Food allergy is one of the most common allergic conditions that develops due to intolerance to certain compounds in certain foods. In recent decades, doctors have noted an increase in the incidence of hypersensitivity to food, which is especially noticeable among the population of developed countries. This may be due to the variety of substances found in them. About half of people suffering from food allergies are children under 12 years of age, but the frequency of manifestations is already significantly increasing among adults.
Sensitization to allergens from food has a hereditary predisposition - many researchers talk about this. For example, Karataeva and Yusupova point out that “approximately half of patients suffering from food allergies have a burdened family or personal allergic history, i.e. either they themselves suffer from some allergic diseases (hay fever, atopic bronchial asthma), or these their closest relatives suffer from diseases” (Karataeva N.A., Karataeva L.A., Yusupova O.I., Inoyatova Sh.K., 2015, p. 128).
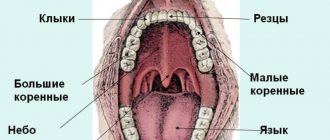
Causes of food allergies
There are several mechanisms for the development of allergies. But a significant proportion of cases are associated with type 1 hypersensitivity. It is explained by the release of immunoglobulin IgE and the activation of basophils. This reaction occurs in response to the entry into the digestive system of protein compounds recognized by immune cells.
Some predisposing factors are unique to children, others are also found in adults. Among the most common reasons are the following:
- Features of allergens in food. The reaction is most often provoked by antigens with high immunogenicity. They easily overcome the aggressive environment of the stomach. They are found in large quantities in whole milk, fish, eggs, cereals, strawberries, citrus fruits, and nuts.
- Hereditary predisposition. Food allergies are associated with hereditary characteristics of the body. They manifest themselves by increased reactivity, disruptions in the functioning of the immune system, as well as other mechanisms.
- Age-related features of the development of the digestive system. Children have high permeability of the stomach walls, and the acidity of gastric juice is lower than in adults. The composition of the microflora is also different. All this creates favorable conditions for the allergen to come into contact with immune cells.
The condition may be associated with the amount of food eaten and the characteristics of culinary processing. There are cases of so-called cross-allergy to pollen and household dust: some food products with similar compounds in their composition trigger an allergic reaction.
According to many researchers, the formation of allergies is facilitated by dietary violations during pregnancy, as well as early transfer of the child to artificial feeding. Gastrointestinal diseases, especially diseases of the liver, gallbladder, and biliary tract, also trigger and contribute to the exacerbation of allergies.
Foods and additives that cause allergies
Doctors Sidorovich and Luss write that “almost any food product can act as an allergen and cause the development of food allergies. However, the most pronounced sensitizing properties are in products of protein origin containing animal and plant proteins” (Sidorovich O.I., Luss L.V., 2016, p. 141). The table shows the most common allergens in food:
| Plant food | Raspberries, strawberries, wild strawberries, black currants, blackberries, pineapple, melon, persimmon, pomegranate, citrus fruits, chocolate, tomatoes, nuts, honey, mushrooms, wheat, soybeans, carrots |
| Animal food | Milk, eggs, fish, crustaceans and seafood, cold processed chicken |
| Supplements | Pesticide residues and agricultural fertilizers in plant foods. Dyes (especially tartrazine, erythrosine, sodium nitrite), flavorings (glutamates), preservatives (benzoates, benzoic acid, sulfites), enzymes, thickeners, emulsifiers, bacteriostatics, flavor enhancers (monosodium glutamate), etc. |
Note that allergen additives provoke so-called false reactions, or pseudo-allergies. In this case, food antigens can act without the participation of allergic antibodies on target cells or activate certain biological systems; they are not based on immune reactions.
An increase in the level of histamine in the blood may not be associated with a true allergy, but with the consumption of foods containing it in large quantities: fermented cheeses, sauerkraut, dried ham, canned food, spinach.
Symptoms of the disease
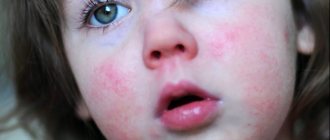
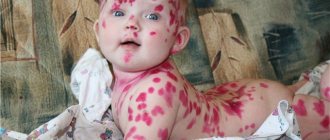
Food allergies often appear within a few minutes of consuming the product. There is a rash, itching, redness, swelling of the skin of the hands, face and neck. Many people complain of a sore throat, heartburn, and bloating. Children and adolescents are at high risk of anaphylactic shock, acute urticaria, eczema, and asthma.
