing, swallowing, speaking, or moving the tongue or jaw.
The number of visits to dentists by Russians is approximately 15 million per year [2]. This figure is higher than any other medical specialty. Therefore, the doctor’s compliance with the external examination algorithm, thoroughness and accuracy during its implementation are the key to the success of early detection of many dangerous diseases of the oral cavity.
List of sources
[1] Zarkumova A.E. Structure of morbidity of the oral mucosa // Bulletin of KazNMU. 2022. No. 3. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/struktura-zabolevaemosti-slizistoy-obolochki-polosti-rta (date of access: 05/22/2020).
[2] Astakhov P. Chief dentist of the Ministry of Health: mortality in the dentist’s chair is below 0.001% // RT, June 7, 2022. URL: https://russian.rt.com/russia/news/397438-glavnyi-stomatolog-minzdrav-smertnost (access date: 05/22/2020).
Teeth brushing methods
Pakhomov method G.N.12
- All teeth are conventionally divided into several sections (chewing left and right, and front)
- They start brushing their teeth with the chewing right teeth, then move on to the front teeth and end with the chewing teeth on the left.
- The anterior (labial) and posterior (lingual) surfaces are cleaned with sweeping movements from the gums to the edge of the tooth, the brush is held at an angle of 45°
- The chewing surface is cleaned with back and forth movements.
Fones method12
- When brushing your teeth using this method, you need to close your teeth together and smile broadly, the front surface of all teeth is brushed in a circular motion.
- Next, with the mouth slightly open, the inner (lingual and palatal) surface of the teeth is cleaned in a circular motion.
- The chewing surface is brushed in a circular motion
Baas method12
- The toothbrush is held like a pen
- Use circular movements to clean each tooth one at a time, without applying too much pressure. This cleanses the outer and inner surfaces of all teeth.
- When cleaning chewing teeth and the inner surface of all teeth, some of the bristles must be placed on the gum, and some on the enamel.
- The chewing surface must be cleaned in a circular motion, the bristles should fit snugly against the tooth, but not bend.
1
Digestive system. Names in Latin
Chapter 5. Splanchnology (internal organs)
| SYSTEMA DIGESTORIUM | DIGESTIVE SYSTEM |
| Os | Mouth |
| Cavitas oris | Oral cavity |
| Tunica mucosa oris | Oral mucosa |
| Vestibulumoris | Vestibule of the mouth |
| Rima oris | Mouth gap |
| Labia oris | Lips of the mouth |
| Labium superius | Upper lip |
| Philtrum | philtrum |
| Tuberculum | Tubercle |
| Labium inferius | Underlip |
| Frenulum labii suorioris | Upper lip frenulum |
| Frenulum labii inferioris | Frenum of the lower lip |
| Commissura labiorum | Lip commissure |
| Anqulusoris | Angle of mouth |
| 8ucca | Cheek |
| Corpus adiposum buccae | Cheek fat pad |
| Orqanum iuxtaorale | Perioral organ |
| Papilla ductus parotidei | Parotid duct papilla |
| Cavitas oris propria | The oral cavity itself |
| Palatum | Sky |
| Palatum durum | Solid sky |
| Palatum molle; Velum palatinum | Soft sky; velum |
| Raphe palati | Palate seam |
| Plicae palatinae transversae; Rugae palatinae | Transverse palatal folds |
| Papilla incisiva | Incisive papilla |
| Ginqiva | Gum |
| Marqoqinqivalis | Gingival edge |
| Papilla quinqivalis; Papilla interdentalis | Gingival papilla; interdental papilla |
| Sulcus qinqivalis | Gingival sulcus |
| Caruncula sublinqualis | Sublingual papilla |
| Plica sublinqualis | Sublingual fold |
| Glandulaeoris | Glands of the mouth |
| Glandulae salivariae majores | Major salivary glands |
| Glandula parotidea | Parotid gland |
| Pars superficialis | Surface part |
| Pars profunda | Deep part |
| Glandula parotidea accessoria | Accessory parotid gland |
| Ductus parotideus | Parotid duct |
| Glandula sublinqualis | Sublingual gland |
| Ductus sublinqualis maior | Greater hypoglossal duct |
| Ductus sublinquales minores | Small sublingual ducts |
| Glandula submandibularis | Submandibular gland |
| Ductus submandibularis | Submandibular duct |
| Glandulae salivariae minores | Minor salivary glands |
| Glandulae labiales | Labial glands |
| Glandulae buccales | Buccal glands |
| Glandulae molares | Molar glands |
| Glandulae palatinae | Palatine glands |
| Dentes | Teeth |
