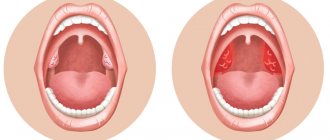
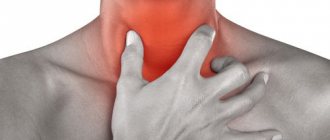
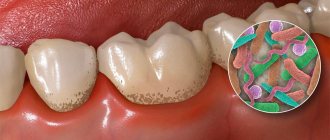
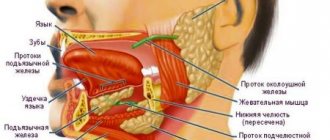
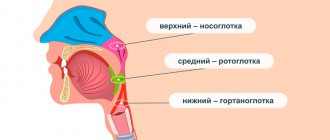
Mouth pain is most often caused by infection, allergies, or injury. A sore throat can easily be confused with pain in the mouth.
THE DOCTOR'S CONSULTATION
Contact your doctor if your child:
- refuses to drink for a long time due to pain in the mouth
- he has a mouth ulcer that has not healed for more than a week
- swelling of the gums, lips, palate
ATTENTION!
Pain in the mouth can lead to a child refusing to drink for a long time, and this is dangerous due to the risk of dehydration.
| ASK YOURSELF A QUESTION | POSSIBLE REASON | WHAT TO DO |
| Is your baby breastfed and has small sores on your tongue? | Incorrect attachment during breastfeeding | Ulcers are formed from pressure from the nipple when the baby is not latched onto the breast incorrectly and go away when proper latching is established. Try changing your feeding position. You can contact a lactation consultant for help in establishing proper feeding. If inflammation or other symptoms occur, contact your child's doctor . |
| Has your child's drooling increased? Does he keep his finger(s) in his mouth all the time? Is he 4-8 months old? | Teeth cutting | If these symptoms are accompanied by signs of illness (fever, loss of appetite, etc.), call your child's doctor for an examination. The appearance of teeth alone cannot cause a high temperature. Some children find it easier if they are given special rubber rings to chew on; others like to live cool objects (see Toothache) |
| Is your baby hungry but refusing to nurse? Are there white spots on the tongue and inside of the cheeks? Did he take antibiotics? | Thrush | This is a fungal disease and can be caused by taking antibiotics. Consult your child's doctor . A good remedy is to treat your mouth with a soda solution. Sometimes it is necessary to take antifungal agents. |
| Is your older child complaining of pain when swallowing? | Viral or bacterial (streptococcal) infection | Take your child to the pediatrician . He will prescribe the necessary treatment |
| Do you have small, painful sores on your tongue and inside your cheeks? | Ulcerative stomatitis | Take your child to the pediatrician. He will prescribe the necessary treatment |
| Painful yellowish spots or blisters on the tongue, gums, inner cheeks, swelling and redness of the oral mucosa? Enlarged cervical lymph nodes, “cold” on the lip? Are your lips bright red, swollen, painful? Temperature 37.5-39 C? Loss of appetite, headache, drooling? | Herpetic or other viral infection | Call a doctor and follow all his instructions. A sick child should have separate dishes; isolation is required. Paracetamol will help with pain and fever. Give non-carbonated, non-acidic drinks (water, milk, milkshakes); broths |
| Are your lips dry and bright red? Are there peeling and cracks in the corners of your mouth? | Seizures (cheilitis); may be caused by B vitamin deficiency or food allergies | Talk to your child's doctor . Use hygienic lipstick, baby cream, especially in cold weather |
| Does your child have a constant sore on the tip or edge of his tongue or one sore on the inside of his cheek? | Biting with a tooth | Contact your dentist |
| Does your child have sores on his tongue or on the inside of his cheek? Is he taking any medication, such as an anticonvulsant or an antibiotic? | Possible side effects of the medication | Show your child to the pediatrician - he will recommend what to do |
FOR INFORMATION
"Geographical" language
A healthy tongue is pink in color, its upper surface is covered with papillae surrounded by taste endings. Sometimes parents notice with concern that the child’s tongue is covered with bright red spots with white borders and resembles a map. The spots are painful and appear and disappear. This inflammation of the tongue is the so-called harmless migratory glossitis. It does not require treatment. The reason is not known for certain.
What is tongue swelling, and how dangerous is it?
Edema is an increase in volume of an organ. The tongue may swell and increase in width, and also partially, for example, when a tumor-like lump forms in some place. Such conditions are extremely alarming; they may indicate the progression of a dental disease or an allergic reaction.
Note! Tongue swelling should not be confused with a slight swelling on the tip of the tongue that appears after biting or eating hot, sour foods.
