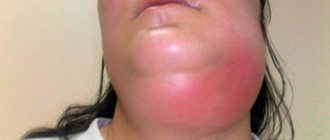
The most common form of jaw injury is a bruise. No one is immune from this. For example, with a strong blow to the jaw, soft tissues, blood vessels, and capillaries are affected, resulting in the formation of hematomas and swelling. This is accompanied by severe pain and discomfort.
To avoid complications, it is recommended to consult a doctor immediately after injury. The fact is that impaired jaw function entails a chain of negative consequences: difficulties while eating, deterioration in the quality of spoken speech, etc.
What causes bruises?
Jaw injury may result from:
- falls;
- blow;
- fights;
- children's games;
- accidents, etc.
The severity of the injury is determined taking into account the following factors:
- features of the surface or object that caused the injury;
- impact intensity;
- affected area of the face;
- condition of bone tissue before the incident.
The strength of the bruise and possible complications depend on the listed indicators. Regardless of the severity, it is important to see a doctor to evaluate the condition and prescribe appropriate treatment. This will avoid unforeseen consequences and quickly restore the damaged area.
Fracture of the lower jaw - features
This type of injury has some features:
- a fracture with displacement of bone fragments or the entire jaw is called complete;
- if the injury is of an open type, then not only the mucous membrane of the oral cavity ruptures, but also the soft tissues of the face;
- It is extremely rare that a comminuted fracture is diagnosed because it requires too much force.
A fracture of the lower jaw is characterized by the following signs:
- pronounced asymmetry of the face, which is formed due to swelling and hemorrhage in the soft tissues at the site of injury;
- acute pain when touching any part of the lower jaw, inability to talk or chew;
- mobility of fragments, if any;
- a radical change in the bite - the lower jaw may be too forward or, conversely, “retracted” deeper.
Anyone can provide first aid for the injury in question - you need to apply a bandage (place any straight object, such as a ruler, between the teeth) so that the damaged part of the jaw is motionless. If there is bleeding, it must be stopped by applying something cold, treating with hydrogen peroxide and other classical methods. Then all that remains is to wait for the ambulance team to arrive.
Clinical picture
First of all, the doctor conducts a visual examination of the bruised area to identify hidden injuries that cannot be identified by a person without medical education. For example, symptoms of dislocations or fractures may not appear immediately. Professional consultation allows you to begin timely treatment, if required.
To recognize a jaw bruise, it is important to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the place where the blow fell, intensifying when pressed;
- visual signs (eg, swelling, redness, abrasions, bruises);
- limitation of jaw mobility when yawning, talking, chewing;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- general weakness.
Jaw bruises are less dangerous than more severe injuries, so recovery is usually quick.
The doctor may order an x-ray or computed tomography to establish an accurate diagnosis. These studies will assess the condition of the internal tissues of the affected area.
Maxillary fracture
During an extraoral examination of patients with type 3 fractures of the upper jaw, a violation of the integrity of the zygomaticalveolar ridges is revealed: tissue swelling, abrasions, an increase in the vertical parameters of the face. At the border of the transition of the immobile mucosa of the alveolar process to the mobile one, as well as on the hard palate, hemorrhages are diagnosed. Displacement of the damaged sections during a fracture of the upper jaw leads to rupture of the mucosa. Downward dislocation of the posterior fragment causes elongation of the soft palate.
During palpation examination, irregularities and recesses are determined on the alveolar process. When pressing on the hooks of the pterygoid processes, the patient feels pain in the area corresponding to the fracture line of the upper jaw. Disocclusion is more often observed in the anterior area, and malocclusion pathologies along the transversal and sagittal planes are less frequently diagnosed. The patient does not feel the tip of the probe touching the mucous membrane of the alveolar process, which indicates a loss of pain sensitivity. A CT scan for a type 3 maxillary fracture reveals areas of integrity disruption in the areas of the pyriform aperture and zygomaticalveolar ridges, and decreased transparency of the maxillary sinuses.
In case of a type 2 fracture of the upper jaw, the symptom of glasses is positive - the periorbital zone immediately after the injury is saturated with blood. Chemosis, exophthalmos, and lacrimation are observed. Pain sensitivity of the skin in areas corresponding to the level of damage is reduced. In the anterior section, as a rule, there is disocclusion. During a palpation examination, the dentist determines the mobility of the maxillary bone at the border with the orbit, in the area of the zygomaticalveolar ridge, as well as in the area of the suture connecting the frontal bone with the upper jaw. These same changes can be diagnosed by radiographic examination.
