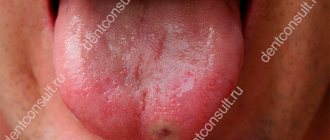
Many people experience symptoms of “astringent tongue” at different times in their lives. Signs of manifestation are expressed by a feeling of dryness in the throat or mouth, thirst, difficulty in swallowing food, bad breath, hoarseness in the voice after waking up, roughness of the tongue, and the formation of cracks on the lips.
These problems are addressed only after the true cause has been determined. Often, a feeling of viscosity in the mouth is a concomitant symptom of another disease. Therefore, you cannot do without consulting a doctor.
Causes of the problem
Constant astringency in the mouth indicates the following pathological conditions:
- HIV AIDS;
- impaired glucose tolerance;
- Hodgkin's disease (oncological disease affecting the lymphatic system);
- cystic fibrosis;
- parkinsonism;
- iron deficiency in the body due to an unbalanced diet;
- hormonal imbalance;
- breathing problems;
- diarrhea;
- damage to muscle or nerve fibers localized in the neck;
- age-related changes.
In rare cases, discomfort in the mouth that persists for a long time may occur after surgery to remove the salivary glands or be the result of a head injury.
Dry mouth, lips, and throat can be temporary, permanent, or morning
Temporary astringent sensations are usually associated with:
- consuming large amounts of excessively salty foods;
- runny nose (acute, chronic);
- insufficient humidity and high air temperature in the living room;
- long-term high-intensity sports;
- smoking (including hookah - smoke dries out the oral mucosa).
Dryness and accompanying symptoms may appear the next day after taking certain drugs.
Medicines
The reasons for the appearance of a feeling of viscosity on the oral mucosa may lie in drug treatment. Most often, changes in taste sensations are provoked by the following drugs: anxiolytics (anti-anxiety drugs), analgesics, laxatives, antifungal and antihistamine medications.
Important! It is noteworthy that dietary supplements can also cause discomfort and a tart taste in the mouth and lips. If such a problem arises, you should carefully read the instructions for the dietary supplement - perhaps a feeling of viscosity on the oral mucosa is listed as a side effect.
Other factors
Sticky saliva after eating is a common problem that many people experience. So, it dries and astringents the mouth after persimmon - a healthy fruit rich in vitamins and minerals, which contains tannin in large quantities (it is this substance that causes some discomfort). To avoid unpleasant sensations, lovers of this fruit can first place it in the freezer, dry it, or, conversely, heat it.
If the feeling of astringency, viscosity in the oral cavity is accompanied by the appearance of plaque on the tongue, these are sure signs of diseases of the digestive tract (stomach, liver, gall bladder)
Features of treatment
Treatment of burning tongue is aimed at eliminating the cause and relieving symptoms. If you have tartar, it is recommended to have your teeth cleaned. If the prostheses are at fault, contact a specialist and replace/correct the design. In case of gastrointestinal diseases, treatment of the identified pathology should be carried out in parallel.
- Rinsing with antiseptics, for example, with “Furacilin”, using “Miramistin” in the form of a spray, will help remove a slight tingling sensation,
- in case of mucosal injury, Lugol's solution can be used,
- the application of “Lidocaine”, “Novocaine” or other anesthetics can relieve pain,
- in case of a neurotic nature, the doctor will prescribe appropriate medications (tincture of valerian, motherwort or more effective sedatives).
In some cases, Miramistin in the form of a spray will help.
In each case, treatment is prescribed only by a doctor, based on diagnostic data.
Types of viscosity
There is morning, constant, temporary dry mouth. The first is usually associated with drinking alcohol the day before (hangover) or nasal congestion. Constant viscosity indicates hormonal transformations in the body (for example, during menopause in women), is a consequence of smoking, eating a large amount of salty foods, or natural age-related changes. Short-term astringency is the result of increased dry air, increased physical activity, or prolonged use of certain groups of medications.
Associated symptoms
Often dry mouth and sticky tongue are not the main disease or its symptoms.
As accompanying symptoms with these phenomena, the following occur:
- Increased sweating;
- Thirst;
- Cracked lips and dryness.