In adults, the following symptoms most often develop:
- chronic urticaria;
- atopic dermatitis;
- rhinitis and conjunctivitis;
- gastritis;
- migraine;
- dermatitis.
According to statistics, skin manifestations are observed much more often. The rash is usually erythematous in nature. Elements of the rash can be located on any part of the skin. Dermatological manifestations persist from several hours to several days, then disappear on their own provided there is no further contact with the allergen.
When it enters the body again, the allergy develops again. There is a possibility that each episode will be more severe and intense.
Food allergies cause gastrointestinal problems within the first hours. The following symptoms are usually noted:
- stool disorders;
- abdominal pain, bloating;
- vomiting
With high allergic readiness, these symptoms develop already at the time of consumption of the allergen. It happens that dyspepsia is accompanied by immediate swelling of the mucous membranes of the mouth, lips, and tongue; nasal congestion.
Some varieties of fish, strawberries, and peanuts cause the most severe systemic reactions - angioedema, anaphylactic shock.
People suffering from bronchial asthma or food allergies often experience an attack that develops as a cross-allergy. Headaches, fatigue, and weakness appear after eating potentially dangerous foods.
Causes and symptoms of sun allergy
It is important to know that the sun's rays themselves are not allergens, they are only provocateurs, a trigger in the chain of an allergic reaction.
Solar allergies can appear both with the first warm rays of the sun, and with prolonged and intense exposure, for example, during a holiday in southern, tropical countries.
Classification of photodermatoses
Photodermatids, depending on the factors that cause them, are divided into:
- exogenous - caused by environmental factors;
- endogenous - caused by internal factors.
Factors contributing to the development of photodermatosis may be:
- A certain skin type is white, thin, with a lot of moles and freckles.
- Acute or chronic diseases of various organs and systems, for example, with pathology of the liver, kidneys, adrenal glands, lack of vitamins in the body, metabolic disorders, as well as any condition that causes a weakened immune system.
- Taking certain medications, especially those with anti-inflammatory effects. Antidiabetic and diuretic drugs can also cause solar urticaria. Photosensitizing drugs include tetracyclines, amiodarone, quinidine, fluoroquinolones, griseofulvin, sulfonamides (the instructions for the drug always indicate possible side and undesirable effects).
- Pregnancy is a period when a woman’s body, due to hormonal changes, can change/intensify its response to solar radiation.
- A combination of the effects of the sun and other irritating external factors, for example, chlorine in the pool, working with chemically active substances, the use of low-quality, “aggressive” cosmetics, various creams, deodorants, oils.
- The influence of several allergens on the body, eating cross-reacting foods with severe hay fever, etc.
Children whose immunity is weakened often suffer from sun allergies after illness.
Symptoms, manifestations of photodermatosis
Manifestations of sun allergies can range from mild irritation to large blisters or spots covering almost the entire surface of the skin. As for time, they can appear after half an hour of continuous exposure to the sun or after some time (up to three days).
It is important to remember that photodermatosis does not always depend on the dose of ultraviolet radiation; it can occur even after visiting a solarium and manifest itself in the form of:
- redness on exposed areas of the body;
- spots that resemble burns;
- rash;
- itching and burning;
- peeling;
- swelling.
Less common symptoms include:
- pustular rashes;
- bronchospasm (attack of suffocation);
- solar syncope – a sharp decrease in blood pressure, loss of consciousness.
In its manifestations, sun allergy often resembles a sunburn, but the distinctive and unpleasant symptom is severe itching, which cannot be tolerated. Another important difference is the clarity of the boundaries of spots or other rashes, which is characteristic only of solar urticaria.
Diarrhea due to food allergies
Researcher Kozyarin points out the high probability of diarrhea with food allergies: “If a person is not treated, then he may experience inflammation of the stomach and small intestine with abdominal pain and constant stool upset” (Kozyarin N.P., 2009, p. 66).
Allergies disrupt the frequency of bowel movements, with diarrhea observed for several days, which is often followed by constipation. This is not harmless, especially for people who already have intestinal problems.
Damage to the walls of the intestines and stomach leads to disruption of the processes of digestion and absorption of nutrients. If measures are not taken in a timely manner, thickening of the walls, a decrease in the intestinal lumen, and serious consequences in the form of persistent stool disorders and abdominal pain are possible.
An allergic reaction disrupts the balance of intestinal microflora . The mechanisms of influence of allergic processes on digestion are so diverse that independent gastroenterological diseases often develop, such as gastritis, peptic ulcers, and enzymatic deficiency in children. At the same time, treatment of these pathologies by a specialized specialist without adjusting the diet and taking measures to eliminate allergies is not always successful.