Edema may also be accompanied by the following symptoms of various diseases:
- choking cough and sneezing;
- profuse lacrimation;
- rash on the surface of the face and body;
- feeling of a “lump in the throat”;
- itching in the mouth and sore throat;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness;
- difficulty swallowing;
- speech problems;
- swelling of the tissues of the oral cavity and face;
- feeling of a foreign body in the mouth, etc.
It is important! The most dangerous symptom is swelling of the tongue at its root, when the tissues block the airways, the person feels a sharp suffocation, blushes, and rolls his eyes upward. In such situations, you should urgently call an ambulance or provide emergency first aid to the patient.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Reactive pancreatitis
Reactive pancreatitis is a reaction of the child’s pancreas to some irritants; it is not a separate disease.
Symptoms of reactive pancreatopathy may occur in a child who has recently suffered:
- ARVI
- other inflammatory diseases
- poisoning with poor quality food products,
- it may also be a reaction to a food allergy.
With reactive pancreatitis, spasm of the pancreatic ducts and swelling of the organ itself occurs.
In children under one year of age, the occurrence of reactive pancreatopathy is associated with:
- improper introduction of complementary foods;
- introduction of grape juice;
- introduction of meat products;
- introduction of seasonings before the prescribed age.
These products not only increase gas formation in the intestines, but also disrupt the functioning of the still immature pancreas.
The most common symptoms of reactive pancreatitis are:
- sharp girdling pain above the navel, which decreases in a sitting position with the torso bent forward;
- severe nausea;
- vomiting of gastric contents;
- temperature rise to 37°C, especially in the first few hours from the onset of the disease;
- stool liquefaction;
- dry mouth;
- white coating on the tongue;
- moodiness;
- irritability;
- refusal of games.
If the above symptoms appear, and especially persistent abdominal pain, you should immediately contact a pediatrician, gastroenterologist, or call an ambulance.
In addition to providing first aid, the doctor will prescribe the necessary examinations (ultrasound of the abdominal organs, tests). Based on the examination results, drug treatment is prescribed.
Why does swelling of the tongue still occur?
We list the most common reasons why an organ may swell:
- an allergic reaction resulting in Quincke's edema;
- glossitis disease or an inflammatory process that affects the tissues of the tongue;
- hypothyroidism or diseases of the endocrine system;
- infectious diseases, when the tongue may suddenly swell;
- injury caused by a broken piece of tooth, or incorrect prosthetics;
- disruption of the metabolic process;
- malignant formations;
- complications caused by piercing, etc.
An experienced doctor will help determine the true cause of swelling of the tongue, who will diagnose the oral cavity under the careful supervision of the patient.
Which doctor should I contact?
Professional oral hygiene is an integral part of dental health. To do this, you need to visit a hygienist regularly. It will remove plaque, hard deposits, and prevent caries. Diagnosis and treatment of oral diseases is carried out by general practitioners - pediatricians, therapists, dentists. When the need arises, the child is examined by gastroenterologists, infectious disease specialists, and neurologists.
During diagnosis, urine and blood tests are taken, and bacterial cultures of deposits from mucous tissues are carried out. Sometimes other tests are recommended. For pain and discomfort, the doctor prescribes painkillers and special baths. To avoid tissue irritation, coarse, hot, and salty foods are removed from the diet. Your child should not be given spicy foods. It is important to promptly treat diseased units and constantly maintain oral health.
First aid for angioedema of the tongue
We have already spoken above about first aid - here we will give an example using a specific clinical case with a patient.
Angioedema is considered one of the most dangerous, often leading to death, as it occurs extremely quickly. Not only does a person’s tongue swell, but the neck, inner surface of the mouth, larynx, cheeks, eyelids, lips, and the entire face may also swell. The skin becomes blue, the tongue turns white, and tearing occurs.
What can be done first in case of angioedema of the tongue before the ambulance arrives?
- clear the airways of mucus;
- raise your head a little so that the swollen tongue does not block the airways;
- give an antihistamine, preferably administered intravenously;
- monitor the patient's condition and wait for an ambulance.
First aid for allergic swelling of the tongue
Another common picture is when the cause of swelling of the tongue is taking medications or foods that cause allergies.
The first aid for allergies is to stop taking the food or medication that caused the swelling.
You should definitely take antihistamines and report the situation to your doctor. If your allergy does not allow you to go to an appointment on your own, call a doctor at home.
You should also remember the drug or product that provoked the swelling and allergy, and exclude its presence (and drugs with a similar active ingredient) from your life for the future.
Feeling hot
Menopause
Diabetes
24970 24 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. The feeling of heat that a person experiences occurs due to a sharp expansion and blood filling of small subcutaneous vessels. This condition is called arterial hyperemia. At the same time, the skin turns red and becomes hot.
The lumen of blood vessels is regulated by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. Its changes depend on signals from the vasomotor (vasomotor) center of the central nervous system, hormones, pyrogenic (heat-causing) substances entering the blood, and a number of other factors.
