Some parents are unreasonably careless about caring for their child’s baby teeth. Indeed, is it worth treating caries of a temporary tooth if you can remove it and wait for the permanent tooth to grow? This statement is fundamentally incorrect; the negative consequences of such removal can be very serious. Dentists pull out baby teeth only in the most extreme cases.
Today we will talk about what premature loss of milk row can lead to, as well as how to take care of your child’s teeth.
Features of tooth extraction in children
Pediatric dentistry is focused on the treatment and prevention of oral diseases. In this case, psychological support for the baby is important. Specialists must act delicately, instilling trust and relieving the child of fears. This is especially important in case of forced tooth extraction. Therefore, there are several unspoken rules of the pediatric dentist.
- Do not use the word “pain” or the particle “not.” Children do not accept denial and react sharply to unpleasant phrases.
- Do not discuss the details of the procedure in the office. Medical terms and unfamiliar words frighten the baby.
- Try to hide dental instruments from the eyes of the small patient. Forceps, packages of syringes and drill attachments can drive even the most courageous tomboy into hysterics.
This procedure requires high professionalism and great care from the doctor. With one careless movement, he can damage the germ of a new tooth and the tissue of the socket, which will cause a delay in eruption and various dentofacial deviations.
General indications for tooth extraction in children
The child’s dentition is formed according to certain patterns: the incisors erupt first, followed by the molars. Then the baby teeth are gradually replaced by permanent teeth. If this process occurs correctly, without deviations from the norm, there is no need to specifically remove baby teeth. However, there are situations when this is necessary:
- advanced caries;
- the last stage of development of a cyst on the gum;
- severe tooth injury;
- a tooth that fails to develop and erupt.
Removing a child’s front tooth is a particularly unpleasant procedure, as the aesthetics of the smile suffers. Usually, surgery is resorted to in the following circumstances:
- exposure of the pulp due to a fracture of the coronal part;
- severe tooth decay with the impossibility of prosthetics;
- inflammatory diseases that cannot be treated.
Most often, children have to part with their teeth in the chewing area. Molars are more susceptible to destruction than premolars and incisors. Removing a child's molars, which are the last in the dentition, is complicated by their inaccessibility and strength: they fit quite tightly to the gums, have wide roots and massive walls.
Sometimes children develop an anomaly such as an extra tooth, which can move the “neighbors” and lead to curvature of the entire row. If it does not interfere with the normal formation of the remaining teeth, you can leave it and try to integrate it into the bite, but most often they resort to removing the supernumerary tooth in the child.
The factors described above are the general and most common indications. Let us consider separately the reasons for the removal of baby and permanent teeth.
Features of the treatment of periodontitis in primary teeth
Before proceeding directly to treatment, the doctor will definitely send the baby for an x-ray. Only by using it can one confirm the diagnosis and see the true picture of the course of the disease.
Based on X-ray data, the dentist decides whether to preserve the tooth. The balance may tip towards removal in cases where:
- there is severe damage to the root;
- tooth mobility is noted;
- the approach of permanent teeth is noticeable.
In all other situations, doctors try to do everything possible to save the tooth.
The choice of methods and means of treatment largely depends on how extensive the inflammation is, how many teeth it affects, as well as on the general health of the child. If the body is severely intoxicated, the tooth is removed at any age of the child, regardless of any additional factors.
If the doctor decides to leave the tooth, then its treatment is in many ways similar to that recommended for permanent teeth. The only difference is the use of special medications. It is especially important to choose the filling material correctly.
In the acute stage of the disease, the best treatment for baby teeth is a special paste that can dissolve over time without harming the baby’s health. In addition, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed and bed rest is prescribed.
When the symptoms characteristic of the acute form subside, they move on to the treatment regimen characteristic of chronic periodontitis. It includes:
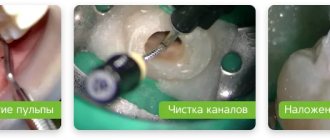
- thorough removal of infected tissues and decay products;
- antiseptic treatment of root canals and tooth cavity;
- filling with paste;
- installation of a permanent filling.
During the treatment process, which requires several visits to the clinic, the doctor constantly monitors the patient’s general condition and changes in symptoms. In cases where there is no improvement, the tooth is usually removed to avoid complications.
If periodontal inflammation provokes the development of purulent periostitis, surgical intervention becomes necessary. In this case, the gum is cut in order to ensure the free outflow of purulent and serous masses. The tooth is left in this form for up to 10 days.