| Arcus dentalis maxillaris; Arcus dentalis superior | Maxillary dental arch; upper dental arch |
| Arcus dentalis mandibularis; Arcus dentalis | Mandibular dental arch; lower |
| inferior | dental arch |
| Dens mcisivus | Cutter |
| Dens caninus | Fang |
| Dens premolaris | Premolar; premolar |
| Dens molaris | large molar; molar |
| Dens molaris tertius; Dens serotinus | Third major molar; third molar; wisdom tooth |
| Corona dentis | Crown of the tooth |
| Cusoisdentis | Tooth tip |
| Apex cuspidis | Tip tip |
| Cuspis accessoria | Additional point |
| Tuberculum dentis | Tubercle of tooth |
| Christa transversalis | Transverse scallop |
| Crista triancularis | Triangular comb |
| Christa obliqua | Oblique comb |
| Fissura occlusalis | Occlusal gap |
| Fossa occlusalis | Occlusal fossa |
| Cuspis buccalis | Buccal cusp |
| Cuspis palatinalis | Palatal tubercle |
| Cuspis linqualis | Lingual tubercle |
| Cuspis mesiobuccalis | Buccal mesial tubercle |
| Cuspis mesiopalatalis | Palatomesial tubercle |
| Cuspis mesiolinqualis | Lingual-mesial tubercle |
| Cuspis distobuccalis | Buccal distal tubercle |
| Cuspis distopalatinalis | Palatodistal tubercle |
| Cuspis distolinqualis | Lingual-distal tubercle |
| Cuspis distalis | Distal tubercle |
| Corona clinic | Clinical crown |
| Cervix dentis | Tooth neck |
| Radix dentis | Tooth root |
| Apex radicis dentis | Apex of tooth root |
| Radix clinic | Clinical root |
| Facies occlusalis | Occlusal surface |
| Facies vestibularis | Vestibular surface |
| Facies buccalis | Buccal surface |
| Facies labialis | Labial surface |
| Facies linqualis | Lingual surface |
| Facies palatinalis | Palatal surface |
| Facies mesialis | Mesial surface |
| Facies distalis | Distal surface |
| Facies approximalis | Approximal surface |
| Area continences | Contact zone |
| Cinqulum | Belt |
| Christa marqinalis | Marginal scallop |
| Maroo incisalis | Cutting edge |
| Cavitas dentis; Cavitas pulparis | Dental cavity, pulp cavity |
| Cavitas coronae | Crown cavity |
| Canalis radicis dentis | Tooth root canal |
| Foramen apicis dentis | Tooth apex hole |
| Pulpa dentis | Dental pulp |
| Pulpa coronalis | Crown pulp |
| Pulpa radicularis | Root pulp |
| Papilla dentis | Dental papilla; gingival papilla |
| Dentinum | Dentine |
| Enamelum | Enamel |
| Cementum | Cement |
| Periodontium | Periodontium |
| Mammillae | Papillae |
| Stria canina; Sulcus caninus | Fang strip; canine groove |
| Fossa canina | Canine fossa |
| Fovea mesialis | Mesial fossa |
| Fovea distalis | Distal fossa |
| Radix buccalis | Buccal root |
| Radix palatinalis | Palatine root |
| Radix mesialis | Mesial root |
| Radix distalis | Distal root |
| Radix mesiobuccalis | Buccal mesial root |
| Radix mesiolinqualis | Glossomesial root |
| Radix accessoria | Accessory root |
| (Tuberculum anomale) | (Abnormal lump) |
| Cuspis paramolaris; Tuberculum paramolare | Perimolar tubercle |
| Tuberculum molare | Molar cusp |
| Alveolus dentalis | Dental alveolus |
| Curvea occlusalis | Occlusal curvature |
| Dentesdecidui | Baby teeth |
| Dentes permanentes | Permanent teeth |
| (Diastema) | (Diastema) |
| Lingua | Language |
| Corpus linquae | Body of tongue |
| Radix linquae | Root of tongue |
| Dorsum linquae | Dorsum of tongue |
| Pars anterior; Pars presulcalis | Front end; pre-furrow part |
| Pars posterior; Pars postsulcalis | Rear end; post-furrow part |
| Facies inferior linquae | Underside of the tongue |
| Plica fimbriata | Fringed fold |
| Marqo linquae | Edge of tongue |
| Apex linquae | tip of tongue |
| Tunica mucosa linquae | Mucous membrane of the tongue |
| Frenulum linguae | Tongue frenulum |
| Papillae Imquales | Tongue papillae |
| Papillae filiformes | Filiform papillae |
| Papillae fungiformes | Fungiform papillae |
| Papillae vallatae | circumvallate papillae |
| Papillae foliatae | Leaf-shaped papillae |
| Sulcus medianus linquae | Median sulcus of tongue |
| Sulcus terminalis linquae | Border groove of tongue |
| Foramen caecum linquae | Blind opening of the tongue |
| (Ductus thyroqlossalis) | (Thyroglossal duct) |
| Tonsilla linqualis | Lingual tonsil |
| Noduli lymphoidei | Lymphoid nodules |
| Septum linquae | Tongue septum |
| Aponeurosis linquae | Aponeurosis of the tongue |
| Musculi linguae | Muscles of the tongue |
| M. qenioqlossus | Genioglossus muscle |
| M.hyoqlossus | Hypoglossus muscle |
