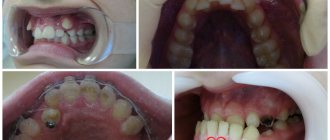
What is retention
Retention is a delay in the growth of baby or molar teeth. With this pathology, the tooth may erupt, but not completely, but can be barely visible above the gum, and it can also grow only under the gum, not showing out at all. First of all, this disease affects the second premolars and third molars located on the lower jaw, as well as the canines of the upper jaw. Maxillary canine impaction is much more common in women. This pathology can occur on one side of the jaw or on both sides at once. Canine impaction in the lower jaw is a very rare occurrence. Impaction of primary teeth is also extremely rare. Such disorders in children can be caused by an acute lack of vitamins in the body or serious pathologies during teething. Impaction of primary teeth can be caused by severe rickets.
Why is it dangerous
Taking into account the number, location, size of the jaw and the age of the patient, the negative consequences are:
- delayed eruption of primary teeth;
- the formation of a diastema - a gap between the front incisors;
- damage to the mucous membrane leading to inflammation;
- inability to comply with hygiene measures;
- violation of the chewing process and digestive problems;
- the impossibility of proper oral hygiene and, as a consequence, the spread of carious bacteria.
Types of pathology
Teeth eruption disorders can be of two types: complete and partial, and the tooth, respectively, impacted and semi-impacted. The last type means that the tooth has erupted a little, i.e. visually observed above the gum. The impacted tooth is completely hidden by the gum and is not accessible to palpation. According to the depth of their occurrence, such teeth can be tissue embedded (the tooth is located in the gum tissue) or bone embedded (lies in the jaw bone). Such teeth can be located:
- Angularly, i.e. at an angle.
- Vertical.
- Horizontally.
Sometimes there are so-called reverse impacted teeth, most often these are the lower eighth teeth. In such teeth, the upper part is turned towards the jaw, and the roots are turned towards the alveolar edge. There are also symmetrical, unilateral or bilateral tooth retention.
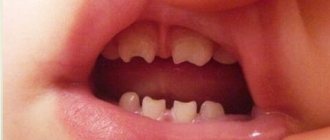
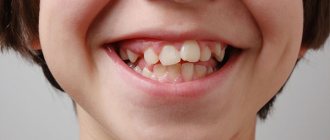
Treatment of supernumerary teeth in children
Babies sometimes develop their first extra teeth immediately after birth. In this case, breastfeeding is a difficult test - the mother's nipple is constantly injured, and the baby's mucous membrane is damaged. In this situation, the teeth need to be removed urgently. If the supernumerary tooth erupted during the period when the child’s milk teeth were not replaced by molars, it will be removed. And to correct the bite, the intervention of an orthodontist will be required.
Difficulties arise if the extra tooth turns out to be impacted or semi-impacted - that is, it did not erupt and remained under the gum. Then dentists will prescribe special procedures:
- vibration stimulation;
- stimulating massage;
- electrical stimulation.
This will help speed up teething. Then the dentists decide whether to remove such a tooth or leave it. Sometimes doctors decide to save extra teeth if they do not interfere with the remaining teeth erupting in their place and do not spoil the bite. Modern techniques quickly solve the problem of hyperdontia if you consult a doctor at an early stage. Therefore, Family Dentistry specialists recommend visiting the dentist twice a year and teaching children to do this from an early age.
Why does a canine or molar not appear?
The concept of retention refers to the anatomical specificity of the jaw or an anomaly in the formation of the tooth germ. Experts believe that this pathology arose in modern society as a result of eating too soft food, i.e. people have practically stopped chewing solid food. Other reasons why retention may occur:
- improper feeding of the child;
- reduced immunity associated with exposure to infections;
- delay in replacing milk teeth with molars;
- the presence of supernumerary teeth that prevent the eruption of a permanent tooth;
- incorrect location of the permanent tooth germ in the jaw bone. With this pathology, the crown of the tooth is directed towards the root of the adjacent tooth, thereby preventing its appearance and the eruption of neighboring teeth;
- bad heredity.
