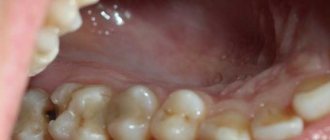
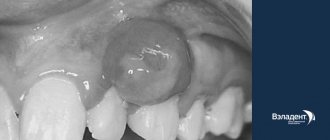
The diagnosis of “wedge-shaped dental defect” is associated in most patients with a wedge-shaped depression at the base of the tooth. But not every cervical defect is wedge-shaped. Moreover, the disease refers to non-carious lesions that require a special approach to treatment. In the “Smile Factor”, the doctor will identify the prerequisites for the formation of such defects, and if the integrity of the dental tissues is already compromised, he will conduct a thorough diagnostic search and restore the tooth using modern techniques.
Restoration. Repairing a chipped front tooth
Direct restoration
Indirect restoration
Restoration of the incisal edge
Selection of material for restoration
A chipped or broken front tooth is not a pleasant occurrence, from which no one is immune. Such an “accident” can happen at any time, even while eating. And how can you smile if instead of a whole tooth there is only half left? Fortunately, you can restore the beautiful shape of your teeth very quickly. This method is called restoration. What it is, what it is like, the main indications - this is discussed in our article.
Dental restoration is a special type of dental services aimed at improving the aesthetics of a smile. This procedure solves several problems at once: it improves the appearance of teeth, gives anatomical shape and restores the function of a damaged tooth.
There are direct and indirect restorations.
Treatment of medium and large wedge-shaped defects
Treatment will consist of filling the wedge-shaped defect and, to be frank, filling such defects is still a big problem in dentistry.
Problem #1 – fillings fall out very quickly. Problem No. 2 – the filling quickly loses its aesthetics in places where it adheres to the hard tissues of the tooth (filling/tooth boundary). Of course, it should be noted that most dentists do not see this as a problem, and redo these fillings every year. Problems arise primarily from the fact that the dentist does not remove the traumatic factor (traumatic load on the tooth, i.e. abfraction), which leads to the persistence of “bending stress” in the cervical area of the tooth... That is. The solution to this problem is to correct everything that we wrote above in the section “Causes of wedge-shaped defects of the abfraction type.”
The second problem is the wrong choice of filling materials. Traditionally, the doctor’s choice here is possible only between two groups of materials: either glass ionomer cement or microphilic composites.
- Glass ionomer cements have advantages: they enter into a chemical bond with dental tissues, are less sensitive to moisture, and have satisfactory aesthetics (which is still significantly inferior to the aesthetics of composite materials).
Cons: high abrasion, discoloration, sensitive to dryness, mouth breathing (therefore, for example, they are not suitable for smokers). Studies have shown that as a result of overdrying, the area of the filling adjacent to the hard tissues of the tooth becomes covered with a small network of cracks, into which dyes then fall. Studies have also shown that exactly the same cracks form when a traumatic load from the antagonist tooth remains on the tooth. As a result, at the end of the first year of service, the filling becomes less aesthetically pleasing if it is located in the smile zone.
- Microphilic composites – advantages: they have very good aesthetics and resistance to wear. However, on the other hand, they are sensitive to moisture and have a very high polymerization shrinkage coefficient. In addition, if the dentist, again, has not eliminated the traumatic load when closing with the antagonist, cracks will also form in the filling made of this material at the border with the tooth tissues. But in general, this material is still slightly better than glass ionomer cements.
Important: however, there is a filling technique that will reduce the negative qualities of each material described. It's called the sandwich technique. Its meaning is that the lower part of the filling is made of glass ionomer cement, and the upper part is made of composite material. Today, this is the only possible way to make high-quality fillings when filling wedge-shaped defects of medium and large size. We hope that our article was useful to you!
Direct restoration
During direct restoration, the doctor places a filling material on the tooth. It is comfortable and flexible, able to take the shape specified by the dentist. The color does not differ from the shade of native enamel, and at the same time it is highly durable.
