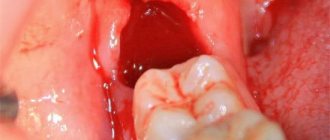
Types of removal Causes of complications How long does the pain last What is the pain associated with?
Aching jaw Painful to swallow Throbbing pain How to relieve pain? Recommendations after removal Dental treatment can be therapeutic or surgical, and pain can occur after any type of intervention. If your wisdom tooth hurts after treatment, in most cases, this is a normal physiological reaction of the tissues to the procedure performed. Usually, painful sensations are quickly relieved with painkillers and go away on their own within a couple of days. But there are situations when pain after removal of the figure eight occurs due to complications or a violation of the technology of the therapeutic manipulation.
The dentist will definitely consult the patient about how the recovery process after the intervention should normally proceed, and if any symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. If all the doctor’s recommendations regarding the rehabilitation period are followed, but the painful sensations only increase, this is a direct indication to come for another appointment.
Types of deletion
Wisdom teeth (eights, third molars) are larger than other dental units in the row. They differ not only in size, but also in the complex anatomy of the root system. Eight has from 2 to 6 roots
, which are often closely intertwined with each other. Given the complex arrangement of wisdom teeth, when they are removed, a significant wound is created.
The risk of complications will directly depend on how difficult the figure eight extraction was. With simple extraction, when the tooth is intact, the roots are not intertwined, and there are no other pathologies (pulpitis, periodontitis, etc.), the risk of complications is minimal. In such a situation, the doctor uses forceps or an elevator to remove the tooth from the socket.
If the wisdom tooth is incorrectly positioned (horizontal eruption, severe curvature), intertwined roots, significant destruction of the coronal part, or the presence of inflammation, a more global surgical intervention may be required. An incision in the gum, cutting a tooth into pieces with a drill, removing root fragments through the jaw bone and other manipulations significantly increase the traumatic nature of the procedure. Aching pain, swelling after removal of the figure eight, increased temperature (up to 37.5℃), hematoma on the cheek - this is a normal reaction to the intervention, which lasts no more than 5-7 days.
Why does my gum hurt?
Unexpressed aching pain and slight swelling of the gums appear due to injuries to soft tissues, nerves, and jaw bone when removing a tooth from its bed. The gum tissue swells, the nerve endings are compressed, hence the pain. How much your gums hurt after tooth extraction depends on:
- Patient's pain sensitivity;
- degree of complexity of the intervention;
- features of the clinical case;
- location of the dental unit (after extraction of molars, the injury is greater, the pain lasts longer);
- state of immunity.
The body’s normal response from the development of complications is distinguished by the following properties: the pain does not intensify, pathological symptoms are present for no more than 7 days, and no other signs of deterioration in well-being are observed.
Why complications arise
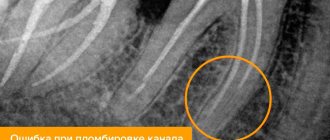
After extraction, a wound is left in the gum and bone in which a blood clot (fibrin) forms. It “seals” the wound, preventing infection, and becomes the basis for the formation of new tissue that fills the space formed after the removal of the 8. After uncomplicated removal, healing lasts about a week. On days 3-4, the blood clot is gradually replaced by granulation tissue, which gradually fills the entire socket. Already after a month, the granulation tissue is completely replaced by connective tissue, and after 3 months - by bone.
Removal of third molars can have negative consequences that appear almost immediately after the intervention. Among the most common complications:
- “dry socket” - when a blood clot does not form or dissolves too quickly;
- paresthesia - damage to the nerve endings around the removed unit;
- alveolitis - inflammation of the socket;
- bleeding;
- cyst - fibrous formation at the site of an extracted tooth;
- endogenous periostitis (flux).
In rare cases, stomatitis, osteomyelitis, jaw trauma, and perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus are observed. The occurrence of complications is usually associated with ignoring the dentist’s recommendations regarding oral hygiene during the healing period, decreased immunity, and violation of surgical technique.
Pain after wisdom tooth removal
Patients are always interested in the question, how many days does the jaw hurt after wisdom tooth removal? Pain after surgery is a standard tissue response to injury. Normally, the pain subsides within a few hours or within 3 days after extraction (in case of complicated removal). The pain a patient experiences after wisdom tooth removal indicates the success of the procedure.
- The first discomfort and pain appear 2-3 hours
after the intervention (when the anesthetic wears off). - The first 3-4 days
there is aching pain, redness and swelling of the soft tissues. If the extraction is successful and the hole is properly cared for, the pain will gradually disappear. - Over the next 2 weeks
, if there are no complications, the wound will heal completely, and minor pain may occasionally occur in the late afternoon. - After 3 weeks,
all discomfort should disappear.
If a wisdom tooth has been pulled out and it hurts for more than 5 days, the intensity of the pain increases, it becomes throbbing, debilitating, accompanied by fever, swelling - this indicates a complication and requires immediate medical intervention.
Why does a tooth hurt after extraction?
Pain after tooth extraction is quite common and manifests itself in most cases in some form. Pain at the extraction site is divided into several types. We will talk about each type of pain.
Aching pain after tooth extraction
This type of toothache is the most common and is observed in almost all patients who have undergone tooth extraction. The first pain appears after the anesthesia wears off and lasts for about two days. By its nature, this pain resembles an aching character. In some cases, pain is experienced when opening the mouth, this is due to the fact that the gums and chewing muscles are stressed and inflamed due to tooth extraction.
Severe pain after tooth extraction
This type of pain usually appears after the removal of impacted and dystopic teeth. When they are removed, a larger volume of mucous membrane is exposed, and the removal operation itself lasts longer compared to conventional removal. Because of this, the impact on the oral cavity is much greater, and inflammation is more pronounced.