The effectiveness of treatment is largely influenced by the professionalism of the dentist. The doctor must know the subtleties of the structure of baby teeth and have the skills to work with them, and also have the ability to win over the baby, ensuring the patient’s psychological state is favorable for work.
Removal of baby teeth in children
Milk teeth maintain the gum contour and ensure proper development of the jaw and chewing muscles. Therefore, it is important to wait until they fall out on their own. Unfortunately, this does not always happen, and the dentist is forced to prescribe surgery if there are the following indications for the removal of baby teeth in children:
- the tooth is loose, but has not fallen out for a long time;
- the temporary tooth caused inflammation of the oral tissues;
- The permanent tooth has begun to emerge;
- a fistula has formed on the gum;
- a cyst appeared on the root;
- The tooth has decayed due to caries.
Removal of a child's front milk tooth may be associated with fractures, chips and other injuries, as well as inflammatory processes.
Anesthesia
Before tooth extraction, anesthesia must be performed, which can be application, infiltration and general.
Application is the application of an anesthetic gel to the mucous membrane and gums, used for high mobility of baby teeth. Infiltration anesthesia involves performing an injection into the desired area of the jaw. It is used for dental diseases, severe inflammation or lack of tooth mobility. General anesthesia or sedation is rarely used in children; it is indicated for fear of dental procedures, allergies to anesthetics, a large amount of work in the oral cavity, or mental illness.
Removal of permanent teeth
Removal of a permanent tooth in a child is carried out only in the following situations:
- Caries.
If the doctor sees that a decayed tooth cannot be treated, most likely he will suggest removing it. - Fracture.
A tooth fragment can injure the mucous membrane; it can either be restored or removed. - Crowding.
When installing braces or plates, it is sometimes necessary to remove one tooth to allow others to develop freely. - Complications after treatment.
Sometimes, after poor-quality dental procedures, problems arise that can only be solved by getting rid of the tooth.
Contraindications
Tooth extraction is not recommended in the following cases:
- Acute inflammatory process in the mouth: gingivitis, stomatitis, sore throat;
- Acute infectious diseases of the body: chicken pox, scarlet fever, whooping cough, influenza, ARVI;
- For serious diseases of the body: epilepsy, oncology, heart defects, heart failure;
- For blood diseases that are accompanied by clotting disorders;
- If possible, treat the tooth therapeutically.
Wisdom tooth removal
Typically, wisdom teeth appear at the age of 20 or older, but in some cases it is recommended to remove their buds. There are the following reasons for the removal of wisdom teeth in children:
- displacement of the follicle of the third molar;
- prerequisites for malocclusion;
- lack of space for wisdom teeth.
A specialist can recommend removal of a child’s wisdom teeth only after a thorough examination and consultation with other specialized doctors. You must first determine what position the molar is in and what place it will later occupy in the jaw.
Anesthesia for tooth extraction
In modern clinics, various types of anesthesia are used to remove teeth for children without pain. The specialist selects the appropriate drug in accordance with the severity of the clinical picture. During the operation, one of the following methods of pain relief is used:
- Sedation is putting you into a sleepy state to reduce anxiety.
- Application anesthesia - treatment of the gums with an anesthetic solution to remove a loose tooth or before injection.
- Local anesthesia is the administration of an anesthetic through an injection.
- Anesthesia is used in difficult cases and when removing teeth for a child under 2 years old.
The importance of general therapy in the treatment of periodontitis of primary teeth
The role of general therapy is especially important in the treatment of acute forms of the disease, as well as in exacerbation of chronic periodontitis. This is due to the fact that in childhood, the general condition of the patient during the illness in these cases is extremely severe, which requires active measures to improve it.
The doctor may prescribe strict adherence to bed rest, 2-3 daily injections of penicillin in a dosage of 50,000-200,000 units (according to the body weight and age of the baby). Additionally, it is recommended to take 10% calcium chloride orally (3 times a day, 1 tsp), and drink plenty of fluids.
In cases where no incision is made in the gums, rinsing with a warm solution of soda or potassium permanganate is mandatory. Herbal solutions are also suitable for this; infusions of chamomile and sage are especially effective.
Throughout the treatment, strict daily monitoring of the little patient’s health is necessary. As soon as a stable decrease in body temperature is recorded, penicillin injections are canceled and sulfonamide drugs are prescribed instead.
While the acute symptoms persist, the root canals and tooth cavity are treated with antibiotic solutions.
If the therapy carried out at this stage is successful, then after the acute phenomena subside, they move on to treatment characteristic of the chronic form. Otherwise, a decision is made to remove the tooth.