Diarrhea due to allergies can independently lead to complications - proctological pathologies, water-salt imbalance, and dehydration. Therefore, it is important to resort to symptomatic therapy before basic measures take effect.
Complications
The most severe complication from strong food allergens is anaphylactic shock. It develops due to hypersensitivity to certain foods or ignoring the first signs for a long time. The entry of an allergen into the human body leads to increased symptoms and further development of shock. The authors Pampura and Khavkin come to the conclusion that “in some patients, anaphylaxis appears only if physical activity is preceded by the consumption of a certain product” (Pampura A.N., Khavkin A.I., 2003, p. 1126).
If the allergy is manifested by vomiting and diarrhea, then prolonged contact with the allergen leads to electrolyte disturbances. They, in turn, often require correction in a hospital setting and also threaten human life and health.
Other complications include the addition of a bacterial infection when scratching the skin, the formation of cross-allergy to pollen or household dust.
Diagnosis of sun allergy
If you notice an unusual reaction to the sun, I recommend contacting an allergist or dermatologist, who will prescribe you a certain range of analyzes and tests that can be used to confirm the presence of an allergy or a predisposition to it.
It is impossible to fight a disease without eliminating its causes, so be prepared to be offered a comprehensive examination:
- skin tests (scarification tests, prick tests, patch tests). Skin allergy tests are the fastest, safest and most reliable method of examination in immunology. Testing is carried out for patients from 5 to 50 years old;
- determination of the level of total immunoglobulin E;
- determination of the level of specific immunoglobulin E to household, epidermal, pollen, fungal, food, medicinal and bacterial allergens, as well as insect poison;
- determination of the level of specific immunoglobulins to food antigens - diagnosis of food intolerance;
- examination of sputum and secretions from the nasal cavity.
First aid for food allergies
They independently provide first aid for allergies to food additives, if the person’s life and health are not in danger.
What symptoms indicate a direct threat:
- breathing problems;
- swelling of the neck, tongue;
- altered speech;
- confusion.
All of the above is a reason to call an ambulance . If an allergic reaction appears for the first time, even without symptoms that threaten health, it is necessary to get medical help as soon as possible, especially if we are talking about a child.
If symptoms are not expressed, it is permissible to take the first measures yourself. The following categories of drugs are used for this:
- Sorbents. They allow you to bind and remove harmful substances from the gastrointestinal tract. Such drugs accelerate the elimination (removal) of allergens, alleviate the condition and speed up recovery.
An effective product from this group is Fitomucil Sorbent Forte, which contains the shell of psyllium seeds, as well as the prebiotic inulin and a complex of live probiotic bacteria. Psyllium seed husk is a natural soluble fiber that absorbs water and allergens into a mucilaginous gel. The drug does not irritate the intestinal walls, gently stops diarrhea, promoting thickening of stool.
- Antihistamines. Today there is a wide range of new generation medications that do not have side effects such as drowsiness and are well tolerated. It is better to choose medications from those you have already taken before, or consult a doctor.
For skin manifestations, it is possible to use local agents with antihistamine and soothing, antipruritic effects. Severe allergies, manifested by severe redness and itching of the skin, will most likely require the use of local hormonal ointments and creams.
But remember that they are prescription drugs and cannot be used for longer than the time prescribed by the doctor - usually about 7-10 days for mild to moderate cases. Hormonal drugs for oral administration or injection also require a prescription from a specialist who will develop a suitable regimen for use.
Developed vomiting and diarrhea require action. Taking sorbents will help in the second case, and in case of uncontrollable vomiting, you should seek emergency help. If vomiting and diarrhea occur sporadically, several times a day, it is necessary to replenish fluid loss with the help of special rehydration solutions - pharmacy or self-prepared.
It is necessary to drink enough fluids to prevent dehydration and the occurrence of associated disorders. Kozyarin suggests using herbal tea, decoctions of plants: “chamomile, St. John’s wort, calendula, calamus, valerian” (Kozyarin N.P., 2009, p. 66).
Solar allergy, solar urticaria, photodermatosis, solar herpes
To our general happiness, summer has come, and with it the constant hot sun.
After a long and cold winter, the first rays of the gentle sun attract us to nature. I want to relax, gain strength, strengthen my immune system, and acquire a healthy and beautiful skin tone.
