What is a wisdom tooth
In everyday life, wisdom teeth are the third molars, or the last, eighth teeth in a row, that is, “eights.”
The upper third molars can vary in shape and size, and are usually smaller than other molars and lower 8s. They have two or three roots, which sometimes grow together into one. But they always have three channels.
The lower wisdom teeth can also vary in shape and size, but, as a rule, they are larger than the upper “eights”. The roots of these teeth are short, sometimes fused, and often have a curved shape.
Features of cutting through “eights”
A characteristic feature of the third molars is the very late time of their eruption - as a rule, this occurs between 16 and 24 years, and sometimes later [1]. That is why in many languages they are called “wisdom teeth”. Late eruption determines the difficulties that many patients face during the development and appearance of “eights.”
The fact is that by this age the upper and lower jaws, as a rule, are already formed. Therefore, the eruption of “eights” is often associated with unpleasant or painful sensations, and often serious complications. Additional difficulties are caused by individual features of the anatomy of the facial skull, for example, the small size of the jaws, in which there is not enough space for the third molars to fully develop. The reason for this, according to most experts, is the evolution of the structure of the human body [2].
Due to the lack of space for full growth, third molars may not fully erupt (retention) or even change the direction of growth (dystopia). Often they begin to grow not vertically up or down, but at an angle to the dentition. Moreover, the size of the slope can be different and largely determines the possible complications of teething. Both retention and dystopia are considered pathological processes [3].
Among the complications of eruption and development of third molars are [3]:
- acute inflammatory process, up to phlegmon (purulent inflammation);
- formation of pathological bone pockets;
- destruction of hard tissues of the adjacent tooth;
- formation of follicular cysts;
- neuralgic pain;
- osteomyelitis and others.
Prevention of teething diseases consists of monitoring the correct development of the jaws and teething, sanitation of the oral cavity and timely orthodontic treatment, compliance with the rules of oral hygiene
“Retention, dystopia. Teething diseases”, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Department of Surgical Dentistry of Moscow State Medical University Panin A. M.
Why wisdom teeth haunt me
The reason should be sought in bone tissue, which becomes significantly denser after reaching 13 years of age. Until this age, root teeth erupt through it without problems or severe pain. Adolescents and adults have difficulties with this: the molar cannot quickly “break through” the already formed dense cement. Due to this, severe pain occurs.
It is also important here that the wisdom tooth appears in a hard-to-reach place (at the very edge of the jaw at the top or bottom). It is not included in the basic package and is optional. Nature simply does not provide a special space for it, due to which its appearance entails compression of neighboring molars. Because of this, an acute feeling of discomfort arises, as if the entire dentition is shifting to the side.
The presence of a “stranger” in the mouth is especially felt if its position is incorrect, when it grows towards the right or left, and not up. It’s also hard for those whose “eight” is only halfway through or even less, and doesn’t want to show up any further. In this case, there may be noticeable pain in the gums, radiating to the ear, throat or head.
The peak of pain occurs during the teething stage, which can last from a month to a year or more.
Increased discomfort is possible against the background of:
- development of oral diseases and their improper treatment;
- infection getting into the dental canals;
- advanced caries;
- the presence of a cyst on the gum.
When several reasons are combined, the situation becomes significantly worse and requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
Free consultation
30-40 minutes
inspection and diagnostics
treatment plan and cost
Make an appointment
Features of pain in the presence of wisdom teeth
Most often, an extra molar appears in the bottom row. In this case, the pain is noticeably stronger than when it erupts at the top. This is due to the fact that the latter less often deviates from the “course of development” and almost never rests against neighboring teeth. This reduces the risk of violating the integrity of the gums, causing bleeding and discomfort. In the case of the lower molar, the bone tissue can become inflamed and cause significant inconvenience when eating.
Most often, the pain is aching and pressing; the patient feels as if they are trying to remove the tooth without anesthesia. These symptoms can occur both with a healthy molar and if there is deep caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, tartar or gingivitis.
You can understand that the situation is very serious when the G8 reacts sharply to the following points:
- warm;
- cold;
- sour foods;
- external pressure;
- chewing food;
- brushing your teeth
In what cases is wisdom teeth removal recommended?
The wisdom tooth removal procedure is carried out in several cases:
- as a prevention of complications of eruption and development;
- in the presence of complications;
- with severe tissue damage.
Various complications of eruption (inflammation, difficult eruption, retention, etc.) occur in almost 75% of owners of third molars [3]. These pathologies more often occur with “eights” on the lower jaw. Moreover, in women such complications occur twice as often as in men, which experts explain by the lack of space behind the teeth (retromolar region) in the lower jaw.
The difficult-to-reach location of the third molars means that even regular hygiene procedures do not clean them completely. Therefore, even if they have grown in accordance with the norm, they are often affected by caries. It also affects the lower (69.05%) “eights” more [3].
In the vast majority of cases, regardless of the gender and age of the patient, wisdom teeth are removed for pulp, periodontal and periodontal diseases. Indications for the procedure are [1]:
- the presence of inflammatory processes;
- impossibility of further prosthetics;
- prevention of the healthy state of second molars;
- maintaining gum health.