This method is suitable for minor corrections:
- restoration of chipped front teeth;
- crack in the enamel;
- tooth restoration after removal of fragments destroyed by caries;
- color correction;
- gap between teeth.
Stages of direct restoration
- The doctor places a rubber dam on top of the tooth. This is a device made of latex and a holding frame. It is necessary to prevent saliva and germs from getting onto the work area, otherwise this will worsen the properties of the filling material.
- Selection of enamel shade.
- Restoration of teeth with filling material using a matrix. This is a dental instrument that allows you to recreate the anatomy of a tooth. Using the matrix, the doctor verifies the contact gaps between the teeth and maintains the boundary of the layer-by-layer application of the composite.
- Carefully polish the tooth using a brush and paste.
Before the procedure, professional oral hygiene is required. It cleans teeth of plaque and microbes and makes it possible to accurately determine the color of the enamel.
Advantages
- Efficiency. Tooth restoration can be done in one appointment.
- Naturalness. The shade is selected in accordance with the shade of your natural teeth.
- Safety. The affected tooth does not require grinding; neighboring teeth also remain unharmed.
One of the disadvantages is that over time, teeth restored with composite material may become dull. Most often this happens due to non-compliance with hygiene rules and the wrong choice of toothpaste.
Artistic restoration of teeth
What factors provoke the destruction of tooth enamel?
The integrity of tooth enamel also depends on the quality of hygiene procedures when using the “correct” brush. If food debris and soft plaque are not removed from the surface of the teeth in a timely manner, acid-forming pathogenic bacteria begin to actively multiply in them. In this case, the acidity of the environment increases sharply, and under the influence of acid, demineralization of the enamel coating occurs. The loss of calcium leads to the destruction of enamel and the looser and softer dentin located underneath.
It has been noted that a wedge-shaped defect is often formed:
- abuse of carbonated drinks and sour juices;
- in patients with malocclusion - due to non-physiological movement of the jaws chewing food and increased chewing load on individual teeth;
- when correcting the bite with braces;
- in patients with periodontal diseases, accompanied by subsidence of inflamed gums and, accordingly, exposure of the necks of the teeth.
Even properly selected treatment helps to avoid undesirable consequences only if the problem is identified at an early stage. Therefore, patients should promptly seek dental care when the very first signs of pathology are detected.
Restoration of the incisal edge
Enamel is the hardest tissue in our body. But over time, it becomes thinner, including due to improper brushing techniques or the use of abrasive pastes. This is fraught with the appearance of microcracks and chips on it. Especially at risk are those who have bad habits: chewing seeds, nuts, or the tip of a ballpoint pen. Restoration of the cutting edge of the tooth helps to correct the shape of the tooth and its cutting edge, and hide enamel defects.
This is not an easy procedure that requires painstakingness and creativity, because the anatomical shape of everyone’s teeth is different. In addition, the tooth has a relief, individual shade and transparency. The specialist’s task is to make sure that the restored tooth does not differ from the rest.
Front Tooth Reconstruction. Source: Futurism YouTube channel
Few people know that the color of the enamel changes from the neck to the cutting edge. It seems that the changes are insignificant, but if this feature is not taken into account, the restored tooth will look like a plastic crown. The same can be said about transparency.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are many reasons for the appearance of a wedge-shaped defect. Among them
- Aggressive tooth brushing. We are talking about excessive pressure on the teeth, chaotic movement of the toothbrush. For daily care, the brush should be directed from top to bottom using soft scrubbing or circular movements. If you rub your teeth horizontally, you injure the enamel. Do not use brushes with hard bristles.
- Exposure to acids that come from food. Their suppliers are citrus juices and soda. Acid disrupts the natural protection of teeth and the enamel wears off faster when brushing your teeth or chewing food.
- Malocclusion. In this case, the load between the teeth is distributed incorrectly and additional pressure falls on the area of the transition of the crown to the root of the teeth. Additional risk factors are bruxism (teeth grinding), dystonia of the masticatory muscles, and dental defects.
