Vincent's ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis
One of the reasons that the tongue hurts on the side is Vincent's ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis. With this disease, ulcers appear in the oral cavity, which can be located not only directly on the tongue, but also on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, and even spread further:
- on the gums;
- sky;
- tonsils.
The disease is caused by bacteria: spirochetes and fusobacteria. What is especially characteristic of this pathology is that the ulcers are covered with a dirty gray coating. Vincent's ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis is treated locally with antimicrobial drugs. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are also prescribed.
What is “bad bite”
Bite (or occlusion) is the closing of the jaws at the moment of their natural compression. The standard is considered to be central occlusion, in which the number of points of contact between the teeth of the upper and lower jaws is maximum.
But all other options for interaction of the jaws when closing are malocclusions. Today it is customary to identify the main forms of malocclusion:
- open: there is no tight closure of the dentition
- cross: the antagonist teeth of the upper and lower jaws overlap each other with segments (in one area the lower ones overlap the upper ones, in the other - vice versa)
- mesial: the lower jaw protrudes forward, the upper teeth overlap the lower ones
- distal: the upper row of teeth is pushed forward, overlapping the lower one,
- deep: a type of distal bite when the upper jaw almost completely hides the lower teeth.
Contrary to the opinion of many people who believe that malocclusions are not a cause for concern, you should know: malocclusion of any form in most cases causes dental problems, and sometimes problems of a different nature.
The absence of several teeth and loose jaw closure can provoke:
- deterioration of the gastrointestinal tract;
- frequent headaches;
- development of facial asymmetry;
- premature appearance of facial wrinkles.
An incorrect primary bite can affect the growth of permanent teeth and lead to even greater deformation of the jaw system.
And very often, malocclusions cause permanent injury to the mucous membrane, including a strong bite of the tongue and the inner surface of the cheek. And the presence of open wounds in the oral cavity is a direct path to infection and the development of inflammation.
Don’t leave the problem unattended, contact your orthodontist on time!
Tongue injuries
Another reason why the tongue hurts on the side lies in mechanical injuries to the organ. They occur when eating food with sharp parts (seeds, nuts, undercooked cereals), hitting, or biting. Damage can occur due to a seizure, sports, falls, or various accidents.
If you are absolutely sure that the soreness is the result of an injury, then you just need to give the tongue time to recover. Nevertheless, examination by a specialist to clarify the diagnosis and treatment will not be superfluous.
Other reasons
- Avitaminosis.
A deficiency of microelements can cause sensitivity of the mucous membranes and the appearance of cracks in the tongue. - Allergy.
New dental care products and foods can cause increased sensitivity of the gums and tongue. - Worms.
The presence of parasites leads to the fact that the body does not absorb nutrients and beneficial microelements, which causes the condition of the mucous membrane to worsen. - Hormonal disbalance.
- Stress.
How to determine health status by language. Source: Yulianna Pliskina YouTube channel
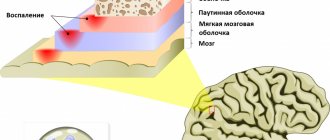
Glossitis
Glossitis
is an inflammation of the tissues of the tongue, manifested in its soreness, changes in color and structure, and the appearance of a dense coating. There is a burning sensation, hyperemia (overflow of blood vessels), food loses its taste, and salivation increases.
If the doctor has diagnosed the patient with glossitis, then the next step is to find out whether this indicates a pathology of other organs. This could be a herpes virus, poisoning with heavy metal salts, etc. Treatment is prescribed depending on the initiating cause, trying to exclude it. It usually includes local antiseptic therapy.
How to speed up wound healing
All wounds heal sooner or later - this is understandable, but the duration of healing largely depends on your actions. How to behave so that the injured mucous membrane heals as quickly as possible and without consequences? Some valuable tips for this case:
- pay increased attention to oral hygiene - this will help avoid infection of an open wound (regular brushing of teeth, careful removal of food debris and bacterial plaque);
- observe the temperature regime, avoid excessively hot or chilled foods for a while: cold is good only as an emergency measure, but subsequently it slows down the healing process; hot food and drinks both irritate and injure damaged tissues;
- use external antiseptics (sprays, ointments, lozenges): the pharmacist at the pharmacy will help you with the choice, ideally you should consult a doctor;
- rinse your mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs: the best for these purposes are chamomile and St. John's wort;
- increase the proportion of foods with vitamins B and C in your diet, which promote wound healing; To heal scratches on the mucous membrane, use ascorbic acid.
Use the advice of traditional medicine with caution: rinsing with medicinal decoctions is not so harmless, you can resort to their help only with the permission of a doctor!
Catarrhal glossitis
If the tongue hurts on the side and a white coating covers its surface, then this is most likely catarrhal glossitis - a special case of this disease. It can be considered as a symptom of other pathologies. In particular, it is called:
- caries;
- stomatitis;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- various infections (measles, diphtheria, etc.).
In addition to pain and plaque, symptoms of catarrhal glossitis include swelling of the tongue and a burning sensation, which is especially worse after eating or talking. The disease is treated by eliminating its causes and rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions.
