Structure of the area under the tongue
Everything that is located under the tongue is called the floor of the mouth. This:
- nerve endings;
- hyoid bone;
- hypoglossal muscles;
- salivary gland;
- connecting folds called frenulums;
- vessels.
Each element of the floor of the mouth serves its own purpose and is irreplaceable. Only if all muscles, tissues, glands and nerves are healthy does the tongue function normally. If there is pain under the tongue, then we are talking about pathology.
What does the tongue say about our health?
The tongue is often called the mirror of our body. Any disturbances in the body are reflected on the surface of the tongue. An external examination of your tongue can tell you whether you are getting enough nutrients and whether you have any digestive problems. Tongue color and texture are important indicators of health problems.
Stand in front of a mirror, open your mouth and stick out your tongue. If it is pink in color with a rough surface, then you are absolutely healthy. With age, the human body ages and health becomes worse, which is reflected in the language. The tongue is an indicator of human health; the state of the tongue can determine the problems occurring in our body.
What does the color of the tongue say?
- Burgundy - infectious diseases
- Pale - heart problems, poor diet
- Yellow - problems with the gastrointestinal tract
- Purple – diseases of the respiratory system
- Gray - indicates the accumulation of bacteria in the grooves of the taste buds
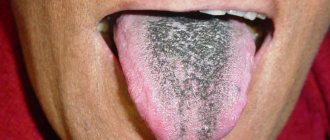
- Black - indicates weakness of the liver and spleen, dysentery, serious viral infections and even abscesses
- Blue - indicates kidney disease
- White is a sign of oral candidiasis, a fungal infection in the mouth
- Bluish - indicates poor blood circulation, scurvy and heavy metal poisoning, especially mercury
- Brown - indicates bleeding in the mouth.
What does the color of plaque on the tongue indicate?
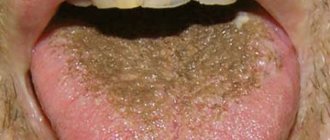
- White plaque is the most common phenomenon in our language. It can be of different nature, it can cover the entire tongue, or it can be located in islands. A light white coating is present on the tongue of a healthy person. Various degrees and forms of white plaque indicate the penetration of infection into the body. As the disease spreads and intensifies, the white coating will gradually thicken and acquire darker shades.
- A yellow tint indicates diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or liver. The rule also applies here - the lighter the plaque, the earlier the stage of the disease. Light yellowness of the plaque in hot weather is considered normal.
- Gray or black plaque - formed as a result of darkening of the white plaque during an exacerbation of the disease or as a result of a chronic disease. The transformation of gray plaque into black will indicate a critical stage of the disease.
- Brown plaque indicates severe or chronic gastrointestinal diseases, as well as lung diseases.
- Greenish-brown plaque - occurs as a result of excess bile in the body against the background of problems with the liver or gallbladder.
- Purple plaque indicates blood stagnation.
- A bluish coating appears with diseases such as dysentery or typhoid.
Signs of internal organs on the tongue.
Traditional Chinese medicine associates certain areas of the tongue with various internal organs. Therefore, disturbances in the functioning of any organ may manifest themselves in the language area associated with this organ. The front of the tongue is a mirror image of the liver, heart and lungs, the middle shows the stomach, pancreas and spleen. Sections of the intestine can be diagnosed by the root of the tongue, but the kidneys can be diagnosed by the lateral sections of the tongue. Various changes in the ulcer, redness of plaque in these projections, indicate one or another pathology of the corresponding organ.
- The tip of the tongue is the heart
Persistent redness close to the tip of the tongue may indicate heart problems. Also, a tongue with a red tip can be a sign of emotional trauma.
- Central part of the tongue - stomach, spleen
A yellow coating on the central part of the tongue indicates problems with digestion, and that there may be something wrong with the stomach, pancreas or spleen.
- Sides of the tongue - liver
The appearance of teeth marks on the sides of the tongue is interpreted as a sign of poor nutrient absorption and may indicate liver problems such as liver enlargement or hepatitis. Bluish-greenish spots on the sides of the tongue can also reflect liver diseases such as cirrhosis.
- The area behind the tip of the tongue is the respiratory system
Red spots on the area of the tongue just behind the tip may indicate lung problems such as pneumonia and asthma. A foam on the front of the tongue can be a sign of congestion in the chest and lungs, and indicate bronchitis and respiratory allergies.
- Back of the tongue – kidneys, intestines
A thick yellow coating on the back (at the base of the tongue) indicates bladder problems and susceptibility to kidney stones and even kidney failure.
All of the above signals from our body for the presence of various diseases require immediate attention to specialists. And one more thing - you need to examine the tongue when it is clean. It can be tidied up with a special tongue massager, which is sold in a pharmacy, or with a soft toothbrush.
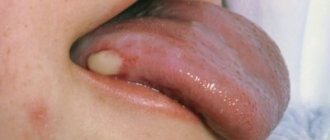
Causes of pain under the tongue
- Allergic reactions cause tissue swelling and pain.
- Harmful microorganisms that appear in the mouth during a sore throat cause acute inflammation. Often, it affects the floor of the mouth.
- Mechanical injuries from a bruise or a fall damage blood vessels, nerves, and soft tissues. Vessels may rupture, which will lead to the accumulation of blood between the muscle fibers.
- Some untreated diseases lead to phlegmon, inflammation with pus inside. In most cases, phlegmon appears under the tongue.
- Ordinary caries, if left untreated, causes inflammation that reaches the sublingual area.