Care after tooth extraction
What frightens the parents more than the removal procedure is the condition of the baby after the operation, since they have already left the specialist’s office and are left with the problem alone. In this situation, all mothers and fathers have almost the same questions.
What to do after a child’s tooth extraction?
The doctor will give the little patient a cotton pad or gauze pad that needs to be placed in the empty hole to stop the bleeding. Removing a baby tooth does not cause excessive blood flow, so after half an hour you can safely remove the cotton wool, but removing a permanent tooth is accompanied by severe bleeding.
The appearance of a blood clot means that the healing process is going well, as it protects the bone from air and prevents inflammation.
What medications should I take?
If the dentist prescribes an antibiotic after a child’s tooth extraction, follow the recommendations and do not give the child other medications so as not to provoke complications.
How to rinse your child's mouth after tooth extraction?
For three days after surgery, rinsing your mouth is strictly prohibited, so as not to dislodge the blood clot and cause an infection. Three days after tooth extraction, the child can rinse the mouth using any means - strengthening tinctures of tree bark, soothing herbal decoctions or medicinal solutions.
How much can you eat after a child’s tooth extraction?
For the first few days, you should refrain from hot dishes and fermented milk products, eating only soft and liquid foods. It is best to chew on the side opposite the extracted tooth.
Features of filling
Our dentists use a variety of treatment options, starting from a very young age. Doctors use treatment approaches that do not cause mental trauma to children.
Installing fillings on milk bone tissue is practically no different from filling adults.
What materials are used
- Amalgam.
- Glass ionomer cement.
- Composites (combined filling).
Advantages of breast filling
- Filled baby teeth look aesthetically pleasing and are visually indistinguishable from natural ones.
- After filling, baby teeth are reliably protected from pathogenic infection; it will not penetrate into the bone tissue.
- Thanks to modern filling materials, even large cavities of destruction can be restored.
Colored fillings
This modern method of breast bone tissue restoration was developed specifically for the treatment of children. The fear and tears of children in front of dentists are replaced by interest when doctors offer children to get such fillings. All kids love bright, beautiful fillings and teeth painted in all the colors of the rainbow. They can choose their own color.
In addition, funny fillings have one advantage - they release fluoride ions, which prevents the development of secondary caries in the future.
The advantages of colored material include:
- eight spectacular, brilliant and bright colors that will not leave any child indifferent;
- fillings are perfectly polished;
- prevention of caries;
- the material is strong, so you won’t need to worry before replacing baby teeth with permanent ones;
- anti-allergenic and safe for children.
Complications after surgery
Do not give in to panic and call the ambulance service at the slightest ailment of the baby. Some consequences of tooth extraction do not harm children's health in any way. The following symptoms are considered normal:
- The child’s gums ache after tooth extraction - apply ice, this will reduce the discomfort.
- After tooth extraction, the child has swelling - after the third day it will begin to subside; ice also helps eliminate the discomfort.
- A swollen cheek after tooth extraction in a child indicates a slight inflammatory process, which will go away on its own after some time.
- Light bleeding in a child after tooth extraction should also not cause concern; even the next day the saliva may be slightly reddish.
- A low temperature after tooth extraction in a child is the result of the child’s worries and nervous overstrain; when he calms down, the temperature will drop.
Contraindications
Tooth extraction is not recommended in the following cases:
- Acute inflammatory process in the mouth: gingivitis, stomatitis, sore throat;
- Acute infectious diseases of the body: chicken pox, scarlet fever, whooping cough, influenza, ARVI;
- For serious diseases of the body: epilepsy, oncology, heart defects, heart failure;
- For blood diseases that are accompanied by clotting disorders;
- If possible, treat the tooth therapeutically.
Flux, fever and diarrhea after tooth extraction
More serious negative consequences when removing a baby tooth in children can only arise as a result of poor quality work by the doctor or due to infection. If the following signs are detected, parents must immediately contact a specialist.
- Flux after tooth extraction in a child, preventing swallowing, breathing and muscle movement.
- Prolonged bleeding.
- Severe and prolonged pain in the gums that does not go away even after taking painkillers.
- After tooth extraction, the child’s temperature rose above 38 degrees.
- Abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea after tooth extraction in a child.
How to relieve pain from periodontitis at home
It is necessary to understand that independent treatment of purulent periodontal inflammation is simply unacceptable. However, in some cases it is simply impossible to immediately go to the dentist: pain and swelling may appear at night or during a trip out of town. What to do in such situations?
