The yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida is always present in the human body, but under certain factors it begins to multiply faster. The consequence of this process can be inflammation. Unpleasant white spots and plaque form on the tongue and oral mucosa - the main manifestation of candidal stomatitis.
Infants are often susceptible to the disease, as their immune system has not yet fully developed. It can appear from the first weeks of life. Moreover, it occurs in children under 10 years of age and in older people, especially if they suffer from dry mouth.
Cause of candidal stomatitis
We have already said above that the main reason is the increase in the concentration of Candida fungus in the body. Let us emphasize once again that normally in the human body, including the oral cavity, these microorganisms are always present and do not cause harm.
We can distinguish two groups of factors that provoke this process: endogenous (internal) and exogenous (external).
Endogenous (internal) factors:
- metabolic disorders, gastrointestinal problems, diabetes and other diseases;
- lack of vitamins;
- acute and chronic infectious and non-infectious general diseases;
- weakened immune system;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics.
Among the exogenous (external) causes: various damage to the mucous membrane (for example, due to dentures), thermal or chemical burns, poor personal hygiene.
Types of disease
Pseudomembranous. One of the most common types, which has several forms. To a mild extent, a white coating appears on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and tongue. In the middle, it becomes denser and begins to grow into the mucous membrane, erosion and bleeding appear, and regional lymph nodes enlarge. In severe form, weakness appears, body temperature rises, ulcers form under a white coating, and local lymph nodes enlarge.
Atrophic. It can develop independently or after the pseudomembranous form. Its manifestation is dry mouth, burning or pain when eating, and spots form on the surface of the tongue. The mucous membrane turns red, swells, and tongue movements become limited. Inflammation begins in the corners of the mouth.
Chronic. Candidomycosis stomatitis develops into this form if treatment is not carried out at the initial stage. In this case, changes begin in the mucous membrane (thinning, drying, redness), it becomes difficult to swallow, and a burning sensation is felt in the mouth. If left untreated, there is a risk of damage to the larynx, esophagus and intestines.
It can also be classified by location: candidal stomatitis of the corners of the mouth, yeast glossitis (appears on the surface of the tongue), thrush (plaque covers the mucous membrane of the cheeks and gums).
Diseases of the oral cavity can develop primarily due to the harmful effects of various agents, but they can also be of a secondary nature, joining, due to the weakening of general and local immunity, to various gastrointestinal diseases, infections, etc.
Stomatitis
Childhood stomatitis has a certain periodization depending on the infectious agent and the cause of the disease. Of course, all types of stomatitis can occur at any age, but there are also patterns.
Fungal or candidal stomatitis develops in children under three years of age; this is the so-called oral thrush. At the age of one to three years, herpetic types of stomatitis are observed with a high frequency with a decrease in specific immunity and infection, as well as the formation of Bernard's aphthae on the palate.
There are several types of stomatitis in children. A common form is catarrhal stomatitis , manifested by redness, swelling of the oral mucosa and especially the gums, which sometimes even bleed slightly. At the same time, there is pain when swallowing, significant salivation; the tongue is covered with a whitish coating. Sometimes slight increases in temperature and swelling of local glands are observed.
Sometimes simple stomatitis can develop into septic stomatitis , with severe purulent inflammation, fibrinous deposits and fever.
In infancy, gangrenous form and aphthous form of stomatitis , but they are more common in older age.
Preventive measures include the following:
– regular oral hygiene, rinsing, using dental floss to reduce the likelihood of bacterial inflammation;
– correction of diet. Some foods contribute to irritation of the oral mucosa. In case of frequent relapses, it is recommended to exclude from the menu such foods as milk, cheeses, tomatoes and tomato paste, sour berries, fruits, juices, chocolate and cocoa in any form. Reduce the amount of spicy and salty foods, as well as rough foods: chips, crackers, crackers, which can injure the surface of the oral mucosa;
– choosing a toothpaste that does not contain sodium sulfate helps to avoid excessive drying of the mucous membrane.
Thrush
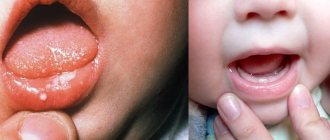
It is observed almost exclusively in infancy. The disease is expressed by the appearance of white spots and plaques on the tongue, reminiscent of the remains of curdled milk, tightly adjacent to the underlying tissue. These deposits can cover the entire surface of the tongue and spread to the mucous membrane of the mouth, pharynx and esophagus. Thrush develops only on the mucosa covered with squamous epithelium and does not spread to those places of the mucosa where there is columnar epithelium. This fungus is an innocent nosoparasite found in the mouths of many mothers. It is transmitted from mother to child through kissing and droplet infection. But in order for the disease to develop, the child must weaken and his immunity decrease. Thrush itself is not dangerous. With proper child care, thrush usually does not occur.
Prevention of oral infections in children
Currently, there are no methods that completely protect children from oral infections.
Prevention consists, first of all, in strengthening the child’s immunity - maintaining a proper sleep and rest schedule, carrying out water procedures, and a nutritious and balanced diet. It is especially important to reduce the likelihood of acute respiratory viral infections, which lead to a significant decrease in the child’s immune defense.
