Author
Gonobobleva Elena Anatolyevna
Leading doctor
Dentist
until January 31
Free* consultation with dentists (generalist, surgeon, orthodontist) More details All promotions
Dental computed tomography
(CT) is a modern method of radiation diagnostics that allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image (3D) of the entire maxillofacial apparatus. Dental computed tomography is currently the most informative study of the condition of the oral cavity and teeth. It helps to identify diseases in the initial stages that are difficult to detect on conventional (2D) radiographs. It is especially important to do a dental CT in preparation for implantation and prosthetics. The resulting 3D image greatly simplifies the production of a three-dimensional model of the jaw.
3D CT – what is this procedure and what is it for?
3D imaging of the jaw is one of the main dental procedures used in diagnosis. The data obtained allows us to assess the condition of a specific maxillofacial area and plan further treatment.
This diagnostic tool is universal; it is used by both therapists and orthopedists, periodontists and implantologists. Using a 3D image, the therapist assesses the condition of the roots and canals of the tooth, and clarifies the localization of the inflammatory process.
An orthopedist can examine the anatomical structure of the temporomandibular joints, an implantologist can examine the volume and density of bone tissue in the area of the upcoming operation, as well as the parameters of the maxillary sinuses (maxillary sinuses).
Sometimes a large part of the tooth remains, as they say, “behind the scenes”, and the dentist simply cannot see it. Then computed tomography comes to the rescue, which allows you to examine the hidden area and prevent unpleasant consequences for the patient.
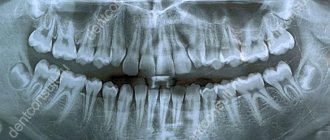
Until recently, the “gold standard” for instrumental diagnostics was a panoramic image. Today there is a more advanced method in which the maxillofacial area is scanned using computer technology.
What can dental tomography show?
Dental computed tomography allows:
- determine the position of the teeth;
- identify damage under fillings and fixed dentures;
- assess the condition of the dental canals;
- identify tumors, cysts, fistulas, foci of inflammation in the gums;
- detect the consequences of injuries (fractures of varying complexity, etc.)
Unique visualization method
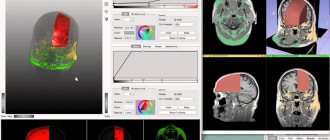
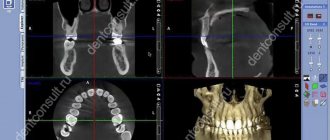
A computed tomograph produces a high-quality three-dimensional image of an individual tooth, maxillary sinuses, one or both jaws. Unlike standard panoramic images, a 3D tomogram allows the doctor to see the desired anatomical structures in a virtual section, from any angle.
During the procedure, the doctor can enlarge, rotate and study the maxillofacial area of interest at the required angle, which is unrealistic with conventional radiography.
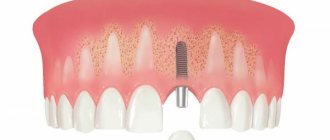
Computed tomography is an integral and primary stage of examination before implantation. It allows you not only to assess the condition of bone tissue, but also to measure its height, width and density. Moreover, three-dimensional beams help to choose the optimal method for installing implants through preliminary virtual surgery.
3D CT is a multi-purpose and indispensable diagnostic tool that makes it possible to avoid many medical errors and complications. Thanks to this examination, the quality of treatment increases significantly and eliminates unnecessary traumatic operations.
What is a 3D dental image?
If you visit an orthodontist, maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist, or even a plastic surgeon for a consultation, most likely one of his first appointments will be to do a computed tomography (CT) scan of the jaw, or a 3D dental scan. This is a modern and very accurate diagnostic technique that allows the doctor to view an image of the patient’s jaw from any angle and in any projection, even when the patient has already left his office. CT, unlike an orthopantomogram, provides a three-dimensional image of the jaw without distortion and allows you to look into any layer of tissue, making a kind of virtual section, without the need to perform unnecessary traumatic procedures on the patient live. The efficiency and safety of diagnosis and treatment are thus significantly increased.