| M.chondroqlossus | Cartilaginous muscle |
| M. ceratoqlossus | Cornoglossus muscle |
| M. stvloqlossus | Styloglossus muscle |
| M. lonqitudinalis superior | Superior longitudinal muscle |
| M. lonqitudinalis inferior | Inferior longitudinal muscle |
| M. transversus linguae | Transverse tongue muscle |
| M. verticalislinquae | Vertical tongue muscle |
| M. palatoqlossus | Palatoglossus muscle |
| Fauces | Zev |
| Isthmus faucium | Isthmus of pharynx |
| Palatum molle; Velum palatinum | Soft sky; velum |
| Uvula palatina | Uvula |
| Arcus palatoglossus; Plica anterior faucium | Palatoglossus arch; anterior throat fold |
| (Plica triancularis) | (Triangular fold) |
| Arcus palatopharyngeus; Plica posterior | Palatopharyngeal arch; back fold |
| faucium | pharynx |
| (Plica semilunaris} | (Semilunate fold) |
| Fossa tonsillaris; Sinus tonsillaris | Tonsil fossa; tonsillar sinus |
| Fossa supratonsillaris | Supramygdaloid fossa |
| Tonsilla palatina | Palatine tonsil |
| Capsula tonsillae | Almond capsule |
| (Fissura tonsillaris; Fissura intratonsillaris) | (Amygdaloid fissure; intratonsilal fissure) |
| Fossulae tonsillae | Almond dimples |
| Cryptae tonsillae | Almond crypts |
| Musculi palati mollis et faucium | Muscles of the soft palate and pharynx |
| Aponeurosis palatina | Palatal aponeurosis |
| M. levator veh palatini | Levator palatine muscle |
| M. tensor veli palatini | Muscle that tenses the velum palatine |
| M. uvulae | Uvula muscle |
| M. palatoqlossus | Palatoglossus muscle |
| M. palatopharynqeus | Velopharyngeal muscle |
| Fasciculus anterior | Front bun |
| Fasciculus posterior; M. sphincter palatopha-fyngeus | Posterior bundle; velopharyngeal sphincter |
| Pharynx | Pharynx |
| Cavitas pharynqis | Pharyngeal cavity |
| Pars nasalis pharyngis | Nasal part of the pharynx |
| Fornix pharynqis | Vault of the pharynx |
| Hypophysis pharynqealis | Pharyngeal pituitary gland |
| Tonsilla pharynqealis | Pharyngeal tonsil |
| Fossulae tonsillae | Almond dimples |
| Cryptae tonsillae | Almond crypts |
| Noduli lymphoidei pharynqeales | Pharyngeal lymphoid nodules |
| (Bursa pharynqealis) | (pharyngeal bursa) |
| Ostium pharyngeum tubae auditivae; Ostium pharynqeum tubae auditoriae | Pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube |
| Torus tubarius | Pipe roller |
| Plica salpinqopharynqea | Tubalopharyngeal fold |
| Plica salpinqopalatina | Tupalatal fold |
| Torus leva tone | The levator soft palate muscle |
| Tonsilla tubaria | Tubal tonsil |
| Recessus pharynqeus | Pharyngeal pocket |
| Crista palatopharynqea | Velopharyngeal ridge |
| Pars oralis pharyngis | Oropharynx |
| Vallecula epiqlottica | Epiglottis fossa |
| Plica qlossoepiqlottica mediana | Median lingual epiglottis fold |
| Plica glossoepiglottica lateralis Pars larynqea pharynqis | Lateral lingual epiglottis fold |
| Laryngeal part of the pharynx | |
| Recessus piriformis | Pear-shaped pocket |
| Plica nervi larynqei superioris | Fold of the superior laryngeal nerve |
| Constrictio pharynqooesophaqealis | Pharyngeal-esophageal constriction |
| Fascia pharynqobasilaris | Pharyngobasilar fascia |
| Tela submucosa | Submucosa |
| Tunica mucosa | Mucous membrane |
| Glandulae pharynqeales | Pharyngeal glands |
| Musculi pharyngis; Tunica muscularis pharynqis | Muscles of the pharynx; muscular layer of the pharynx |
| Raphe pharyngis | Suture of the pharynx |
| Raphe ptervqomandibularis | Pterygomandibular suture |
| M. constrictor pharynqis superior | Superior pharyngeal constrictor |
| Pars pteryqopharynqea | Pterygopharyngeal part |
| Pars buccopharynqea | Buccal-pharyngeal part |
| Pars mylopharvnqea | Maxillopharyngeal part |
| Pars qlossopharynqea | Glossopharyngeal part |
| M. constrictor pharynqis medius | Middle pharyngeal constrictor |
| Pars chondropharynqea | Cartilaginous part |
| Pars ceratopharynqea | Cornopharyngeal part |
| M. constrictor pharynqis inferior | Inferior pharyngeal constrictor |
| Pars thyropharynqea; M. thyropharynqeus | Thyropharyngeal part |
| Pars cricopharynqea; M. cricopharvnqeus | Cricopharyngeal part |
| M.stylopharynqeus | Stylopharyngeal muscle |
| M. salpmqopharynqeus | Tubalopharyngeal muscle |
| M. palatopharyngeus | Velopharyngeal muscle |
| Fascia buccopharynqealis | Buccal pharyngeal fascia |
| Spatium penpharynqeum | Periopharyngeal space |