Reasons for retention
Most often, the reason for the development of retention is associated with the incorrect location of neighboring teeth, which become an obstacle to the eruption of retention teeth. In other cases, the problem may be due to too dense bone or gum tissue.
Other factors influencing the development of pathology include the following phenomena:
- supernumerary (abnormally large number of teeth),
- diseases of internal organs, which leads to disruption of the full development of the entire skeletal system,
- loss of baby teeth at too early an age,
- genetic predisposition.
The main symptoms of the pathology
Retention in dentistry is quite common, and there are some signs by which this pathology can be detected:
- pain in the gums, radiating to the ear and temporal part;
- regular injury to the same place in the oral mucosa;
- numbness and swelling;
- painful sensations when opening the mouth and while chewing food;
- mobility or displacement of teeth;
- deterioration of general health due to the inflammatory process (fever, weakness, chills, etc.);
- the appearance of a cyst or abscess.
What can happen if you refuse the help of a specialist?
If the tooth root remains under the layer of gum tissue, decay can spread to neighboring units. In this case, treatment will be longer and more expensive. The main symptoms of this problem are a strong odor from the mouth and periodic pain that radiates to the head. Harmful microorganisms will begin to accumulate under the gums, which can lead to the development of caries.
In 99% of cases, the patient has a small sac with purulent filling at the apex of the root. After some time, it inevitably turns into a painful swelling called gumboil. The only correct solution when gums grow on a tooth is to quickly contact an experienced dentist. It will not only eliminate inflammation, but will also be able to save the destroyed unit.
previous post
What happens if you swallow toothpaste?
next entry
Elimination of anomaly
Treatment of retention is a rather complex process that requires qualified assistance from dentists of several specializations. Treatment is selected individually for each patient and depends on the clinical picture of the oral cavity. The first question that a dentist needs to decide is whether to remove or save a diseased tooth. There are several treatment methods, most often this is a surgical intervention in which a specialist cuts the gingival hood so that nothing prevents the tooth from erupting outward. Surgical procedures of this kind are used in situations where the tooth grows correctly and does not interfere with neighboring teeth. In other cases, most often, the tooth is removed. Removing an impacted tooth is a rather difficult operation. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia, after which the gum is cut, and the specialist uses a bur to create access to the tooth, after which it is completely removed. Then a special medicine is placed into the tooth socket. If necessary, sutures are applied and removed ten days after the procedure. Swelling may occur after removal of an impacted tooth. Most often, after removing such a tooth, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and painkillers. Also, the patient, for the first few days, needs to stop eating solid foods, hot and cold foods and drinks.
Causes of hyperdontia
There is no consensus among experts about the reasons for the appearance of extra teeth. There are several versions:
- hyperdontia is a manifestation of atavism;
- the embryonic plate has split into too many tooth germs;
- genetic and hereditary factor.
It is not possible to prevent hyperdontia, so we recommend that parents pay more attention to the dentist’s findings. Timely measures are a guarantee of successful treatment.
A wisdom tooth remains in the gum - is this critical?
Retention or partial eruption is characterized by incomplete emergence of the crown above the gum. Only 1-2 bumps or part of the tooth crown may appear. Retention can be independent or together with dystopia - incorrect positioning of the molar. Symptoms of the disease will depend on the individual clinical situation.
Depending on the location, retention can be vertical, horizontal or angular. With a vertical crown, the tooth crown is located normally in the bone, in accordance with other teeth. Horizontal is characterized by the location of the tooth perpendicular to the others, horizontally to the arch of the jaw. With angular retention, the crown is tilted to the side. According to the depth of its location, the tooth can be covered only by gum, but by a bone plate.
Retention is accompanied by the ingress of food debris and plaque under the gum. This causes inflammation, redness, tissue swelling, and pain. Pericoronaritis may occur - acute inflammation of the gums and mucous hood above the crown of the impacted tooth. The disease can be serous and purulent, causes acute pain, hyperemia, tissue swelling, and makes it difficult to open the mouth.