Indications
Computed tomography is prescribed to identify:
- hidden carious lesions;
- defects in the structure of the jaw and dentition;
- fully or partially unerupted teeth;
- dystopic dental units with incorrect location or direction of growth;
- supernumerary teeth;
- damage to the dentition due to jaw fractures and other injuries;
- pathologies of the temporomandibular joint TMJ;
- tumors, cysts and other neoplasms in the jaws;
- condition of periodontal and periodontal tissues in case of gum disease, inflammation in the root area;
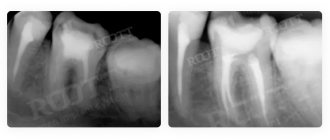
- number of roots, canals of teeth;
- cracks in the roots of teeth;
- features of the structure of bone tissue before jaw surgery (installation of implants, bone augmentation).
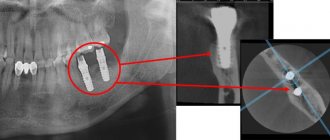
A 3D photo must be taken before dental implantation. The fact is that the jaw bone is clearly visible on a regular x-ray, but it does not allow assessing the soft tissues. On a three-dimensional tomogram, you can see in detail not only the bone, but also the nerve of the lower jaw, as well as blood vessels.
A 3D tomogram is much more informative than a panoramic image or targeted photographs of all teeth.
CT scan before implantation
Diagnostics using a computed tomograph before installing implants allows, first of all, to determine whether implantation is necessary at all. The image will give a complete picture, and the doctor will see where the teeth are missing, whether there are problem units, and whether they can be cured.
The 3D tomogram will show:
- hidden carious cavities;
- unerupted and “extra” teeth, which may interfere with the installation of artificial pins;
- properties of roots, canals - curved, narrow and long canals require a special approach, which should be taken into account before implantation;
- bone dimensions in height and width, on the basis of which the type and size of the implant is selected;
- condition of bone beams, partitions, voids in the jaw bone;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the root area - cysts, granulomas, abscesses where implants are planned to be installed. All this needs to be treated or removed before surgery;
- inflammation in the paranasal sinuses and lacrimal ducts, which can become a temporary obstacle to implantation;
- density, size, inclination of the alveolar process, thickness of the cortical bone layer, taking into account which the optimal type of artificial pin is selected;
- the physiological structure of the maxillary sinuses, the mandibular canal to determine the angle of inclination of the implant rod;
- defects and anomalies in the structure of the dentofacial apparatus;
- quality of installation, strength of fixation of implants after surgery for their implantation;
- severity and nature of traumatic injuries in fractures.
Based on the results obtained, a virtual operation to install the rods is performed. The appropriate size of the titanium pin is selected, its inclination and the point of implantation are determined, bypassing the anatomical structures. Thus, the final outcome of implantation is modeled.
Next, the tomographic data is loaded into the computer, and the program creates a three-dimensional model. The patient’s personal surgical template is printed on a 3D printer - an overlay with guide holes for inserting rods.
During implantation, the template is placed tightly on the gums, and the placement of the pins is carried out with extreme precision.
3D CT
Main features of the procedure
Features of 3D CT
CT is one of the types of fluoroscopy, carried out due to the passage of X-rays through the human body. Therefore, each procedure must be strictly justified. But modern devices give such a small radiation dose that no traces of radiation exposure remain in the body and the method is considered absolutely safe.
Unlike classic X-rays, 3D tomography is more informative, tomographs are almost 50 times more sensitive than X-ray machines, and accordingly, the images obtained as a result of diagnostics will give the specialist much more information to study. During an X-ray examination, a two-dimensional image is obtained; the high-quality interpretation of the image depends only on the experience and qualifications of the doctor. CT is a standardized method, all protocols of the procedure are verified, the resulting images will help detect pathological changes of even the smallest size, many of which cannot be diagnosed by any other means.
CT will help not only during diagnostic procedures, tomography is widely used for targeted biopsy, many therapeutic manipulations, it helps to establish the stage of formation of pathology, monitor the dynamics of therapy and recovery, evaluate the results of chemotherapy, and monitor the condition after various surgical interventions.
Preparation for the procedure
Preparation for 3D tomography depends on the area that will be examined.
Most often, no preparation is required, but there are areas for which it is still necessary to prepare for inspection.
Any type of CT scan is performed on an empty stomach; it is especially important to follow this rule if a study is planned with the introduction of a contrast agent. In this case, the last meal should take place at least 4 hours before the procedure, this will help prevent possible nausea.
When planning an examination of the abdominal cavity, retroperitoneal space, CT colonoscopy , it is recommended to follow a light diet three days before the tomography. Eliminate baked goods and any type of legumes from your diet, do not drink carbonated drinks and foods that cause flatulence.