- There are many ducts in the salivary gland, and if an infection gets into it, then through these ducts it can easily enter the gland tissue.
- Injury to the frenulum of the tongue. In people with a congenital short frenulum, injuries occur more often. Even a normal conversation can cause a breakup. However, people with a normal frenulum size also suffer. Inflammatory diseases and allergic reactions often lead to injury, leading to swelling of the tongue and the appearance of ulcers. But also improper oral hygiene leads to damage to the frenulum - the so-called dangerous brushing.
Some people have asymmetry of the hyoid bone from birth, and sometimes this anomaly is formed due to injury. Asymmetry prevents the organs of the floor of the mouth from functioning properly.
How is the sublingual area treated?
Considering the above reasons, if you have the slightest pain in the sublingual space, you should immediately consult a doctor. The doctor will find out the source of the pain and determine a treatment regimen. In some cases, allergists and therapists provide treatment. But more often, pain in the floor of the mouth is treated by dentists.
In case of injury to the frenulum or the tissues of the area under the tongue, rinsing will be prescribed: with a solution of soda, romazulan, stomatophyte, hexoral, chlorophyllipt or iodinol. You should rinse your mouth according to the following schedule:
- morning and evening before bedtime;
- after meal.
The doctor also treats the area of injury with an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Inflammations caused by dental problems require immediate treatment - the specialists at Family Dentistry will get rid of caries, pulpitis or periodontitis and prescribe a course of anti-inflammatory drugs to cope with sublingual inflammation.
But one of the most dangerous diseases in the floor of the mouth is inflammation of the salivary glands. It is important to begin treatment before an abscess appears and complications develop. In this case, the doctor prescribes:
- antibacterial therapy - the doctor injects medicine into the gland and also prescribes a broader-spectrum antibiotic;
- drugs to activate saliva secretion - either a solution of potassium iodide or pilocarpine is used, sometimes regular lemon is used;
- hot dry compresses;
- physiotherapy course.
If the inflammation is advanced and pus appears or a stone has formed, the patient is sent to a surgeon, who cleans the gland cavity of pus and removes the stone.
Treatment methods for stomatitis
Local treatment of stomatitis involves treating ulcers on the palate, tongue, or other areas of the oral mucosa with antiseptic agents. If stomatitis ulcers appear in the throat, the patient is prescribed gargling with an antiseptic solution or medicinal herbs.
General therapy for the disease includes drugs that are aimed at eliminating the causes of stomatitis in the mouth: antibiotics (for a bacterial infection), antiviral drugs (for example, acyclovir for herpetic stomatitis in the mouth), antifungals (if the cause of stomatitis is a fungus of the genus Candida or what -other), antihistamines (for allergic stomatitis or to relieve swelling during the inflammatory process), etc.
For prevention, increasing the defenses of the human body and in order to prevent complications and the development of chronic stomatitis, the patient is prescribed immunomodulatory agents and vitamin complexes. To relieve pain and reduce fever during stomatitis, doctors use painkillers.
The closure and disappearance of stomatitis ulcers with appropriate treatment of stomatitis disease and inflammation that occurs in the human mucosa usually occurs within 1-2 weeks, but you should take medications prescribed by your doctor strictly within the course. The fact that you felt better and stopped experiencing pain and discomfort due to stomatitis in the mouth does not yet indicate that the disease has been cured.
Strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations and do not try to cure stomatitis yourself, using the advice of friends or photographs and recipes for preparing medicinal potions found on the Internet. At best, you simply will not achieve the desired effect, and at worst, you will increase the symptoms of the disease.
Prevention of inflammation of the floor of the mouth
To prevent diseases of the sublingual area, dentists give recommendations on proper oral care:
- take care of your gums;
- avoid the accumulation of bacterial plaque;
- visit the dentist 2 times a year;
- prevent the occurrence of caries;
- brush your teeth 2 times a day.
But if the patient has congenital or acquired anomalies in the development of the floor of the oral cavity, such as a shortened frenulum or structural asymmetry, then you will have to be more careful to prevent injury. Some abnormalities can be treated. Come to an appointment at Family Dentistry and experienced specialists will tell you how to get rid of defects, tumors and inflammations.
Symptoms
The disease most often develops acutely. The patient's body temperature rises. He complains of weakness and decreased performance. Pain appears in the arms and legs. Your head may hurt a lot.
The skin of the tongue becomes very sensitive. Small lesions appear on its surface, and when touched, severe pain occurs. The ulcers are getting larger every day. It gets to the point where they merge with each other. Then the course of stomatitis worsens. The tissues swell.
A person cannot eat, smile, or talk normally. Bleeding gums may occur. The smell from the mouth becomes unpleasant and foul. No hygiene products intended for treating the oral cavity can help eliminate it. Salivation increases significantly.
Despite the fact that stomatitis affects only the tissues of the tongue and oral cavity, it negatively affects the well-being of a person as a whole. With a strong decrease in immunity, it often comes to the point that the patient develops severe intoxication.
How to treat
If the disease is not advanced, it is quite possible to cure it on your own by rinsing and using antiseptic pharmaceutical ointments. But if after two or three days of self-therapy the situation has not improved or, even worse, the disease has begun to progress even more actively, it is recommended to immediately consult a dentist. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis, determine the true cause of the pathology and select an effective treatment.
to monitor oral hygiene during therapy After every meal you need to rinse your mouth. For this purpose, it is allowed to use self-prepared decoctions and infusions of herbs, special dental solutions, or at least warm water.