There are frequent cases of removal of an uncut “eight”. This procedure is performed to prevent complications during teething, as well as the development of crowding of teeth.
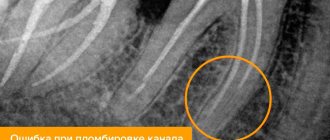
When choosing a treatment tactic for a “figure of eight”, specialists evaluate the location of the molar or its rudiment. For an accurate diagnosis, an x-ray examination is performed; it helps to assess the location of the tooth and identify changes in the tissues. In addition, radiation examination helps prevent complications during surgery.
If the eruption of third molars is difficult, the dentist will evaluate the possibility of saving them. As a rule, they try to maintain the “eight” if [3]:
- the tooth is in the correct vertical position;
- its roots are straight;
- periodontal tissues have no changes;
- there is enough space in the dental arch;
- The angle of inclination of the molar does not exceed 150 degrees.
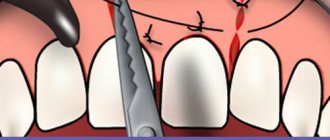
The operation to remove the figure eight is performed under local conduction anesthesia. The specialist may prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics 40 minutes before the procedure. The oral cavity is treated with antiseptics. The surgeon then performs the removal procedure. After this, the wound is treated and sutured tightly or openly, depending on the dentist’s decision.
Wisdom tooth removal is often associated with various complications. Therefore, there are a number of special techniques that are used by surgeons during the operation. This may be an incision of soft tissue, if necessary, sawing a tooth or other manipulations.
It hurts to open your mouth after dental treatment
It happens that after dental treatment we do not receive the desired relief due to complications that have developed as a result of dental procedures.
Causes
There may be several reasons why it is painful for a patient to open his mouth after dental treatment:
- consequences of wearing braces
: after each correction, the doctor changes the pressure exerted by the arches on the dentition. It takes time to get used to it. However, if after a week the discomfort does not go away, you should additionally consult a doctor; - root canal filling
: moderate pain may be felt for several days, and this is considered normal. But if the pain does not go away longer and even worsens, it is necessary to take an x-ray and consult a doctor; - neuralgic complications
: can occur when a nerve is pinched or inflamed as a result of anesthesia, tooth extraction, incorrectly performed endodontic treatment, etc. A characteristic difference is that the pain manifests itself even at rest and tends to periodically intensify. It not only becomes painful for a person to open his mouth after dental treatment, but also absolutely everything in general. This kind of pain cannot be tolerated. The sooner the patient receives medical help, the better the treatment prognosis; - tissue injury during tooth extraction
. Extraction of a dental unit is considered a full-fledged operation, during which the surrounding tissues, the ligamentous apparatus that holds the dental unit in the socket, and the vessels that supply it are damaged. Often such manipulations are accompanied by the formation of large edema, and suppuration may develop. All this leads to the appearance of severe pain, which makes it painful not only to chew, but also to simply open your mouth. Therefore, if the pain increases over several days, you should additionally consult with your dentist; - dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint
can develop as a result of incorrectly performed dental prosthetics or overestimation of the filling over the bite; - Trismus of the jaw
(spasm of the masticatory muscles) can also be triggered by dental treatment.
Thus, moderate discomfort for several days after dental procedures is normal. But if it hurts to open your mouth after dental treatment after 3-7 days, consult your doctor. Perhaps this is a consequence of complications.
Read more:
- Complications after dental treatment
- Perforation of the maxillary sinus
Contraindications for wisdom tooth removal
The surgeon assesses the patient’s condition before surgery based on the medical history and the results of preliminary studies. Removal of wisdom teeth is postponed in the presence of infectious diseases in the acute and subacute periods. These include, among others, influenza, tonsillitis, stomatitis, ARVI and others [1].
If complications of the eruption of “eights”, for example, an inflammatory process, can worsen the patient’s condition, tooth extraction is forced. In such cases, the operation is performed against the background of antibiotic therapy and other anti-inflammatory drugs.
A separate decision is required in cases where wisdom tooth removal is required for cardiovascular diseases, such as a previous myocardial infarction and hypertensive crisis, extrasystole and others. In such situations, the acute condition is usually treated.
The “eight” tooth is removed with special care in case of concomitant blood diseases: hemophilia, thrombopenia, acute leukemia and others. As a rule, the removal procedure is carried out in specialized hospitals.
How can I solve the problem?
If, after the figure eight removal procedure, you experience difficulty opening your mouth, a second consultation with your dentist is necessary. The specialist will accurately determine the cause and prescribe measures to eliminate the problem. To alleviate the condition, you may need to re-clean the socket, physiotherapy, take antibiotics or special exercises.
Re-cleaning the hole
Socket after wisdom tooth removal
Socket is an open cavity that remains after the removal of molars. Repeated cleaning may be necessary if there is a dry socket, the area does not heal, or becomes inflamed, which causes difficulty opening the mouth. During repeated cleaning, the dentist performs a number of manipulations:
- checks whether roots remain inside;
- treats with antibacterial drugs;
- closes the hole with a sterile swab.