| Spatium retropharynqeum | Retropharyngeal space |
| Spatium lateropharyngeum; Spatium pha-rynqeum laterale; Spatium parapharynqeum | Lateral parapharyngeal space |
| Oesophagus | Esophagus |
| Parscervicalis: Pars colli | Neck part |
| Pars thoracica | Thoracic part |
| Constrictio partis thoracicae; Constrictio bronchoaortica | Narrowing of the chest; bronchoaortic narrowing |
| Constrictio phrenica; Constrictio diaphragmatica | Diaphragmatic constriction |
| Pars abdominalis | Abdominal part |
| Tunica serosa | Serosa |
| Tela subserosa | Subserosal membrane |
| Tunica adventitia | Adventitia |
| Tunica muscularis | Muscularis |
| Tendo cncoesophaqeus | cricoesophageal tendon |
| M. bronchoesophaqeus | Bronchoesophageal muscle |
| M. pleurooesophaqeus | Pleuroesophageal muscle |
| Tela submucosa | Submucosa |
| Tunica mucosa | Mucous membrane |
| Lamina muscularis mucosae | Muscular plate of the mucous membrane |
| GASTER | STOMACH |
| Paries anterior | Front wall |
| Paries posterior | Rear genka |
| Curvatura major | greater curvature |
| Curvatura minor | Small curvature |
| Incisura anqualis | Corner cut |
| Cardia;Parscardiaca | Cardia; cardiac part |
| Ostium cardiacum | Cardiac foramen |
| Fundus quastricus | Fundus of the stomach |
| Fornix qastricus | Gastric vault |
| Incisura cardialis | Cardiac notch |
| Corpus quastricum | Body of stomach |
| Canalis qastricus | Stomach channel |
| Pars pvlorica | Pyloric (pyloric) part |
| Antrum pyloricum | Gatekeeper Cave |
| Canalis pyloricus | Gatekeeper channel |
| Pylorus | Gatekeeper (pylorus) |
| Ostium pyloricum | Pyloric hole |
| Tunica serosa | Serosa |
| Tela subserosa | Subserosal base |
| Tunica muscularis | Muscularis |
| Stratum lonqitudmale | Longitudinal layer |
| Stratum circulare | Circular layer |
| M. sphincter pyloricus | Pyloric sphincter |
| Fibrae obliquae | Oblique fibers |
| Tela submucosa | Submucosa |
| Tunica mucosa | Mucous membrane |
| Plicae qastricae | Folds of the stomach |
| Lamina muscularis mucosae | Muscular plate of the mucous membrane |
| Areae qastricae | Gastric fields |
| Plicae villosae | Villous folds |
| Foveolae qastricae | Gastric dimples |
| Glandulae qastricae | Stomach glands |
| Intestinum tenue | Small intestine |
| Tunica serosa | Serosa |
| Tela subserosa | Subserosal base |
| Tunica muscularis | Muscularis |
| Stratum longitudinale; Stratum helicoidale lonqiqradus | Longitudinal layer; long pitch spiral layer |
| Stratum circulare; Stratum helicoidale brevis qradus | Circular layer; short pitch spiral layer |
| Plicae circulares | Circular folds |
| Tela submucosa | Submucosa |
| Tunica mucosa | Mucous membrane |
| Lamina muscularis mucosae | Muscular plate of the mucous membrane |
| Villi intestinales | Intestinal villi |
| Glandulae intestinales | Intestinal glands |
| Noduli lymphoidei solitarii | Single lymphoid nodules |
| Noduli lymphoidei aqqreqati | Group lymphoid nodules |
| DUODENUM | DUODENUM |
| Pars superior | Top part |
| Ampulla; 8ulbus | Ampupa; button |
| Flexura duodeni superior | Superior flexure of the duodenum |
| Pars descendens | Descending part |
| Flexura duodeni inferior | Lower and lower flexure of the duodenum |
| Pars horizontalis; Pars inferior | Horizontal part; Bottom part |
| Pars ascendens | Rising part |
| Flexura duodenojejunalis | Duodenum-jejunum |
| bend | |
| Pars tecta duodeni | Hidden part of the duodenum |
| M. suspensorius duodeni; Lig. suspensorium duodeni | Duodenal suspensory muscle; duodenal suspensory ligament |
| Pars phrenicocoeliaca | Diaphragmatic-celiac part |
| Pars coeliacoduodenalis | Celiac-duodenal part |
| Plica longitudinalis duodeni | Longitudinal fold of the duodenum |
| Papilla duodeni major | Major duodenal papilla |
| GUTS | |
| Papilla duodeni minor | Lesser duodenal papilla |
| Glandulae duodenales | Duodenal glands |
| Ileum | Ileum |
| Pars terminalis | End part |
| (Oiverticulum ilei) | (Ileal diverticulum) |
| Intestinum crassum | Colon |
| Tunica serosa | Serosa |
| Tela subserosa | Subserosal base |
| Tunica muscularis | Muscularis |
| Tela submucosa | Submucosa |
| Tunica mucosa | Mucous membrane |
| Lamina muscularis mucosae | Muscular plate of the mucous membrane |
| Glandulae intestinales | Intestinal glands |
| Caecum | Cecum |
| Papilla ilealis | Ileointestinal papilla |
| Ostium ileale | Ileum intestinal orifice |
