People lose teeth for a variety of reasons, and such losses always need to be replaced so as not to disrupt the normal digestion process and the aesthetics of the dentition. When can prosthetics be done after tooth extraction? There is no clear answer to this question, since the clinical situation, the chosen type of prosthetics, and the condition of the tissues after the operation play a role here.
What can be put in place of an extracted tooth?
There are many options for replacing an extracted tooth. An experienced orthopedic surgeon will offer removable and fixed structures, solutions for restoring individual teeth or a number of missing units, and reconstruction of a completely edentulous jaw. For each case, protocols, methods, and treatment techniques are provided.
How to insert a tooth in place of a removed one - options:
- prosthetics on dental implants;
- bridge prosthesis;
- removable prosthetics;
- clasp prosthesis.
What can be put in place of an extracted tooth depends on:
- number of units removed;
- condition of bone tissue;
- dental diagnoses;
- patient's age.
Based on the preliminary diagnosis, the doctor makes a decision on the timing and features of treatment.
Other useful material
New implantation technologies without bone grafting
Open and closed sinus lift during implantation
Implantation of several teeth in a row
Implant installation
How long does it take for gums to heal after tooth extraction for dental prosthetics?
How many days after extraction you can insert teeth determines the speed of healing of the hole. The process is individual for everyone and depends on many factors:
- type of removed unit - incisor, canine, molar, premolar;
- complexity of the operation - simple extraction or removal with dissection of the gums and sawing of the crown;
- features of the root system - compact, even roots or sinuous, strongly curved, occupying a large area;
- The doctor’s professionalism and experience determines the size of the extracted tooth socket and the likelihood of complications.
How long after tooth extraction can you get dentures?
How long after tooth extraction you can get dentures depends on the speed of tissue healing. Average indicators of restoration of gums and bone structures:
- the first 2 hours after removal - the hole fills with blood, a blood clot forms;
- a week after surgery - the wound heals, new gum tissue forms;
- after 4-6 months, the bone tissue is restored, completely filling the space of the socket.
For removable and fixed dentures, crowns on implants and bridges, different treatment periods are provided:
- removable dentures - in 3-7 days, how will it be possible to make an impression for the manufacture of a prosthetic structure;
- bridges - in a month or two, after complete healing of the tissues;
- prosthesis on implants - depending on the protocol, immediately or after a few months.
If the patient immediately plans to insert a tooth in place of the extracted one, it is better to make an appointment with an implant surgeon. The doctor will prepare directions for mandatory examinations, conduct careful removal, and offer optimal options for restoring the dentition.
Questions and answers
— What to do if swelling occurs after tooth extraction and implantation?
Swelling is a normal reaction after any implantation protocol, because... This is a surgical type operation. The dentists of our clinic always provide consultations and give instructions to patients on how to act before surgery.
— Differences between immediate and delayed implantation (Briefly)
| One-step | Deferred | |
| Restoring aesthetics in 1 day | The implant can be loaded with a temporary crown, which is removed from the bite. | The only way to restore the beauty of a smile is to attach a removable denture to the adjacent teeth. |
| Jaw bone resorption | Doesn't happen, because the implant is installed immediately. | Does not occur if implantation is carried out within six months after the removal of a dental unit. |
| Restoring bone volume | Not required or can be performed simultaneously with implant installation | If the atrophy process has already begun in the bone, an osteoplasty procedure will be needed before restoring the teeth. |
| Formation of the gingival margin | Required before installing a temporary crown | Performed before installation of an orthopedic prosthesis |
| Cost of services | Acceptable | In the future, higher than one-stage (due to the need for more procedures) |
— Is it possible to implant an artificial root after tooth and cyst removal?
A cyst is a new formation that can reach a diameter of 0.9 to 3 cm. It is usually located at the very edge of the tooth root. In most cases, the formation can be cured with medication.
But in later stages, the cyst can lead to loosening of the root. At the same time, the periodontal tissues are in an inflamed state, which makes it impossible to carry out immediate implantation (the risk of rejection increases to almost 100%).
Experienced dentists recommend waiting for complete recovery and installing the implant using a delayed protocol.
— Why is implantation called the best method of restoring teeth? (Comparison with alternatives)
Installation of a dental bridge.
Involves preparation (grinding) of adjacent units. A bridge is secured to these teeth, covering the gap. Used when 1 to 4 teeth are missing.
How is implantation different?
In case of implantation, it is possible to restore one, several in a row (or several scattered ones), as well as all teeth in the jaw. No turning of adjacent units is required.
Removable prosthesis.
It is used when most or all teeth in the jaw are missing. Can be attached to remaining teeth using special hooks. With complete edentia (the absence of all teeth), the prosthesis is held in place by adhesion forces and may fall out. Also, the removable orthopedic design does not prevent jaw bone resorption, which requires relining the prosthesis every 5 years.