If there are roots left inside, they must be removed immediately, as they may begin to rot. For removal, dentists use tweezers or a scalpel to cut through the gums. Then a repeat x-ray is prescribed to determine the cleanliness of the hole. A clean hole heals after 2 weeks.
Physiotherapy
Ultraviolet (UVR)
Irradiation of the well with a spectrum of rays. Start with 2 and end with 6 biodoses. The course of treatment is 4-6 treatments.
Result:
- Reducing the virulence of bacteria.
- Activation of regeneration processes.
- Anti-inflammatory effect.
Fluctuarization
It is carried out in conjunction with the Ural Federal District. The well is exposed to the first form of current. Drug electrophoresis of anesthetics (usually Trimecaine). The session lasts 20 minutes, the number of repetitions is 6. Reduces pain and relieves swelling.
Laser therapy
Infrared exposure in the oral cavity for 1-2 minutes. Course – 2-3 repetitions. Reduces inflammation, reduces swelling and tissue hyperemia.
Physiotherapy
Magnetotherapy
Exposure to magnetic field. Course – 20 procedures. The duration of one is 25 minutes. Relieves severe pain.
Antibiotics
Medicines in this group are prescribed only in the presence of an infectious-inflammatory process at the site of wisdom tooth extraction. Antibiotics are also indicated if at the time of the procedure the patient had an abscess, gumboil, or periodontitis. Medicines will also help eliminate complications after the intervention. Dentists prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics:
- Amoxiclav;
- Vilprafen;
- Lincomycin;
- Neomecin;
- Olethetrin.
Lincomycin
Other actions
If trismus is caused by a normal reaction of the body, it is recommended to develop and restore jaw mobility. Before performing such gymnastics, consultation with a dentist is required. Throughout the day, you need to carefully open and close your mouth, more and more each time.
You can chew gum, but not very intensely. Trismus can develop only with mild painful sensations. You can combine exercises with rinsing your mouth with herbal solutions.
You can unclench and open your jaws only when trismus is a normal phenomenon and is not accompanied by acute pain. Making efforts, applying force, or stretching the jaws is prohibited.
What to do after wisdom tooth removal
After the removal of third molars, complications are more common than with the removal of other teeth. This is due to the peculiarities of their anatomical structure, retention, complexity and traumaticity of surgical intervention. The most common complications after removal: socket bleeding, “dry socket” and others [9].
After the procedure, it is not recommended to do anything that could remove the blood clot from the wound and impair healing or cause bleeding. The patient is advised to refrain from eating for 2 hours after surgery. At the same time, hot food and drinks are prohibited throughout the day after the procedure, and mouth rinsing is prohibited for the next 24 hours. It is not advisable to smoke, eat sweet, sticky, hard foods or drink with a straw.
List of sources
1. Dentistry. Textbook Aleksandrov M. T., Bazhanov N. N., Medvedev Yu. A., Platonova V. V., Sergeev Yu. N. / Ed. N. N. Bazhanova. - M.: GEOTAR, 2008.
2. Iordanishvili A.K., Ponomarev A.A., Gaivoronskaya M.G., Korovin N.V. Age-related features of wisdom teeth diseases // Kursk scientific and practical bulletin “Man and his health”. 2015. No. 4. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/vozrastnye-osobennosti-zabolevaniy-zubov-mudrosti (date of access: 06/13/2020).
3. Marugina T. L., Kan V. V., Fedotov V. V., Zagorodnikh E. S. Diagnosis, prevention and treatment of diseases of the eruption of the lower eighth teeth // Russian Journal of Education and Psychology. 2012. No. 4. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/diagnostika-profilaktika-i-lechenie-bolezney-prorezyvaniya-nizhnih-vosmyh-zubov (date of access: 06.13.2020).
4. Iordanishvili A.K., Ponomarev A.A., Korovin N.V., Lyskov N.V. Complications after removal of wisdom teeth and their treatment // Kursk scientific and practical bulletin “Man and his health”. 2022. No. 2. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/oslozhneniya-posle-udaleniya-zubov-mudrosti-i-ih-lechenie (date of access: 06/13/2020).
Causes of pain
Pain after wisdom tooth removal is the body’s protective reaction to external intervention. This is absolutely normal, since an open, fresh wound remains in place of the figure eight. Gradually, a blood clot forms in the socket, acting as a “protective cushion” that prevents pathogenic microflora from entering and multiplying. That is, the pain syndrome appears due to damage that occurred during the operation:
- injuries to bone tissue or gums;
- damage to nerve fibers or blood vessels;
- inflammation of the gums.
In addition to pain after removing the figure eight, there are a number of other symptoms that should be taken into account:
- in the first few hours it hurts to open your mouth;
- soft tissue swelling;
- pain radiating to the temple;
- increase in temperature (37-37.5°C);
- feeling of ear fullness;
- bad breath;
- swelling of the cheeks or lips.
The listed symptoms are considered normal if they begin to subside after 1-2 days.