| Frenulum ostii ilealis | Frenum of the ileo-intestinal foramen |
| Labrum ileocolicum; Labrum superius | Ileocolic lip; upper lip |
| Labrum ileocaecal; Labrum inferius | Ileocecal lip; underlip |
| Appendix vermiformis | Appendix, appendix |
| Ostium appendicis vermiformis | Foramen of the appendix |
| Noduli lymphoidei aqqreqati | Group lymphoid nodules |
| (Fascia precaecocolica) | (Prececal fascia) |
| Colon | Colon |
| Colon ascendens | Ascending colon |
| Flexura coli dextra; Flexura coli hepatica | Right flexure of the colon; hepatic flexure of the colon |
| Colon transversum | Transverse colon |
| Flexura coli sinistra; Flexura coli splenica | Left flexure of the colon; splenic flexure of the colon |
| Colon descendens | Descending colon |
| Colon siqmoideum | Sigmoid colon |
| Plicae semilunares coli | Semilunate folds of the colon |
| Haustra coli | Gaustra of the colon |
| Appendices omentales; Appendices adiposae coli; Appendices epiploicae | Omental processes |
| Tunica muscularis | Muscularis |
| Stratum lonqitudmale | Longitudinal layer |
| Taeniae coli | Colon tapes |
| Taenia mesocolica | mesenteric band |
| Taenia omentalis | Oil seal tape |
| Taenia libera | Free Tape |
| Stratum circulare | Circular layer |
| Rectum | Rectum |
| Flexura sacralis | Sacral flexure |
| Flexurae lateralis | Lateral bends |
| Flexura superodextra lateralis; Flexura superior lateralis | Upper right lateral flexure; superior lateral bend |
| Flexura intermediosmistra lateralis; Flexura intermedia lateralis | Intermediate left lateral flexure; lateral intermediate bend |
| Flexura inferodextra lateralis; Flexura inferior lateralis | Inferior right lateral flexure; inferior lateral bend |
| Plicae transversae recti | Transverse folds of the rectum |
| Ampulla recti | Rectal ampoule |
| Tunica muscularis | Muscularis |
| Stratum lonqitudmale | Longitudinal layer |
| M. rectococcyqeus | Rectococcygeus muscle |
| Mm. anorectoperineales; Mm. recto-urethrales | Anal-rectal-perineal muscles; rectourethral muscles |
| M. rectopermealis; M. rectourethralis superior | Rectoperineal muscle; superior rectourethral muscle |
| M. anopermealis; M. rectourethralis inferior | Anal-perineal muscle; inferior rectourethral muscle |
| M. rectovesicalis | Rectovesical muscle |
| Stratum circulare | Circular layer |
| Liq. recti laterale | Lateral ligament of the rectum |
| Canalis analis | Anal canal; anal canal |
| Flexura anorectalis; Flexura perinealis | Anal-rectal flexure; perineal curve |
| Junctio anorectalis | Anal-rectal junction |
| Columnae anales | Anal pillars; anal poles |
| Valvulaeanales | Anal valves; anal valves |
| Sinus anales | Anal sinuses; anal sinuses |
| Zona transitionalis analis | Anal transition zone; anal transition zone |
| Linea anocutanea | Anal-cutaneous line; anal cutaneous line |
| Linea pectinata | Comb line |
| Pecten analis | Anal ridge; anal comb |
| M. sphincter ani intemus | Internal anal sphincter |
| Sulcus intersphinctericus | Intersphincteric groove |
| M. sphincter ani externus | External anal sphincter |
| Pars profunda | Deep part |
| Pars superficialis | Surface part |
| Pars subcutanea | Subcutaneous part |
| Anus | Anus |
| Hepar | Liver |
| Facies diaphragmatica | Diaphragmatic surface |
| Pars superior | Top part |
| Impressiocardiaca | Cardiac depression |
| Pars anterior | Front end |
| Pars dextra | Right part |
| Pars posterior | Rear end |
| Area nuda | Extraperitoneal field |
| Sulcus venae cavae | Groove of the inferior vena cava |
| Fissura liqamenti venosi | Venous ligament gap |
| Liq. venosum | Venous ligament |
| Facies visceralis | Visceral surface |
| Fossa vesicae biliaris; Fossa vesicae felleac | Gallbladder fossa |
| Fissura liqamenti teretis | Round ligament gap |
| Liq. teres hepatis | Round ligament of the liver |
| Porta hepatis | Gate of the liver |
| Tuber omentale | Omental tubercle |
| Impressio oesophaqeale | Esophageal depression |
| Impressioqastrica | Gastric depression |
| Impressio duodenalis | Duodenal depression; duodenal depression |
| Impressio juice | Colon indentation |
| Impressio renalis | Renal depression |
| Impressio suprarenalis | Adrenal depression |
| Marqo inferior | Bottom edge |
| Incisura liqamenti teretis | Cutting of the round ligament |
| Lobus hepatis dexter | Right lobe of the liver |
| Lobus hepatis sinister | Left lobe of the liver |