Phantom pain after tooth extraction
After complex removal surgery, in rare cases, phantom pain may occur. This occurs due to the sprouting of nerve fibers into the tissue. This type of toothache occurs in people with weak immunity or autoimmune diseases of the body.
Due to the sprouting of nerve fibers, the removal site becomes very sensitive. When chewing soft food, severe pain can spread to other teeth.
What could be causing the pain?
If the pain after removing the figure eight does not subside within 5-7 days, but rather intensifies, this may indicate the following complication:
- Alveolitis
is an inflammation of the socket associated with the absence of a blood clot, poor hygiene, infection of the wound, or the presence of a bone fragment in the socket (if the tooth was extracted in parts). - Severe damage to the blood vessels
of the surrounding tissues - in addition to pain, there is a hematoma, swelling of the gums and cheeks. - Allergy
to anesthetic, hemostatic sponge (if it was used during the procedure).
As inflammation develops, pain is accompanied by an unpleasant odor, purulent discharge from the socket, the formation of gray plaque, enlarged lymph nodes, increased temperature, and deterioration in general well-being. In this case, you need to see a doctor immediately.
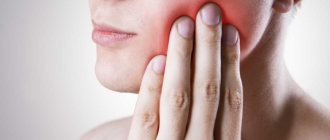
Aching jaw
When the jaw hurts after wisdom tooth removal, it is usually due to the fact that the surgeon put pressure on it to gain access to the molar. Or during the procedure, blood vessels, nerve endings, and ligaments of adjacent dental units were injured. These symptoms are quite normal, if there is no difficulty opening the mouth, there is no pronounced swelling of the gums or soft tissues of the face.
It hurts to swallow
After extraction of the lower 8, you may experience a sore throat or pain when swallowing. This symptom appears against the background of severe damage to soft tissues, with severe swelling of the gums, cheeks, or due to trauma to the trigeminal nerve. If the trigeminal nerve was affected during the operation, there is not only pain, which can radiate to the temple, ear, neck, but numbness on the face, in the area of the removed unit, and increased salivation. Also, a sore throat may occur if there is inflammation or purulent process around the affected molar. This symptom can last up to 2 weeks. To avoid complications, you should visit a neurologist or dentist.
Throbbing pain
If your gums ache after wisdom tooth removal, but the discomfort is quickly relieved with an analgesic and disappears after 2-3 days, this is evidence of normal healing. On the contrary, throbbing pain in the jaw or gums indicates possible inflammation, damage to blood vessels and nerves. With neuritis (damage to the jaw nerves), it can radiate to the neck, throat, temple, ear, eye. The pain increases, prevents you from falling asleep, and interferes with normal life - in this case, you need to immediately consult a dentist, this is a sign of inflammation.
Possible complications
There are several reasons why complications arise after the removal of the eighth molar: improper oral care, inexperience or negligence of the surgeon, complex removal with severe trauma to the gums. The most common complications include:
- Paresthesia.
If the nerve endings are damaged, the cheeks, lips, tongue and chin become numb. Possible diction problems. Symptoms may last up to two weeks.
- Alveolitis.
The most common complication after removal of the eighth molar. Development is provoked by an incompletely removed tooth or an open socket, without a blood clot. The “true friend” of such a complication is bad breath, which does not go away for a long time.
- Hematomas.
The reasons for the appearance are damaged blood vessels during removal.
- Flux.
If hygiene is not observed, bacteria enter the wound, which provokes inflammation of the periosteum. Symptoms: pain, fever, redness and swelling of the gums.
If severe pain after the removal of a wisdom tooth does not subside, but rather intensifies, symptoms such as swelling, bruising and edema progress - this is already a pathological process that requires the intervention of a specialist.
How to relieve pain and discomfort
- Do not touch the blood clot in the socket with your tongue, toothbrush, hands or foreign objects;
- make oral baths from herbal decoctions and antiseptic solutions;
- if the pain radiates to the ear or another part of the head, take a painkiller;
- exclude hot food and drinks.
If your gums hurt for several days after wisdom tooth removal or you have a headache, you don’t need to worry too much. Analgesics prescribed by your dentist will help you cope with these symptoms. If the discomfort does not go away after a week, painkillers do not help much - you need to go to the doctor. If the temperature is above 37.5℃, which does not decrease to normal, the development of an allergic reaction (to an analgesic, hemostatic sponge), or a sharp deterioration in health, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Limited osteomyelitis of the tooth socket
Inflammation of the bone tissue in the area of the extracted tooth :
- in the socket of the extracted tooth , and pain occurs in the adjacent teeth;
- Weakness, severe headache;
- Body temperature is 37.6-37.8°C and above, sometimes there is chills;
- Loss of sleep and performance;
- The bottom and walls of the hole are covered with a dirty gray mass with a fetid odor;
- Touching the gum is sharply painful;
- When you tap adjacent teeth, pain occurs;
- The perimandibular soft tissues are swollen, the submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged, dense, painful;
The symptoms of acute inflammation last 6-8 days, sometimes 10 days, then they decrease, the process passes into the subacute and then into the chronic stage.
- The pain becomes dull and weak;
- General condition improves;
- Body temperature normalizes;
- After 12-15 days, the tooth socket is filled with loose, sometimes protruding pathological granulation tissue, which, when pressed, releases pus.
Please note that pain relief during a complication does not mean that the process has begun to heal; perhaps it has entered a chronic, more dangerous stage. As a rule, the surgeon schedules a follow-up examination for the patient after removal; ATTENDANCE IS MANDATORY!