- Frequent teeth whitening. Enamel is destroyed not only by uncontrolled home bleaching with lemon juice, soda and improvised abrasive substances, but by professional procedures if carried out more often than 1-2 times a year. To avoid becoming the owner of tooth enamel wearing away in the cervical area, replace frequent whitening with remineralization and fluoridation. Whitening pastes should also not be used constantly. They work great in courses lasting no more than 30 days, 1-2 times a year.
- Gastrointestinal diseases and hormonal imbalance. Increased stomach acidity can weaken the enamel and lead to the formation of a wedge-shaped defect. Women over 40 years of age are also at risk - hormonal changes lead to calcium leaching.
- Gum diseases. With periodontitis and periodontal disease, the necks of the teeth are exposed and their thin enamel is destroyed by acids and plaque bacteria.
- Alcohol abuse and smoking. Alcoholic drinks and tobacco smoke are aggressive to the microflora of the mouth. This leads to demineralization and tooth decay.
- Frequent consumption of solid foods.
- Incorrect treatment by an orthodontist.
- Heredity.
- Chemotherapy in the treatment of cancer.
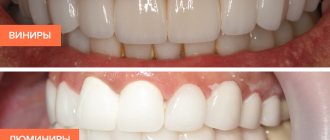
Selection of material for restoration
For direct tooth restoration, special composite materials are used, which have high strength, ductility, and also help achieve the effect of tooth transparency.
Most popular materials:
- Filtek (USA) - considered a universal material. It is suitable for restoring anterior teeth and chewing teeth. The main thing is to choose the right shade.
- Venus (Germany) is a more expensive option for the restoration of anterior teeth. The material consists of nanoparticles, which helps to achieve maximum aesthetic effect.
- Enamel Plus (Italy) - sometimes it is called a “chameleon” for its ability to adapt to its native enamel color.
- During indirect restoration, ceramics, zirconium dioxide, and metal ceramics are used.
Treatment of small wedge-shaped defects –
Not deep wedge-shaped defects of small size (up to 0.5 mm) - usually there is no urgent need for filling. But if the doctor sees a high risk of rapid deepening of the defects, then they are filled with liquid-flowing composites, for example, “Flow It” or “Filtek Flow”. Liquid-flowing materials are used because they have high elasticity (but only with a material layer thickness of up to 0.5 mm). The high elasticity of the material makes it possible to partially compensate for the pathological occlusal load from antagonist teeth.
If the dentist says that filling can be delayed, then the emphasis in treatment should be on increasing the strength of the enamel to mechanical and chemical factors (but before that, again, you need to visit an orthopedic dentist and grind down the incorrect contacts between the antagonist teeth). What will you need to do to strengthen your teeth enamel...
Firstly, regular courses of remineralizing therapy with calcium-containing preparations, and secondly, fluoridation of tooth enamel (it is best to start doing both only after removing plaque from the dentist). It must be said that dental clinics use more effective drugs with higher concentrations of active components, but you can come up with something at home.
- Professional remineralization and fluoridation – one of the most effective drugs that allows for simultaneous remineralization + fluoridation is the drug “enamel-sealing liquid Tiefenfluorid” (made in Germany). This drug contains 2 components: the first component is highly active calcium hydroxide, the second is highly active fluorine. The components are applied to the teeth by the dentist one by one.
This product has only 1 disadvantage - its price. A more budget-friendly solution, but still quite effective, would be to treat teeth with fluoride varnish or fluoride gel (this will cost about 1,000 rubles). It will also be much more effective than home therapy, because... The fluoride concentration in the best medicated toothpastes is only 1,450 ppm, while the fluoride concentration in dental products is 20,000 ppm.
- Remineralization and fluoridation at home – there are semi-professional products that have a more or less good effect, but only with regular long-term use. A good effect can be achieved with the following combination of products. To brush your teeth 2-3 times a day, use your choice -
→ ROCS Medical Minerals remineralizing gel, → or PRESIDENT Unique toothpaste.These products contain large amounts of active calcium. After brushing your teeth, do not immediately spit out the foam, but hold it in your mouth for at least 1 more minute - this will allow more calcium ions to penetrate the enamel. After this, it is necessary to fix the calcium that has just penetrated there into the enamel using a fluoride rinse. We recommend choosing Elmex mouthwash (contains 250 ppm fluoride as amino fluoride) and rinsing your mouth for 1 minute.