We all know that ultraviolet radiation and, accordingly, the effects expected from it can be divided into positive and negative. The positive ones include: an even, beautiful tan, a decrease in the visibility of cosmetic defects, the production of vitamin D, a lot of positive emotions, giving a charge of vigor and health for the whole year. The negative side of tanning is reflected in faster skin aging, an increased risk of tumor and autoimmune processes, and some people may develop sun allergy (photodermatosis is a broader concept), or as it is also called solar urticaria.
Causes of sun allergies
It is important to know that the sun's rays themselves are not allergens, they are only provocateurs, a trigger in the chain of an allergic reaction.
Solar allergies can appear at the first warm rays of the sun, and in some people, only with prolonged and intense exposure, for example, during a vacation in southern, tropical countries.
Classification
Photodermatids, depending on the factors that cause them, are divided into:
- exogenous - caused by environmental factors
- endogenous – caused by internal factors
Factors contributing to the development of photodermatosis may be:
- A certain skin type is white, thin, with a lot of moles and freckles.
- Acute or chronic diseases of various organs and systems, for example, pathologies of the liver, kidneys, adrenal glands, lack of vitamins in the body, metabolic disorders, as well as any condition that causes a weakened immune system.
- Taking certain medications, especially those with anti-inflammatory effects, antidiabetic and diuretic drugs, can also cause solar urticaria. Such drugs include tetracyclines, amiodarone, quinidine, fluoroquinolones, griseofulvin, sulfonamides (the instructions for the drug always indicate possible side effects and undesirable effects).
- Pregnancy is a period when a woman’s body, due to changes in hormonal levels, can change/intensify its reaction to previously normal things.
- A combination of the effects of the sun and other irritating external factors, for example, chlorine in the pool, working with chemically active substances, the use of low-quality, “aggressive” cosmetics, various creams, deodorants, oils.
- The influence of several allergens on the body, eating cross-reacting foods with severe hay fever, etc.
Children whose immunity is weakened often suffer from sun allergies after illness.
Symptoms, manifestations of photodermatosis
Manifestations of sun allergies can vary from mild irritation to large blisters with purulent contents; by time - can appear after half an hour of continuous exposure to the sun or after some time (up to three days).
It is important to remember that photodermatosis does not always depend on the dose of ultraviolet radiation; it can occur even after visiting a solarium.
- Redness on exposed areas of the body
- Spots that resemble burns
- Rash
- Itching, burning
- Peeling
- Edema
Less common:
- pustular rashes
- bronchospasm (attack of suffocation)
- solar syncope – a sharp decrease in blood pressure, loss of consciousness.
In its manifestations, sun allergy often resembles a sunburn, but the distinctive and unpleasant symptom is severe itching, which cannot be tolerated.
Diagnostics
Despite all of the above, don’t panic in advance, don’t set yourself up for what might happen, because you can’t foresee everything.
If you notice an unusual reaction to the sun, I recommend contacting an allergist or dermatologist, who will prescribe you a certain range of analyzes and tests that can be used to confirm the presence of an allergy or a predisposition to it.
It is impossible to fight a disease without eliminating its causes, so be prepared to be offered a comprehensive examination.
Drug treatment of sun allergy
Important! – contact a qualified specialist at the first manifestations of solar allergy; be careful with the use of traditional medicine, because delaying time and self-medication can lead to worsening of symptoms.
Due to the fact that internal disorders of the body provoke the disease, treatment should be aimed at overcoming both the external consequences and the internal causes of solar allergies.
To cope with the most unpleasant external manifestation - itching, the use of ointments and gels that contain skin-soothing, cooling, wound-healing components will help. Antihistamine drugs that do not have negative reactions to sunlight are usually used. The doctor may also, if necessary, prescribe the use of hormonal ointments, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.
It is imperative to prescribe medications that help normalize metabolism, liver function, and skin cell renewal. In most cases, these are vitamins C, E and B, antioxidants, as well as nicotinic acid.
Timely intake, starting from mid-February - early March, of medications that improve metabolic processes, significantly increases tolerance to ultraviolet radiation and several times reduces the frequency of relapses or makes their clinical manifestations weaker. In addition, in some patients it is possible to achieve a 10-20-fold increase in resistance to sunlight when using phototherapy (repeated irradiation of the skin in gradually increasing doses).
Preventing sun allergies
Remember that rest should be moderately active; you should not burden your body by consuming unfamiliar, exotic food in large quantities, alcohol and tonic drinks - after all, all this is a huge stress for the whole body! And constant exposure to the open sun, despite the fact that the wave range in hot countries differs from what we are used to, can cause the development of solar allergies.