The appearance of these signs does not mean the presence of a dangerous or serious disease.
If the patient is aware of his illness, he may notice more specific symptoms:
- Viscosity in the oral cavity is caused by a deficiency of vitamin A, which is accompanied by various problems with the skin, conjunctivitis, severe brittleness and dryness of hair, peeling and pale skin;
- Iron deficiency anemia provokes, in addition to dry mouth, dizziness more often than usual, tinnitus, fatigue, and severe weakness;
- Patients with diabetes suffer from polyuria and rapid weight loss.
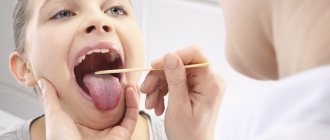
Diagnostics
Since astringency and dry mouth can be associated with various pathological conditions and malfunctions of the body, only a doctor should determine the cause of this phenomenon, based on the accompanying manifestations. Thus, a tart taste, viscosity in the oral cavity in combination with general weakness, white tongue nausea, pain in the stomach, as a rule, indicate gastritis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of this digestive organ). It is also accompanied by the release of acid from the stomach into the esophagus (heartburn).
The feeling of viscosity on the oral mucosa is a signal notifying of various health problems.
If all of the above is also accompanied by a high body temperature, we are talking about a bacterial or viral infection. Viscosity, mucus, bitter taste, gray coating on the tongue, accompanied by acute pain in the right hypochondrium, indicate the presence of gallstones.
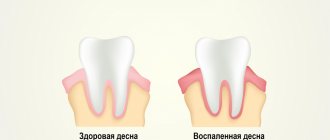
Important! The presence of a metallic taste in the mouth is a sure symptom of gingivitis (inflammation of the gums).
You can determine why your mouth feels sticky using the following diagnostic methods:
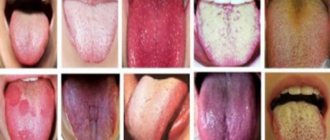
Why is there a white coating on my tongue?
- professional examination of the oral cavity by a dentist;
- hormonal research;
- urine and blood tests (including vitamins and minerals);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- MRI of the head and neck;
- endoscopic examination of the condition of the gastric mucosa;
- tests for tumor markers, infections, etc.
In addition, during the examination, the doctor must constantly monitor the patient’s blood pressure, since its “jumps” can also be one of the factors causing the appearance of viscosity on the oral mucosa.
How does the disease progress?
Candidiasis has two forms: acute and chronic. Options for the acute form:
- The appearance of a whitish coating.
White masses appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth, often with a cheesy consistency. The plaque is easily removed, but forms again. Under the removed plaque you can notice severe redness and slight swelling.
- Atrophic candidiasis.
In this case, the mucous membrane, on the contrary, dries out, and plaque does not appear. Redness quickly forms, the lingual papillae begin to atrophy and the roughness of the tongue gradually smoothes out.
The chronic form has the following manifestations:
- Hyperplastic candidiasis.
The mucous membrane becomes red and swollen, and white or gray plaques form on it.
- Chronic atrophic candidiasis.
Appears in the mouth of those who wear dentures.
Both of these forms occur in different ways:
- the acute form of the disease lasts no more than 2 months;
- Chronic candidiasis can last more than 2 months.
Solution
Treatment is selected by a specialist based on the results of the examination and depends on the reason for the discomfort. If treatment measures are not taken in a timely manner, a lack of saliva will lead to an increased risk of developing various dental diseases.
In addition, a malfunction of the salivary glands will certainly affect local immunity (the protective functions of the oral mucosa). So, subsequently, patients may encounter the following problems: candidiasis, sore throat, stomatitis, inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
Surgery to remove salivary glands subsequently leads to dry mouth
In this regard, if for unknown reasons you begin to feel a knot in your mouth and such sensations persist for a long time, you should seek medical help from a therapist. If necessary, the doctor will refer you for consultation to a more specialized specialist - a dentist, gastroenterologist, neurologist.
How to prevent burning in the future
In order not to encounter a burning sensation of the tongue and oral mucosa, you need to follow preventive measures:
- Try to sleep at least 7-8 hours a day. This will protect you from stress and weakened immunity - phenomena that often provoke a feeling of heat on the mucous membrane.