Dangerous symptoms
Typically, cracks in the tongue do not cause any discomfort; their appearance is often discovered at a doctor’s appointment. But this is not always the case. Sometimes unpleasant symptoms may appear that indicate health problems:
- pain;
- burning, change in taste;
- itching or swelling;
- pain when chewing, problems with speech;
- temperature increase.
If cracks appear on the tongue, there are several of the listed symptoms, then perhaps the cause is an inflammatory process in the oral cavity - glossitis. If the tongue becomes covered with cracks and ulcers, the cause is ENT diseases (tonsillitis, pharyngitis). In any case, professional treatment is necessary.
Inflammation of the salivary glands
This disease is called sialadenitis. Any salivary glands can be affected by it, but painful sensations in the tongue, closer to the base, occur if the sublingual gland is affected. Pathology is caused by viruses or bacteria. Symptoms of sialadenitis include:
- pain at the base of the tongue;
- the formation of a compacted swelling underneath;
- decreased salivation.
How to treat the disease if the tongue hurts on the side precisely for this reason? Antibacterial and antiviral drugs.
Causes of pain in the tongue
13.09.2021
Pain in the tongue can occur for a variety of reasons, and describing them all is difficult. But still, let's try to sort out the most
the main sources of its occurrence, because depending on the cause of the pain, its nature and location, proper treatment is prescribed.
The most common causes of tongue pain include:
• mechanical damage; • inflammatory processes in the oral ; • blockage of the salivary glands; • neuralgia ; • allergies ; • oncological diseases.
The tip of the tongue hurts
It is not always necessary to resort to drug treatment for pain in the tongue, so let's take a closer look at the main
the reasons for its occurrence. For example, symptoms of mechanical injuries are: pain on the tip of the tongue, edge or sides.
In most cases, such damage occurs while eating. The most common sources of origin of these microtraumas include:
• burns from hot food or drinks; • biting with your own teeth ; • scratches or cuts that appear from certain foods; • injuries caused by sharp edges of poor quality fillings.
Therefore, for example, if pain occurs in the tip of the tongue, there is no need to worry too much right away. Most likely it arose as a result of a trivial mini-trauma,
for example, such as a burn or accidentally biting your tongue.
Despite the unpleasant sensations resulting from such injuries, they do not require special treatment and go away on their own, without any negative consequences.
consequences. But it also happens that seeking medical help is still necessary. For example, when painful inflammatory processes appear in
oral cavity , such as: glossary, glossitis and stomatitis.
Pain under the tongue
The localization of pain in inflammatory diseases of the tongue may be at its base. For this reason, pain also occurs under the tongue. There may be pain
concentrated in one place, or move throughout the entire oral cavity.
Such discomfort can also be caused by one of the following diseases:
• allergies ; • gastrointestinal disease; • vitamin deficiency.
If you experience severe pain, excessive salivation, bad breath , swelling of the tongue, which makes speech and breathing difficult, you should
pay attention to such dangerous diseases as abscess or phlegmon . With these diseases, the listed symptoms are accompanied by problems with closing the mouth .
The above diseases are a serious reason to consult a doctor , who, after making a correct diagnosis, will prescribe appropriate treatment,
depending on the causes and nature of the pain.
The base of the tongue hurts
If pain bothers you in the area of the lateral surfaces of the tongue, then in addition to mechanical damage, the following factors can also be its causes:
Smoking can often cause severe pain in the tongue; neuralgia - you should think about it if you do not smoke and have not noticed mechanical
damage, but the pain in the tongue still continues.
Above, we have listed the most common causes of tongue pain, now let’s move on to ways to eliminate this ailment.
Troubleshooting
As already mentioned, if your tongue hurts severely, the first thing to do is seek medical help. Doctors dealing with diseases
oral cavity specialists are an otolaryngologist and a dentist . During the examination, a specialist will exclude possible mechanical damage and determine the main cause.
the occurrence of pain, as well as the nature of its course. Then he will make a diagnosis and determine the required treatment.
Compliance with hygiene rules will help to minimize the risk of inflammatory processes in the mouth , such as: do not neglect hand washing;
do not eat unwashed fruits and vegetables; rinse your mouth after every meal. Also, it is necessary to give up bad habits and constantly
monitor the condition of your teeth . Let us remind you that following these simple rules will help you in the fight for oral health .
Published in Articles without category Premium Clinic
What is in the sublingual area
The tissues located on the lower jaw under the tongue are called the floor of the mouth. Due to the complexity of the structure, as well as the natural functionality of this area, a person often experiences problems accompanied by pain.
Structure of the sublingual region:
- Hyoid muscles - have an elastic structure and are responsible for the motor function of the area;
- Hyoid bone - has an anatomical shape in the form of a horseshoe, located in the muscle layer. It is the only bone in the human body that has no connections with other bones of the body;
- Nerve endings are elements of the peripheral nervous system, responsible for the sensitivity of the sublingual area to various physical, mechanical and thermal stimuli;
- Salivary glands - responsible for the production of saliva, which is involved in the process of wetting the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and the digestion process;
- Blood vessels - provide nutrition to the tissues of the sublingual area;
- Frenules are connecting folds in the sublingual area, responsible for connecting the sublingual tissues with the tongue.
Each of the above elements ensures the natural functionality of the dentofacial apparatus and participates in all physiological processes of the oral cavity.