In most cases, a tooth in the gum is a source of various complications: pericoronitis, the formation of caries and its complications, cysts, stomatitis, periostitis, abscess. Therefore, in case of pathology, dentists recommend removal.
To date, exact methods for preventing retention are unknown. General measures include proper hygienic care of the oral cavity and monitoring the correct development of the child’s jaws and bite. As well as timely and correct orthodontic treatment of malocclusions.
Why is retention dangerous?
A partially erupted tooth is covered with a “hood” of adjacent tissues, under which food debris collects and colonies of pathogenic microflora develop, which can provoke purulent inflammation. With complete retention, another problem arises: a tooth embedded in the tissues constantly affects its “neighbor,” causing it to move from its correct position. The situation may sooner or later become more complicated:
- caries of adjacent teeth and resorption of their roots;
- malocclusion, crowded teeth and other dental anomalies;
- pulpitis and periodontitis;
- periodontal cyst;
- pericoronitis (inflammation of the gingival “hood”) and its complication, periostitis;
- purulent lymphadenitis;
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve;
- abscess and phlegmon.
Therefore, when diagnosing retention, the patient is offered the optimal way to solve the problem.
What can be done about an impacted tooth?
- According to indications, based on the general clinical situation, removal of an impacted wisdom tooth may be recommended (especially for patients undergoing treatment with braces for an abnormal bite).
- In some cases, not accompanied by obvious problems, when removal is not necessary, the doctor will suggest observing the tooth.
- Healthy impacted incisors and canines located in the smile zone, subject to certain conditions, can be “pulled out” from the dental tissues and returned to the dentition.
How is retention diagnosed?
Impacted teeth are often detected by dentists in children. They are brought to the appointment by parents who have noticed that after a baby tooth fell out, a permanent tooth did not erupt in its place. Quite often, the problem is revealed during medical examinations of children aged 11–12 years - when the eruption of permanent teeth is delayed. So, if by this time there is still a primary canine in the oral cavity, the child is prescribed an x-ray.
The ideal option for diagnosing tooth impaction is an orthopantomogram. A panoramic photograph of the jaws clearly shows all the upper and lower teeth, located both physiologically and abnormally. Some patients aged 20–30 years have baby teeth, the roots of which have not been resolved due to retention of permanent teeth. Using an overview image, the doctor determines the type of retention, assesses the complexity of the situation and develops a treatment plan.
Indications for removal
Retention can manifest itself as a stage of eruption. Over time, the crown completely appears above the gum and the tooth can function normally. Therefore, the decision on the need for removal should be made by a doctor only after examining and diagnosing the condition of the dental system. Indications for surgery are the following clinical cases:
- Constant pain;
- Complications of eruption;
- Trauma to an adjacent molar;
- Pressure on the dentition and its deformation;
- Horizontal or angular position of the third molar in the jaw;
- Dental crowding, which can be aggravated by wisdom teeth;
- Orthodontic and orthopedic indications, that is, the need for extraction to correct the bite or prosthetics.
What to do after surgery
The recovery period after removing an overgrown root, as a rule, is longer. This is due to the need to cut the gums. Medicines are selected by the doctor individually, depending on the initial condition and complexity of the operation. Typically prescribed:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. The doctor may prescribe oral anti-inflammatory drugs and rinses.
- Painkillers. After any dental surgery, the patient feels pain. There is no need to take painkillers constantly. If discomfort occurs, you can take any analgesic.
- Healing agents. After surgery, it is important to ensure rapid healing of the wound channel. For better healing of the cut gum and tooth socket, the doctor may prescribe medications that accelerate tissue regeneration and promote rapid healing.
It is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, otherwise there is a risk of developing an inflammatory process. After final healing, the patient undergoes prosthetics.
Despite the fact that in the vast majority of cases the overgrown tooth is removed, there are exceptions. For example, if the crown was destroyed due to injury, the root is strong and healthy, a new crown can be built on it. In any case, the doctor makes the decision to remove or preserve the root based on the results of the examination.