It is also important to cleanse the intestines the day before the test and immediately before going to the clinic.
When preparing for a pelvic diagnosis , in addition to diet, it is important to come to the procedure with a moderately full bladder. To do this, you should drink as much liquid as possible for you an hour before the tomography, this should be at least one liter and not urinate until the diagnosis is completed.
Before a CT scan of the heart and blood vessels, you should consult with your doctor about the possibility of temporarily stopping or replacing medications taken, if any, since many drugs can distort the results of the study.
Diagnosis does not require hospitalization, and after it, patients immediately go home. There are no side effects or complications with 3D CT. The exception is procedures with contrast, after which the patient will be given recommendations or he may be asked to stay in the clinic to monitor the condition, since these studies may cause minor side effects and intolerance, which can be relieved with allergy suppressants.
Methodology
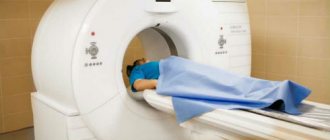
Computed tomography does not take more than 30 minutes. The patient lies down on a special motorized couch that moves towards a circular scanner that generates radiation around the patient's body. A CT scanner has a much wider ring than an MRI scanner; there is a lot of space around, which eliminates such contraindications as claustrophobia; patients with this syndrome feel comfortable during the procedure.
Doctors will be present and monitor the progress of the study from a separate room, hear and communicate with the patient using a speakerphone. The radiologist may periodically ask you to hold your breath to get clearer images. During the procedure, characteristic tapping sounds produced by the tomograph will be heard. After diagnosis, the patient is given a tomogram and the results recorded on a disk or memory card.
Indications for testing
Indications for CT diagnostics
A CT scan is prescribed by the attending physician on a routine or emergency basis. It is used to solve diagnostic problems in many areas of medicine. To carry out therapeutic measures and monitor the progress of therapy, after performing or when planning operations or punctures.
Indications for the use of computed tomography:
- Regular, severe pain in the head, accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- Fainting, convulsions, epileptic attacks, stroke;
- Various injuries, fractures;
- Identified circulatory disorders;
- Inflammatory processes in the body of any nature;
- Suspicion of malignant formations.
3D CT is also used for less dangerous pathologies, as an additional diagnostic procedure.
Contraindications to 3D CT
There are no absolute contraindications to computed tomography. The decision on the necessity and rationality of conducting the study is made by the attending physician for each patient and each specific case. This type of radiation diagnosis is not recommended for pregnant women and children under 14 years of age. If necessary, the method can be used by patients in any condition.
It is also worth discussing with a specialist the possibility of using contrast. In a number of studies, it significantly expands the boundaries of the data obtained, but is accompanied by the risk of a possible allergic reaction to the iodine contained in the contrast agent. Before and after the administration of contrast, antiallergic measures are taken.
Computed tomography is not recommended for:
- kidney and liver diseases;
- body weight above 200 kg;
- metal inserts or plaster casts in the area of study;
- diabetes mellitus in a severe stage;
- pregnant women;
- children under 14 years of age.
During lactation, women are advised not to breastfeed their baby for 48 hours following the procedure.
Advantages of the procedure
Advantages of computed tomography
CT is a leading diagnostic method for many diseases. It is used for initial research and to clarify the diagnosis, which was previously made after a clinical examination, ultrasound or x-ray. Computed tomography has many advantages, here are some of them:
- A high degree of information content of the method, unattainable using two-dimensional images.
- Low dose of X-ray radiation that does not have a negative effect on the body.
- Creation of three-dimensional models necessary for subsequent prosthetics.
- The ability to use one image instead of several, reducing the radiation dose and saving on diagnostics.
- The result obtained makes it possible to detect even the smallest pathological foci and tumors at an early stage.
This makes 3D CT one of the most popular diagnostic methods today.
Research results
After the diagnosis, the patient will be given the results in the form of a tomogram - a snapshot of the area under study, which is printed on a special film. And the recorded results on a disk or flash card.
The results obtained will help the doctor conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of the area under study, make a diagnosis, make a prognosis for the development of the detected pathology and prescribe timely effective treatment.
Sign up for 3D CT
At the Open Clinic, consultations are conducted by doctors with extensive experience and high qualifications; diagnostics are carried out using powerful modern equipment, which allows us to conduct research with maximum accuracy. You can sign up for a CT scan in any way convenient for you - on the website, by calling the clinic at the indicated numbers or via messenger.