In type 1 fractures of the upper jaw, diplopia, chemosis, exophthalmos, subconjunctival hemorrhages, and eyelid edema are observed. If the patient is lying down, enophthalmos is detected. In a sitting position, diplopia increases, and when the teeth are closed, it decreases. By palpation, in case of an upper fracture of the upper jaw, it is possible to identify unevenness in the areas of the frontomaxillary, as well as the zygomatic-frontal sutures and the zygomatic arch. The load test is positive. Computed tomography reveals a violation of the integrity of the root of the nose, zygomatic arch, frontozygomatic suture, and sphenoid bone. A diagnostic test to determine the presence of rhinorrhea is the handkerchief test. After drying, the structure of the fabric soaked in liquor remains unchanged. If the scarf has become stiff, it means there is no liquorrhea, serous contents are released from the nasal passages.
It is necessary to differentiate a fracture of the upper jaw from other injuries of the bones of the maxillofacial skeleton. All patients should be examined by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon, as well as a neurologist. If the maxillary sinuses, optic nerve, or skull bones are damaged, treatment is carried out jointly with a neurosurgeon, resuscitator, ophthalmologist, or otolaryngologist.
Primary treatment
A bruise can be diagnosed by external signs even before seeing a doctor. To eliminate pain and discomfort, it is recommended to perform the following measures:
- apply a tight bandage;
- Apply a cold compress to the bruised area.
For quick and painless treatment, the face must be at rest. It is better to avoid warming compresses, as they can lead to the development of inflammatory processes.
The consequences of bruises can be such conditions as fractures, fractures, dislocations of the hard tissues of the jaw and even a concussion. Treatment differs depending on each case, so you should not self-medicate. It is also worth noting that most injuries have similar symptoms, so they are easy to confuse. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis. If you cannot go to the hospital yourself, it is recommended to call emergency medical help.
Medical care for jaw injuries
There is no specific treatment plan in such cases. But there is a list of general recommendations. Visits to the doctor are usually limited to one visit to evaluate the x-ray or CT scan.
If the patient escaped with an ordinary bruise, then treatment will be carried out at home. The patient will be given a bandage to hold the bones in the correct position. As mentioned above, you need to apply cold compresses. Ice, snow, and sterile gauze moistened with cold water are suitable for these purposes. Warming the affected area is contraindicated to avoid inflammation and worsening the clinical condition.
To eliminate pain, taking analgesics is allowed. Following simple rules will allow you to quickly get rid of the consequences of a bruise and return to your normal life.
Likely consequences
Any injury with negligence and non-compliance with medical recommendations can lead to all sorts of complications. If we talk about a bruise of the jaw, then it can develop into a post-traumatic form of periostitis, myositis or deformation of bone tissue. Any complications will require lengthy and likely expensive treatment. Injury to the masticatory muscles can cause limited mobility of the lower jaw, complicate chewing and swallowing, which directly affects the state of the gastrointestinal tract and metabolic functions of the body.
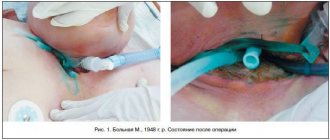
Deformations of the maxillofacial region as a result of trauma: treatment in Ufa
During the treatment of such deformities, various methods can be tried, such as osteotomy and repositioning of the facial bones, after which they are fixed in the desired position. Implants and special fixators are also used, and sometimes proprietary methods for eliminating deformities. After the end of treatment, you can observe the elimination of the main and concomitant dysfunctions and the restoration of facial configurations.
Incomplete development of the upper jaw
Signs of the disease, which has the scientific name “upper micrognathia,” is a pathology of the structure of the dentition in the upper part of the jaw. The patient's teeth are crowded, there are teeth that have not erupted or are incorrectly positioned. On the bottom row, the teeth are arranged in accordance with the norm. Pathology can be either minor or pronounced. In the second case, the shape of the face changes - the upper lip recedes, and the size of the nose noticeably increases. The anterior teeth have no occlusal contact. Food is difficult to bite and chew. Mouth breathing is possible due to shrinkage of the nasal sinuses and deformation of the nasal septum. The patient's face takes on an “offended profile.”
The lower teeth, in the absence of antagonists, move forward and upward together with the alveolar process. It becomes very difficult to make “biting” movements. The nasolabial furrows become pronounced. Speech is impaired, patients pronounce sounds unclearly. The lower jaw develops too much.
Incomplete development of the lower jaw
Superior macrognathia may be congenital or acquired over time. As a result of exposure to extraneous factors, normal development of the dental system does not occur.
This pathology involves deformation of the lower jaw. The profile of the face is distorted, an incorrect bite is formed, the tongue has no support, it sinks, and breathing difficulties arise.