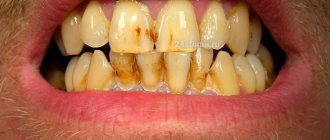
How is cervical caries diagnosed?
If the carious lesion is localized on the visible part of the tooth, the doctor makes a diagnosis after an external examination. But to confirm it, a special test is performed using a dye solution. It is applied to the enamel and left for 3-4 minutes. The affected area turns blue. After a few hours, the dye is completely washed out of the mouth.
The doctor may also prescribe an x-ray to assess the nature of the spread of caries, the depth of the carious cavity, the condition of the nerve endings, etc. Based on the results of the examination, a treatment method is selected. It is determined, first of all, by the stage of the disease.
Classification
In practical dentistry, classification is carried out based on the causative factors that caused V-shaped damage to the teeth.
- Mechanical factor.
The formation of wedge-shaped pathology occurs due to aggressive brushing techniques and exposure to overly abrasive toothpastes.
- Erosive factor.
The disease occurs due to frequent consumption of acidic foods and juices, as well as the influence of aggressive environments in the body, which “corrode” the enamel, causing its destruction. This also includes the impact on the enamel of chemically altered saliva (there is a decrease in some protective enzymes in it) and hot cigarette smoke, which causes dehydration and destruction of dental tissue.
- Occlusal factor.
Chipping of pieces of the tooth in the cervical area is observed when there are too many mechanical loads on the tooth, if the patient has an abnormal bite or bruxism.
In addition, wedge-shaped defects are classified according to their location.
- Cervical.
It mainly affects the upper small molars, lower and upper sixes.
- Coronal.
They are located at some distance from the gums (usually no more than 2 mm). They often occur acutely, the transition from the first to the last stage occurs in just 1 - 2 years. As a rule, the anterior teeth of the upper jaw and sometimes the small chewing teeth below are affected.
- Root.
They are localized on the root part of the canines of both jaws, premolars below and sevens above.
- Combined.
They combine several forms of damage at the same time, for example, coronal and cervical.
V-shaped defects are also distinguished by stages: initial, superficial, medium and deep. The speed of their transition to one another depends on the activity of the process:
- in acute cases, the stages replace each other within 3–5 months;
- in case of chronic course – for 2 – 3, and sometimes 4 years.
At the initial stage, the gap-like defect is not visible to the naked eye and is practically not felt, but can be determined by probing the tooth and studying its surface with a microscope.
At the stage of the superficial process, slight sensitivity of the tooth appears; a wedge-shaped formation up to 3.5 mm in length and no more than 0.2 mm in depth is visible along the gum.
When the defect passes beyond the transition between enamel and dentin, the tooth becomes quite sensitive to chemical and temperature irritants, as well as to touch with a brush. The dimensions of the wedge increase both in length and depth, which is fraught with opening of the pulp chamber. This happens at the next stage, when the wedge reaches 4.5 - 5.5 mm in length, and can be up to 0.6 mm in depth. If there is a strong mechanical impact on such a tooth, the crown may break off.
What you can do at home
We described the features of caries treatment at different stages in the dentist's office. Many people are interested in the question of what to do if the disease develops at home, whether it can be stopped on their own. The only thing available to the patient is prevention. If a carious lesion has already begun, it is impossible to reverse it with the help of rinses or folk remedies.
However, you can slow it down or stop it if you follow a number of simple rules:
- brush your teeth twice a day and rinse your mouth after eating;
- give up sweet foods and sodas;
- quit bad habits, in particular smoking;
- use irrigators to clean the oral cavity.
In addition, do not forget to check your teeth every six months, even if you are not worried about caries symptoms.