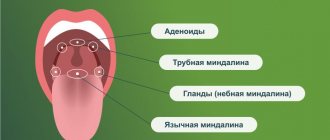
Pharyngitis is an inflammatory process that forms on the back wall of the larynx and affects the mucous membrane, as well as deeper layers, tissues of the soft palate and lymph nodes. The acute form of pharyngitis can develop into chronic if the patient does not seek help from a doctor and self-medicates.
Since the pathological process in the larynx is caused by the spread of pathogenic bacteria, the risk of developing pharyngitis increases in people with a weak immune system and in those who suffer from ENT diseases or are predisposed to them.
How dangerous is pharyngitis and how does it manifest itself? Which doctor should I contact and how to treat the disease? We will answer these and other questions in this article.
Reasons for the development of pharyngitis
Experts believe that the peak development of pathology occurs at the end of winter and the beginning of spring, since at this time the human immune system is especially susceptible to colds. Often in the spring season, a lack of vitamins and microelements in the human body leads to the appearance of vitamin deficiency, the body weakens and creates an excellent environment for the development of pathogenic bacteria. Inflammatory processes are also possible: both separately and against the background of the underlying disease.
The first signs of pharyngitis and its further treatment may differ depending on the stage of the pathology, gender, age and general health of the patient.
We include the following as the main reasons for the development of pharyngolaryngitis:
- hypothermia, eating too cold foods;
- deformation of the nasal septum;
- strains of microorganisms that cause the development of chlamydia, candidiasis, whooping cough, scarlet fever, measles;
- adenovirus, influenza virus;
- streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci;
- sinusitis, tonsillitis, caries, rhinitis;
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract: reflux, heartburn, hernia;
- abuse of bad habits;
- regular high loads on the vocal cords;
- polluted, toxic air;
- hormonal disorders and endocrine pathologies (diabetes mellitus, obesity, hypothyroidism, etc.);
- tonsillectomy, which was performed on the patient previously;
- infectious diseases in chronic form;
- weakened immunity.
Symptoms of pharyngitis
The first signs of the disease may differ depending on the type of pharyngitis. They are both local and general in nature. But there are common signs that are characteristic of any type of pharyngitis: sore throat, bad breath, stuffy ears and difficulty swallowing. With an active inflammatory process, an increase in body temperature above 38° can be observed - this is how the body fights a foreign infection. General signs: sweating, poor appetite, weakness, dizziness, fatigue, fever, chills. Some complain of pain and noise in the ears, and discomfort when exposed to loud sounds.
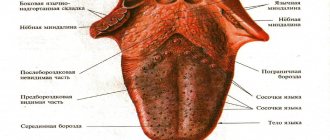
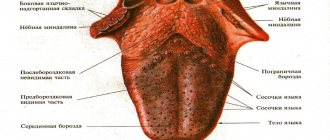
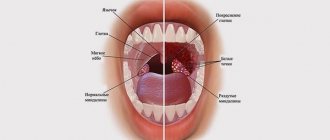
- During acute catarrhal pharyngitis, swelling and redness of the mucous membranes of the larynx appears. Also, red follicles may form on the back wall of the throat, and clear and slightly cloudy mucus may accumulate. There is swelling and redness of the tongue.
- In the purulent form of acute pharyngitis, ulcers with an accumulation of purulent masses appear on the surface of the posterior pharyngeal wall.
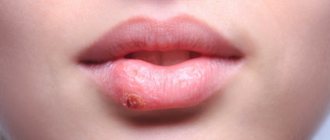
Herpetic stomatitis
With stomatitis, spots in the throat range from light pink to red. Areas with the rash may merge or be located far from each other. There are several types of stomatitis, among which herpetic stomatitis is especially common.
This disease is accompanied by headache, high fever, and red dots form on the upper palate, tongue, lips, and cheeks. These points turn into bubbles and explode to form red erosions. The herpes virus remains in the body for life. With strong immunity, it is in an inactive phase, and will manifest itself in the following cases:
- With exacerbation of chronic inflammatory processes.
- After a course of corticosteroids.
- In case of trauma to the mucous membrane.
- During emotional turmoil, allergies, vitamin deficiency.
- When the immune system is weakened.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis should be prescribed by a qualified dentist.