- when preparing for the “holiday” season, start with short sunbathing, gradually increasing the time spent in the open sun;
- It is advisable to avoid solar radiation between 10 and 14 hours - during the period of maximum radiation in the spectrum of 290-320 nm.
- remember that near water, in strong winds, our skin receives several times more radiation;
- try to alternate between being in the sun and in the shade;
- when staying in open areas for a long time, on the beach you can use light capes, panama hats, hats, etc.;
- if you are predisposed to sun allergies, it is recommended to wear clothes made from natural fabrics that cover the body from direct exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- try to avoid taking medications that can cause sun allergies (consult your doctor);
- use cosmetics with a sun filter, consult a cosmetologist or dermatologist which products are suitable for your skin type;
- do not use cosmetics not intended for use in the sun;
- If possible, minimize the use of perfumes, aromatic oils and deodorants.
Remember that timely contact with a specialist will help you avoid or reduce the manifestations of solar urticaria.
After a long and cold winter, the first rays of the gentle sun attract us to nature. I want to relax, gain strength, strengthen my immune system, and acquire a healthy and beautiful skin tone. However, the sun's rays are not always as welcoming as we thought. If you notice the appearance of rashes and spots on open areas of the body that have been exposed to the sun, as well as itching, burning of the skin or a feeling of “pins and needles”, “tingling”, “tingling” - or any other signs of photodermatosis - you should contact an allergist or dermatologist for extensive consultation.
Ultraviolet radiation and, accordingly, the effects expected from it can be divided into positive and negative. The positive ones include: an even, beautiful tan, a decrease in the visibility of cosmetic defects, the production of vitamin D, a lot of positive emotions, giving a charge of vigor and health for the whole year. The negative side of tanning is reflected in faster skin aging, an increased risk of tumor and autoimmune processes, and some people may develop sun allergy (photodermatosis is a broader concept), or as it is also called solar urticaria.
Treatment
The course of treatment can be divided into two parts: the use of medications when symptoms immediately appear and therapy aimed at prevention. Doctor Luss o (Luss L.V., 2005, p. 140).
Antihistamines are not a panacea, since both with true allergies and with pseudo-allergies, it is important to promptly eliminate risk factors for the development of severe manifestations.
The main ones include concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to failure of the digestion process, changes in the permeability of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract, and a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice. For this purpose, enzyme preparations, enterosorbents, and probiotics are used.
The most important point after the first measures is to accelerate the elimination of the allergen and prevent further contact with it. The main stages of treatment look like this:
- Symptomatic therapy: taking antihistamines for first aid.
- Elimination of the allergen from the body: prescribing a hypoallergenic diet, pharmacological methods, or a combination of these approaches. If the “provocateur” entered the digestive system recently (several hours ago), enterosorbents will be especially effective. They bind substances in the intestinal lumen, preventing them from further entering the bloodstream. If allergens have been in the body for a long time or a lot of time has passed after a single exposure, elimination occurs naturally, and sorbents will only help in eliminating symptoms.
- Allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT). This stage follows only after elimination, comprehensive diagnosis, and accurate identification of the provoking antigen.
ASIT is relevant when irreplaceable dishes are added to the list of those prohibited for consumption; the human body is not provided with everything necessary. This method consists of introducing certain dosages of the allergen, which are gradually increased, which allows the development of immunological tolerance.
Author Luss emphasizes that “the attitude towards ASIT in patients with IPA is not yet clear and contradictory. Basically, preference is given to prescribing elimination diets” (Luss L.V., 2005, p. 140). Perhaps this is due to the need to undergo comprehensive diagnostics and constant long-term treatment when the allergy no longer manifests itself. After all, ASIT can be recommended six months after changing the diet. However, this method is the only option to get everything you need from food when you have allergies.
Nutrition for food allergies
The complex of therapeutic measures necessarily includes a nutritional method. Eliminating the cause—the antigen—is extremely important to improve the condition and prevent exacerbations. A complete avoidance of intolerant foods is expected. For convenience, we have provided a list of permitted and prohibited items in the table:
| Allowed | Prohibited |
| Unfortunate bread | Smoked meats |
| Tea | Vinegar |
| Sugar | Fish |
| Boiled lean beef | Mushrooms |
| Butter and vegetable oils | Bird |
| Fresh cucumbers | Nuts |
| Parsley dill | Whole cow's milk |
| Watermelons | Honey |
| Baked apples | Nuts |
| One-day fermented milk products | Fruits and berries: strawberries, melon, pineapple, citrus fruits |
| Cereals: rice, buckwheat, oatmeal | Vegetables: eggplant, radish, horseradish |
Fasting is strictly prohibited for people with chronic diseases, blood diseases, malignant neoplasms, sore throat, other respiratory diseases, liver and circulatory diseases in history.