| Appendix fibrosa hepatis | Fibrous process of the liver |
| Lobus quadratus | Square fraction |
| Lobus caudatus | Caudate lobe |
| Processus papillaris | Papillary process |
| Processus caudatus | Caudate process |
| Segmentatio hepatis: lobi, paries, divisions et segmenta | Liver segmentation: lobes, parts, sections and segments |
| Fissura umbilicalis | Umbilical shel |
| Fissura portalis principalis | Main gateway |
| Fissura portalis dextra | Right portal slit |
| Pars hepatis sinistra | Left side of the liver |
| Divisio lateralis sinistra | Left lateral area |
| Segmentum posterius laterale sinistrum; Segmentum II | Posterior left lateral segment; segment II |
| Segmentum anterius laterale sinistrum; Segmentum III | Anterior left lateral segment - segment III |
| Divisio medialis sinistra | Left medial area |
| Seqmentum mediale sinistrum; Seqmentum IV | Left medial segment, segment IV |
| Pars posterior hepatitis; Lobus caudatus | Posterior part of the liver: caudate lobe |
| Segmentum posterius; Lobus caudatus; Seqmentum 1 | Posterior segment; caudate lobe; segment 1 |
| Pars hepatis dextra | Right side of the liver |
| Divisio medialis dextra | Right medial area |
| Segmentum anterius mediale dextrum; Seqmentum V | Anterior right medial segment; segmentU |
| Segmentum posterius mediale dextrum; Seqmentum VIII | Posterior right medial segment; segment VIII |
| Divisio lateralis dextra | Right side section |
| Segmentum anterius laterale dextrum; Seqmentum VI | Anterior right lateral segment; segment VI |
| Segmentum posterius laterale dextrum; Seqmentum VII | Posterior right lateral segment; segment VII |
| Tunica serosa | Serosa |
| Tela subserosa | Subserosal base |
| Tunica fibrosa | Fibrous membrane |
| Capsula fibrosa perivascularis | Perivascular fibrous capsule |
| Lobuli hepatis | Liver lobules |
| Aa. interlobu lares | Interlobular arteries |
| Vv. interlobu lares | Interlobular veins |
| Vv. centrales | Central veins |
| Ductus bihferi interlobulares | Bile interlobular ducts |
| Ductus hepaticus communis | Common hepatic duct |
| Ductus hepaticus dexter | Right hepatic duct |
| R. anterior | Anterior branch |
| R. posterior | Posterior branch |
| Ductus hepaticus sinister | Left hepatic duct |
| R. lateralis | Lateral branch |
| R. medialis | Medial branch |
| Ductus lobi caudati dexter | Right duct of the caudate lobe |
| Ductus lobi caudati sinister | Left duct of the caudate lobe |
| Vesica biliaris; Vesica fellea | Gallbladder |
| Fundus vesicae biliaris; Fundus vesicae felteae | Gallbladder bottom |
| Infundibulum vesicae biliaris; Infundibulum vesicae felleae | Funnel of the gallbladder |
| Corpus vesicae biliaris; Corpus vesicae felleae | Body of the gallbladder |
| Collum vesicae biliaris; Collum vesicae felleae | Neck of gallbladder |
| Tunica serosa | Serosa |
| Tela subserosa | Subserosal base |
| Tunica muscularis | Muscularis |
| Tunica mucosa | Mucous membrane |
| Plicae mucosae; Ruqae | Folds of the mucous membrane |
| Ductus cysticus | Cystic duct |
| Plica spiralis | Spiral fold |
| Ductus choledochus; Ductus biliaris | Common bile duct |
| M. sphincter ductus choledochi; M. sphincter ductus biliaris | Sphincter of the common bile duct |
| M. sphincter superior | Upper sphincter |
| M. sphincter inferior | Lower sphincter |
| Ampulla hepatopancreatica; Ampulla bili- aropancreatica | Hepatic-pancreatic ampulla |
| M. sphincter ampullae | Sphincter ampulla |
| Glandulae ductus choledochi; Glandulae ductus biliaris | Glands of the common bile duct |
| Pancreas | Pancreas |
| Caput pancreatis | Head of the pancreas |
| Processus uncinatus | Uncinate process |
| Incisura pancreatis | Pancreatic Tenderloin |
| Collum pancreatis | Neck of the pancreas |
| Corpus pancreatis | Body of the pancreas |
| Facies anterosuperior | Anterosuperior surface |
| Facies posterior | Rear surface |
| Facies anteroinferior | Anteroinferior surface |
| Marqo superior | Top edge |
| Marqo anterior | Front edge |
| Marqo inferior | Bottom edge |
| Tuber omentale | Omental tubercle |
| Cauda pancreatis | Tail of the pancreas |
| Ductus pancreaticus | Pancreatic duct |
| M. sphincter ductus pancreatici | Pancreatic duct sphincter |
| Ductus pancreaticus accessorius | Accessory duct of the pancreas |
| (Pancreas accessorium) | (Accessory pancreas) |
| Insulae pancreaticae | Pancreatic islets |