Basic hygiene standards should be observed: clean toys, do not lick nipples and spoons when feeding a child, reduce the frequency of contact between the child and adults with obvious manifestations of recurrent herpetic infection. Avoid contact of your own children with a child who has signs of herpetic lesions.
Branch "Children's Clinic" of the Pinsk Children's Hospital Pediatrician: V.A. Shchaveleva
Symptoms of candidal stomatitis
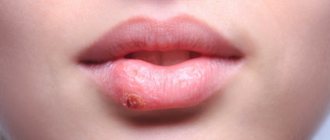
Clinical manifestations of oral candidiasis are varied. As a rule, a milky-white cheesy coating forms on the back of the tongue, palate, and cheeks. When it is removed, the eroded bleeding surface of the mucous membrane is exposed, and painful sensations appear when swallowing. A common symptom is dry mouth and an unpleasant metallic taste.
In the earliest stages, a small number of white spots form. As the disease progresses, their number increases and they turn into ulcers. In severe forms, the white plaque cannot be removed and it completely covers the oral cavity.
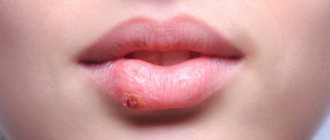
If left untreated, the fungus can invade the area of the larynx, esophagus and even the intestines. The pain intensifies and the red border of the lips and corners are affected. When the lips are affected, candidal cheilitis begins to develop, due to which cracks and erosions form, thin films and crusts grow. Seizures may also appear in the corners of the mouth, which bleed and cause pain when opened.
Diagnosis of oral candidiasis
Candidiasis (thrush) of the oral cavity can be detected during an examination by a dentist if the patient has characteristic complaints. The doctor examines the condition of the oral mucosa, examines scrapings, and carefully examines the hair and skin. If you have oral candidiasis, you also need a blood test to check your glucose levels and rule out diabetes. The sooner you detect the presence of this infection, the easier it will be to get rid of it, so you should not delay diagnosis just because the symptoms do not cause you discomfort.
Diagnosis of the disease
Before starting treatment for stomatitis, you should consult a dentist. The doctor will listen to complaints, conduct a visual examination of the oral cavity and skin, and also take scrapings from the affected areas. In some cases, consultation with a therapist, dermatologist, allergist and endocrinologist may be required.
Remember that timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment and easy progression of the disease. Also, regardless of the causes and form of the disease, treatment in newborns should be carried out under the supervision of doctors.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis
The course of treatment depends on the type and severity. Often the complex includes local and general methods:
- rinsing with antiseptic, antimycotic and analgesic drugs;
- use of antifungal ointments, aerosols, gels;
- when it spreads to other body systems, systemic antimycotics are prescribed.
With properly selected therapy, its duration is two weeks. If stomatitis has become chronic, then courses of treatment must be repeated to avoid relapses. In the most advanced cases, this is from 1 to 3 months.
With a mild degree of the disease, candidiasis can be eliminated forever. In other cases, there is a possibility of relapses, and even the development of candidal sepsis, so prevention is of great importance.
How to treat fungal stomatitis?
In order not only to reduce inflammation of the mucous membrane, but also to prevent relapses, treatment of candidal (fungal) stomatitis in adults and children is carried out only in a comprehensive manner. Therapy involves taking several drugs at once:
- antimycotics – antifungal drugs for topical use;
- local antiseptic solutions for rinsing and irrigation (to prevent additional infection);
- antihistamines (recommended for the development of allergies to fungal activity);
- vitamin complexes (to eliminate deficiency of substances in the body).
To speed up recovery, the patient will have to follow a special diet. It is necessary to restore the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and pharynx.
Often sick patients are interested in how to treat candidal stomatitis at home, putting off going to the dentist. But it is impossible to cure candidiasis at home. Probably, it will only be possible to relieve the acute symptoms of the pathology, which will manifest itself again after a while. To prevent inflammation from becoming chronic, you should consult a doctor as soon as you notice the first symptoms of the disease.
Prevention
To prevent the manifestation of candidal stomatitis, you must adhere to the following rules:
- learn to brush your teeth so as not to injure the mucous membrane;
- use mouth rinses to cleanse the mouth;
- change your toothbrush every 2 months and rinse thoroughly after use;
- if you wear a denture, you must wash it thoroughly using special products, and also follow the storage rules;
- get rid of bad habits;
- if you are taking antibiotics, you must use antifungal drugs and probiotics as prescribed by your doctor;
- wash and treat with boiling water accessories that small children come into contact with;
- Nursing mothers are advised to maintain breast hygiene;
- hardening, physical education in the fresh air;
- visit the dentist regularly.
Candidiasis (thrush)
Candida
enter the oral cavity . In children, thrush is often confused with stomatitis. It is most often transmitted from poorly washed, unsterile nipples, bottles, as well as from an infected mother, through the birth canal, with low immunity. Most children get sick before they are one year old. Parents complain about a white, curd-like coating.
Treatment
Infants are not prescribed serious medications for uncomplicated cases. The dentist recommends cleaning this plaque with a soda solution (1 teaspoon per glass of warm water). An ear stick, as an option. The same solution is used to treat nipples, bottles, toys, and mother's nipples during breastfeeding. In most cases, candidiasis quickly passes without leaving a trace. Prevention includes regular monitoring of the sterility of items used by the child.