You will need to limit or eliminate ready-to-eat cereals, pasta (without eggs), ready-made pies, gingerbread cookies, colored marshmallows, and caramels due to the tartrazine they contain. It is necessary to limit the consumption of wine, beer, fruit juices, gelatin, baking mixes, marinades, and most prepared sauces, as they contain sulfites.
There are different options for therapeutic nutrition:
- Grain-free diet. Involves avoiding cereals, flour products, seasonings, and sauces. Preference is given to meat, vegetables, fruits, and dairy products.
- Egg-free diet. Excludes eggs, seasonings, mayonnaise, sauces and creams, pasta, baked goods containing eggs. The diet consists of meat, dairy products, cereals, vegetables, and fruits.
- Dairy-free diet. Milk, milk porridge, cottage cheese, confectionery, and butter are excluded from the diet. The menu is based on dishes of meat, fish, eggs, cereals, vegetables and fruits.
- Diet excluding milk, cereals, eggs.
Thus, it is not necessary to give up all possible allergens. When you consult a doctor, you will receive accurate recommendations. It is important to make your own assumptions about what exactly could have been the source of unpleasant manifestations.
Keeping a diary will help determine which food allergens could cause a response and which ones are not perceived aggressively by the body. At the same time, you should write down not only everything you eat during the day, but also the cooking methods. Note exactly what manifestations of allergies are observed: skin itching, stool disorders, redness of the skin, nausea.
The main feature of nutrition for allergies is not simply to refuse a certain food, but to find an adequate replacement. The diet must remain balanced, otherwise severe restrictions are likely to lead to vitamin and mineral deficiencies. If you are forced to completely give up milk and eggs, your diet should include a variety of meat and fish dishes. It is better to search for alternatives together with your doctor.
Treatment of photodermatosis
Contact a qualified specialist at the first manifestations of sun allergy; be careful with the use of traditional medicine, because delaying time and self-medication can lead to worsening of symptoms.
Due to the fact that the disease is provoked by internal disorders of the body, treatment should be aimed at overcoming both external consequences and chronic diseases and foci of infection.
To cope with the most unpleasant external manifestation - itching, the use of ointments and gels that contain skin-soothing, cooling, wound-healing components will help. Antihistamine drugs that do not have negative reactions to sunlight are usually used. The doctor may also, if necessary, prescribe the use of hormonal ointments, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.
It is imperative to prescribe medications that help normalize metabolism, liver function, and skin cell renewal. In most cases, these are vitamins C, E and B, antioxidants, as well as nicotinic acid.
Timely intake, starting from mid-February - early March, of medications that improve metabolic processes, significantly increases tolerance to ultraviolet radiation and several times reduces the frequency of relapses or makes their clinical manifestations weaker. In addition, in some patients it is possible to achieve a 10-20-fold increase in resistance to sunlight when using phototherapy (repeated irradiation of the skin in gradually increasing doses).
Preventing sun allergies
Remember that rest should be moderately active; you should not burden your body by consuming unfamiliar, exotic food in large quantities, alcohol and tonic drinks - after all, all this is a huge stress for the whole body! And constant exposure to the open sun, despite the fact that the wave range in hot countries differs from what we are used to, can cause the development of solar allergies.
- In preparation for the “holiday” season, start with short sunbathing, gradually increasing the time spent in the open sun;
- It is advisable to avoid solar radiation between 10 and 14 hours - during the period of maximum radiation in the spectrum of 290-320 nm.
- Remember that near water, in strong winds, our skin receives several times more radiation;
- Try to alternate between being in the sun and in the shade;
- If you spend a long time in open areas, on the beach, you can use light capes, panama hats, hats, etc.;
- If you are predisposed to sun allergies, it is recommended to wear clothes made from natural fabrics that cover the body from direct exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- Try to avoid taking medications that can cause sun allergies (consult your doctor);
- Use cosmetics with a sun filter, consult a cosmetologist or dermatologist which products are suitable for your skin type;
- Do not use cosmetics that are not intended for use in the sun;
- If possible, minimize the use of perfumes, aromatherapy oils and deodorants.
Remember that timely contact with a specialist will help you avoid or reduce the manifestations of solar urticaria.