What are the advantages of implants?
They prevent the development of bone tissue atrophy due to the fact that they evenly distribute the load across the entire jaw. The structure cannot fall out.
| Expert, author of the article: Akhtanin Evgeniy Alexandrovich Dental surgeon, implantologist 13 years of implantation experience Material updated: October 11, 2022 |
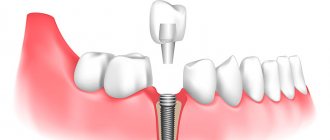
Bridge prosthesis in place of an extracted tooth
The design of a dental bridge consists of the main crowns for replacing missing units and two additional ones for fixing the prosthesis on the jaw. During the treatment process, the doctor grinds down the living teeth and attaches crown caps to them. Advantages of a dental bridge for the patient:
- durable permanent installation;
- affordable price;
- aesthetics.
Flaws:
- Delayed prosthetics. The minimum period when a bridge can be installed after tooth extraction is a month after the operation.
- Grinding healthy units. Physical damage to the integrity of the enamel and partially crowns.
- Excessive load on supporting teeth. And degradation of bone tissue under the overhanging part of the denture.
- Gradual loss of aesthetics and functionality. Due to tissue subsidence, a gap is formed between the denture and the gum, visible when speaking. Also, food particles get into the empty space, which often causes inflammation.
- Fragility. The prosthesis and supporting teeth are usually removed 5-7 years after installation.
Doctors explain not only how long after tooth extraction a bridge can be installed, but also why. 4-8 weeks is a reasonable interval, since the tissue at the site of the lost tooth should be completely restored. Otherwise, there is a risk of changing the shape of the gums under the installed prosthesis, and the likelihood of tissue injury at the time of prosthetics increases.
Removal of the dental nerve before prosthetics
If the tooth often bothers the patient with severe pain, a procedure to remove the dental nerve will be performed before prosthetics. This will eliminate the source of discomfort and save the patient’s budget. If the nerve is not immediately removed and a crown is installed on the painful tooth, the patient will soon turn to the dentist for help again, which will entail additional costs.
Other indications for nerve removal:
- caries on the root system of the tooth;
- low landing of the dental crown;
- uncharacteristic anatomical features of the tooth, for example, strong axis tilt;
- periodontitis;
- pulp inflammation.
If no indication for nerve removal is identified, crowns are installed on a living tooth.
Removable prosthetics
A removable denture is recommended when several units are removed or when the entire jaw is missing. For a single replacement, doctors recommend a temporary option - an immediate prosthesis, which is placed in place of the removed incisor or canine to preserve aesthetics. Then the product is replaced with a permanent and more convenient to wear option.
For removable prosthetics of one tooth, a high-quality impression of the jaw is required, which is made 3-4 days after the extraction operation. To make extended structures for several teeth, doctors recommend waiting until the tissue is completely restored. It takes about 30 days for the gums to heal before prosthetics.
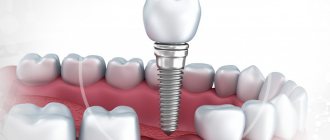
Crown instead of an extracted tooth - implantation
Implantation is a modern solution for partial and complete adentia. This is what doctors recommend to patients, and there are many reasons for this:
- complete replacement of a lost tooth - not only the upper part, but also the root system;
- restoration of chewing and other functions - after prosthetics, the patient is not limited in the choice of menu, and the quality of speech does not suffer;
- aesthetics - both the crown itself and the artificial gum contour, if present, look natural;
- preservation of bone tissue - bones experience full load, which eliminates atrophy and degradation of bone structures;
- speed of prosthetics - some protocols allow you to restore a tooth immediately after removal.
Implantation options:
- Classic two-step protocol. After removal, the doctor waits for complete healing of the gums and restoration of soft and bone tissues. Then he installs the implant and, after its complete engraftment (4-6 months), places an artificial crown or bridge on the implants without damaging neighboring units. The treatment is long and is recommended for patients who, immediately after extraction, were unable to replace their teeth with prosthetics - the socket has healed, and the tissues have partially atrophied. It is possible to speed up treatment using a two-stage protocol. Premium dental implants Nobel, Strauman take root in 2-4 months, which reduces the period of prosthetics by half.
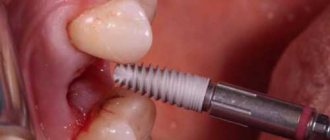
- One-stage implantation protocol. When a tooth is removed, the patient is immediately implanted with an implant, a gum former or a full-fledged temporary crown. Such treatment requires removal by an experienced implant surgeon, as well as preliminary examination to reduce risks.
- One-stage implantation protocol. It completely eliminates the question of when a tooth can be replaced with a prosthetic after extraction, as it combines all three stages of treatment. The doctor performs an extraction, places a dental implant and immediately loads it with a crown. The patient simply replaces the damaged tooth with a new artificial one, which significantly speeds up the recovery process.