Acute pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis can occur independently, and can also be accompanied by acute inflammation affecting the upper respiratory tract: rhinitis or inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx.
Depending on the cause of development, acute pharyngitis occurs:
- Viral – most often caused by rhinovirus;
- Bacterial – caused by streptococci, staphylococci and pneumococci;
- Fungal – source of the inflammatory process – Candida;
- Traumatic - caused by damage to the pharynx and larynx: the throat was scratched by a sharp bone or burned by boiling water, severe stress on the ligaments;
- Allergic – occurs when inhaling allergens or irritants, such as tobacco, exhaust fumes or dusty air.
Chronic pharyngitis
According to the depth of damage to the pharyngeal mucosa, chronic pharyngitis is divided into: catarrhal, hypertrophic and atrophic forms.
- Chronic catarrhal pharyngitis - there is slight swelling of the tissue layers of the pharyngeal mucosa. Individual areas are sometimes covered with clear or slightly cloudy mucus. It develops as a result of acidic gastric contents entering the throat, for example, in the case of a hiatal hernia. Therefore, catarrhal chronic pharyngitis is a consequence of the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Chronic hypertrophic pharyngitis is a significant severity of swelling of the mucous membrane. Additionally, thickening of the uvula and swelling of the soft palate are observed.
- Chronic atrophic pharyngitis is characterized by some thinning of the lining of the pharynx. They are usually pale pink, sometimes shiny varnished. Some of their areas become covered with crusts, viscous mucus and pus.
Any type of chronic pharyngitis develops due to the fact that the acute form of the disease was not cured in time and developed into a more serious form. Chronic pharyngitis also appears as a consequence of rhinitis, sinusitis, deviated nasal septum, nasal polyps - that is, when nasal breathing is difficult for a long time. In addition, long-term use of vasoconstrictor drops also leads to the appearance of chronic pharyngitis.
How does pharyngitis manifest and progress in children?
Children suffer from pharyngitis more severely than adults. This especially applies to babies under one year old. Swelling of the mucous membrane can cause signs of suffocation; the pain that accompanies the disease reduces the child’s appetite. Often, a baby’s body temperature can reach 40°. The most difficult thing in this situation is that a small child cannot say what hurts.
Incorrect treatment can lead to irreparable consequences for a small, fragile organism. Therefore, at the first signs of pharyngitis, consult a doctor immediately.
Angina
Herpetic sore throat is also a fairly common cause of the formation of red dots in the throat on the roof of the mouth. The disease is characterized by high fever that lasts for several days, pain when swallowing, discomfort in the abdomen, and enlarged lymph nodes.
Streptococcal sore throat is accompanied by general malaise, headache, and high body temperature. The tonsils become loose and covered with plaque. In this case, antibiotic therapy is used, but the treatment regimen must be drawn up by a qualified specialist.
Sore throat and pharyngitis: what is the difference?
The general condition of the patient with acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis can be confused with the symptoms of pharyngitis. If the disease is diagnosed incorrectly, then treatment of pharyngitis in adults will not have any effect. And the acute form of the pathology can develop into a chronic one.
Unfortunately, many patients self-medicate and start using medications without a doctor’s specific prescription. This is extremely contraindicated! It is better to take care of your health in time and seek help from an experienced otolaryngologist.
It is important to remember that during pharyngitis, the larynx becomes inflamed, and during tonsillitis, the tonsils become inflamed. During a sore throat, it is always painful to swallow, and the pain intensifies even more when eating food. With pharyngitis, the opposite happens - while eating warm food or warm drinks, the sore throat decreases.
During the development of a sore throat, there is no cough or sore throat, only a sore throat and sometimes the formation of a white coating. With pharyngitis, there is a sore throat, as well as noise, pain, or congestion in the ears. The difficulty in distinguishing between these two diseases is further complicated by the fact that one patient can simultaneously develop both pathologies, since they are caused by the same pathogen.