- Any bad habits, be it cigarettes or alcohol, must be eliminated from your lifestyle.
- Follow the basics of proper nutrition. Include as many fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet as possible. This is useful not only for teeth and gums, but also for the gastrointestinal tract.
- Maintain good hygiene. Simply brushing your teeth regularly is not enough; you need to visit a specialist once every 6 months, use mouth rinses, dental floss and other aids.
- Pay attention to the composition of hygiene products. If you have sensitive gums and teeth, try to choose toothpastes and rinses with gentler ingredients that do not cause a burning sensation in the mouth.
- Limit your use of chewing gum. Choose only those that do not contain sugar or xylitol.
- Reduce your intake of bitter, hot and sour foods.
- Avoid treating damaged areas with products based on alcohol, potassium permanganate and brilliant green.
When you notice the first unpleasant symptoms, contact a specialist for proper diagnosis and timely treatment.
Prevention
If the feeling of a sticky mouth is not associated with pathological processes in the body, following simple rules will help prevent the recurrence of discomfort. So, you should drink more water, monitor the temperature and humidity in the living (working) room, and ventilate it more often.
It is mandatory to visit the dentist at least once a year and undergo appropriate treatment. As you can see, the feeling of viscosity on the oral mucosa is just a signal notifying about various malfunctions in the body. Timely identification of the causes of this pathological phenomenon and appropriate treatment will help to avoid more serious health problems.
Causes of oral candidiasis
How does the disease occur? The fungus Candida lives in the body from birth and, under certain circumstances, provokes illness. What becomes the trigger for infection:
- weakened immunity;
- taking antibiotics;
- long-term use of removable dentures, especially if they do not fit tightly;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- smoking;
- oncology;
- use of inhalers for asthma;
- excess simple carbohydrates in the diet;
- pregnancy period;
- infancy or old age.
It can be seen that there are many reasons, often they act together, less often - individually. In general, oral candidiasis is rare in adults. It mainly affects children in the first years of life and older people. Among these categories, the prevalence of the disease reaches 10%.
Child's tongue burns
Experts call the most common reason for a child's tongue tingling to be a decrease in immunity due to a lack of vitamins, minerals and nutritional compounds. In childhood, the need for these substances is especially high. Even the slightest deficiency can provoke a number of disorders in the body, the symptoms of which include burning of the mucous membrane.
Poor dental hygiene, malocclusion and other dental problems are also common in children and cause inflammation in the mouth. Moreover, it is children who are most likely to get an infection in their mouth or get injured (a child can “taste” metal on their tongue in the winter, bite it while rushing while eating, and so on).
In childhood, a lack of vitamins and minerals can cause burning of the mucous membrane
Important! The reason why a child has a burning sensation in his mouth may be a diet that is inappropriate for his age. For example, young children should not be given foods that are too salty, smoked, or spicy. The baby's mucous membrane has increased permeability to salt, medications, herbs and other active substances; their high concentration in food promotes rapid absorption and subsequent drying of the mucous membrane. Therefore, you need to be careful when preparing a children's diet.
Diseases that cause increased salivation
Experts note a number of diseases that cause our salivary glands to work hard. Among them: central and peripheral paralysis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, mental development disorders, abnormally large tongue, Parkinson's disease, pregnancy (severe toxicosis), poisoning, stroke, rabies.
In addition, there are a number of drugs that cause excess salivary fluid. These include: drugs against schizophrenia, antiepileptic drugs, as well as medications prescribed to patients undergoing radiotherapy. The common medical term for excess salivation is sialorrhea or hypersalivation.
What can you do at home?
How to remove an unpleasant symptom at home? To do this, you can use the following techniques:
- put ice on the itchy area,
- rinse with soda solution, water with added honey (if there is no allergy), potato juice,
- chew sugar-free gum
- rinse with herbal decoctions - chamomile, coltsfoot, oak, sage,
- hold a piece of propolis in your mouth.
Rinsing with a decoction of oak bark will help in treatment.
Recovery will come faster if you exclude damaging factors: alcohol and cigarettes, sour foods and drinks, soda, spicy foods.