Total prosthetics after tooth extraction
The situation is considered separately - the removal of all teeth immediately before prosthetics. In this case, the patient is faced with complete adentia, which requires emergency treatment.
Option two:
- Removable prosthetics - quickly, inexpensively, with guaranteed atrophy of bone tissue subsequently, frequent replacement of the prosthesis and inconvenience of wearing the product.
- Implantation with installation of a fixed prosthesis - according to all-on-4 or all-on-6 protocols. The essence of the treatment is the installation of a fixed number of dental implants and the attachment of a full denture prosthesis to them. Implantation of 4 or 6 artificial roots is performed on the day of removal. An impression is immediately made, from which artificial teeth are made in a dental laboratory. The longest waiting period is 3 days, after which the patient receives a full-fledged jaw capable of withstanding all physiological loads.
Installation of titanium root after 6 months or more
It is worth considering that this delayed implantation protocol is used only in the most advanced clinical cases.
Implant surgeons at Family Dentistry recommend implanting titanium roots in the period from 8 to 25 weeks after tooth extraction. At a later date, the risk of resorption (decrease in volume) of bone tissue increases. To restore the bone to normal volume, expensive osteoplasty surgery will be required.
For cases when alveolar process atrophy has already begun to manifest itself, there are 3 ways to build bone tissue to the required volume. And only after the process of complete osseointegration of bone materials can surgery be performed.
Sinus lifting open, closed and endoscopic type
Jaw type:
only for the top one.
Osseointegration period:
2-6 months.
Before the sinus lift procedure (scientific name subantral augmentation), the position and volume of the patient’s maxillary sinuses are examined. During the operation, the bottom of these sinuses is raised, and the resulting voids are filled with bone material.
| Type of sinus lift | Peculiarity |
| Closed | For low level bone tissue atrophy. The sinuses must be raised by 2-3 mm. |
| Open | Required for medium or critical level resorption. |
| Endoscopic | The procedure is performed using an endoscope. This is a low-traumatic type of surgery |
Guided regeneration
Jaw type:
for the bottom.
Integration period:
8-24 weeks.
Operation stages:
- a small surgical incision is made in the gum;
- in places where there is insufficient volume of the alveolar ridge, bone-forming material is added;
- the surgical site is “covered” with a biomembrane, which accelerates the process of osteogenesis;
- The gum is sutured until the osteoplastic tissue is completely engrafted.
Note:
Over time, the biomembrane dissolves under the soft tissue of the gums.
Primary and secondary autotransplantation
Jaw type:
for top and bottom.
Engraftment period:
2-6 months.
A bone block of the required size is transplanted from the patient himself (this avoids rejection of the material) to where the implantation will be performed.
This bone block can be surgically removed from the area of the third molar (wisdom tooth), chin, base of the skull or pelvic bone.
| Type of autotransplantation | Indications |
| Primary | Used immediately after injury or surgery (for example, removal of a tumor, cyst, etc.) |
| Secondary | It is used if more than six months have passed since injury or surgery (in some clinical cases, complete healing of the injury is necessary). |
Is it necessary to insert a tooth after extraction?
Many patients do not even ask questions about how many days after tooth extraction they can get a crown or dentures. But in vain. Even a short-term absence of a tooth in the jaw row is fraught with serious consequences:
- displacement of adjacent units and teeth of the opposite jaw towards the empty space;
- jaw deformation, malocclusion;
- improper redistribution of chewing loads, gastrointestinal problems;
- deterioration of diction, the appearance of complexes due to aesthetics and speech.
The longer the interval between removal and prosthetics, the more serious the orthodontic defects and the more expensive the treatment.
What happens if you don't restore a tooth?
While eating, the load is evenly distributed over the entire upper and lower row and is transferred to the bone tissue. This stimulates its trophism, ensures normal density, as well as reliable fixation of natural roots.
Single or multiple defects in a row lead to the fact that certain areas of the jaw remain without load. The slowdown in trophism provokes gradual resorption of the bone. It loses volume and becomes less dense.
Compensatory mechanisms ensure the displacement of the remaining teeth. The chewing load is distributed unevenly, which leads to protrusion and accelerated wear of the antagonists. The units move towards the defect where the bone is less dense. Due to the weakening of the ligamentous apparatus, they become mobile.
The visible results of these processes are bite defects, enamel abrasion, and changes in facial contours. Functional inferiority of a number, as well as problems with chewing food lead to chronic gastrointestinal diseases. The severity of the described changes depends on the length of life without teeth.
Atrophic processes are irreversible. It is impossible to slow them down with removable dentures. Only implantation can stop the loss of spongy bone, since it restores trophic processes in the jaw.