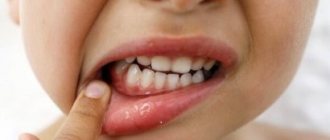
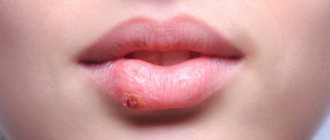
Causes of hematoma formation on the oral mucosa
The general scheme of hematoma formation is as follows: a rupture of a vessel causes the leakage of a certain amount of blood, followed by its compaction and the appearance of a blood clot. A bubble forms, noticeable on the smooth surface of the mucosa due to its dark coloring and relief. Often a similar picture can be observed during teething, when the gums bleed and become inflamed. The formation of multiple small hematomas, covering the entire surface of the mucous membrane in the mouth with unattractive dark spots, looks very unpleasant for the patient. But don’t panic if you suspect you have a serious illness. As practice shows, most of these phenomena occur due to mechanical trauma to the mucous membrane. But there are exceptions when the symptom indicates:
- allergic reaction;
- chronic injury;
- consequences of stressful situations;
- burns or cuts to the mucous membrane.
There have also been cases when multiple hematomas in the oral cavity are signs of:
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypertension;
- renal failure;
- complex types of stomatitis;
- blood diseases;
- vitamin deficiency, which causes fragility of blood vessels.
The exact cause and stage of formation of the pathology can only be determined after a thorough examination and diagnosis. For this reason, you should not self-medicate, so as not to further injure damaged tissues.
Diagnosis of pharyngitis
Detection of all types of pharyngitis begins with a visual examination of the larynx using a special device and taking an anamnesis. A throat swab is also taken for examination to test for diphtheria.
Other types of diagnostics:
- Cultural examination - inoculation of taken materials on a nutrient medium.
- Rapid diagnosis - identification of streptococcal antigen in throat swabs.
- Immunoserological diagnosis - the method is used in case of streptococcal infection.
Laboratory research:
- Complete blood count – exclusion of blood diseases, infectious mononucleosis;
- A general urine test helps rule out kidney disease (glomerulonephritis).
Depending on the symptoms of the disease, as well as the condition of the larynx, the presence or absence of cough, fever, plaque on the tonsils and soreness and increased size of the lymph nodes, additional consultations with other specialists may be necessary: an endocrinologist, a cardiologist, an allergist.
Treatment methods for pharyngitis
Treatment must be comprehensive. The patient is prescribed medications that will relieve pain and reduce inflammation. It is also important to adhere to a special diet and exclude from the diet foods that irritate the mucous membrane of the throat and bring even more discomfort: alcoholic beverages, spicy and salty foods, sour foods, carbonated drinks.
Drug therapy
Depending on the clinical picture and general condition of the patient, the doctor may prescribe antihistamines, antitussives and antiviral medications. Lozenges/lozenges are used to relieve pain.
In some cases, they resort to the use of antibiotics. They can only be taken as directed by a doctor.
Local impact
Rinsing with special solutions also has a good effect on the inflammatory process and redness of the larynx. They have a gentle effect, relieve pain and improve the general condition of the patient.
To diagnose and identify the disease, you need to consult an otolaryngologist. At the city clinic, you can contact your primary care physician, who will issue a referral to an ENT specialist. However, this takes time. You often have to wait 2 weeks for an appointment with a doctor. In some cases, this is simply impossible, since it is necessary to quickly conduct an examination and prescribe treatment before the situation becomes critical.
Therefore, we recommend contacting the Medunion medical clinic. We employ practicing otolaryngologists, and you don’t have to wait several weeks for appointments. Sign up today for a time convenient for you, and get tested tomorrow.
Patients choose us because we provide the service of a specialist coming to your home if you cannot come to the clinic on your own. You can also take samples directly at home.
The cost of an initial consultation with an otolaryngologist in Krasnoyarsk at the Medunion clinic starts from 1,300 rubles. You can sign up on the website or by calling 201-03-03.
Afta Bednara
This is an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa of a non-infectious nature, occurring in weak, bottle-fed infants in the first months of life.
Causes of the disease:
- permanent mechanical injury to the mucous membrane of the palate due to a nipple that is too long and too hard;
- may occur in breastfed children if the mother's nipple is very rough.
Main signs of the disease:
round or oval erosions, covered with loose plaque and located symmetrically at the border of the hard and soft palate, redness of the surrounding mucous membrane. The child becomes restless, eats and sleeps poorly.
In order to prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is necessary
promptly replace the pacifier or pacifier if irritation occurs on the oral mucosa.
If there are signs of disease, you should consult a pediatric dentist!
If any changes appear on the oral mucosa, you should visit a pediatric dentist to avoid complications and conduct a comprehensive examination and treatment!!!