Molluscum contagiosum in children
Molluscum contagiosum is more common in children than in adults. Children up to one year old practically do not get sick with molluscum contagiosum. This is due to the fact that in the first year of life the child’s circle of contacts is small: the child moves in a limited space, often specially prepared for him and under the strict supervision of adults, without trying to come into contact with other children. But as soon as a child begins to actively communicate and independently explore the world, the threat of becoming infected with molluscum contagiosum increases sharply.
The peak incidence of molluscum contagiosum in children occurs between the ages of 2 and 6 years. Immunity at this age is still weak. Children become infected through toys or dirty hands. The virus penetrates the skin in the place where the integrity of the skin is damaged - through wounds, abrasions, cracks. Children's skin is delicate and sensitive, and the activity of a preschool child is great. As a result, numerous microtraumas occur, opening the way for infection. Cases of infection with molluscum contagiosum while swimming in the pool have also been described.
From 6 to 10 years, the incidence of molluscum contagiosum decreases. Instilling household hygiene skills is of great importance. The sooner your child starts taking care of clean hands, the better.
Causes
A child develops a food allergy due to:
- genetic predisposition;
- decreased protective functions of the intestinal mucosa;
- large amounts of food consumed, etc.
In circumstances where tolerance fails, the immune system produces an Ig E antibody response against the specific food. The process begins in the intestines (although it can also affect other areas, such as the respiratory system or skin).
When a patient consumes a “dangerous” product, the antigen associated with Ig E is detected on the surface of basophils and mast cells. At this time, they are activated, and histamine and other inflammatory substances are released.
Symptoms of molluscum contagiosum
The incubation period of the disease ranges from two weeks to several months, but most often the rash appears on the 14-15th day.
At first, single rashes appear, then there are more of them. Molluscum contagiosum can affect any area of the skin except the palms and soles. In children, exposed areas of the arms and legs, as well as the face and neck are most often affected. In adults, the genital area and the inner thighs are most often affected.
In the typical form of the disease, the rashes are located only in one anatomical area; in the generalized form, they spread throughout the body.
Rash
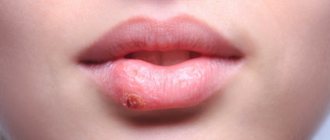
The elements of the rash look like protrusions (papules), firm and painless to the touch, pink or flesh-colored, with a pearlescent top. In the center of the papule there is a small depression, from which, when pressed, a white pasty mass is squeezed out. Papules have a round or oval shape, the size usually varies in the range of 2-5 mm, but sometimes the nodules merge, and then such formations can reach a diameter of 1 cm or more.
More about the symptom
Itching
In some cases, the rash is accompanied by itching, which intensifies when scratching. Under no circumstances should papules be scratched, as this can lead to a bacterial infection. The presence of a bacterial infection is indicated by redness of the skin around the papules, swelling, and suppuration.
More about the symptom
Treatment and prevention of allergies
According to the latest WHO recommendations, the basis for the prevention of food allergies in children is breastfeeding. Children who receive exclusively breast milk in the first months of life are much less likely to suffer from food allergies. At the same time, mothers of healthy children who are breastfed do not require special diets. Their diet should be complete and varied, including proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. As well as microelements and vitamins. Mothers of children who are at risk for food intolerance are advised not to limit their diet too much. It is necessary to completely exclude those foods to which the mother herself has a reaction and keep a food diary.
If artificial feeding is necessary, children prone to allergies choose special hypoallergenic formulas. To treat existing manifestations, the mixture should be selected by a specialist. According to the latest clinical recommendations, if you are intolerant to cow's milk protein, choose mixtures with fully hydrolyzed protein or amino acid composition. In this case, it is not correct to prescribe hypoallergenic mixtures and mixtures based on goat’s milk protein. Soy-based mixtures themselves can cause an allergic reaction.
Another important step for the prevention and treatment of food allergies is the correct introduction of complementary foods. Complementary foods should be introduced in a timely manner - no earlier than 4 months and no later than 6. To begin with, hypoallergenic foods are selected - white and green vegetables, gluten-free cereals. On one day, the baby is given only one complementary food product, in small quantities, and the possible reaction is observed. At the beginning, a new product should be introduced no more than once a week. Mothers of babies who are predisposed to allergies or already have allergic manifestations are recommended to keep a food diary. There, the mother writes down all the foods she fed the child during the day and possible reactions to them.
The doctor, if necessary, can prescribe medications to the baby. They can be either for oral administration or for skin treatment. Children with chronic allergic rashes require special skin care. It is necessary to use special children's detergents with a neutral pH. And after washing, use special care products - emollients. It is better to consult a doctor about which emollient to choose. If there are manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract or respiratory system, the child needs specific treatment, which can only be prescribed by a doctor during an in-person examination.