| Cavitas abdominis; Cavitas abdominalis | Abdominal cavity; abdomen |
| Cavitas pelvis; Cavitas pelvina | Pelvic cavity; pelvic cavity |
| Spatium extraperitoneale | Extraperitoneal space |
| Spatium retroperitoneale | Retroperitoneal space |
| Spatium retropubicum | Retropubic space |
| Peritoneum | Peritoneum |
| Tunica serosa | Serosa |
| Tela subserosa | Subserosal base |
| Peritoneum parietale | Parietal peritoneum |
| Peritoneum viscerate | Visceral peritoneum |
| Mesenterium | Mesentery of the small intestine |
| Radix mesenterii | Root of the mesentery of the small intestine |
| Mesocolon | Mesentery of the colon |
| Mesocolon transversum | Mesentery of the transverse colon |
| (Mesocolon ascendens) | (Mesentery of the ascending colon) |
| (Mesocolon descendens) | (Mesentery of the descending colon) |
| Mesocolon siqmoideum | Mesentery of the sigmoid colon |
| Mesoappendix | Mesentery of the appendix (appendix) |
| Omentum minus | Small seal |
| Liq. hepatophrenicum | Hepatophrenic ligament |
| Liq. hepatoesophaqeale | Hepatoesophageal ligament |
| Liq. hepatoqastricum | Hepatogastric ligament |
| Liq. hepatoduodenal | Hepatoduodenal ligament |
| (Liq. hepatocolicum) | (Hepatocolic ligament) |
| Omentum majus | Big seal |
| Liq. qastrophrenicum | Gastrophrenic ligament |
| Lig. qastrosplenicum; Lig. gastroliennale | Gastrosplenic ligament |
| Plica presplenica | Presplenic fold |
| (Liq. qastrocohcum) | (Gastrocolic ligament) |
| Liq. phrenicosplenicum | Phrenosplenic ligament |
| Liq. splenorenal; Liq. lienorenale | Splenorenal ligament |
| Lig. pancreaticosplenicum | Pancreasplenic ligament |
| Liq. pancreaticocolicum | Pancreatocolic ligament |
| Liq. splenocolicum | Splenocolonic ligament |
| Liq. phrenicocolicum | Phrenocolic ligament |
| Ligamenta bepatis | Ligaments of the liver |
| Lig. coronarium | Coronary ligament |
| Liq. falciforme | Falciform ligament |
| Liq. tnanqulare dextram | Right triangular ligament |
| Liq. trianqulare sinistrum | Left triangular ligament |
| Liq. hepatorenal | Hepatorenal ligament |
| Recessus, fossae et plicae | Depressions, pits and folds |
| Bursa omentalis | Omental bag |
| Foramen omentale; Foramen epiploicum | Stuffing box hole |
| Vestibulum | vestibule |
| Recessus superior | Upper recess |
| Recessus inferior | Bottom recess |
| Recessus splenicus; Recessus lienalis | Splenic recess |
| Plica qastropancreatica | Gastropancreatic fold |
| Plica hepatopancreatica | Hepatopancreatic fold |
| Plica duodenalis superior; Plica duodenoje- junalis | Superior duodenal fold; duodenal-jejunal fold |
| Recessus duodenalis superior | Superior duodenal recess |
| Plica duodenalis inferior; Plica duodenome- socolica | Inferior duodenal fold; duodenomesenteric fold |
| Recessus duodenalis inferior | Inferior duodenal recess |
| (Plica paraduodenalis) | (Paraduodenal fold) |
| (Recessus paraduodenalis) | (Paraduodenal recess) |
| (Recessus retroduodenalis) | (Retroduodenal recess) |
| Recessus intersiqmoideus | Intersigmoid recess |
| Recessus ileocaecalis superior | Superior ileojecal recess |
| Plica caecalis vascularis | Vascular cecal fold |
| Recessus ileocaecalis inferior | Inferior ileocecal recess |
| Plica ileocaecalis | Ileocecal fold |
| Recessus retrocaecalis | Retrocolic recess |
| Plicae caecales | Cecal folds |
| Sulci paracolici | Paracolic grooves |
| Recessus subphrenicus | Subphrenic recess |
| Recessus subhepaticus | Subhepatic recess |
| Recessus hepatorenalis | Hepatorenal deepening |
| Triqonum cystohepaticum | Vesicohepatic triangle |
| Plica umbilicalis mediana | Median umbilical fold |
| Fossa supravesicalis | Supravesical fossa |
| Plica umbilicalis medialis | Medial umbilical fold |
| Fossa inquinalis medialis | Medial inguinal fossa |
| Trigonum inguinale | Inguinal triangle |
| Plica umbilicalis lateralis; Plica epiqastrica | Lateral umbilical fold |
| Fossa inquinalis lateralis | Lateral inguinal fossa |
| Peritoneum urogenitale | Urogenital peritoneum |
| Fossa paravesicalis | Paravesical fossa |
| Plica vesicalis transversa | Transverse vesical fold |
| Excavatio vesicouterina O | Vesicouterine cavity O |
| Liq. latum uteri 0 | Broad ligament of uterus O |
| Mesometrium 0 | Mesentery of the uterus 0 |
| Mesosalpinx 0 | Mesentery of the fallopian tube O |
| Mesovarium 0 | Mesentery of the ovary O |