You can get a computed tomography scan in Moscow at our centers on Presnya and on Mira Avenue.
Multispiral or cone beam?
A multispiral tomograph performs layer-by-layer scanning of an object along a spiral trajectory caused by the continuous movement of the table and the X-ray tube relative to each other.
Most often, MSCT - multislice computed tomography - is used in maxillofacial surgery for facial injuries and pathologies of the temporomandibular joint.
In dental practice, especially when planning implantation, this method is not widely used due to insufficient data accuracy. Since the patient lies down during the examination, the jaw connection is distorted.
In addition, the radiation level of MSCT can reach 1000 μSv, which is unacceptable, since implantological treatment involves more than one procedure over several months.
Cone beam CBCT is a more modern, accurate and safe method compared to MSCT. Its radiation exposure is less, about 25-50 μSv, which makes it possible to carry out the procedure several times a year.
Carrying out dental tomography
No preparation is required for a dental CT scan. The study is not carried out during pregnancy.
The research procedure itself does not cause any difficulties for patients. Dental computed tomography is performed in a standing position. It is necessary to place the chin on a special stand. After which the protection is put on. The picture is taken by the rotating part of the device in one revolution. Do not swallow during the examination.
You can get a dental computed tomography scan in Moscow at the Dental Center of Polyclinic No. 5 of JSC “Family Doctor”.
Sign up for diagnostics Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
3D CT or panoramic image?
An orthopantomogram allows the doctor to assess the condition of the teeth, root canals, and soft tissues. With its help, hidden inflammations, abscesses and abnormally located teeth are revealed.
However, a panoramic photo does not give a 100% accurate picture; the error is about 20%. Even a slight shift causes the focal spot to shift, and the image is compressed or stretched.
Due to the difference in the refraction of X-rays by tissues of different densities, it is impossible to assess the properties of the cancellous bone layer, since it is simply not visible behind the denser periodontium.
A two-dimensional orthopantomogram is, in fact, an auxiliary technique that gives a general idea of the condition of the oral cavity and identifies mainly obvious pathologies. It does not show the configuration and structure of the alveolar process at the desired level.
The advantage of a three-dimensional 3D tomogram is that it produces not one flat photo, but several consecutive images from different angles.
The doctor sees and evaluates all necessary objects located at any depth, from all sides and at different angles.
Contraindications for 3D dental imaging
The radiation exposure of CT scans ranges from 0.045 to 0.06 mSv. This is relatively little, given the recommendations of SanPiN, which indicate the upper possible threshold of radiation exposure for research purposes equal to 1 mSv per year. However, if you compare a CT scan with a dental x-ray, where radiation occurs in the range of 0.002 - 0.003 mSv, a 3D photograph of teeth no longer seems so harmless. In this regard, there are a number of contraindications to CT scanning. If we are talking about simple tomography, then, as a rule, it is not done during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester. The doctor will always consider the need for radiation exposure for a pregnant patient based on the balance of benefit to the mother and risk to the fetus. If tomography with contrast is necessary (for better visualization of soft tissues and blood vessels, it is rarely used for CT of the jaw), then the number of contraindications expands. It should not be given to pregnant women, nursing mothers, or to persons suffering from thyroid disease, severe diabetes mellitus, renal failure, or an allergy to iodine. If you have any allergies or have ever experienced drug intolerance, be sure to tell your doctor.
How to make a 3D tomogram
Usually the procedure is performed standing, the patient bites a small flat plate with his teeth and stands without moving for 15 to 30 seconds. The device makes several rotations around the head, managing to take about two hundred pictures in various projections.
In 10-15 minutes, the information is processed and transferred to electronic media.
We invite you to make a three-dimensional tomogram in our clinic using the latest generation dental tomograph. Sign up for the procedure online or by phone at a time convenient for you.
How is the research going?
The examination is carried out in 1-3 minutes:
- The doctor takes the patient to the CT scanner and helps fix the head in the desired position. Depending on the design of the tomograph, the examination takes place while sitting or standing.
- A small plate covered with a disposable cover is placed in the mouth, which fixes the position of the jaws.
- The scanning arc of the tomograph makes one revolution around the patient's head. The exposure time to X-ray radiation does not exceed 20 seconds.
The specialist writes the obtained data onto a CD and, if necessary, prints it onto film.