Online consultation with a pediatrician
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
Methods for diagnosing molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum can be confused with manifestations of other diseases, including serious ones such as syphilis or cancer. Also, the activity of the molluscum contagiosum virus increases with a decrease in immunity, so in 20% of cases molluscum contagiosum accompanies HIV infection. This means that when rashes appear that correspond to the description of molluscum contagiosum, a medical examination is required to rule out such options.
When contacting a dermatologist, the doctor will examine the patient, make a diagnosis and suggest a treatment method.
Inspection
In most cases, the diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is made by a dermatologist based on the results of an examination of the patient.
PCR diagnostics
Since HIV often accompanies molluscum contagiosum, PCR diagnostics for HIV can be prescribed.
More information about the diagnostic method
Serological blood test
When molluscum contagiosum is detected in adults, a serological blood test is prescribed to identify sexually transmitted infections (hepatitis B and C, HIV, syphilis, etc.).
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Causes of food allergies in newborns
Food allergies in babies who have just been born are very rare. The baby receives only mother's milk. This is food that nature created for your baby and nothing can be better than it. Therefore, the peak age of food allergies in breastfed infants can be considered around 4–5 months, when the baby begins to receive complementary foods - products added to breast milk: vegetables, fruits, cereals, meat, dairy products and others. The situation is somewhat different with bottle-fed babies. The formula itself can cause food intolerances. Therefore, when choosing a mixture, it is better to consult a specialist.
Treatment methods for molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum should be treated by a doctor. You should not try to remove papules yourself - this can lead to bacterial infection.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum depends on a number of factors, primarily on the stage of development of the disease, the severity of symptoms and the state of the patient’s immunity. The following methods can be used:
Instrumental removal
Papules can be removed instrumentally, followed by treating the wound with antibacterial agents.
Credestruction
Cryodestruction is the removal of papules using exposure to low temperatures. Papules are treated with liquid nitrogen. Tissues treated in this way freeze and die.
Radio wave removal
Molluscum contagiosum papules can be removed using the radio wave method (using the Surgitron apparatus) and using a laser.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is the effect of high-frequency current on papules. It is popularly described as “cauterization with electricity.” At the moment of discharge, a local strong thermal effect occurs, the tissues coagulate, which virtually eliminates the risk of infection at the treatment site.
Conservative treatment
The course of treatment for molluscum contagiosum may include conservative treatment with ointments and creams, as well as taking antiviral drugs (if the affected area is large).
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Possible complications
The danger is that this condition gradually worsens if no measures are taken over time:
1. First, against the background of sensitization, the body develops dermatitis.
2. Then the respiratory system is damaged in the form of atopic rhinitis.
3. If the antigen is not excluded, then bronchial asthma manifests itself.
The most dangerous complication is anaphylactic shock. It develops rapidly – 1-3 minutes after contact with the antigen. It is characterized by bronchospasm, laryngeal edema and collapse, which can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Consequences of acne
Acne can cause more than just rashes. Some people believe that acne is a skin condition that eventually outgrows, but it can have a profound and lasting impact on one's life. Many people experience one or more of the following after acne appears.
Acne scars: When the breakout goes away, it leaves behind a permanent scar. Some scars cause indentations in the skin. The rest are gradually disappearing. It's impossible to predict who will develop scars after their acne goes away, but the following factors increase your risk:
- acne has been present for a long time because the teenager does not treat it or the treatment does not work;
- One or more close blood relatives have had acne in the family.
Dark spots on the skin: As acne breakouts fade, some people see the area where acne once was. This completely flat spot can be pink, red, purple, black or brown, and is often mistaken for a permanent acne scar. Source: Modern Treatments and Rehabilitation of Acne Vulgaris. Barinova A.N. Russian family doctor, 2022. p. 5-18.
How to diagnose allergies?
An allergic rash in children is often confused with an infectious one. If the treatment is incorrect, then the consequences of such a therapeutic course will not be the best. Before choosing an effective remedy, you need to learn to distinguish one disease from another. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, since a visual examination is not always enough to determine the cause of the disease; tests are required.
| Features | Allergic rash | Infection |
| General form | It can be in the form of both small dots and large blisters. In addition to them, there are often crusts, erosions and serous wells (ulcers from which fluid oozes). | The rashes are pinpoint and do not “merge” into a large spot. |
| Place of appearance | Face (forehead, cheeks, chin). Neck, arms, legs, buttocks. Rarely – stomach, back. | Belly, back. Rarely – arms, legs. Very rarely - forehead. |
| Heat | The temperature is rare, and if it rises, it is not higher than 37-38°C. | The disease is accompanied by fever, from 37°C to 41°C. |
| Itching | Happens. | Happens. |
| Swelling | Well visible. In some situations it is life-threatening. | They happen very rarely. |
| Associated symptoms | Lacrimation, conjunctivitis, hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the eye, decreased blood pressure, cough, upset stomach. | Running nose, general loss of strength, body aches. |
| How quickly it goes | Often the rash goes away immediately after taking the medicine. | Remains until the course of treatment is completed. |