| Triqonum panetale laterale pelvis 0 | Triangle of the lateral wall of the pelvis O |
| Fossa ovarica 0 | Ovarian fossa O |
| Liq. suspensorium ovarii 0 | Ovarian suspensory ligament |
| Plica rectouterina 0 | Rectal uterine fold O |
| Excavatio rectouterina 0 | Rectumuterine recess O |
| Excavatio rectovesicalis 0 | Rectovesical recess O |
| Fossa pararectalis | Periacolic fossa |
Professional hygiene
Professional oral hygiene should be carried out every 6 months. For brace wearers, hygiene is mandatory every quarter.
Stages of professional hygiene: 11
- ultrasonic treatment (scaling) - removal of hard dental plaque
- Air Flow cleaning – removing soft plaque
- polishing with a brush and abrasive paste
- fluoridation, calcination – if necessary
The Skyler is used for ultrasonic cleaning of plaque and tartar from the surface of the tooth and under the gum. Scaling can be performed under local anesthesia.
The second stage is Air Flow - teeth cleaning with a special device using fine powder, air and water supplied under high pressure.
Benefits of Air Flow:7
- cleaning hard-to-reach areas from plaque
- polishing the enamel surface
- decreased adhesion (sticking) of bacteria
- whitening effect
After cleaning, polishing is carried out using a rotating brush and a special paste. It is very important. By making the surface of the teeth smooth, the doctor prevents bacteria from attaching to the enamel.
At the end of the procedure, a mineralizing gel containing fluoride and calcium salts, necessary for the prevention of caries and increased sensitivity of the gums, is applied to the teeth. The gel is applied only when necessary.
Symptoms and their manifestation
Oral diseases can be diagnosed independently at home. It is only necessary to notice changes that have characteristic signs of a pathological process:
- The appearance of itching, burning or pain;
- Swelling;
- Formation of ulcers and pustules;
- Bleeding gums;
- Damage to tooth enamel;
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor;
- Weakness and sickness.
Popular questions
Can I lighten my teeth with Air Flow?
Yes, but you need to understand that hygiene is not a substitute for bleaching. After brushing, your teeth will become 2-3 shades lighter due to the removal of plaque. But there are pigmentations that have penetrated deeply into the teeth and cannot be removed. This requires special whitening procedures.
Recommendations: what to do after hygiene?
It is necessary to adhere to the “white diet” to maximize the whitening effect. You should change your toothbrush. Do not eat anything hot or cold for at least 4 hours after hygiene.
What is the “white diet”?
“White diet” is a special type of nutrition in which a person eats light, non-coloring foods, that is, without pronounced pigment.
Is blood after professional hygiene normal?
Yes, a small amount of blood may appear after the procedure. After some time it should go away on its own.
Can teeth sensitivity increase after hygiene?
Yes, sensitivity may persist for several days after cleansing. If the sensitivity does not go away, you need to contact your dentist to prescribe treatment.
Can regular dental floss be used to clean children's teeth?
Yes, children can use adult dental floss. The main thing is that the taste suits the child, so it is recommended to choose fruity or tasteless threads.
What to do if after hygiene there is still bad breath?
Home hygiene needs to be adjusted. If hygiene measures do not help, then it is worth checking the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system and endocrine system.
Types of hygiene
Measures to maintain the microflora of the oral cavity are divided into 2 types:
- Personal hygiene.
This is the basis for maintaining healthy teeth, preventing gum inflammation, caries and enamel destruction. High-quality and effective personal hygiene is not only about brushing your teeth. And it is advisable to know the basic measures to maintain “order” in the mouth from childhood.
- Professional cleaning.
It is performed by a dentist in a medical office.
It is important to note that these points do not exclude, but complement each other. It is necessary to undergo a preventive examination (2 times a year), observe the rules of personal hygiene and periodically resort to deep cleaning. All this will help prevent oral diseases and maintain the attractiveness of your smile.