Types of sensations of heat
The vessels are constantly influenced by factors that have a vasoconstrictor or vasodilator effect. For example, under stress, blood vessels narrow under the influence of the hormone adrenaline, and the skin turns pale. At the end of the stressful situation, the vessels relax and fill with blood.
Pathological arterial hyperemia, which is accompanied by a feeling of heat, develops either under the influence of irritants (infections, toxins, tissue breakdown products from burns, pyrogenic substances), or due to a violation of nervous regulation.
There are
neurogenic
arterial hyperemia (occurring in response to irritation of nerve endings) and
metabolic
(caused by the action of local chemical factors). An example of neurogenic arterial hyperemia is redness of the face and neck during hypertension, menopausal syndrome, and also during strong emotions.
Blood electrolytes have a metabolic effect on vascular tension: calcium and sodium constrict blood vessels and increase blood pressure, while potassium and magnesium, on the contrary, dilate them. Metabolic regulators include carbon dioxide, organic acids, and hormones.
Possible causes of feeling hot
Hot, hot and spicy foods can cause a rush of blood to the skin and a feeling of heat.
Alcohol has the same effect on the body.
, which promotes the dilation of blood vessels.
Taking certain medications
can also cause a feeling of heat spreading throughout the body. These include vasodilators, hormonal agents, antidepressants, etc.
The causes of arterial hyperemia and, as a result, feelings of heat can be different. If the regulation of vascular tone is disturbed, arterial hypertension may develop, accompanied by a sudden increase in blood pressure - a hypertensive crisis. The most common cause of this condition is hypertension. However, in a third of cases, arterial hypertension is caused by diseases of the internal organs: acute glomerulonephritis and other kidney damage, adrenal tumors and other diseases of the endocrine system. The magnitude of the rise in blood pressure during a hypertensive crisis depends on the age and individual characteristics of the person. At a young age, symptoms of a crisis may occur at a lower level of blood pressure, and at an older age – at a higher level.
A sharp increase in blood pressure is accompanied by headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances (“floaters”, double vision). Possible numbness of the limbs, a feeling of pins and needles, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath.
Due to a violation of nervous regulation, chills occur, followed by fever, and increased sweating. The end of the crisis is accompanied by frequent urination.
Increased blood pressure and the symptoms accompanying this condition also occur with an adrenal tumor - pheochromocytoma
and other hormone-producing tumors. The tumor secretes large amounts of catecholamines (adrenaline and norepinephrine).
Clinical signs of pheochromocytoma may include headache, sweating, increased heart rate, irritability, weight loss, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, weakness, and fatigue. In some cases, patients may experience fever, shortness of breath, hot flashes, increased thirst, increased urination, dizziness, and tinnitus.
Many women complain of hot flashes during menopause
. Changes in hormonal levels occur even before the cessation of menstruation, during premenopause (menopausal transition). At first, its manifestations are insignificant, and most often they are not given importance or are attributed to the consequences of fatigue and mental stress. Hormonal and metabolic changes, in particular, a decrease in the level of estrogen, progesterone and an increase in the production of GnRH, are accompanied by hot flashes, which can be repeated several times a day.
Women describe them as a periodic short-term feeling of heat followed by chills, increased sweating, and rapid heartbeat.
In most cases, hot flashes only slightly affect your well-being.
Arterial hyperemia and a feeling of heat can be a sign of dysfunction of the thyroid gland, for example, with thyrotoxicosis
. Patients with thyrotoxicosis complain of general weakness, fatigue, irritability, sleep disturbance, sweating, trembling fingers, palpitations, and sometimes pain in the heart area.
Despite the increased appetite, patients with thyrotoxicosis lose weight.
Violation of thermoregulation, which occurs due to accelerated metabolism, leads to an increase in body temperature and causes a constant feeling of heat. The skin becomes warm and moist, the skin vessels dilate, which is accompanied by redness of the face. Sweating increases, nails become brittle, and hair falls out.
Sometimes hot flashes and a feeling of heat in combination with high blood pressure occur with diabetes mellitus
. These symptoms are accompanied by general malaise, sweating, thirst, and an increase in the volume of urine produced.
Which doctors should I contact?
If symptoms such as fever and hot flashes appear regularly, you need to contact, who, based on the complaints and tests, will refer you to or.
Diagnostics and examinations
The appearance of periodic hot flashes, accompanied by a feeling of heat, sweating, and redness of the facial skin, requires mandatory diagnosis.
The doctor evaluates the patient's complaints, taking into account age, gender and concomitant diseases. When blood pressure increases, turning into crises, it is necessary to determine the nature of the pathology - primary (associated with a violation of nervous regulation) or secondary (due to diseases of the internal organs). For this purpose, a clinical blood test and a general urine test, a urine test according to Nechiporenko, a blood test for glucose, cholesterol, and creatinine are prescribed.