The following remedies will help ease your child's suffering:
- taking painkillers - paracetamol and ibuprofen effectively reduce toothache, the dosage of which must necessarily correspond to the age of the baby;
- Gently brush your teeth using children's toothpaste;
- rinsing with a soda solution - to prepare it, dilute a teaspoon of baking soda in one glass of warm boiled water.
But warming compresses are unacceptable in any form. Even holding your cheek with your hand is contraindicated, since heat can significantly accelerate the development of the disease.
As you can see, treating periodontitis in baby teeth is a troublesome matter, requiring considerable effort and a lot of time, so parents should try to prevent the disease from developing in their child by taking preventive measures in a timely manner.
How much does tooth extraction cost?
Many people believe that the cost of the procedure for adults is much higher than for children, and the price for removing a baby tooth in children is lower than for extracting a permanent tooth. This is not entirely true. The amount of payment for the pediatric dentist depends on the complexity of the case, and the cost of removing temporary and permanent teeth is determined by the indications and concomitant diseases. In the table below, we have listed the main problems with which people turn to a pediatric dentist and the prices for tooth extraction for children.
| Service | Price |
Consultation | from 500 rubles |
Removing a baby tooth | from 1,100 rubles |
Removal of a permanent single-root tooth | from 1,200 rubles |
Removal of a permanent multi-rooted tooth | from 3,000 rubles |
Complex tooth extraction | from 4,000 rubles |
Wisdom tooth removal | from 3,000 rubles |
Removal of a supernumerary tooth | from 1,200 rubles |
Application anesthesia | from 250 rubles |
Local anesthesia | from 500 rubles |
Sedation | from 1,500 rubles |
General anesthesia for 30 minutes | from 4,000 rubles |
General anesthesia for 60 minutes | from 10,000 rubles |
General anesthesia for more than an hour | from 12,000 rubles |
Anesthesia
Before tooth extraction, anesthesia must be performed, which can be application, infiltration and general.
Application is the application of an anesthetic gel to the mucous membrane and gums, used for high mobility of baby teeth. Infiltration anesthesia involves performing an injection into the desired area of the jaw. It is used for dental diseases, severe inflammation or lack of tooth mobility. General anesthesia or sedation is rarely used in children; it is indicated for fear of dental procedures, allergies to anesthetics, a large amount of work in the oral cavity, or mental illness.
How to prepare a child for tooth extraction
If tooth extraction is unavoidable, try your best to minimize the child’s stress. For example, tell him a fairy tale about how one tooth began to behave badly and interfere with the others, so it needs to be “pulled out.” Before going to the clinic, you can also discuss some pleasant event with your child, be it going to the movies, the circus, or buying a toy, which you will do immediately after removing a capricious tooth. The main thing is not to panic, and then the confident and calm attitude of the parents will certainly give the child the strength to courageously endure this frightening but necessary procedure.
You can avoid tooth extraction surgery in children if you carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity throughout the entire period of dentition formation, monitor the quality of hygienic procedures and regularly take children to preventive appointments with the dentist.
Filling or silver plating
Silver ions stop the growth and division of pathogenic microorganisms. This means that caries will not develop in the future. But silvering is prescribed only in the initial stages of the disease. When large areas are damaged, it is useless to silver a baby tooth; over time, it will still collapse. A puncture may occur, which certainly will not be pleasant for the baby.
Is it possible to do a filling without a drill?
Today, medicine has made great progress and dentistry is no exception. Our clinic has ultra-modern equipment that does not produce frightening noisy sounds. In addition, filling is currently performed chemically. Its essence is the application of a special gel-like substance, which, after 30 minutes of exposure, is removed along with the damaged tissues. Then filling material is applied to this place.
Anesthesia
In order not to traumatize the psyche of children, dentists use injections extremely rarely. Pain-relieving gels and sprays are mainly used. Injection anesthesia is used only in extreme cases.
Anesthetics are selected in each individual case and are used only when there are no contraindications.
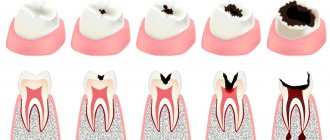
Causes of caries
- artificial feeding;
- genetic predisposition;
- poor nutrition (lack of sufficient fluoride in the diet),
- injuries;
- defects, features of the anatomical structure of bone tissue;
- poor oral hygiene;
If the development of the disease is associated with inheritance or poor health, it is necessary to regularly show the child to the pediatric dentist.
The post Filling baby teeth appeared first on.
]]>