Inferior micrognathia
Characteristic signs of the disease: protrusion of the upper jaw, asymmetry regarding the position of the lower jaw. The pathology has some externally noticeable features: a visually noticeable convexity (similar to swelling) of the face, its short lower part, a reduced upper lip, despite the fact that the lower one is behind the incisors, and other deformations. With this anomaly, normal biting and chewing of food is impossible.
Treatment takes place in three stages:
- orthodontic - fixation of braces to correct rows of teeth for several months;
- surgery, namely correction of cranial bone structures;
- final orthodontic correction of the jaw.
Fractures and injuries of facial bones
Injuries of the alveolar processes. The most common among other types of fractures. They are observed in the area where the incisors are located, since this area is more susceptible to injury than others. This type of fracture is stabilized using wires.
Injuries of the condylar processes. The jaw is expected to bend to the side if you try to open your mouth wide. With a bilateral injury, the victim has a deformed bite.
Median fractures
A deviation towards the lower row of teeth and curvature of the dental arch are expected. When diagnosing, fragments are quite easy to displace.
Injuries in the area of the angle and body of the lower jaw. Occur after loss of connection between the masticatory and the pterygoid muscles located inside. Very visible on x-rays. The goal of treatment is to restore the anatomically correct structure of the jaw and the functions of the injured bones.
If surgery is necessary, the patient is given anesthesia and local anesthetic. Fastenings are made using titanium structures. Incisions are made with a scalpel in the cavity if possible. In case of severe damage, plastic surgery is performed to reduce aesthetic damage. The main goal when eliminating an injury is to return the patient to a normal bite as soon as possible.
Fracture and trauma of the upper jaw
There is a gradation of the degree of damage to the upper jaw. Diagnosis is often difficult due to facial swelling and hemorrhages that occur. Symptoms of the disease:
- visual lengthening of the face;
- pain when closing;
- bite deformation;
- nose bleed.
The latter often occurs in the most severe cases. An impacted type of injury, in which it is difficult for a specialist to see the main symptom - movement of fragments and abnormal mobility.
Today there are many effective techniques for eliminating such injuries.
They are diagnosed upon examination and suggest deformities, for example, retraction in this area, complications when attempting lateral manipulation of the jaw, hemorrhage in the eye and a number of other symptoms. With significant deformation, diplopia and hemorrhage from the nasal sinus are possible. An X-ray examination is required.
Zygomatic bone: fracture
To eliminate the consequences of the injury, reduction and fixation is carried out in a certain state. Surgical intervention is unlikely, only in complex cases.
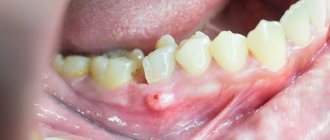
The teeth in the front of both jaws are most susceptible to injury. The dislocation can be complete or incomplete, in some cases impacted.
In the first case, the entire root falls out of the hole; in some cases, its contact with the soft tissues remains. In the second case, a deviation in the location of the tooth relative to the row is assumed. Pain occurs, especially when trying to chew food.
Treatment of injury is carried out by a specialist together with a dentist, possibly with an orthopedist.
Damage, fractures and dislocations of teeth
Dislocation of the lower part of the jaw. Dislocations are divided into anterior and posterior. More often than others, the anterior type of dislocation is diagnosed as a result of opening the mouth or injury.
Treatment is carried out by manual reduction. Local anesthesia is used. After the procedure, the lower part of the jaw is fixed without movement for 1-2 weeks, and physiotherapy is performed.
Nasal fractures, treatment methods
The back of the nose becomes retracted or deformed, bleeding occurs, breathing problems occur, and hematomas occur.
The nasal bones are thinner than the rest of the facial bones and their fractures are mostly comminuted. Therefore, treatment is carried out as soon as possible after diagnosis or after swelling in the damaged area of the nose subsides. Plastic surgery can be performed within a couple of months.
Treatment of a jaw fracture
Therapy for injury should be carried out only by doctors, and the sooner qualified medical care is provided, the lower the risk of complications. Treatment of a jaw fracture may include the following manipulations:
- if there is a wound (rupture of soft tissues, mucous membranes), then first the bleeding stops and disinfection measures are carried out;
- manual comparison of bone fragments, giving the correct shape to the damaged jaw;
- A splint must be applied - if the jaw is fractured, it must be completely immobilized for at least one month.
Additionally, painkillers and anti-inflammatory therapy are prescribed. If a fracture of the jaw processes is diagnosed, then, most likely, surgical intervention will be prescribed, which involves the implantation of specific metal plates. Your doctor will tell you more about the operation during your consultation. Sign up on our website Dobrobut.com.
Rehabilitation after a jaw fracture includes physiotherapy, massage and facial exercises. Patients often have to relearn how to chew and speak without distorting sounds.